JavaScript数据结构与算法(1)(数组、栈、队列、链表)(ES6)
注意:原教学视频:JavaScript(ES6)数据结构和算法 | JavaScript数据结构与算法 (都是CoderWhy老师的教学)
原作者(笔记)链接:JavaScript 数据结构与算法 | JavaScript数据结构与算法博客目录
PS:本文仅在学习过程中,对两篇笔记进行整合及总结(包含少量补充),以作学习之用。
Part1: 数组、栈、队列、优先队列、单向链表、双向链表。
前言
1. 什么是数据结构?
数据结构就是在计算机中,存储和组织数据的方式。
解决问题方法的效率,根据数据的组织方式有关。我们无需关心数据结构到底是什么,我们需要考虑的问题是:**以什么样的方式,来存储和组织我们的数据才能在使用数据时更加方便呢?**这才是学习数据结构的意义。
常见的数据结构:
- 数组(Aarray)
- 栈(Stack)
- 链表(Linked List)
- 图(Graph)
- 散列表(Hash)
- 队列(Queue)
- 树(Tree)
- 堆(Heap)
注意:数据结构与算法与语言无关,常见的编程语言都有直接或间接的使用上述常见的数据结构。
2. 什么是算法?
算法(Algorithm)的定义:
- 一个有限指令集,每条指令的描述不依赖于语言。
- 接收一些输入(有些情况下不需要输入)。
- 产生输出。
- 一定在有限步骤之后终止。
通俗理解:解决问题的办法/步骤逻辑。数据结构的实现,离不开算法。
数组结构
普通语言的数组封装(如Java的ArrayList):
- 常见语言的数组不能存放不同的数据类型,因此所有在封装时通常存放在数组中的是Object类型
- 常见语言的数组容量不会自动改变(需要进行扩容操作)。一般需要创建一个新数组放入以前的数组数据再放入其他内容
- 常见语言的数组进行中间插入和删除操作性能比较低
几乎所有的编程语言都原生支持数组类型,因为数组是最简单的内存数据结构。 数组通常情况下用于存储一系列同一种数据类型的值。 但在 JavaScript 里,数组中可以保存不同类型的值。但我们还是要遵守最佳实践,别这么做(大多数语言都没这个能力)。
创建和初始化数组
-
new Array()
const daysOfWeek = new Array('Sunday', 'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday','Thursday', 'Friday', 'Saturday'); -
[ ]
const daysOfWeek = ['Sunday', 'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Friday', 'Saturday'];
数组常见操作
添加元素
-
添加一个元素到数组的最后位置
array.push(item) -
在数组首位插入一个元素
array.unshift(item) -
在指定索引位置插入元素
array.splice(index.js, 0, item)splice() 第二个参数为 0 时,表示插入数据。
let myArray = [1, 2, 3]; // 在 索引 0 的位置,插入 A myArray.splice(0, 0, "A"); console.log(myArray); //--> ['A', 1, 2, 3]
删除元素
-
删除数组最后的元素
array.pop(item) -
删除数组首位的元素
array.shift(item) -
删除指定索引位置的元素
array.splice(start, number)例如:
let myArray2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; // 删除索引 4 位置起,2 个元素 myArray2.splice(4, 2); console.log(myArray2); //--> [1, 2, 3]
修改元素
-
修改指定索引位置的元素
array.splice(index.js, 1, item)let myArray3 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]; // 修改 索引 1 的位置的元素为 AA myArray2.splice(1, 1, "AA"); console.log(myArray3); //--> [1, "AA", 3, 4, 5, 6] -
修改指定索引位置的几个元素
