java练习题之多态练习
1:关于多态描述错误的是(D)
A. 父类型的引用指向不同的子类对象
B. 用引用调用方法,只能调用引用中声明的方法
C. 如果子类覆盖了父类中方法,则调用子类覆盖后的方法
D. 子类对象类型会随着引用类型的改变而改变
2:class Super{
public void m1(){}
public void m2(){}
}
class Sub extends Super{
public void m2(){}
public void m3(){}
public void m4(){}
}
创建对象Super s=new Sub();用s引用可以调用的方法(A B)
A.m1() B. m2() C. m3() D. m4()
3:class Super{}
class Sub extends Super{}
class ClassA extends Super{}
public class TestSuper{
public static void main(String[] args){
//1
}
}
对于1处代码及对其描述错误的是(CD)
A. Super s=new Sub();
B. Sub s=new Sub();
Super sup=s;
C. Super s=new Sub();
Sub s2=s; 强转
D. Super s=new Sub();
ClassA c=(ClassA)s;
4:class Super{
public int getLength(){
return 4;
}
}
class Sub extends Super{
public long getLength(){
return 5;
}
}
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Super s1=new Super();
Super s2=new Sub();
System.out.println(s1.getLength()+"\t"+s2.getLenght());
}
}
以上程序输出的结果是(D)
- 4 4 B. 4 5 C.5 5 D.编译报错 父类不能调用子类独有方法
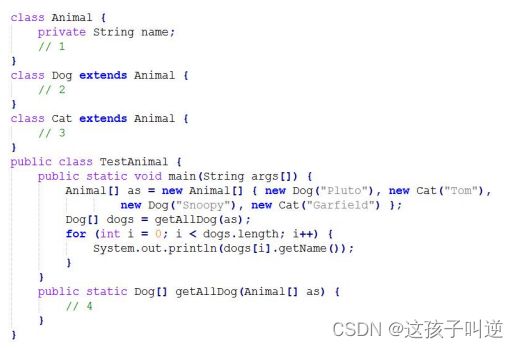
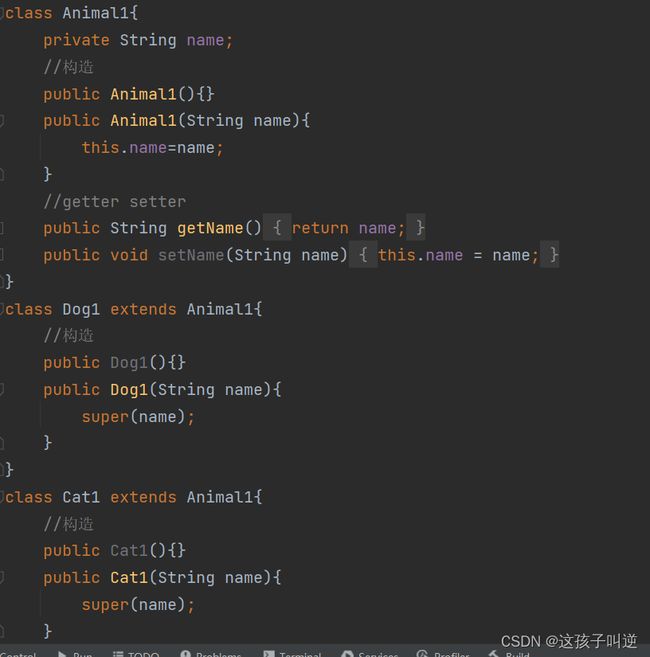
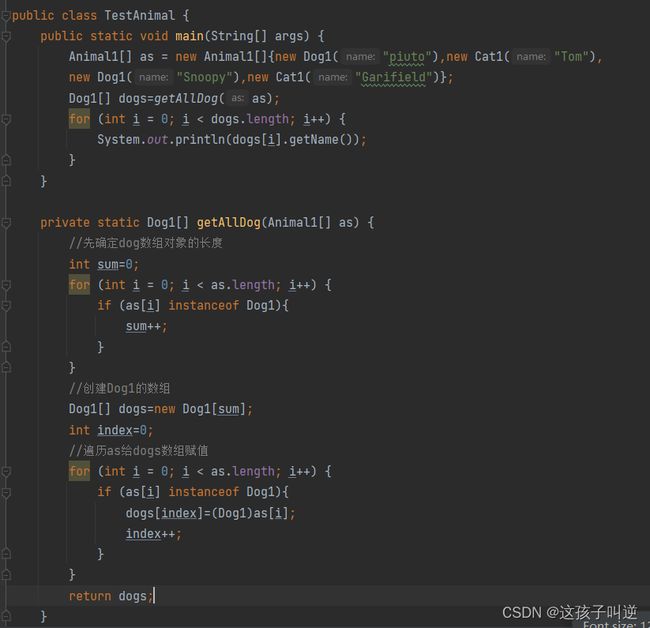
5:完成(1、2、3、4、5)处代码(要求将完整题目抄写)
1:public Animal(){}
public Anamal(String name){
this.name=name;
}
2:public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
3:public Dog(){}
public Dog(String name){
this.name=name;}
4:Animal[] animal={new Dog,new Cat,new Dog,new Cat}
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i if(animal[i]instanceof new Dog){ count++; } } System.out.println(count); } 不能通过 Sub sub=(Sub)s; sub.method(“Hello”); method() in sub method() in super (1) 统计并打印输出数组中所有学生干部的个数 (2) 打印输出所有学生的信息 (1) 在程序的 1、2、3 处填上适当的 构造方法或 get/set 方法 (2) 完成 4 处的填空:getAllDog 方法从一个 Animal 数组中挑选出所有的 Dog 对象,并把这 些对象放在一个 Dog 数组中返回6:(多态)仔细阅读以下代码,编译是否通过,如果通过,写出输出结果;如果不能通过,则如何修改?
