SpringBoot3-Web开发
WebMvcAutoConfiguration原理
1. 生效条件
@AutoConfiguration(after = { DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class }) //在这些自动配置之后
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET) //如果是web应用就生效,类型SERVLET、REACTIVE 响应式web
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class) //容器中没有这个Bean,才生效。默认就是没有
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)//优先级
@ImportRuntimeHints(WebResourcesRuntimeHints.class)
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
}
2. 效果
- 放了两个Filter:
- a. HiddenHttpMethodFilter;页面表单提交Rest请求(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE)
- b. FormContentFilter: 表单内容Filter,GET(数据放URL后面)、POST(数据放请求体)请求可以携带数据,PUT、DELETE 的请求体数据会被忽略
- 给容器中放了WebMvcConfigurer组件;给SpringMVC添加各种定制功能
- a. 所有的功能最终会和配置文件进行绑定
- b. WebMvcProperties: spring.mvc配置文件
- c. WebProperties: spring.web配置文件
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class) //额外导入了其他配置
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ WebMvcProperties.class, WebProperties.class })
@Order(0)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer, ServletContextAware{
}
3. WebMvcConfigurer接口
4. 静态资源规则源码
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
//1、
addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getWebjarsPathPattern(),
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (registration) -> {
registration.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
if (this.servletContext != null) {
ServletContextResource resource = new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, SERVLET_LOCATION);
registration.addResourceLocations(resource);
}
});
}
- 规则一:访问: /webjars/**路径就去 classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/下找资源.
- a. maven 导入依赖
- b.
- 规则二:访问: /**路径就去 静态资源默认的四个位置找资源
- a. classpath:/META-INF/resources/
- b. classpath:/resources/
- c. classpath:/static/
- d. classpath:/public/
- 规则三:静态资源默认都有缓存规则的设置
- a. 所有缓存的设置,直接通过配置文件: spring.web
- b. cachePeriod: 缓存周期; 多久不用找服务器要新的。 默认没有,以s为单位
- c. cacheControl: HTTP缓存控制;https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/HTTP/Caching
- d. useLastModified:是否使用最后一次修改。配合HTTP Cache规则
如果浏览器访问了一个静态资源 index.js,如果服务这个资源没有发生变化,下次访问的时候就可以直接让浏览器用自己缓存中的东西,而不用给服务器发请求。
registration.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod()));
registration.setCacheControl(this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl());
registration.setUseLastModified(this.resourceProperties.getCache().isUseLastModified());
5. EnableWebMvcConfiguration 源码
//SpringBoot 给容器中放 WebMvcConfigurationSupport 组件。
//我们如果自己放了 WebMvcConfigurationSupport 组件,Boot的WebMvcAutoConfiguration都会失效。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebProperties.class)
public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration implements ResourceLoaderAware
{
}
- HandlerMapping: 根据请求路径 /a 找那个handler能处理请求
a. WelcomePageHandlerMapping:
ⅰ. 访问 /**路径下的所有请求,都在以前四个静态资源路径下找,欢迎页也一样
ⅱ. 找index.html:只要静态资源的位置有一个 index.html页面,项目启动默认访问
6. 为什么容器中放一个WebMvcConfigurer就能配置底层行为
- WebMvcAutoConfiguration 是一个自动配置类,它里面有一个 EnableWebMvcConfiguration