array.splice(index.js, number, item)let myArray4 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]; // 在 索引 2 的位置起,修改两个元素为 AA BB myArray2.splice(2, 2, "AA", "BB"); console.log(myArray3); //--> [1, 2, "AA", "BB", 5, 6, 7]
栈结构
数组也是一种线性结构,并且可以在任意位置插入和删除数据;
但是有时候,我们为了实现某些功能,必须对这种任意性加以限制;
而栈和队列就是比较常见的受限的线性结构。
**栈结构示意图 **
![]()
栈的定义
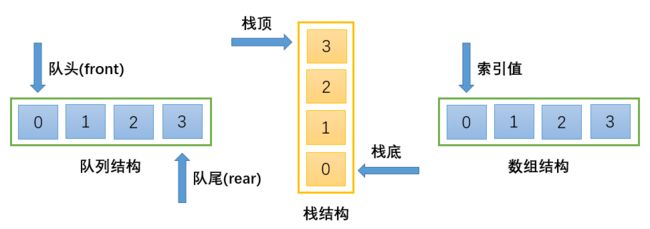
栈(stack),是一种受限的线性表。栈的特点为后进先出(LIFO)。
- 其限制是仅允许在表的一端进行插入和删除运算。这一端被称为栈顶,相对的。另一端称为栈底。
- LIFO(last in first out)表示后进入的元素,先弹出栈空间。
- 向一个栈插入新元素又称作进栈、入栈或压栈,它是把新元素放到栈顶元素的上面,使之成为新的栈顶元素。
- 从一个栈删除元素又称作出栈或退栈,它是把栈顶元素删除掉,使其相邻的元素成为新的栈顶元素。
程序中的栈结构
- 函数调用栈:A(B(C(D()))): 即 A 函数中调用 B,B 调用 C,C 调用 D;在 A 执行的过程中会将 A 压入栈,随后 B 执行时 B 也被压入栈,函数 C 和 D 执行时也会被压入栈。所以当前栈的顺序为:A->B->C->D(栈顶);函数 D 执行完之后,会弹出栈被释放,弹出栈的顺序为 D->C->B->A;
- 递归: 为什么没有停止条件的递归会造成栈溢出?比如函数 A 为递归函数,不断地调用自己(因为函数还没有执行完,不会把函数弹出栈),不停地把相同的函数 A 压入栈,最后造成栈溢出(Queue Overfloat)。
栈结构面试题
有六个元素6,5,4,3,2,1的顺序进栈,问下列哪一个不是合法的出栈序列?
A: 5 4 3 6 1 2 B:4 5 3 2 1 6 C:3 4 6 5 1 2 D:2 3 4 1 5 6
(注意:题目所说的按顺序进栈指的不是一次性全部进栈,而是有进有出,进栈顺序为6 -> 5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1)
解析:
- A答案:65进栈,5出栈,4进栈出栈,3进栈出栈,6出栈,21进栈,1出栈,2出栈(整体入栈顺序符合654321);
- B答案:654进栈,4出栈,5出栈,3进栈出栈,2进栈出栈,1进栈出栈,6出栈(整体的入栈顺序符合654321);
- C答案:6543进栈,3出栈,4出栈,之后应该5出栈而不是6,所以错误;
- D答案:65432进栈,2出栈,3出栈,4出栈,1进栈出栈,5出栈,6出栈。符合入栈顺序;
栈常见的操作
push(element):添加一个新元素到栈顶位置pop():移除栈顶的元素,同时返回被移除的元素peek():返回栈顶的元素,但不对栈做任何修改isEmpty():若栈中没有任何元素就返回true,否则返回falsesize():返回栈里元素的个数。与数组的length属性类似toString():将栈结构的内容以字符形式返回
代码实现
实现栈结构有两种比较常见的方式:基于数组和基于链表。(Js中没有自带链表)
//封装栈类
function Stack() {
//栈中的属性
this.items = [];
//栈的相关操作
//1.压栈
//方式一(不推荐):给对象添加方法,其他对象不能复用
// this.push = () => { }
//方式二(推荐):给Stack类添加方法,能够多对象复用
Stack.prototype.push = function (element) {
this.items.push(element);
}
//2.栈中取出元素
Stack.prototype.pop = function () {
return this.items.pop();
}
//3.查看栈顶元素
Stack.prototype.peek = function () {
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
//4.判断栈是否为空
Stack.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
return this.items.length == 0;
}
//5.获取栈中元素的个数
