NLP实战之BERTopic主题分析
在自然语言处理(NLP)领域,主题分析一直是一个讨论比较火热的话题。通过主题分析,我们可以揭示文本数据中的隐藏主题,这对于信息检索、文本分类、舆情分析等任务非常有用。本篇博客将介绍一种基于BERT和Topic Modeling的主题分析方法——BERTopic,它的强大之处在于可以自动发现文本数据中的主题,而无需预先定义主题数。
BERTopic简介
BERTopic是一种结合了预训练模型BERT和主题建模的强大工具。它允许我们将大规模文本数据集中的文档映射到主题空间,并自动识别潜在的主题。它背后的核心思想是通过BERT模型来捕获文档的语义信息,并然后使用主题建模技术来对这些语义信息进行聚类,从而得出主题。对于大部分小伙伴而言,知道如何去使用BERTopic模型进行主题分析就足够了。所以BERTopic原理就不做过多解释了,感兴趣的小伙伴可以自己去了解一下。
1 数据准备与预处理
在进行主题分析之前,先进行数据准备和预处理:
1.1 数据准备:首先,我们需要准备文本数据。这可以是一组文档,例如新闻文章、论文摘要或任何其他文本数据。这里我选取的是WOS核心合集中图情领域关于VR和metaverse的500篇论文摘要。文件类型是xlsx格式的excel文件。如果要加载csv只需要将读取文件部分的代码修改一下即可。
import os
import pandas as pd
import re
output_path = 'D:/notebook/LDAsklearn_origin/result'
file_path = 'D:/notebook/BERTopic/data'
os.chdir(file_path)
data=pd.read_excel("dataset.xlsx").astype(str)#content type
#加载csv文件
#data=pd.read_csv("dataset.csv").astype(str)#content type
os.chdir(output_path)
dic_file = "D:/notebook/LDAsklearn_origin/stop_dic/dict.txt"
stop_file = "D:/notebook/LDAsklearn_origin/stop_dic/stop_words.txt"1.2 数据预处理:这里可以采用jieba(中文分词)、NLTK(英文分词)等库做相应的处理。我只是做了一个简单的示例,所以在数据预处理时,只是进行了去除停用词,后续可以使用NLTK进行完善。
def english_word_cut(mytext):
stop_list = []
try:
with open(stop_file, encoding='utf-8') as stopword_list:
stop_list = [line.strip() for line in stopword_list]
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"Error: Stop file '{stop_file}' not found.")
word_list = []
# 使用正则表达式将文本分割为单词
words = re.findall(r'\b\w+\b', mytext)
for word in words:
# 将单词转换为小写,以便统一处理
word = word.lower()
# 如果单词在停用词列表中,跳过该单词
if word in stop_list or len(word) < 2:
continue
word_list.append(word)
return " ".join(word_list)
data["content_cutted"] = data.content.apply(english_word_cut)
print(data["content_cutted"])2 BERTopic Moudel构建
接下来,让我们看一下BERTopic主题模型分析的流程:
2.1 导入bertopic及相关第三方库
