【ITK库学习】使用itk库进行图像配准:“Hello World”配准
目录
- 1、itkImageRegistrationMethod / itkImageRegistrationMethodv4
- 2、itkTranslationTransform
- 3、itkMeanSquaresImageToImageMetric / itkMeanSquaresImageToImageMetric4
- 4、itkRegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv / itkRegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv4
图像配准
将一幅图上的点映射到另一幅图像上同源点的空间转换过程;是同意吗目标的两幅图想在空间位置上的对准。
基本组成:参考图像、待配准图像、传递函数、路劲选择、校对机、优化器
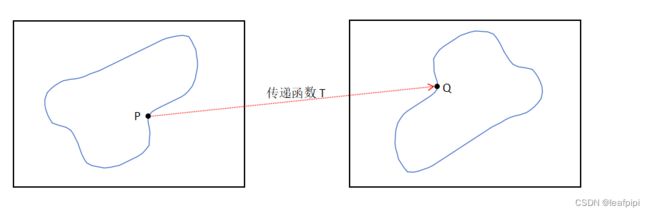
传递函数:从参考图像上的点到待配准图像上点的空间映射关系
校对机:评估待配准图象在非网格位置的程度
路劲选择:提供一种参考图像呗待配准图像配准的程度
优化器:路径选择形成数量上的标准,优化器通过寻找被传递参数定义的空间去最大优化此标准
1、itkImageRegistrationMethod / itkImageRegistrationMethodv4
该类为图像配准方法的基类。
该类定义配准方法的通用接口。它根据要配准的两个图像的类型进行模板化,使用通用 Transform,允许在运行时选择用于配准图像的特定转换类型。该方法使用通用度量来比较两个图像,配准方法的最终目标是找到优化度量的转换参数集。
此类中使用术语:固定图像和移动图像来指示变换正在映射什么图像。
此类使用固定图像的坐标系作为参考,并搜索将点从固定图像的空间映射到移动图像的空间变换。
为此,将连续应用度量来将固定图像与变换后的移动图像进行比较,此过程还需要从移动图像中插入值。
itkImageRegistrationMethodv是基于传统的优化方法,如梯度下降法等,算法复杂度相对简单一些,更容易上手。支持可以在运行时选择通用优化器,优化器的唯一限制是它应能在单值成本函数中运行,因为用于比较图像的指标提供单个值作为输出。
itkImageRegistrationMethodv4是基于图像类的优化方法,使用图像类提供的优化接口进行配准,算法更复杂,如多分辨率策略、局部变形场模型等,可以处理更复杂的配准问题,参数设置和使用稍微复杂一些,需要一定的图像处理和算法知识。允许多阶段配准,其中每个阶段的特征在于可能不同的变换和不同的图像度量。 例如,许多执行线性配准,然后执行变形配准,其中两个阶段都在多个级别中执行。
对算法和参数设置要求较高,可以选择itkImageRegistrationMethodv4,如果只需要简单的图像配准,可以选择itkImageRegistrationMethodv。
共同的成员函数:
SetFixedImage():设置/获取固定图像(参考图像)Set/GetMovingImage():设置/获取移动图像(待配准图像)SetOptimizer()/GetModifiableOptimizer():设置/获取优化器SetMetric()/GetModifiableMetric():设置/获取度量(校对机)
itkImageRegistrationMethodv常用的成员函数:
SetTransform()/GetModifiableTransform:设置/获取变换(传递函数)Set/GetFixedImageRegion():将固定图像的区域设置/获取为在配准期间被视为感兴趣区域,该区域将被传递给ImageMetric,以限制度量计算仅考虑该区域SetFixedImageRegionDefined():打开/关闭固定图像区域的使用,ImageMetric将限制其计算GetFixedImageRegionDefined():如已为固定图像定义了ImageMetric将限制其计算的区域,则为 TrueSet/GetInitialTransformParameters():设置/获取初始转换参数SetInterpolator()GetModifiableInterpolator():设置/获取插值器Set/GetLastTransformParameters():为派生类提供设置此私有变量的能力StartOptimization():初始化GetMTime():返回该对象或其任何缓存的 ivar 的最新修改时间的方法
itkImageRegistrationMethodv4常用的成员函数:
Set/GetOptimizerWeights():设置/获取优化器权重,允许设置每个局部参数的加权数组,如果未设置,权重将被视为同一性, 权重用于在优化期间屏蔽特定参数以保持其恒定, 或者它们可以用来应用另一种先验知识, 权重的大小必须等于局部变换参数的数量Set/GetFixedPointSet():设置/获取固定点集Set/GetFixedInitialTransformInput():设置/获取初始固定变换SetMovingPointSet():设置移动点集Set/GetMovingInitialTransformInput():设置/获取初始移动变换Set/GetNumberOfLevels():设置/获取多分辨率级别的数量, 在设置级别数时,需要为每个级别设置以下内容:a)虚拟域的收缩因子,b)Sigma平滑参数,c)使用指定级别的特定参数转换适配器Set/GetMetricSamplingStrategy():设置/获取指标采样策略SetMetricSamplingPercentagePerLevel():设置指标采样百分比,有效值范围[0.0,1.0]SetMetricSamplePoints():设置度量采样点SetInPlace():请求将 InitialTransform 移植到输出上,而不创建副本Set/GetInitialTransformInput():设置/获取要优化的初始变换,该变换与MovingInitialTransform 一起指定从运动图像到虚拟图像的初始变换,它用于默认参数,可用于指定变换类型,如果过滤器设置了 “InPlace” ,则此变换将是输出变换对象或“嫁接”到输出,否则,此 InitialTransform 将被深度复制或“克隆”到输出,如果未设置此参数,则使用默认构造的输出变换SetInitializeCenterOfLinearOutputTransform():使用队列中前一个变换的中心初始化要优化的当前线性变换,这提供了比默认原点更好的初始化Set/GetTransformParametersAdaptorsPerLevel():设置/获取转换适配器Set/GetSmoothingSigmasPerLevel():设置/获取每个级别的平滑Sigma值,在每个分辨率级别,都会应用高斯平滑滤波器( itkDiscreteGaussianImageFilter ),Sigma值根据选项 m_SmoothingSigmasAreSpecifiedInPhysicalUnits 指定Set/GetSmoothingSigmasAreSpecifiedInPhysicalUnits():设置/获取是否以物理单位(默认)或体素指定每个级别的平滑SigmaSetShrinkFactorsPerLevel():设置每个级别的收缩因子,其中每个级别的每个维度都有一个恒定的收缩因子,例如,输入到 Factors = [4,2,1] 函数将在第一级将每个维度的图像缩小 4,然后在第二级缩小 2,最后一级的1原始分辨率(使用 itkShrinkImageFilter )SetShrinkFactorsPerDimension():为每个维度设置特定级别的收缩因子
2、itkTranslationTransform
向量空间的平移变换(例如空间坐标)
使用映射变换可以获得相同的功能,但性能差异很大。
常用的成员函数:
Set/GetParameters():设置/获取指定的变换值的参数SetIdentity():将参数设置为 IdentityTransformSetFixedParameters():设置固定参数并更新内部变换,Translation Transform 不需要固定参数,因此该方法的实现是空操作Set/GetOffset():设置平移变换的偏移量,此方法将 TranslationTransform 的偏移量设置为用户指定的值IsLinear():表明该变换是线性的,也就是说,给定两个点 P 和 Q,以及标量系数 a 和 b,则T(aP+bQ)=aT§+bT(Q)GetInverseTransform():返回该变换的逆变换
3、itkMeanSquaresImageToImageMetric / itkMeanSquaresImageToImageMetric4
这两个类用于计算图像间均方差的度量类。
指标越小,表示两幅图像的相似度越高。
使用该指标需要调用SetFixedImage()和SetMovingImage()函数设置待比较的两幅图像,并可以使用SetFixedImageRegion()函数进一步指定比较区域,然后调用Initialize()函数进行初始化,然后可以通过调用GetValue()函数计算出指标值。
itkMeanSquaresImageToImageMetric是ITK中较早的版本的度量类,它使用的是传统的像素级别的计算方法。它使用的计算公式为:sum((pixel1 - pixel2)^2) / N,其中pixel1和pixel2分别表示两个图像中的像素值,N表示图像中的像素总数。这种计算方法简单直观,但是对于图像配准等应用可能不够灵活,无法适应复杂的数据类型、图像的变换等。
itkMeanSquaresImageToImageMetricv4在ITK在新版本中被引入,它使用的是基于像素间距离场的计算方法。它使用的计算公式为:sum(weight * (distance1 - distance2)^2) / N,其中weight是像素间的权重值,distance1和distance2分别表示两个图像中的像素距离值,N表示图像中的像素总数。这种计算方法可以更灵活地处理图像间的变换和重采样,并且可以用于处理多通道和向量图像等复杂数据。
常用的成员函数:
GetValueThreadProcessSample():获取匹配测量值GetValueAndDerivative():获取单值优化器的值和导数GetValue():获取值GetDerivative():获取匹配度量的导数
4、itkRegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv / itkRegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv4
二者均为梯度下降优化器,ITK新旧版本的不同。
itkRegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv基于固定步长的梯度下降算法,它有固定的步长参数,需要手动设置。
常用的成员函数:
- StepAlongGradient():考虑由因子表示的步长,沿着校正的梯度前进一步,该方法由 AdvanceOneStep 调用,它预计会被非向量空间中的优化方法覆盖
itkRegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv4基于线搜索的梯度下降算法,它的步长在每次迭代时根据目标函数的变化情况进行动态调整,在许多情况下也具有更好的优化性能和更快的收敛速度。为防止采取太大的步骤,在每次迭代中,该优化器将沿着度量导数的方向采取一步,每次导数的方向突然改变时,优化器都会假设已通过局部极值,并通过将步长减小默认设置为 0.5 的松弛因子来做出反应,初始步长的默认值为 1,并且该值只能通过 SetLearningRate() 手动更改,因为此优化器不使用 ScaleEstimator来自动估计学习率,另请注意,与itkRegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv不同,它 没有“最大化/最小化”选项来修改度量导数的效果,假定指定的度量返回“改进”优化的参数导数结果。
常用的成员函数:
Set/GetRelaxationFactor():设置/获取松弛因子值Set/GetMinimumStepLength():设置/获取用于收敛检查的最小步长(学习率)值,当通过大步越过局部极小值时,将通过松弛因子调整(减小)步长,以便朝着最小值点(收敛)采取更小的步,当步长值达到较小值时,视为收敛,默认值设置为 1e-4 以通过所有测试Set/GetGradientMagnitudeTolerance():设置/获取梯度幅度容差值以进行收敛检查Set/GetCurrentLearningRateRelaxation():设置/获取学习率的当前比例EstimateLearningRate():根据当前梯度估计学习率AdvanceOneStep():沿着梯度方向前进一步,包括变换更新StartOptimization():启动并运行优化
示例代码:
#include "itkImageRegistrationMethodv4.h"
#include "itkTranslationTransform.h"
#include "itkMeanSquaresImageToImageMetricv4.h"
#include "itkRegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv4.h"
#include "itkImage.h"
using namespace itk;
const unsigned int Dim2D = 2; //数据的Dimension
typedef itk::Image<float, Dim2D> FixedImageType;
typedef itk::Image<float, Dim2D> MovingImageType;
class CommandIterationUpdate : public itk::Command
{
public:
using Self = CommandIterationUpdate;
using Superclass = itk::Command;
using Pointer = itk::SmartPointer<Self>;
itkNewMacro(Self);
protected:
CommandIterationUpdate() = default;
public:
using OptimizerType = itk::RegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv4<double>;
using OptimizerPointer = const OptimizerType*;
void
Execute(itk::Object* caller, const itk::EventObject& event) override
{
Execute((const itk::Object*)caller, event);
}
void
Execute(const itk::Object* object, const itk::EventObject& event) override
{
auto optimizer = static_cast<OptimizerPointer>(object);
if (!itk::IterationEvent().CheckEvent(&event))
{
return;
}
std::cout << optimizer->GetCurrentIteration() << " = ";
std::cout << optimizer->GetValue() << " : ";
std::cout << optimizer->GetCurrentPosition() << std::endl;
}
};
bool imageRegistration1(FixedImageType* fixImage, MovingImageType* moveImage, bool useEstimator)
{
typedef itk::LinearInterpolateImageFunction<FixedImageType, double> FixedLinearInterpolatorType;
typedef itk::LinearInterpolateImageFunction<MovingImageType, double> MovingLinearInterpolatorType;
typedef itk::TranslationTransform<double, Dim2D> TransformType;
typedef itk::MeanSquaresImageToImageMetricv4<FixedImageType, MovingImageType> MetricType;
typedef itk::RegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv4<double> OptimizerType;
typedef itk::ImageRegistrationMethodv4<FixedImageType, MovingImageType, TransformType> RegistrationType;
typename TransformType::Pointer movingInitialTransform = TransformType::New();
typename TransformType::ParametersType initialParameters(movingInitialTransform->GetNumberOfParameters());
initialParameters[0] = 0.0; // Initial offset in mm along X
initialParameters[1] = 0.0; // Initial offset in mm along Y
//initialParameters[2] = 0.0; // Initial offset in mm along Z
movingInitialTransform->SetParameters(initialParameters);
typename TransformType::Pointer identityTransform = TransformType::New();
identityTransform->SetIdentity();