Stack.prototype.size = function () {
return this.items.length;
}
//6.toString()方法
Stack.prototype.toString = function () {
var resultString = '';
for (var i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++) {
resultString += this.items[i] + '';
}
return resultString;
}
}
简单应用:十进制转二进制
封装源码:
function dec2bin(decNumber) {
//定义栈对象
var stack = new Stack();
while (decNumber > 0) {
//1.获取余数,并放入栈中
stack.push(decNumber % 2);
//2.获取整除后的结果
decNumber = Math.floor(decNumber / 2); //Math.floor():向下取整
}
//3.从栈中取出0和1
var binaryString = '';
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
binaryString += stack.pop();
}
return binaryString;
}
队列结构
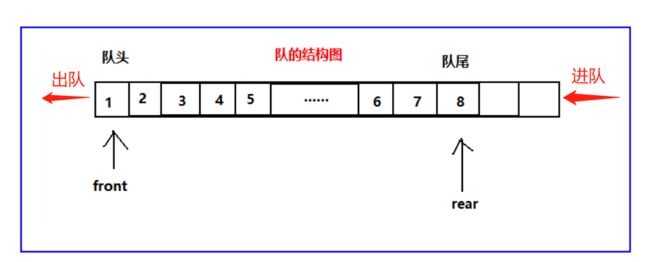
队列(Queue),它是一种受限的线性表,先进先出(FIFO)。
受限之处在于它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作,而在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作。
队列的实现
队列的实现和栈一样,可以基于数组和链表实现。
队列的常见操作
enqueue(element):向队列尾部添加一个(或多个)新的项dequeue():移除队列的第一(即排在队列最前面的)项,并返回被移除的元素front():移除队列中的第一个元素——最先被添加,也将是最先被移除的元素队列不做任何变动(不移除元素,只返回元素信息——与Stack类的peek方法非常类似)isEmpty():如果队列中不包含任何元素,返回true,否则返回falsesize():返回队列包含的元素个数,与数组的length属性类似toString():将队列中的内容,转成字符串形式
代码实现
// 基于数组封装队列类
function Queue() {
// 属性
this.items = [];
// 方法
// 1.enqueue():将元素加入到队列中
Queue.prototype.enqueue = element => {
this.items.push(element)
}
// 2.dequeue():从队列中删除前端元素
Queue.prototype.dequeue = () => {
return this.items.shift()
}
// 3.front():查看前端的元素
Queue.prototype.front = () => {
return this.items[0]
}
// 4.isEmpty:查看队列是否为空
Queue.prototype.isEmpty = () => {
return this.items.length == 0;
}
// 5.size():查看队列中元素的个数
Queue.prototype.size = () => {
return this.items.length
}
// 6.toString():将队列中元素以字符串形式输出
Queue.prototype.toString = () => {
let resultString = ''
for (let i of this.items){
resultString += i + ' '
}
return resultString
}
}
队列应用:击鼓传花
使用队列实现小游戏:击鼓传花。
分析:传入一组数据和设定的数字num,循环遍历数组内元素,遍历到的元素为指定数字num时将该元素删除,直至数组剩下一个元素。
代码实现:
// 队列应用:面试题:击鼓传花
let passGame = (nameList, num) => {
//1.创建队列结构
let queue = new Queue()
//2.将所有人依次加入队列
// 这是ES6的for循环写法,i相当于nameList[i]
