概述
- Stream也叫Stream流, 是Jdk8开始新增的一套API (java.util.stream.*),可以用于操作集合或者数组的数据。
- 优势: Stream流大量的结合了Lambda的语法风格来编程,提供了一种更加强大,更加简单的方式操作集合或者数组中的数据,代码更简洁,可读性更好。
Stream流的使用步骤
- 获取Stream流得到流水线。
- 根据Stream流提供的各种方法对数据进行处理。
- 获取处理后的结果。
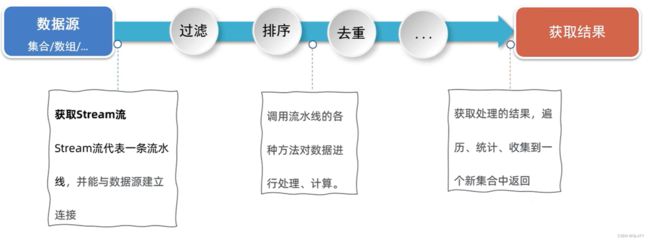 Stream流的使用步骤图解
Stream流的使用步骤图解
常用方法
获取Stream流
| Collection提供的如下方法 |
说明 |
| default Stream stream() |
获取当前集合对象的Stream流 |
不能直接获取Map集合的Stream流,可以先取出Map中的键或值组成一个集合获取这个集合的Stream流,还可以用Entry这个方法吧Map的键和值看成一个整体创建这一个整体的Stream流。
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map. put("A",1);
map. put("B",2);
map. put("C",3);
map. put("D",4);
Set keys = map.keySet();
Stream ks = keys.stream();
Collection values = map.values();
Stream VS = values.stream();
Set> entries = map.entrySet();
Stream> kvs = entries.stream();
| Arrays类提供的如下方法 |
说明 |
| public static Stream stream(T[] array) |
获取当前数组的Stream流 |
| Stream类提供的如下方法 |
说明 |
| public static Stream of(T... values ) |
获取当前接收数据的Stream流 |
Stream流常见的中间方法
方法
●中间方法指的是调用完成后会返回新的Stream流,可以继续使用(支持链式编程)。
| Stream提供的常用中间方法 |
说明 |
| Stream filter(Predicate predicate ) |
用于对流中的数据进行过滤。 |
| Stream sorted( ) |
对元素进行升序排序 |
| Stream sorted(Comparator comparator) |
按照指定规则排序 |
| Stream limit(long maxSize) |
获取前几个元素 |
| Stream skip(long n) |
跳过前几个元素 |
| Stream distinct() |
去除流中重复的元素。 |
| Stream map( Function mapper) |
对元素进行加工,并返回对应的新流 |
| static Stream concat(Stream a, Stream b) |
合并a和b两个流为一个流 |
示例
List scores = new ArrayList<>();
Collections. addALl(scores,88.5, 100.0, 60.0, 99.0, 9.5, 99.6, 25.0);
scores.stream().filter(s -> s >= 60).sorted();
在写下边的例子前先构建一个学生类。
public class Student{
private String name;
private int age;
private double hight;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, double hight) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.hight = hight;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getHight() {
return hight;
}
public void setHight(double hight) {
this.hight = hight;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student= (Student) o;
return age == student.age && Double.compare(hight, student.hight) == 0 && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age, hight);
}
}
基于上边创建的学生类演示Stream流常见的常用中间方法
List students = new ArrayList<>();
Student s1 = new Student("蜘蛛精" , 26 , 172.5);
Student s2 = new Student("蜘蛛精" , 26 , 172.5);
Student s3 = new Student("紫霞" , 23 , 167.6);
Student s4 = new Student("白晶品" , 25 , 169.0);
Student s5 = new Student("牛魔王" , 35 , 183.3);
Student s6 = new Student("牛夫人" , 34 , 168.5) ;
Collections.addAll(students, s1, s2,s3, s4, s5, s6);
//找出年龄大于等于23,且年龄小于等于30岁的学生,并按照年龄降序。
students.stream().filter(s -> s.getAge() >= 23 && s.getAge() <= 30).sorted((o1, o2) -> o2.getAge() - 01.getAge()).forEach(System.out::printLn);
//取出身高最高的前3名学生。
students.stream().sorted((o1, 02) -> DoubLe.compare(o2.getHeight(), 01.getHeight())).limit(3).forEach(System.out::printLn);
//找出身高超过168的学生叫什么名字,要求去除重复的名字。
students.stream().filter(s -> s.getHeight() > 168).map(s - s.getName()).forEach(System.out::printLn);
// distinct去重复,自定义类型的对象(希望内容一样就认为重复,需要重写hashCode和equals方法)
students.stream().filter(s -> s.getHeight() > 168).distinct().forEach(System.out::printLn);
//合并两个流
Stream st1 = Stream.of("A","B");
Stream st2 = Stream. of("A2","B2","C");
Stream allSt = Stream. concat(st1,st2);
allSt.forEach(System.out::printLn);
Stream流常见的终结方法
- 终结方法指的是调用完成后,不会返回新Stream了,没法继续使用流了。
| Stream提供的常用终结方法 |
说明 |
| void forEach(Consumer action) |
对此流运算后的元素执行遍历 |
| long count() |
统计此流运算后的元素个数 |
| Optional max(Comparator comparator) |
获取此流运算后的最大值元素 |
| Optional min(Comparator comparator) |
获取此流运算后的最小值元素 |
收集Stream流
- 收集Stream流:就是把Stream流操作后的结果转回到集合或者数组中去返回。
- 流只能收集一次。
- Stream流:方便操作集合/数组的手段;集合/数组才是开发中的目的。
| Stream提供的常用终结方法 |
说明 |
| R collect (Collector collector) |
把流处理后的结果收集到一个指定的集合中去 |
| 0bject[ ] toArray() |
把流处理后的结果收集到一个数组中去 |
| CollectorsI具类提供了具体的收集方式 |
说明 |
| public static Collector toList() |
把元素收集到List集合中 |
| public static Collector toSet() |
把元素收集到Set集合中 |
| public static Collector toMap(Function keyMapper , Function valueMapper) |
把元素收集到Map集合中 |
//找出身高超过17日的学生对象,并放到一个新集合中去返回。
List students1 = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).collect(Collectors.toList());
Set students2 = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).collect(Collectors.toSet());
//找出身高超过170的学生对象,并把学生对象的名字和身高,存入到一个Map集合返回。
Map map = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170). distinct().collect(Collectors.toMap(a -> a.getName(), a -> a.getHeight()));
//收集到一个数组里
Object[] arr = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() >170).toArray();
//也可以收集到该类型的数组中
Student[] arr = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).toArray(len -> new Student[len]);