- EnableWebMvcConfiguration继承与 DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration,这两个都生效
- DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration利用 DI 把容器中 所有 WebMvcConfigurer 注入进来
- 别人调用
DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration的方法配置底层规则,而它调用所有 WebMvcConfigurer的配置底层方法。
7. WebMvcConfigurationSupport
提供了很多的默认设置。
判断系统中是否有相应的类:如果有,就加入相应的HttpMessageConverter
jackson2Present = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper", classLoader) &&
ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonGenerator", classLoader);
jackson2XmlPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.xml.XmlMapper", classLoader);
jackson2SmilePresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.smile.SmileFactory", classLoader);
Web场景
1. 自动配置
1、整合web场景
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
2、引入了 autoconfigure功能
3、@EnableAutoConfiguration注解使用@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)批量导入组件
4、加载 META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports 文件中配置的所有组件
5、所有自动配置类如下
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration
====以下是响应式web场景和现在的没关系======
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveMultipartAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebSessionIdResolverAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration
================以上没关系=================
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration
6、绑定了配置文件的一堆配置项
● 1、SpringMVC的所有配置 spring.mvc
● 2、Web场景通用配置 spring.web
● 3、文件上传配置 spring.servlet.multipart
● 4、服务器的配置 server: 比如:编码方式
2. 静态资源
静态资源映射
静态资源映射规则在 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 中进行了定义:
/webjars/**的所有路径 资源都在classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars//**的所有路径 资源都在classpath:/META-INF/resources/、classpath:/resources/、classpath:/static/、classpath:/public/- 所有静态资源都定义了缓存规则。【浏览器访问过一次,就会缓存一段时间】,但此功能参数无默认值
a.period: 缓存间隔。 默认 0S;
b.cacheControl:缓存控制。 默认无;
c.useLastModified:是否使用lastModified头。 默认 false;
静态资源缓存
如前面所述
- 所有静态资源都定义了缓存规则。【浏览器访问过一次,就会缓存一段时间】,但此功能参数无默认值
- a. period: 缓存间隔。 默认 0S;
- b. cacheControl:缓存控制。 默认无;
- c. useLastModified:是否使用lastModified头。 默认 false;
欢迎页
欢迎页规则在 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 中进行了定义:
- 在静态资源目录下找 index.html
- 没有就在 templates下找index模板页
Favicon
1.在静态资源目录下找 favicon.ico
缓存实验
server.port=9000
#1、spring.web:
# 1.配置国际化的区域信息
# 2.静态资源策略(开启、处理链、缓存)
#开启静态资源映射规则
spring.web.resources.add-mappings=true
#设置缓存
#spring.web.resources.cache.period=3600
##缓存详细合并项控制,覆盖period配置:
## 浏览器第一次请求服务器,服务器告诉浏览器此资源缓存7200秒,7200秒以内的所有此资源访问不用发给服务器请求,7200秒以后发请求给服务器
spring.web.resources.cache.cachecontrol.max-age=7200
#使用资源 last-modified 时间,来对比服务器和浏览器的资源是否相同没有变化。相同返回 304
spring.web.resources.cache.use-last-modified=true
自定义静态资源规则
自定义静态资源路径、自定义缓存规则
1. 配置方式
spring.mvc: 静态资源访问前缀路径
spring.web:
● 静态资源目录
● 静态资源缓存策略
#1、spring.web:
# 1.配置国际化的区域信息
# 2.静态资源策略(开启、处理链、缓存)
#开启静态资源映射规则
spring.web.resources.add-mappings=true
#设置缓存
spring.web.resources.cache.period=3600
##缓存详细合并项控制,覆盖period配置:
## 浏览器第一次请求服务器,服务器告诉浏览器此资源缓存7200秒,7200秒以内的所有此资源访问不用发给服务器请求,7200秒以后发请求给服务器
spring.web.resources.cache.cachecontrol.max-age=7200