for(let i of nameList){
queue.enqueue(i)
}
// 3.开始数数
while(queue.size() > 1){//队列中只剩1个人就停止数数
// 不是num的时候,重新加入队列末尾
// 是num的时候,将其从队列中删除
// 3.1.num数字之前的人重新放入队列的末尾(把队列前面删除的加到队列最后)
for(let i = 0; i< num-1; i++ ){
queue.enqueue(queue.dequeue())
}
// 3.2.num对应这个人,直接从队列中删除
/*
思路是这样的,由于队列没有像数组一样的下标值不能直接取到某一元素,所以采用,把num前面的num-1个元素先删除后添加到队列末尾,这样第num个元素就排到了队列的最前面,可以直接使用dequeue方法进行删除
*/
queue.dequeue()
}
//4.获取剩下的那个人
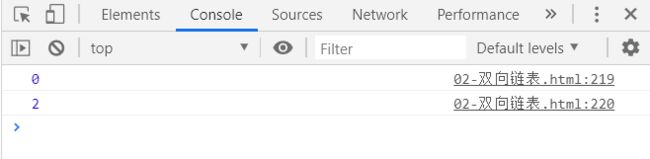
console.log(queue.size());
let endName = queue.front()
console.log('最终剩下的人:' + endName);
return nameList.indexOf(endName);
}
//5.测试击鼓传花
let names = ['lily', 'lucy', 'Tom', 'Lilei', 'Tony']
console.log(passGame(names, 3));
优先级队列
优先级队列的特点
- 普通的队列插入一个元素,数据会被放在后端,并且需要前面所有的元素都处理完成后才会处理前面的数据。
- 但是优先级队列,在插入一个元素的时候会考虑该数据的优先级。
- 和其他数据优先级进行比较。
- 比较完成后,可以得出这个元素在队列中正确的位置。
- 其他处理方式,和基本队列的处理方式一样。
优先级队列主要考虑的问题:
- 每个元素不再只是一个数据,还包含数据的优先级;
- 在添加数据过程中,根据优先级放入到正确位置;
优先级队列的实现
使用构造函数实现
// 封装优先级队列
function PriorityQueue() {
//内部类:在类里面再封装一个类;表示带优先级的数据
function QueueElement(element, priority) {
this.element = element;
this.priority = priority;
}
// 封装属性
this.items = []
// 1.实现按照优先级插入方法
PriorityQueue.prototype.enqueue = (element, priority) => {
// 1.1.创建QueueElement对象
let queueElement = new QueueElement(element, priority);
// 1.2.判断队列是否为空,没有其他元素可以直接插入
if(this.items.length == 0){
this.items.push(queueElement);
}else{
// 定义一个变量记录是否成功添加了新元素
let added = false;
for(let i of this.items){
// 让新插入的元素与原有元素进行优先级比较(priority越小,优先级越大)
if(queueElement.priority < i.priority){
this.items.splice(i, 0, queueElement);
added = true;
// 新元素已经找到插入位置了可以使用break停止循环
break;
}
}
// 新元素没有成功插入,就把它放在队列的最前面
if(!added){
this.items.push(queueElement);
}
}
}
// 2.dequeue():从队列中删除前端元素
PriorityQueue.prototype.dequeue = () => {
return this.items.shift();
}
// 3.front():查看前端的元素
PriorityQueue.prototype.front = () => {
return this.items[0];
}
// 4.isEmpty():查看队列是否为空
PriorityQueue.prototype.isEmpty = () => {
return this.items.length == 0;
}
// 5.size():查看队列中元素的个数
PriorityQueue.prototype.size = () => {