from bertopic import BERTopic
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
from umap import UMAP
from hdbscan import HDBSCAN
from bertopic.vectorizers import ClassTfidfTransformer在安装bertopic第三方库时可能会出现很多问题,后续我会专门写一篇讲解如何安装bertopic的文章
2.2 嵌入文档
使用默认的英文文本嵌入模型all-MiniLM-L6-v2进行文档嵌入,paraphrase-multilingual-MiniLM-L12-v2 支持中文或其他50多种语言,该模型与基本模型非常相似,但经过多种语言训练,并且体系结构略有不同。这里建议大家在使用的时候先去huggingface.co网站把模型下载到本地。一方面,可以大大减少嵌入的时间,另一方面,避免在使用SentenceTransformer时访问失败。
# Step 1 - Embed documents
embedding_model = SentenceTransformer('D:/notebook/BERTopic/all-MiniLM-L6-v2')SentenceTransformer:all-MiniLM-L6-v2(英文)、paraphrase-multilingual-MiniLM-L12-v2(中文或其他)
2.3 聚类文档
先利用UMAP算法降低嵌入的维数,再运用HDBSCAN算法创建语义相似文档的聚类。
2.3.1 向量降维
使用UMAP进行词嵌入向量降维,
# Step 2 - Reduce dimensionality
umap_model = UMAP(n_neighbors=15, n_components=5,min_dist=0.0,metric='cosine')
n_neighbors:近似最近邻数。它控制了UMAP局部结构与全局结构的平衡,数值较小时,UMAP会更加关注局部结构,反之,会关注全局结构,丢掉一些细节。
n_components:设置将数据嵌入的降维空间的维数。
min_dist:点之间的最小距离。此参数控制UMAP聚集在一起的紧密程度,值较小时,会更紧密,反之,会更松散。
2.3.2 聚类
使用HDBSCAN对降维向量聚类,聚类方法不局限于HDBSCAN,也可以使用K-means聚类等。一般常用HDBSCAN聚类方法。
# Step 3 - Cluster reduced embeddings
hdbscan_model = HDBSCAN(min_cluster_size=10, metric='euclidean', prediction_data=True)min_cluster_size:控制集群的最小大小,它通常设置为默认值10。值越大,集群越少但规模更大,而值越小,微集群越多。
metric:用于计算距离,通常使用默认值euclidean.
prediction_data:一般始终将此值设置为True,可以预测新点。如果不进行预测,可以将其设置为False。
2.4 构建表征主题
2.4.1 c-TF-IDF
通过c-TF-IDF算法提取主题候选词。
# Step 4 - Create topic representation
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
vectorizer_model = CountVectorizer(stop_words="english")
ctfidf_model = ClassTfidfTransformer()stop_words: 设置停用词语言。
2.4.2 训练bertopic主题模型
topic_model = BERTopic(
embedding_model=embedding_model, # Step 1 - Extract embeddings
umap_model=umap_model, # Step 2 - Reduce dimensionality
