《数据结构、算法与应用C++语言描述》- 最小输者树模板的C++实现
输者树
完整可编译运行代码见:Github::Data-Structures-Algorithms-and-Applications/_31loserTree
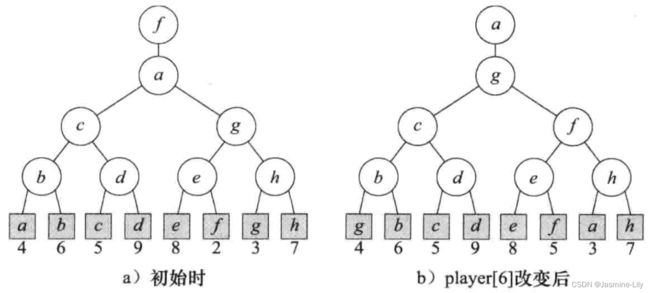
输者树:每一个内部节点所记录的都是比赛的输者,晋级的节点记录在边上。本文中,赢者是分数较低的那个,输者是分数高的那个。教材的举例是这样的。
更好理解的解释是,参考地址。
- a与b比赛,输者是b,赢者是a,将b放到内部节点,将a放到边上
- c与d比赛,输者是d,赢者是c,将d放到内部节点,将c放到边上
- e与f比赛,输者是e,赢者是f,将e放到内部节点,将f放到边上
- g与h比赛,输者是h,赢者是g,将h放到内部节点,将g放到边上
- a与c比赛,输者是c,赢者是a,将c放到内部节点,将a放到边上
- f与g比赛,输者是g,赢者是f,将g放到内部节点,将f放到边上
- a与f比赛,输者是a,赢者是f,将a放到内部节点,将f放到边上
- 将最终赢者放到数组的第0个元素
在loserTree的模板实现中,可以使用一个数组来存储输者、另一个数组存储赢者。
输者树比赢者树的优势
当改变的元素是上一场比赛的最终赢家的话,内部节点存储了所有该赢家的输者。在重新组织比赛时,只需要与父亲节点进行比较,而不需要获取到父亲节点的另外一个节点,然后与其比较,可以减少访存的时间。
输者树的实现
main.cpp
/*
Project name : _30winnerTree
Last modified Date: 2023年12月19日16点48分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 最小输者树——main函数
*/
#include "MinimumLoserTree.h"
int main(){
MinimumLoserTreeTest();
return 0;
}
MinimumLoserTree.h
/*
Project name : _30winnerTree
Last modified Date: 2023年12月19日16点48分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 最小输者树——模板类
*/
#ifndef _31LOSERTREE_MINIMUMLOSERTREE_H
#define _31LOSERTREE_MINIMUMLOSERTREE_H
#includeMinimumLoserTree.cpp
/*
Project name : _30winnerTree
Last modified Date: 2023年12月19日16点48分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 最小输者树——测试函数
*/
#include "MinimumLoserTree.h"
void MinimumLoserTreeTest(){
int n;
cout << "Enter number of players, >= 2" << endl;
cin >> n;
if (n < 2)
{cout << "Bad input" << endl;
exit(1);}
int *thePlayer = new int[n + 1];
cout << "Enter player values" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> thePlayer[i];
}
MinimumLoserTree<int> *w =
new MinimumLoserTree<int>(thePlayer, n);
cout << "The loser tree is" << endl;
w->output();
w->rePlay(2, 0);
cout << "Changed player 2 to zero, new tree is" << endl;
w->output();
w->rePlay(3, -1);
cout << "Changed player 3 to -1, new tree is" << endl;
w->output();
w->rePlay(7, 2);
cout << "Changed player 7 to 2, new tree is" << endl;
w->output();
delete [] thePlayer;
delete w;
}
loserTree.h
/*
Project name : _30winnerTree
Last modified Date: 2023年12月19日16点48分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 最小输者树——虚基类
*/
#ifndef _31LOSERTREE_LOSERTREE_H
#define _31LOSERTREE_LOSERTREE_H
template<class T>
class loserTree {
public:
virtual ~loserTree() {}
virtual void initialize(T *thePlayer, int number) = 0;
virtual int getTheWinner() const = 0;
virtual void rePlay(int thePLayer, T newvalue) = 0;
};
#endif //_31LOSERTREE_LOSERTREE_H
myExceptions.h
/*
Project name : _30winnerTree
Last modified Date: 2023年12月18日16点28分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 异常汇总
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#define _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#include 运行结果
"C:\Users\15495\Documents\Jasmine\prj\_Algorithm\Data Structures, Algorithms and Applications in C++\_31loserTree\cmake-build-debug\_31loserTree.exe"
Enter number of players, >= 2
8
Enter player values
4
6
5
9
8
2
3
7
The loser tree is
number of players = 8 lowExt = 8 offset = 7
complete winner tree pointers are
1 3 7 2 4 5 8
Changed player 2 to zero, new tree is
number of players = 8 lowExt = 8 offset = 7
complete winner tree pointers are
6 3 7 1 4 5 8
Changed player 3 to -1, new tree is
number of players = 8 lowExt = 8 offset = 7
complete winner tree pointers are
6 2 7 1 4 5 8
Changed player 7 to 2, new tree is
number of players = 8 lowExt = 8 offset = 7
complete winner tree pointers are
6 2 7 1 4 5 8
Process finished with exit code 0