代码随想录27期|Python|Day5|哈希表基础|242.有效的字母异位词|349. 两个数组的交集|202. 快乐数|1. 两数之和
哈希表(散列表)基础
文章链接:代码随想录
定义:哈希表是根据关键码的值而直接进行访问的数据结构。例如数组。(图:代码随想录)
复杂度角度:要枚举的话时间复杂度是O(n),但如果使用哈希表的话, 只需要O(1)就可以做到。
哈希函数
定义:哈希函数如下图所示,通过hashCode把名字转化为数值,一般hashcode是通过特定编码方式,可以将其他数据格式转化为不同的数值。(图:代码随想录)
哈希碰撞
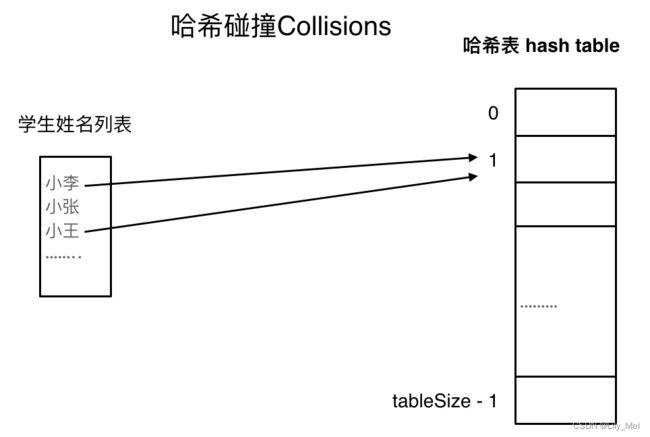
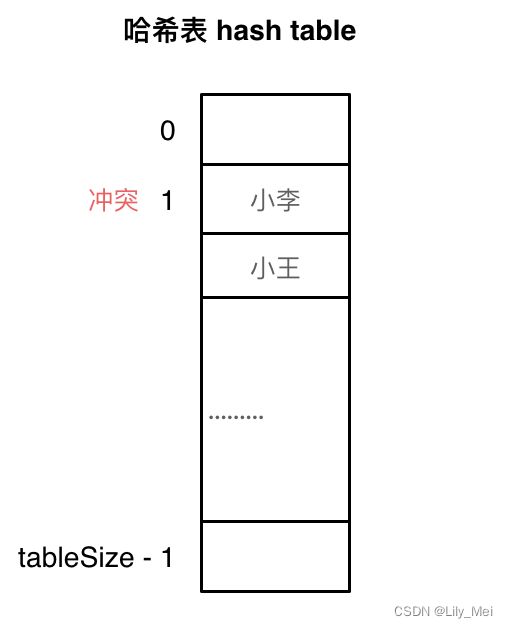
描述:列表元素数量大于哈希表的长度。导致多个元素映射到同一个hashCode下。(图:代码随想录)
拉链法
发生冲突的元素都被存储在链表中。其实就是要选择适当的哈希表的大小,这样既不会因为数组空值而浪费大量内存,也不会因为链表太长而在查找上浪费太多时间。(图:代码随想录)
线性探测法
依靠哈希表中的空位来解决碰撞问题,一定要保证tableSize大于dataSize。(图:代码随想录)
总结
在做面试题目的时候遇到需要判断一个元素是否出现过的场景应该第一时间想到哈希法!(比如链表专题遇到的判断是否有环)
但是哈希法也是牺牲了空间换取了时间,因为我们要使用额外的数组,set或者是map来存放数据,才能实现快速的查找。
204.有效的字母异位词
暴力法
两层for循环,每一个字母都遍历另外一个,时间复杂度![]() 。在字符串大小比较小的时候可以。
。在字符串大小比较小的时候可以。
哈希表法
遍历第一个字符串,统计每一个字母的出现次数。遍历另外一个字符串,每出现一个,对应次数-1。最后统计结果应该全是0,返回true,其余情况(小于0、还有剩余)都为false。时间复杂度![]() 。(图:代码随想录)
。(图:代码随想录)
数组实现(遍历数组比较次数)
class Solution(object):
def isAnagram(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: bool
"""
# 数组实现
shown = [0] * 26
for char in s:
shown[ord(char) - ord('a')] += 1 # 需要使用ord()转换Unicode
for char in t:
shown[ord(char) - ord('a')] -= 1
for num in shown:
if num != 0:
return False
return Truedefaultdict实现(直接比较字典)
class Solution(object):
def isAnagram(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: bool
"""
# defaultdict实现
from collections import defaultdict # 从collection库调用defaulydict
# 实例化,定义value的值为int
s_dict = defaultdict(int)
t_dict = defaultdict(int)
#遍历
for char in s:
s_dict[char] += 1
for char in t:
t_dict[char] += 1
# 直接比较字典
return s_dict == t_dictCounter实现(更方便的写法,直接统计比较counter)
class Solution(object):
def isAnagram(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: bool
"""
# Counter实现
from collections import Counter
return Counter(s) == Counter(t)349.两个数组的交集
注意!!这一题的交集只是数字,不用考虑个数。例子:22233和22445的交集是:2。
另外这题输入数组中每个数字的范围是1000以内的正整数,所以数组方法反而更简便。
暴力法
和上一题一样,使用双层for遍历,时间复杂度![]() 。
。
哈希表法
数组实现(输入数组长度小于1000)
trick:由于输入是正整数,所以在判断每个数字的统计值是否都大于0的时候使用乘积大于0的方式。
class Solution(object):