7:(多态)仔细阅读以下代码,写出程序运行之后输出的结果。
8:(多态)仔细阅读以下代码,下列几个选项中,有哪几个放在//1 位置能够编译通过()
9:(多态)在继承题目的基础上,定义一个 Person 类型的数组,存储多个不同类型的子类 型对象,
package com.by.homework4.person;
public class Person {
private String name;
private String sex;
private int age;
private String nationality;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, String sex, int age, String nationality) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
this.nationality = nationality;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getNationality() {
return nationality;
}
public void setNationality(String nationality) {
this.nationality = nationality;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("人的吃饭方法");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("人的睡觉方法");
}
public void work(){
System.out.println("人的工作方法");
}
}
package com.by.homework4.person;
public class Student extends Person {
private String school;
private String schoolNum;
public Student(){}
public Student(String school, String schoolNum) {
this.school = school;
this.schoolNum = schoolNum;
}
public Student(String name, String sex, int age, String nationality, String school, String schoolNum) {
super(name, sex, age, nationality);
this.school = school;
this.schoolNum = schoolNum;
}
public String getSchool() {
return school;
}
public void setSchool(String school) {
this.school = school;
}
public String getSchoolNum() {
return schoolNum;
}
public void setSchoolNum(String schoolNum) {
this.schoolNum = schoolNum;
}
public void work(){
System.out.println("学生的学习方法");
}
}
package com.by.homework4.person;
public class StudentLead extends Student {
private String zhiwu;
public StudentLead(){}
public StudentLead(String zhiwu) {
this.zhiwu = zhiwu;
}
public StudentLead(String school, String schoolNum, String zhiwu) {
super(school, schoolNum);
this.zhiwu = zhiwu;
}
public StudentLead(String name, String sex, int age, String nationality, String school, String schoolNum, String zhiwu) {
super(name, sex, age, nationality, school, schoolNum);
this.zhiwu = zhiwu;
}
public String getZhiwu() {
return zhiwu;
}
public void setZhiwu(String zhiwu) {
this.zhiwu = zhiwu;
}
public void kaihui(){
System.out.println("学生的开会方法");
}
}
package com.by.homework4.person;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[]args){
Person []person={new Student("张yi","男",18,"中国","一中","123"),
new Student("张er","男",18,"中国","一中","123"),
new Student("张三","男",18,"中国","一中","123"),
new Student("张si","男",18,"中国","一中","123"),
new Student("张wu","男",18,"中国","一中","123"),
new Student("张liu","男",18,"中国","一中","123")};
for(int i=0;i< person.length;i++){
Student students=(Student) person[i];
System.out.println(students.getName()+students.getSex()+students.getAge()+students.getNationality()
+students.getSchool()+students.getSchoolNum());
}
Student []student={new StudentLead("张yi","男",18,"中国","一中","123","团长"),
new StudentLead("张二","男",18,"中国","一中","123","团长"),
new StudentLead("张三","男",18,"中国","一中","123","团长"),
new StudentLead("张四","男",18,"中国","一中","123","团长"),
new StudentLead("张五","男",18,"中国","一中","123","团长"),
new StudentLead("张六","男",18,"中国","一中","123","团长")};
for(int i=0;i10:编程:在继承题目的基础上,创建一个长度为 3 的数组,里面有三个不同类型的对象, 分别打印这三个圆形、矩形、正方形的周长和面积。
11:编程:阅读以下代码,根据要求完成程序功能
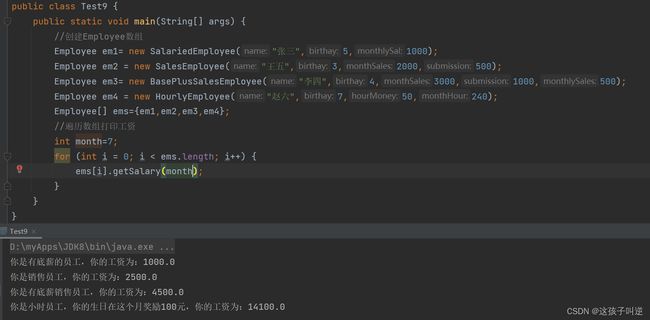
12:编程:在在继承题目的基础上,创建一个 Employee 数组,分别创建若干不同的 Employee 对象,并打印某个月的工资。