LLM之RAG实战(八)| 使用Neo4j和LlamaIndex实现多模态RAG
人工智能和大型语言模型领域正在迅速发展。一年前,没有人使用LLM来提高生产力。时至今日,很难想象我们大多数人或多或少都在使用LLM提供服务,从个人助手到文生图场景。由于大量的研究和兴趣,LLM每天都在变得越来越好、越来越聪明。不仅如此,他们的理解也开始跨越多种模态。随着GPT-4-Vision和随后的其他LLM的引入,今天的LLM似乎可以很好地处理和理解图像。以下是ChatGPT描述图像中内容的一个示例。
正如所观察到的,ChatGPT非常善于理解和描述图像。我们可以在RAG应用程序中使用其理解图像的能力,在该应用程序中,我们现在可以将文本和图片中的信息结合起来,生成比以往任何时候都更准确的答案,而不仅仅依靠文本来生成准确和最新的答案。使用LlamaIndex,实现多模态RAG pipeline非常容易。受(https://github.com/run-llama/llama_index/blob/main/docs/examples/multi_modal/gpt4v_multi_modal_retrieval.ipynb)的启发,来测试是否可以使用Neo4j作为数据库来实现多模态RAG应用程序。
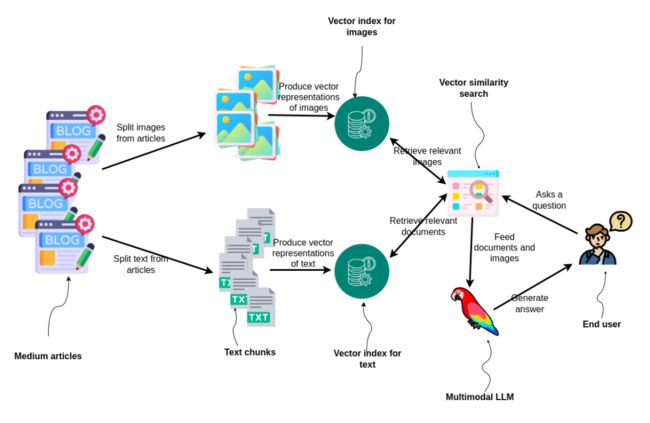
要使用LlamaIndex实现多模态RAG管道,只需实例化两个矢量存储,一个用于图像,另一个用于文本,然后查询这两个矢量,以便检索相关信息以生成最终答案。
多模态RAG首先需要将数据分为图像和文本,然后分别进行embedding并单独构建索引。对于文本,我们将使用ada-002文本嵌入模型;而对于图像,我们将采用[双编码器模型CLIP](https://github.com/openai/CLIP),CLIP可以将文本和图像嵌入到同一嵌入空间中。当最终用户提出问题时,执行两个向量的相似性搜索:一个用于查找相关图像,另一个用于文档。结果被输入到多模态LLM中,该LLM为用户生成答案,展示了处理和利用混合媒体进行信息检索和响应生成的综合方法。
数据预处理
我们将使用[Medium](https://github.com/tomasonjo/blog-datasets/blob/main/articles.zip)作为RAG应用程序的基础数据集。这些文章包含了关于Neo4j图形数据科学库以及将Neo4j与LLM框架相结合的大量信息。从Medium下载的文章是HTML格式。因此,我们需要使用一些编码来分别提取文本和图像。
def process_html_file(file_path):with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as file:soup = BeautifulSoup(file, "html.parser")# Find the required sectioncontent_section = soup.find("section", {"data-field": "body", "class": "e-content"})if not content_section:return "Section not found."sections = []current_section = {"header": "", "content": "", "source": file_path.split("/")[-1]}images = []header_found = Falsefor element in content_section.find_all(recursive=True):if element.name in ["h1", "h2", "h3", "h4"]:if header_found and (current_section["content"].strip()):sections.append(current_section)current_section = {"header": element.get_text(),"content": "","source": file_path.split("/")[-1],}header_found = Trueelif header_found:if element.name == "pre":current_section["content"] += f"```{element.get_text().strip()}```\n"elif element.name == "img":img_src = element.get("src")img_caption = element.find_next("figcaption")caption_text = img_caption.get_text().strip() if img_caption else ""images.append(ImageDocument(image_url=img_src))elif element.name in ["p", "span", "a"]:current_section["content"] += element.get_text().strip() + "\n"if current_section["content"].strip():sections.append(current_section)return images, sections
不会详细介绍解析代码,但我们根据标题h1–h4分割文本并提取图像链接。然后,我们只需通过此函数运行所有文章,即可提取所有相关信息。
