UVM:config_db
文章目录
- 前言
- 1、config_db的作用
- 2.component的路径索引 uvm_component::get_full_name();
-
- 2.1. 获取component索引信息的其他方法
- 3、config_db的使用
-
- 3.1 传递interface
- 3.2 传递变量
- 2.3传递object
前言
在Systemverilog搭建的验证平台中,需要对各组件进行参数配置,但是配置各组件必须得在各组件实例化之后才能配置参数,例如test中必须得执行env = new();才能配置env.i_agt.drv.pen_num = 10;。再比如接口指针,需要就需要为每个组件设定设定set_interface();方法,非常繁琐。
而UVM提供的config_db机制可在组件实例化前就设定好配置信息,这样就可在tb的initial块中就进行设定了。真正将这些配置信息落实在各component,是在testbench运行过程build_phase中。
1、config_db的作用
UVM提供了uvm_config_db配置类以及几种方便地变量设置方法来实现仿真的环境控制
uvm_config_db类的使用方式包括:
- 传递virtual interface 到环境中
- 设置单一变量值,例如int、string、enum等
- 传递配置对象(config object)到环境
set与get函数的参数:
config_db机制用于在UVM验证平台间传递参数,set()是寄信,get()是收信
uvm_config_db#(T)::set(uvm_component cntxt, string inst_name, string field_name, T value);
uvm_config_db#(T)::get(uvm_component cntxt, string inst_name, string field_name, inout T value);
- T是传递信息的类型
- cntxt是一个uvm_component实例的指针,cntxt+inst_name组成目标路径
- inst_name是相对此实例的路径
- field_name变量名set和get的第三个参数必须一致
2.component的路径索引 uvm_component::get_full_name();
在UVM:类库中提到了UVM树和各component路径索引的概念,此处再强调一下,config_db机制需要写明路径。
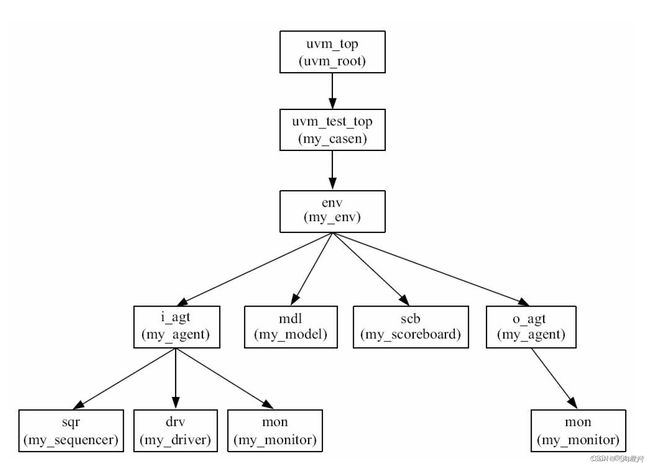
component路径索引就是UVM树中从树根到对应component的路径,使用uvm_component类的get_full_name()方法
即
function void my_agent::build_phase(uvm_phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
drv = my_driver::type_id::create("drv",this); //在i_agt的build_phase中这样例化drv
...
endfunction
function void my_driver::build_phase(uvm_phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
uvm_report_info("my_driver",get_full_name(),UVM_LOW); //消息打印路径索引
endfunction
//打印消息为:"uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv"
注意,打印的路径是从uvm_test_top实例开始的,这是因为开发者只需定义my_test,而UVM树根uvm_top实例是自动创建的无需开发者定义。
打印出来的路径中,取的是各component的name,而不是对象名称!
也就是说如果drv = my_driver::type_id::create(“driver”,this);,那么打印的路径就变成了"uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.driver",但绝不推荐这么做,强烈建议各component的name与对象名保持一致!