typename FixedLinearInterpolatorType::Pointer fixedInterpolator = FixedLinearInterpolatorType::New();
typename MovingLinearInterpolatorType::Pointer movingInterpolator = MovingLinearInterpolatorType::New();
typename MetricType::Pointer metric = MetricType::New();
metric->SetFixedInterpolator(fixedInterpolator);
metric->SetMovingInterpolator(movingInterpolator);
typename OptimizerType::Pointer optimizer = OptimizerType::New();
optimizer->SetLearningRate(4);
optimizer->SetMinimumStepLength(0.001);
optimizer->SetRelaxationFactor(0.5);
if (useEstimator)
{
using ScalesEstimatorType =
itk::RegistrationParameterScalesFromPhysicalShift<MetricType>;
auto scalesEstimator = ScalesEstimatorType::New();
scalesEstimator->SetMetric(metric);
scalesEstimator->SetTransformForward(true);
optimizer->SetScalesEstimator(scalesEstimator);
optimizer->SetDoEstimateLearningRateOnce(true);
}
optimizer->SetNumberOfIterations(200);
auto observer = CommandIterationUpdate::New();
optimizer->AddObserver(itk::IterationEvent(), observer);
constexpr unsigned int numberOfLevels = 1;
typename RegistrationType::Pointer registration = RegistrationType::New();
typename RegistrationType::ShrinkFactorsArrayType shrinkFactorsPerLevel;
shrinkFactorsPerLevel.SetSize(1);
shrinkFactorsPerLevel[0] = 1;
typename RegistrationType::SmoothingSigmasArrayType smoothingSigmasPerLevel;
smoothingSigmasPerLevel.SetSize(1);
smoothingSigmasPerLevel[0] = 0;
registration->SetFixedImage(fixImage); //参考图像
registration->SetMovingImage(moveImage); //待配准图像
registration->SetMetric(metric); //校对机
registration->SetOptimizer(optimizer); //优化器
registration->SetMovingInitialTransform(movingInitialTransform); //初始移动变换
registration->SetFixedInitialTransform(identityTransform); //初始固定变换
registration->SetNumberOfLevels(numberOfLevels); //多分辨率级别的数量
registration->SetSmoothingSigmasPerLevel(smoothingSigmasPerLevel); //每个级别的平滑Sigma值
registration->SetShrinkFactorsPerLevel(shrinkFactorsPerLevel); //每个级别的收缩因子
try
{
registration->Update();
}
catch (itk::ExceptionObject& ex)
{
//读取过程发生错误
std::cerr << "Error: " << ex << std::endl;
return false;
}
TransformType::ConstPointer transform = registration->GetTransform();
TransformType::ParametersType finalParameters = transform->GetParameters();
const double TranslationAlongX = finalParameters[0];
const double TranslationAlongY = finalParameters[1];
const unsigned int numberOfIterations = optimizer->GetCurrentIteration(); //抵达收敛的迭代的实际次数
const double bestValue = optimizer->GetValue(); //参数集合的图像量规值
return true;
}
注:调试过程中报错:itkStatisticsAlgorithm.hxx的533行报: ”InsertSort”: 找不到标识符,是4.13版本的InsertSort引用在函数定义前,修改文件内容,将InsertSort函数定义放在引用函数前bug解决
bug解决办法参考自博客:https://blog.csdn.net/assjaa/article/details/111317338