【Spring】DI依赖注入(构造器、set、命名空间)
闲话
昨晚睡得有点晚,早上八点多起来了,真想睡个午觉,但是又怕下午没时间看书
一、DI依赖注入
1、构造器注入(利用有参构造创建对象)
假设我们想要使用有参构造创建对象,那么我们就需要调整beans.xml配置文件,有以下三种配置可选
- 通过下标给属性赋值,下标从0开始
public class Bean {
// 有参构造方法
public Bean (int age, String name) {
// ...
}
}
<bean id="Bean" class="com.decade.pojo.Bean">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="7500000"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="42"/>
bean>
- 通过参数的类型进行赋值,基本数据类型可以直接写,但是引用数据类型需要写完整
这种方法不建议使用,因为会出现2个参数都是同种类型的情况,这样就需要按照构造器中参数的顺序来进行声明
public class Bean {
// 有参构造方法
public Bean (int age, String name) {
// ...
}
}
<bean id="Bean" class="com.decade.pojo.Bean">
<constructor-arg type="int" value="7500000"/>
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="42"/>
bean>
- 直接通过参数名来设置或者某个属性需要引用其他类的情况
public class Bean {
// 有参构造方法
public Bean (ThingTwo thingTow, String name) {
// ...
}
}
<beans>
<bean id="beanOne" class="com.decade.pojo.Bean">
<constructor-arg ref="beanTwo"/>
<constructor-arg name="name" value="decade"/>
bean>
<bean id="beanTwo" class="x.y.ThingTwo"/>
beans>
2、set注入(利用无参构造创建对象)
依赖注入:依赖无参构造,注入属性
- 依赖:bean对象的创建依赖于容器
- 注入:bean对象中的所有属性,由容器来注入
1)结合demo做一个简单的了解
首先,我们创建一个实体类Hello,并且声明set方法,因为依赖注入就是使用set方法进行注入的
public class Hello {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
// 依赖注入就是使用set方法进行注入的,去掉此行,bean.xml里面使用property对对象属性进行赋值的操作就会报错
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hello{"
+ "name='" + name + '\''
+ '}';
}
}
然后我们需要在resource路径下创建与bean相关的配置文件,这里就命名成beans.xml
注意,创建XML文件时,idea右上角会提示该配置文件没有配置到项目中,我们点击配置一下即可
在这里可以查看哪些文件配置已经到项目中
ref:用来引用spring容器中创建好的bean对象
value:设置为具体的值,基本数据类型
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="hello" class="com.decade.pojo.Hello">
<property name="name" value="decade"/>
bean>
beans>
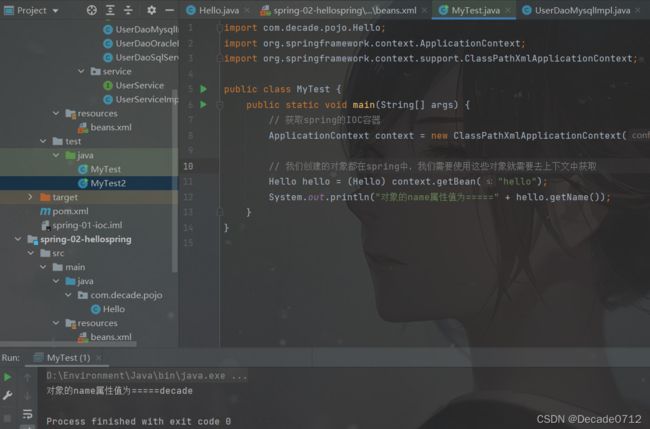
然后我们创建对应的测试类去测试一下
import com.decade.pojo.Hello;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取spring的IOC容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
// 我们创建的对象都在spring中,我们需要使用这些对象就需要去上下文中获取
Hello hello = (Hello) context.getBean("hello");
System.out.println("对象的name属性值为=====" + hello.getName());
}
}
2)深入拓展
实际开发中,我们需要创建很多复杂的对象,他的属性不可能仅仅是上面那些简单的基本数据类型
所以,我们还需要做一些拓展,也可以参照 spring官方文档
首先我们创建一个具有各种不同类型属性的实体类
public class Address {
private String address;
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Student {
private String name;
private Address address;
private String[] books;
private List<String> hobbies;
private Map<String, String> card;
private Set<String> games;
private String phone;
private Properties info;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String[] getBooks() {
return books;
}
public void setBooks(String[] books) {
this.books = books;
}
public List<String> getHobbies() {
return hobbies;
}
public void setHobbies(List<String> hobbies) {
this.hobbies = hobbies;
}
public Map<String, String> getCard() {
return card;
}
public void setCard(Map<String, String> card) {
this.card = card;
}
public Set<String> getGames() {
return games;