return this.items.length;
}
// 6.toString():以字符串形式输出队列中的元素
PriorityQueue.prototype.toString = () => {
let resultString = '';
for (let i of this.items){
resultString += i.element + '-' + i.priority + ' ';
}
return resultString;
}
}
// 测试代码
let pq = new PriorityQueue();
pq.enqueue('Tom',111);
pq.enqueue('Hellen',200);
pq.enqueue('Mary',30);
pq.enqueue('Gogo',27);
// 打印修改过后的优先队列对象
console.log(pq);
使用class实现
// 优先队列内部的元素类
class QueueElement {
constructor(element, priority) {
this.element = element;
this.priority = priority;
}
}
// 优先队列类(继承 Queue 类)
export class PriorityQueue extends Queue {
constructor() {
super();
}
// enqueue(element, priority) 入队,将元素按优先级加入到队列中
// 重写 enqueue()
enqueue(element, priority) {
// 根据传入的元素,创建 QueueElement 对象
const queueElement = new QueueElement(element, priority);
// 判断队列是否为空
if (this.isEmpty()) {
// 如果为空,不用判断优先级,直接添加
this.items.push(queueElement);
} else {
// 定义一个变量记录是否成功添加了新元素
let added = false;
for (let i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++) {
// 让新插入的元素进行优先级比较,priority 值越小,优先级越大
if (queueElement.priority < this.items[i].priority) {
// 在指定的位置插入元素
this.items.splice(i, 0, queueElement);
added = true;
break;
}
}
// 如果遍历完所有元素,优先级都大于新插入的元素,就将新插入的元素插入到最后
if (!added) {
this.items.push(queueElement);
}
}
}
// dequeue() 出队,从队列中删除前端元素,返回删除的元素
// 继承 Queue 类的 dequeue()
dequeue() {
return super.dequeue();
}
// front() 查看队列的前端元素
// 继承 Queue 类的 front()
front() {
return super.front();
}
// isEmpty() 查看队列是否为空
// 继承 Queue 类的 isEmpty()
isEmpty() {
return super.isEmpty();
}
// size() 查看队列中元素的个数
// 继承 Queue 类的 size()
size() {
return super.size();
}
// toString() 将队列中元素以字符串形式返回
// 重写 toString()
toString() {
let result = '';
for (let item of this.items) {
result += item.element + '-' + item.priority + ' ';
}
return result;
}
}
const priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue();
//测试
// 入队 enqueue() 测试
priorityQueue.enqueue('A', 10);
priorityQueue.enqueue('B', 15);
priorityQueue.enqueue('C', 11);
priorityQueue.enqueue('D', 20);