## 共享缓存
spring.web.resources.cache.cachecontrol.cache-public=true
#使用资源 last-modified 时间,来对比服务器和浏览器的资源是否相同没有变化。相同返回 304
spring.web.resources.cache.use-last-modified=true
#自定义静态资源文件夹位置
spring.web.resources.static-locations=classpath:/a/,classpath:/b/,classpath:/static/
#2、 spring.mvc
## 2.1. 自定义webjars路径前缀
spring.mvc.webjars-path-pattern=/wj/**
## 2.2. 静态资源访问路径前缀
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/static/**
2. 代码方式
● 容器中只要有一个 WebMvcConfigurer 组件。配置的底层行为都会生效
● @EnableWebMvc //禁用boot的默认配置
@Configuration //这是一个配置类
public class MyConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
//保留以前规则
//自己写新的规则。
registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/a/","classpath:/b/")
.setCacheControl(CacheControl.maxAge(1180, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
}
@Configuration //这是一个配置类,给容器中放一个 WebMvcConfigurer 组件,就能自定义底层
public class MyConfig /*implements WebMvcConfigurer*/ {
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer(){
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/a/", "classpath:/b/")
.setCacheControl(CacheControl.maxAge(1180, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
};
}
}
3. 路径匹配
Spring5.3 之后加入了更多的请求路径匹配的实现策略;
以前只支持 AntPathMatcher 策略, 现在提供了 PathPatternParser 策略。并且可以让我们指定到底使用那种策略。
1. Ant风格路径用法
Ant 风格的路径模式语法具有以下规则:
● :表示任意数量的字符。
● ?:表示任意一个字符。
● **:表示任意数量的目录。
● {}:表示一个命名的模式占位符。
● []:表示字符集合,例如[a-z]表示小写字母。
例如:
● .html 匹配任意名称,扩展名为.html的文件。
● /folder1//.java 匹配在folder1目录下的任意两级目录下的.java文件。
● /folder2/**/.jsp 匹配在folder2目录下任意目录深度的.jsp文件。
● /{type}/{id}.html 匹配任意文件名为{id}.html,在任意命名的{type}目录下的文件。
注意:Ant 风格的路径模式语法中的特殊字符需要转义,如:
● 要匹配文件路径中的星号,则需要转义为\。
● 要匹配文件路径中的问号,则需要转义为\?。
2. 模式切换
● PathPatternParser 在 jmh 基准测试下,有 6~8 倍吞吐量提升,降低 30%~40%空间分配率
● PathPatternParser 兼容 AntPathMatcher语法,并支持更多类型的路径模式
●PathPatternParser “**” 多段匹配的支持仅允许在模式末尾使用
@GetMapping("/a*/b?/{p1:[a-f]+}")
public String hello(HttpServletRequest request,
@PathVariable("p1") String path) {
log.info("路径变量p1: {}", path);
//获取请求路径
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
return uri;
}
总结:
● 使用默认的路径匹配规则,是由 PathPatternParser 提供的
● 如果路径中间需要有 **,替换成ant风格路径
# 改变路径匹配策略:
# ant_path_matcher 老版策略;
# path_pattern_parser 新版策略;
spring.mvc.pathmatch.matching-strategy=ant_path_matcher
内容协商
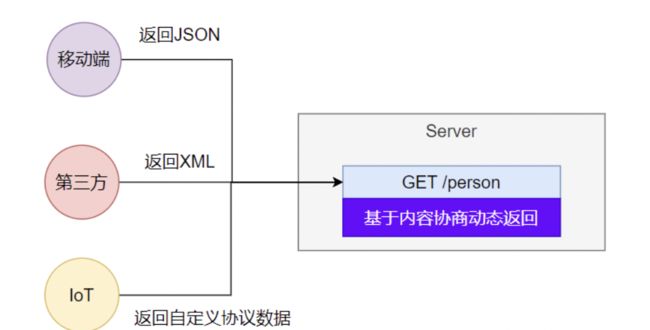
1. 多端内容适配
1. 默认规则
- SpringBoot 多端内容适配。
1.1. 基于请求头内容协商:(默认开启)- 1.1.1. 客户端向服务端发送请求,携带HTTP标准的Accept请求头。
- 1.1.1.1. Accept: application/json、text/xml、text/yaml
- 1.1.1.2. 服务端根据客户端请求头期望的数据类型进行动态返回
- 1.1.1. 客户端向服务端发送请求,携带HTTP标准的Accept请求头。
1.2. 基于请求参数内容协商:(需要开启)
1.2.1. 发送请求 GET /projects/spring-boot?format=json
1.2.2. 匹配到 @GetMapping(“/projects/spring-boot”)
1.2.3. 根据参数协商,优先返回 json 类型数据【需要开启参数匹配设置】
1.2.4. 发送请求 GET /projects/spring-boot?format=xml,优先返回 xml 类型数据
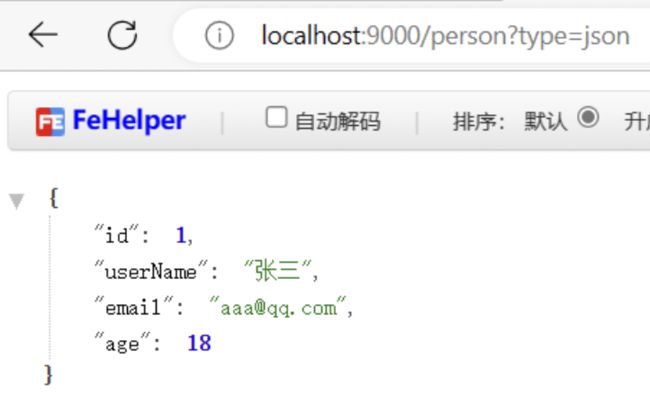
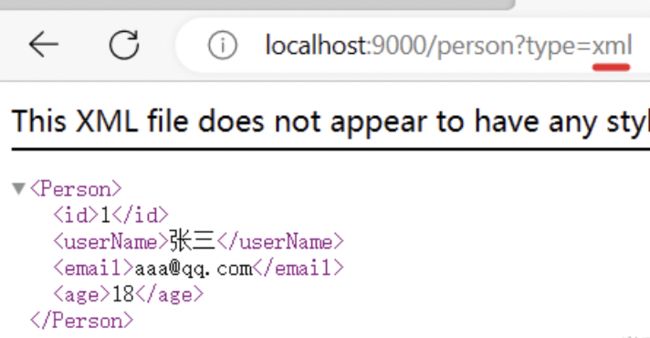
2. 效果演示
请求同一个接口,可以返回json和xml不同格式数据
1.引入支持写出xml内容依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformatgroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xmlartifactId>
dependency>