all_documents = []all_images = []# Directory to search in (current working directory)directory = os.getcwd()# Walking through the directoryfor root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):for file in files:if file.endswith(".html"):# Update the file path to be relative to the current directoryimages, documents = process_html_file(os.path.join(root, file))all_documents.extend(documents)all_images.extend(images)text_docs = [Document(text=el.pop("content"), metadata=el) for el in all_documents]print(f"Text document count: {len(text_docs)}") # Text document count: 252print(f"Image document count: {len(all_images)}") # Image document count: 328
总共得到252个文本块和328个图像。
对数据创建索引
如前所述,我们必须实例化两个矢量存储,一个用于图像,另一个用于文本。CLIP嵌入模型的尺寸为512,而ada-002的尺寸为1536。
text_store = Neo4jVectorStore(url=NEO4J_URI,username=NEO4J_USERNAME,password=NEO4J_PASSWORD,index_name="text_collection",node_label="Chunk",embedding_dimension=1536)image_store = Neo4jVectorStore(url=NEO4J_URI,username=NEO4J_USERNAME,password=NEO4J_PASSWORD,index_name="image_collection",node_label="Image",embedding_dimension=512)storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(vector_store=text_store)
现在向量索引已经创建好了,我们使用MultiModalVectorStoreIndex来索引这两种模态的信息。
# Takes 10 min without GPU / 1 min with GPU on Google collabindex = MultiModalVectorStoreIndex.from_documents(text_docs + all_images, storage_context=storage_context, image_vector_store=image_store)
MultiModalVectorStoreIndex使用文本和图像嵌入模型来计算嵌入,并在Neo4j中存储和索引结果。仅为图像存储URL,而不是实际的base64或图像的其他表示。
多模态RAG pipeline
这段代码是直接从LlamaIndex多模式烹饪书中复制的。我们首先定义一个多模态LLM和prompt template,然后将所有内容组合为一个查询引擎。
openai_mm_llm = OpenAIMultiModal(model="gpt-4-vision-preview", max_new_tokens=1500)qa_tmpl_str = ("Context information is below.\n""---------------------\n""{context_str}\n""---------------------\n""Given the context information and not prior knowledge, ""answer the query.\n""Query: {query_str}\n""Answer: ")qa_tmpl = PromptTemplate(qa_tmpl_str)query_engine = index.as_query_engine(multi_modal_llm=openai_mm_llm, text_qa_template=qa_tmpl)
现在我们可以继续测试它的性能了。
query_str = "How do vector RAG application work?"response = query_engine.query(query_str)print(response)
我们还可以可视化检索提取的图像以及用于帮助提供最终答案的图像。
LLM得到了两个相同的图像作为输入,说明数据集中有重复的图。然而,我对CLIP嵌入感到惊喜,因为他们能够检索到该系列中最相关的图像。在生产环境中,一般需要对数据做预处理,去除重复数据,本文不做此介绍。
结论
LLM的发展速度比我们历史上习惯的要快,并且跨越了多种模态。我坚信,到明年年底,LLM将很快能够理解视频,因此能够在与你交谈时获得非语言提示。另一方面,我们可以使用图像作为RAG管道的输入,并增强传递给LLM的各种信息,使响应更好、更准确。使用LlamaIndex和Neo4j实现多模式RAG管道非常简单。
参考文献:
[1] https://blog.llamaindex.ai/multimodal-rag-pipeline-with-llamaindex-and-neo4j-a2c542eb0206
[2] https://github.com/tomasonjo/blogs/blob/master/llm/neo4j_llama_multimodal.ipynb