priorityQueue.enqueue('E', 18);
console.log(priorityQueue.items);
//--> output:
// QueueElement {element: "A", priority: 10}
// QueueElement {element: "C", priority: 11}
// QueueElement {element: "B", priority: 15}
// QueueElement {element: "E", priority: 18}
// QueueElement {element: "D", priority: 20}
// 出队 dequeue() 测试
priorityQueue.dequeue();
priorityQueue.dequeue();
console.log(priorityQueue.items);
//--> output:
// QueueElement {element: "B", priority: 15}
// QueueElement {element: "E", priority: 18}
// QueueElement {element: "D", priority: 20}
// isEmpty() 测试
console.log(priorityQueue.isEmpty()); //--> false
// size() 测试
console.log(priorityQueue.size()); //--> 3
// toString() 测试
console.log(priorityQueue.toString()); //--> B-15 E-18 D-20
补充
数组的push方法在数组、栈和队列中的形式:
- 数组:在数组[0,1,2]中,pop(3),结果为[0,1,2,3];
- 栈:执行pop(0),pop(1),pop(2),pop(3),从栈底到栈顶的元素分别为:0,1,2,3;如果看成数组,可写为[0,1,2,3],但是索引为3的元素3其实是栈顶元素;所以说栈的push方法是向栈顶添加元素(但在数组的视角下为向数组尾部添加元素);
- 队列:enqueue方法可以由数组的push方法实现,与数组相同,相当于在数组尾部添加元素。
单向链表
认识链表
链表和数组
链表和数组一样,可以用于存储一系列的元素,但是链表和数组的实现机制完全不同。
数组
-
存储多个元素,数组(或列表)可能是最常用的数据结构。
-
几乎每一种编程语言都有默认实现数组结构,提供了一个便利的
[]语法来访问数组元素。 -
数组缺点:
-
数组的创建需要申请一段连续的内存空间(一整块内存),并且大小是固定的,当前数组不能满足容量需求时,需要扩容。 (一般情况下是申请一个更大的数组,比如 2 倍,然后将原数组中的元素复制过去)
-
在数组开头或中间位置插入数据的成本很高,需要进行大量元素的位移。
-
链表
-
存储多个元素,另外一个选择就是使用链表。
-
不同于数组,链表中的元素在内存中不必是连续的空间。
-
链表的每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(有些语言称为指针)组成。
-
链表优点:
-
内存空间不必是连续的,可以充分利用计算机的内存,实现灵活的内存动态管理。
-
链表不必在创建时就确定大小,并且大小可以无限延伸下去。
-
链表在插入和删除数据时,时间复杂度可以达到 O(1),相对数组效率高很多。
-
-
链表缺点:
-
访问任何一个位置的元素时,需要从头开始访问。(无法跳过第一个元素访问任何一个元素)
-
无法通过下标值直接访问元素,需要从头开始一个个访问,直到找到对应的元素。
-
虽然可以轻松地到达下一个节点,但是回到前一个节点是很难的。
-
单向链表的定义
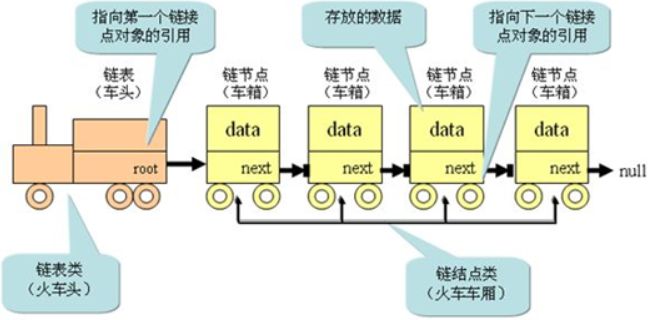
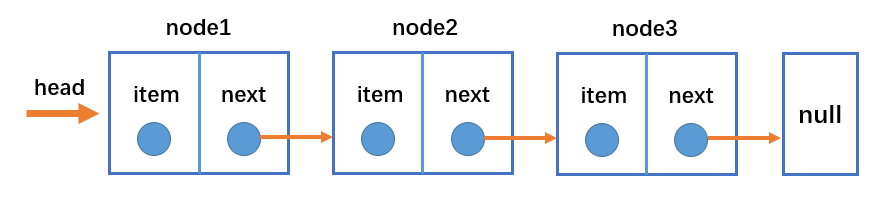
单向链表类似于火车头,一节车厢载着乘客(数据),通过节点连接另一节车厢,以此类推。
- head属性指向链表的第一个节点;
- 链表中的最后一个节点指向null;
- 当链表中一个节点也没有的时候,head直接指向null;
链表中的常见操作