2.标注注解
@JacksonXmlRootElement // 可以写出为xml文档
@Data
public class Person {
private Long id;
private String userName;
private String email;
private Integer age;
}
3.开启基于请求参数的内容协商
# 开启基于请求参数的内容协商功能。 默认参数名:format。 默认此功能不开启
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.favor-parameter=true
# 指定内容协商时使用的参数名。默认是 format
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.parameter-name=type
4.效果
配置协商规则与支持类型
1.修改内容协商方式
#使用参数进行内容协商
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.favor-parameter=true
#自定义参数名,默认为format
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.parameter-name=myparam
2.大多数 MediaType 都是开箱即用的。也可以自定义内容类型,如
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.media-types.yaml=text/yaml
自定义内容返回
1. 增加yaml返回支持
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformatgroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-yamlartifactId>
dependency>
把对象写出成YAML
public static void main(String[] args) throws JsonProcessingException {
Person person = new Person();
person.setId(1L);
person.setUserName("张三");
person.setEmail("[email protected]");
person.setAge(18);
YAMLFactory factory = new YAMLFactory().disable(YAMLGenerator.Feature.WRITE_DOC_START_MARKER);
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(factory);
String s = mapper.writeValueAsString(person);
System.out.println(s);
}
编写配置
#新增一种媒体类型
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.media-types.yaml=text/yaml
增加HttpMessageConverter组件,专门负责把对象写出为yaml格式
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer(){
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override //配置一个能把对象转为yaml的messageConverter
public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
converters.add(new MyYamlHttpMessageConverter());
}
};
}
2. 思考:如何增加其他
● 配置媒体类型支持:
○ spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.media-types.yaml=text/yaml
● 编写对应的HttpMessageConverter,要告诉Boot这个支持的媒体类型
○ 按照3的示例
● 把MessageConverter组件加入到底层
○ 容器中放一个WebMvcConfigurer 组件,并配置底层的MessageConverter
3. HttpMessageConverter的示例写法
public class MyYamlHttpMessageConverter extends AbstractHttpMessageConverter<Object> {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = null; //把对象转成yaml
public MyYamlHttpMessageConverter(){
//告诉SpringBoot这个MessageConverter支持哪种媒体类型 //媒体类型
super(new MediaType("text", "yaml", Charset.forName("UTF-8")));
YAMLFactory factory = new YAMLFactory()
.disable(YAMLGenerator.Feature.WRITE_DOC_START_MARKER);
this.objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(factory);
}
@Override
protected boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
//只要是对象类型,不是基本类型
return true;
}
@Override //@RequestBody
protected Object readInternal(Class<?> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException {
return null;
}
@Override //@ResponseBody 把对象怎么写出去
protected void writeInternal(Object methodReturnValue, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
//try-with写法,自动关流
try(OutputStream os = outputMessage.getBody()){
this.objectMapper.writeValue(os,methodReturnValue);
}
}
}
内容协商原理-HttpMessageConverter
● HttpMessageConverter 怎么工作?合适工作?