hdbscan_model=hdbscan_model, # Step 3 - Cluster reduced embeddings
vectorizer_model=vectorizer_model, # Step 4 - Tokenize topics
ctfidf_model=ctfidf_model, # Step 5 - Extract topic words
diversity=0.5, # Step 6 - Diversify topic words
nr_topics='none',
top_n_words = 10
)top_n_words:设置提取的每个主题的字数,通常为10-30之间。
min_topic_size:设置主题最小大小,值越低,创建的主题就越多。值太高,则可能根本不会创建任何主题。
nr_topics:设置主题数量,可以设置为一个具体的数字,也可设置为‘none’不进行主题数量约束,设置为‘auto’则自动进行约束。
diversity:是否使用MMR(最大边际相关性)来多样化主题表示,可以设置0~1之间的值,0表示完全不多样化,1表示最多样化,设置为‘none’,不会使用MMR。
2.4.3 文档主题概率
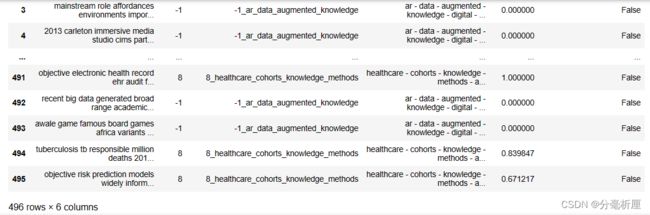
使用fit_transform对输入文本向量化,然后使用topic_model模型提取主题topics,并且计算主题文档概率probabilities
filtered_text = data["content_cutted"].tolist()
topics, probabilities = topic_model.fit_transform(filtered_text)
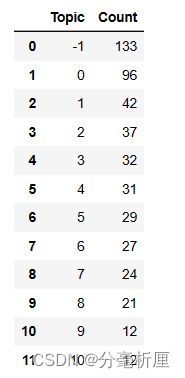
topic_model.get_document_info(filtered_text)查看每个主题数量
topic_model.get_topic_freq()其中-1为噪声,没有聚到任何一类中。
查看某个主题-词的概率分布
topic_model.get_topic(0)3 BERTopic可视化
BERTopic还提供了丰富的可视化工具,可以帮助您理解生成的主题。
3.1 主题-词概率分布
topic_model.visualize_barchart()3.2 文档主题聚类
embeddings = embedding_model.encode(filtered_text, show_progress_bar=False)
# Run the visualization with the original embeddings
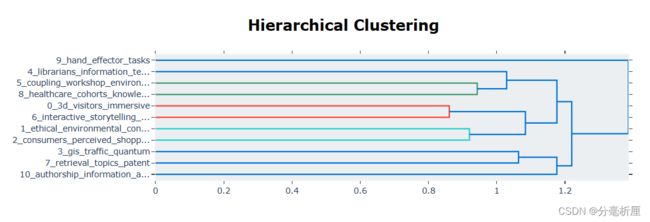
topic_model.visualize_documents(filtered_text, embeddings=embeddings)3.3 聚类分层
topic_model.visualize_hierarchy()3.4 主题相似度热力图
topic_model.visualize_heatmap()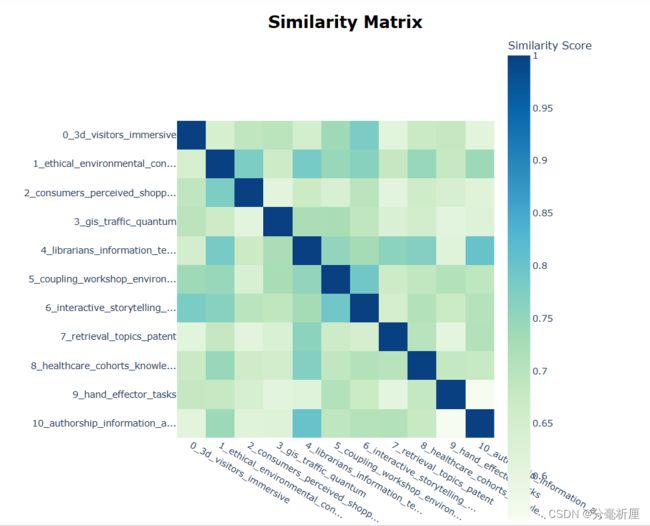 3.5 隐含主题主题分布图
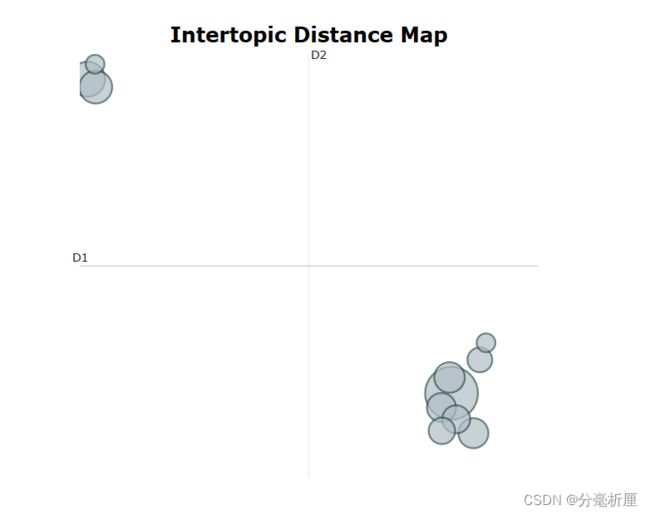
3.5 隐含主题主题分布图
topic_model.visualize_topics()结语
BERTopic是一种强大的主题分析工具,它能够自动识别文本数据中的主题,而无需预先定义主题数。通过结合BERT的语义表示和传统主题建模技术,BERTopic为主题分析任务提供了一个高效而精确的解决方案。希望这篇博客能够帮助您入门BERTopic,并在NLP实战中发挥其潜力。如果您想深入了解BERTopic,不妨尝试在自己的数据集上应用它,以发掘更多有趣的主题!
参考资料
Parameter tuning - BERTopic (maartengr.github.io)
【主题建模】一种基于深度学习的主题建模方法:BERTopic(实战篇)-CSDN博客