json多边形标签转yolo标签,yolo标签画框到图片上并保存
将json中标注的多边形提取为矩形标注并保存为txt格式,代码如下,适合一种类别,多种自己修改:
import json
import os
from os import listdir, getcwd
from os.path import join
import os.path
rootdir = '/home/lwf/下载/images' # 写自己存放图片的数据地址
def position(pos):
# 该函数用来找出xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax即bbox包围框
x = []
y = []
nums = len(pos)
for i in range(nums):
x.append(pos[i][0])
y.append(pos[i][1])
x_max = max(x)
x_min = min(x)
y_max = max(y)
y_min = min(y)
b = (float(x_min), float(x_max), float(y_min), float(y_max))
return b
def convert(size, box):
# 该函数将xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax转为x,y,w,h中心点坐标和宽高
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def convert_annotation(image_id):
load_f = open("/home/lwf/下载/json/%s.json" % (image_id), 'r') # 导入json标签的地址
load_dict = json.load(load_f)
out_file = open('/home/lwf/下载/txt/%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w') # 输出标签的地址
# keys=tuple(load_dict.keys())
w = load_dict['imageWidth'] # 原图的宽,用于归一化
h = load_dict['imageHeight']
# print(h)
objects = load_dict['shapes']
nums = len(objects)
# print(nums)
# object_key=tuple(objects.keys()
for i in range(0, nums):
labels = objects[i]['label']
# print(i)
if (labels in ['apple']):
# print(labels)
pos = objects[i]['points']
b = position(pos)
bb = convert((w, h), b)
cls_id = 0 # 类别设为0
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
# print(type(pos))
#以下用不到
elif (labels in ['car', 'truck', 'bus', 'caravan', 'trailer']):
# print(labels)
pos = objects[i]['polygon']
b = position(pos)
bb = convert((w, h), b)
cls_id = 1 # 我这里把各种类型的车都设为类别1
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
def image_id(rootdir):
a = []
for parent, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(rootdir):
for filename in filenames:
filename = filename.strip('.jpg')
# print(filename)
a.append(filename)
return a
names = image_id(rootdir)
for image_id in names:
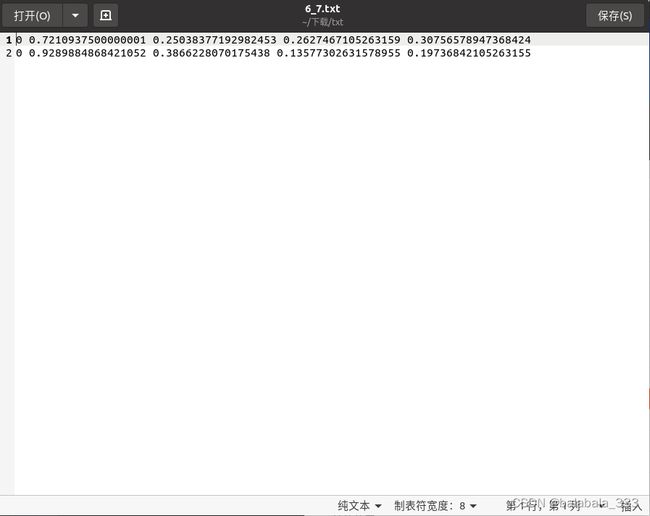
convert_annotation(image_id)得到的格式如下:
----------------------------------------分割线-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
再将yolo标签画在图片上,可以预览,也可以批量保存下来,代码如下:
import os
import cv2
def main():
# 总的检测根目录
path_root_labels = '/home/lwf/下载/txt'
# 总的检测根目录
path_root_imgs ='/home/lwf/下载/数据/JPEGImages'
type_object = '.txt'
#保存画框后的图片路径
path_save_imgs ='/home/lwf/下载/数据/save_image'
for ii in os.walk(path_root_imgs):
for j in ii[2]:
type = j.split(".")[1]
if type != 'jpg' and type != 'png':
continue
path_img = os.path.join(path_root_imgs, j)
print(path_img)
label_name = j[:-4]+type_object
path_label = os.path.join(path_root_labels, label_name)
if os.path.exists(path_label) == True:
f = open(path_label, 'r+', encoding='utf-8')
img = cv2.imread(path_img)
img_tmp = img.copy()
w = img.shape[1]
h = img.shape[0]
new_lines = []
while True:
line = f.readline()
if line:
msg = line.split(" ")
# print(x_center,",",y_center,",",width,",",height)
x1 = int((float(msg[1]) - float(msg[3]) / 2) * w) # x_center - width/2
y1 = int((float(msg[2]) - float(msg[4]) / 2) * h) # y_center - height/2
x2 = int((float(msg[1]) + float(msg[3]) / 2) * w) # x_center + width/2
y2 = int((float(msg[2]) + float(msg[4]) / 2) * h) # y_center + height/2
print(x1,",",y1,",",x2,",",y2)
cv2.rectangle(img_tmp,(x1,y1),(x2,y2),(0,0,255),2)
else :
break
# cv2.imwrite(path_save_imgs + '/'+j[:-4]+'.jpg', img_tmp)#保存图片
cv2.imshow('test',img_tmp)#预览画框的图片
cv2.waitKey(0)
print(img_tmp)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
效果如下:
参考博文:
将实例分割数据集转为目标检测数据集_逍遥王可爱的博客-CSDN博客