def intersection(self, nums1, nums2):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type nums2: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
# 数组实现
count1 = [0] * 1001
count2 = [0] * 1001
ans = []
for num in nums1:
count1[num] += 1
for num in nums2:
count2[num] += 1
for i in range(1001):
if count1[i] * count2[i] > 0:
ans.append(i)
return ansset实现(输入数组长度为上亿)
class Solution(object):
def intersection(self, nums1, nums2):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type nums2: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
# set实现
return list((set(nums1) & set(nums2)))202.快乐数
关键点:不满足要求的会出现无限循环,意味着我们只需要判断这些循环的数字是否已经出现就可以了。
set+in实现
class Solution(object):
def isHappy(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: bool
"""
record = set() # 储存出现过的数字
while 1:
n = self.get_sum(n)
if n == 1: # 只有是10···0的
return True
if n in record: # 如果不是,就加入record
return False
else:
record.add(n)
def get_sum(self, n):
new_num = 0
while n:
n, r = divmod(n, 10) #返回商和余数
new_num += r ** 2
return new_num也可以舍弃自定义函数进行简化,
class Solution(object):
def isHappy(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: bool
"""
# set实现(simplified)
record = set()
while n != 1:
n = sum(int(i) ** 2 for i in str(n))
if n in record:
return False
record.add(n)
return True1.两数之和
本题除了暴力法以外,只需一次遍历数组的方式就是储存已经过存在的值,这样在后来查询不用继续遍历,所以使用能够按照值查询的数据结构,也就是字典dict和集合set。
使用字典dict{index: value}
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
records = dict() # 按照index--value存放数对
for index, value in enumerate(nums): # 取出索引和对应的值
if target - value in records: # 如果配对的值在已经出现过的字典里
return index, records[target - value] # 返回这个配对
records[value] = index # 每出现过就记录
return [] # 走完了都没发现有出现过的,返回空的列表使用集合set()+index()函数
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
# 集合实现
record = set()
# set没有可以自定义的key,所以不能添加索引进去,所以需要判定后用nums返回
for index, value in enumerate(nums):
cur_complement = target - value
if cur_complement in record:
return index, nums.index(cur_complement) # 这里使用index函数返回数组中值的对应下标
record.add(value)
return []第五天完结