}
public void setGames(Set<String> games) {
this.games = games;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public Properties getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(Properties info) {
this.info = info;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\''
+ ", address=" + address.toString()
+ ", books=" + Arrays.toString(books)
+ ", hobbies=" + hobbies
+ ", card=" + card
+ ", games=" + games
+ ", phone='" + phone + '\''
+ ", info=" + info
+ '}';
}
}
然后通过beans.xml配置文件对属性进行赋值
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="address" class="com.decade.pojo.Address">
<property name="address" value="南京"/>
bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.decade.pojo.Student">
<property name="name" value="decade"/>
<property name="address" ref="address"/>
<property name="books">
<array>
<value>雪中悍刀行value>
<value>龙族value>
<value>吞噬星空value>
array>
property>
<property name="hobbies">
<list>
<value>听歌value>
<value>看电视value>
<value>打游戏value>
list>
property>
<property name="card">
<map>
<entry key="ID" value="1024"/>
<entry key="存款账户" value="一百一十爽"/>
map>
property>
<property name="games">
<set>
<value>LOLvalue>
<value>王者value>
<value>保卫萝卜value>
set>
property>
<property name="phone">
<null/>
property>
<property name="info">
<props>
<prop key="ip">127.0.0.1prop>
<prop key="port">3306prop>
<prop key="userId">rootprop>
props>
property>
bean>
beans>
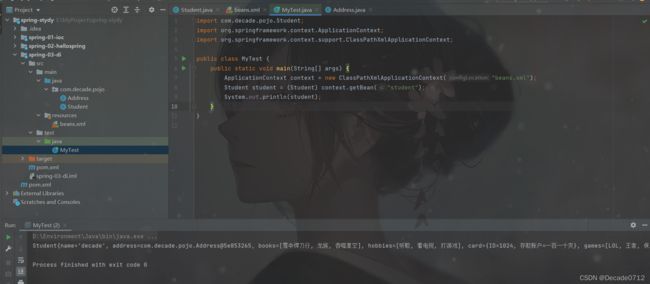
最后,我们写一个测试类进行测试
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student);
}
}
3、拓展方式注入
1)c命名和p命名空间注入
可参考官方文档为,具体链接如下
p命名空间 c命名空间
p命名空间是针对上面的set注入,而c命名空间是针对构造器注入
我们结合一个代码实例来进行分析
首先我们创建一个User实体类
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private Address address;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age, Address address) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\''
+ ", age=" + age
+ ", address=" + address.getAddress()
+ '}';
}
}
然后我们使用XML配置文件去管理对象的创建
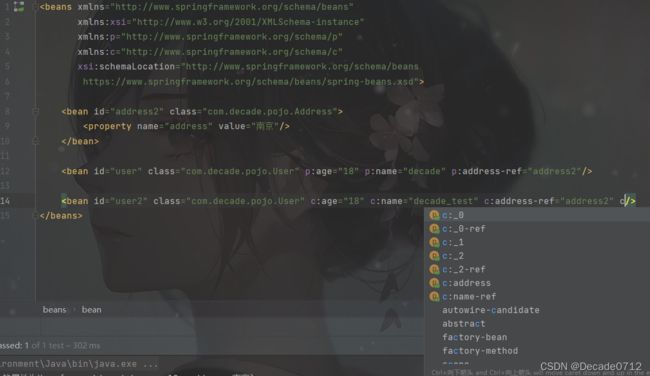
注意:使用p命名空间和c命名空间需要导入xml约束
xmlns:p=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/p”
xmlns:c=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/c”
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="address2" class="com.decade.pojo.Address">
<property name="address" value="南京"/>
bean>
<bean id="user" class="com.decade.pojo.User" p:age="18" p:name="decade" p:address-ref="address2"/>
<bean id="user2" class="com.decade.pojo.User" c:age="18" c:name="decade_test" c:address-ref="address2"/>
beans>
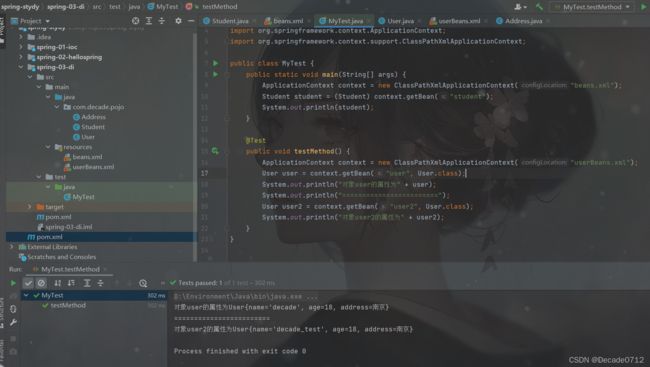
最后我们编写一个测试类进行测试
import com.decade.pojo.Student;
import com.decade.pojo.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void testMethod() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("userBeans.xml");
User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println("对象user的属性为" + user);
System.out.println("========================");
User user2 = context.getBean("user2", User.class);
System.out.println("对象user2的属性为" + user2);
}
}
如有错误,欢迎指正