2.1. 获取component索引信息的其他方法
get_full_name()可获取索引路径,还有其他一些方法可获取该component的其他信息。
//...\questasim\verilog_src\uvm-1.2\src\base\uvm_component.svh
function void uvm_component::get_children(ref uvm_component children[$]);
function int uvm_component::get_first_child(ref string name);
function int uvm_component::get_next_child(ref string name);
function uvm_component uvm_component::get_child(string name);
function int uvm_component::get_num_children();
function string uvm_component::get_full_name();
function uvm_component uvm_component::get_parent ();
function int unsigned uvm_component::get_depth();
//...\questasim\verilog_src\uvm-1.2\src\base\uvm_root.svh
extern static function uvm_root uvm_root::get(); //即返回指向实例uvm_top的uvm_root类句柄,注意是static类型
3、config_db的使用
3.1 传递interface
接口的传递从硬件世界到UVM环境中的传递可以通过uvm_config_db来实现。
在实现的过程中需要注意几点:
接口的传递应该发生在 run_test() 之前。这保证了在进入build_phase之前virtual interface已经被传递到uvm_config_db中;
应当把interface和virtual interface 的声明分开,在传递的过程中的类型应该为virtual interface(接口句柄)
interface intf1;
logic enable = 0;
endinterface
class comp1 extends uvm_component;//底层组件拿到config
`uvm_component_utils(comp1);
virtual intf1 vif;//声明接口要带virtual
...
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
//这里的this的绝对路径是root.test.c1.vif
//第二个参数"",表示要找comp1里面的vif
if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual intf1)::get(this, "", "vif", vif))begin//判断是否有误
`uvm_error("GETVIF", "no virtual interface is assigned")
end
`uvm_info("SETVAL", $sformatf("vif.enable is %b after set", vif.enable),UVM_LOW)
vif.enable = 1;
endfunction
endclass
class test1 extends uvm_test;//顶层test中传递config
`uvm_component_utils(test1)
comp1 c1;
...
endclass
module tb;
intf1 intf();
initial begin
uvm_config_db#(virtual intf1)::set(uvm_root::get(), "uvm_test_top.c1", "vif", intf);//在run_test之前,将配置发送出去
run_test("test1");
end
endmodule
3.2 传递变量
在各个test中,可以在build phase对底层组件的变量加以配置,进而在环境例化之前完成配置,使得环境可以按照预期运行
class comp1 extends uvm_component;
'uvm_component_utils(comp1)
int val1 = 1;
string str1 = "null";
...
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
'uvm_info("SETVAL", $sformatf("vall is %d before get", vall), UVM_LOW)
'uvm_info("SETVAL", $sformatf("str1 is %s before get", str1), uvm_low)
uvm_config_db#(int)::get(this,"","vall",vall);
uvm_config_db#(string)::get(this,"","str1",str1);
endfunction
endclass
class test1 extends uvm_test;
'uvm_component_utils(test1)
comp1 c1;
...
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
uvm_config_db#(int)::set(this,"c1","vall",100);//例化之前set
uvm_config_db#(string)::set(this,"c1","str1","comp1");
c1 = comp1::type_id::create("c1",this);
endfunction
endclass
2.3传递object
如果要给底层配置的参数很多,就可以把封装在一个object类中,在顶层test中将类的实例对象句柄进行set传递;
底层通过get拿到对象句柄,就可以通过句柄获取配置类中的变量设置
//将参数封装到object中
class config1 extends uvm_object;
int vall = 1;
int str1 = "null";
'uvm_object_utils(config1)
endclass
//底层组件拿到config
class comp1 extend uvm_component;
'uvm_component_util(comp1)
config1 cfg;
...
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
uvm_object tmp;
uvm_config_db#(uvm_object)::get(this, "","cfg", tmp);
//传递的是父类uvm_object,要获得子类的成员变量,所以要做类型转换
void'($cast(cfg,tmp));
'uvm_info("SETVAL",
$sformatf("cfg.vall is %d after get",cfg.vall),UVM_LOW)
'uvm_info("SETVAL",
$sformatf("cfg.str1 is %s after get", cfg.srt1),UVM_LOW)
endfunction
endclass
//顶层test中传递config
class test1 extends uvm_test;
'uvm_component_utils(test1)
comp1 c1,c2;
config cfg1,cfg2;
...
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
cfg1 = config1::type_id::create("cfg1");
cfg2 = config1::type_id::create("cfg2");
cfg1.val1 = 30;
cfg1.str1 = "c1";
cfg2.val1 = 50;
cfg2.str1 = "c2";
//设置set
uvm_config_db#(uvm_object)::set(this, "c1", "cfg", cfg1);
uvm_config_db#(uvm_object)::set(this, "c2", "cfg", cfg2);
c1 = comp1::type_id::create("c1", this);
c2 = comp1::type_id::create("c2", this);
endfunction
endclass
- 这里config传递的是一个父类句柄,所以要做句柄类型转换
- set和get的类型必须相同,要不都是父类,要不都是子类
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「Starry丶」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Starry__/article/details/123007408
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「卢卡猫」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_41774721/article/details/121796065