● 定制 HttpMessageConverter 来实现多端内容协商
● 编写WebMvcConfigurer提供的configureMessageConverters底层,修改底层的MessageConverter
1. @ResponseBody由HttpMessageConverter处理
标注了@ResponseBody的返回值 将会由支持它的 HttpMessageConverter写给浏览器
- 如果controller方法的返回值标注了 @ResponseBody 注解
1.1. 请求进来先来到DispatcherServlet的doDispatch()进行处理
1.2. 找到一个 HandlerAdapter 适配器。利用适配器执行目标方法
1.3. RequestMappingHandlerAdapter来执行,调用invokeHandlerMethod()来执行目标方法
1.4. 目标方法执行之前,准备好两个东西
1.4.1. HandlerMethodArgumentResolver:参数解析器,确定目标方法每个参数值
1.4.2. HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler:返回值处理器,确定目标方法的返回值改怎么处理
1.5. RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 里面的invokeAndHandle()真正执行目标方法
1.6. 目标方法执行完成,会返回返回值对象
1.7. 找到一个合适的返回值处理器 HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler
1.8. 最终找到 RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor能处理 标注了 @ResponseBody注解的方法
1.9. RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 调用writeWithMessageConverters ,利用MessageConverter把返回值写出去
上面解释:@ResponseBody由HttpMessageConverter处理
2. HttpMessageConverter 会先进行内容协商
2.1. 遍历所有的MessageConverter看谁支持这种内容类型的数据
2.2. 最终因为要json所以MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter支持写出json
2.3. jackson用ObjectMapper把对象写出去
2. WebMvcAutoConfiguration提供几种默认HttpMessageConverters
● EnableWebMvcConfiguration通过 addDefaultHttpMessageConverters添加了默认的MessageConverter;如下:
○ ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter: 支持字节数据读写
○ StringHttpMessageConverter: 支持字符串读写
○ ResourceHttpMessageConverter:支持资源读写
○ ResourceRegionHttpMessageConverter: 支持分区资源写出
○ AllEncompassingFormHttpMessageConverter:支持表单xml/json读写
○ MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter: 支持请求响应体Json读写
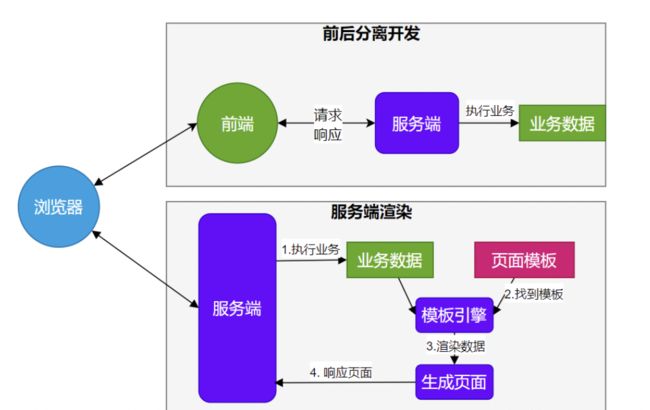
模板引擎
● 由于 SpringBoot 使用了嵌入式 Servlet 容器。所以 JSP 默认是不能使用的。
● 如果需要服务端页面渲染,优先考虑使用 模板引擎。
模板引擎页面默认放在 src/main/resources/templates
SpringBoot 包含以下模板引擎的自动配置
- FreeMarker
- Groovy
- Thymeleaf
- Mustache
Thymeleaf官网:https://www.thymeleaf.org/
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Good Thymes Virtual Grocerytitle>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" media="all" th:href="@{/css/gtvg.css}" />
head>
<body>
<p th:text="#{home.welcome}">Welcome to our grocery store!p>