append(element)向链表尾部添加一个新的项。insert(position, element)向链表的特定位置插入一个新的项。getData(position)获取对应位置的元素数据。indexOf(element)返回元素在链表中的索引。如果链表中没有该元素就返回-1。update(position, element)修改某个位置的元素。removeAt(position)从链表的特定位置移除一项。remove(element)从链表中移除一项。isEmpty()如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回 trun,如果链表长度大于 0 则返回 false。size()返回链表包含的元素个数,与数组的 length 属性类似。toString()由于链表项使用了 Node 类,就需要重写继承自 JavaScript 对象默认的 toString 方法,让其只输出元素的值。
封装单向链表类
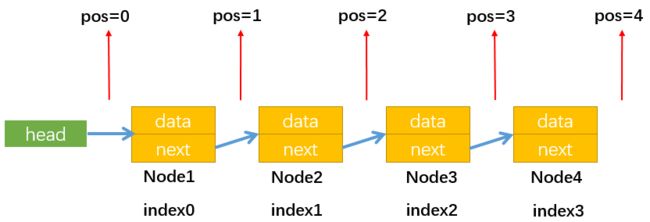
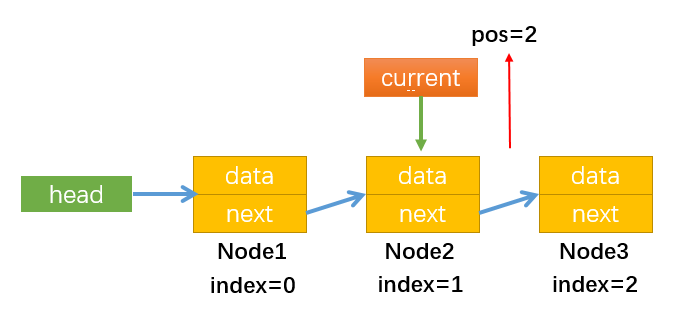
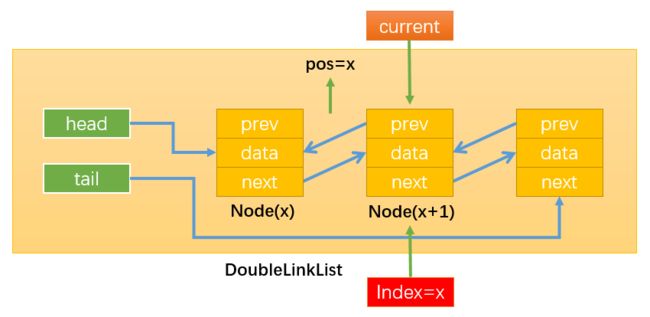
首先需要弄清楚:下文中的position指的是两个节点之间,并且与index的关系如下图所示:
position的值一般表示position所指位置的下一个节点。当position的值与index的值相等时,比如position = index = 1,那么它们都表示Node2。
0. 创建单向链表类
先创建单向链表类LinkedList,并添加基本属性,再逐步实现单向链表的常用方法:
// 封装单向链表类
function LinkedList(){
// 封装一个内部类:节点类
function Node(data){
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
// 属性
// 属性head指向链表的第一个节点
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
}
/*ES6使用class实现*/
class LinkedList {
// 初始链表长度为 0
length = 0;
// 初始 head 为 null,head 指向链表的第一个节点
head = null;
// 内部类(链表里的节点 Node)
Node = class {
data;
next = null;
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
}
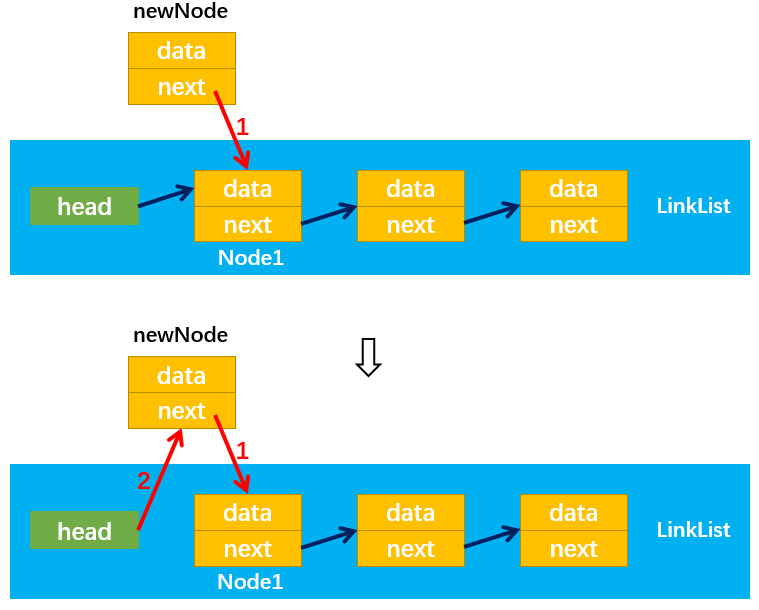
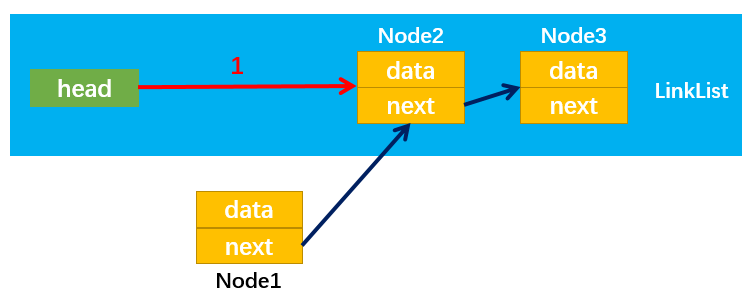
1. append(element)
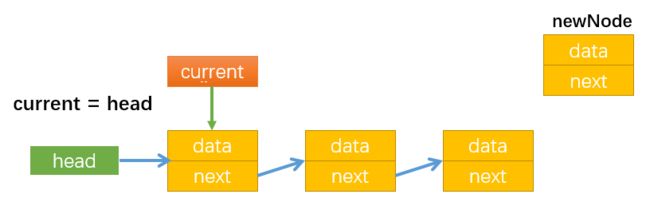
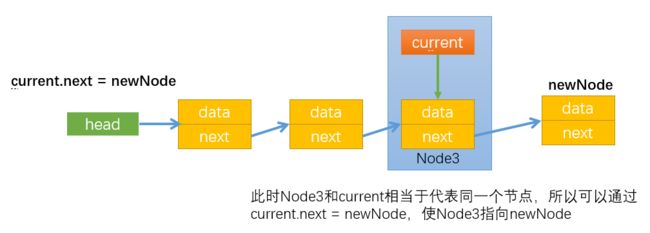
过程详解:
- 首先让current指向第一个节点:
- 通过while循环使current指向最后一个节点,最后通过current.next = newNode,让最后一个节点指向新节点newNode:
代码实现:
// 一.实现append方法
LinkedList.prototype.append = (data) => {
//1.创建新节点
let newNode = new Node(data);
//2.添加新节点
//情况1:只有一个节点时候
if(this.length == 0){
this.head = newNode;
//情况2:节点数大于1,在链表的最后添加新节点
} else {
//让变量current指向第一个节点
let current = this.head;
//当current.next(下一个节点不为空)不为空时,一直循环,直到current指向最后一个节点
while (current.next){
current = current.next;
}
// 最后节点的next指向新的节点
current.next = newNode;
}
//3.添加完新结点之后length+1
this.length += 1;
}
/*ES6使用class实现,此处仅做一个示例,后面的单向链表方法实现相同,方法块中的内容和不用class实现的代码一样,便不再赘述*/
// append() 往链表尾部追加数据
append(data) {
// 1、创建新节点
const newNode = new this.Node(data);
// 2、追加新节点
if (this.length === 0) {
// 链表长度为 0 时,即只有 head 的时候
this.head = newNode;
} else {
// 链表长度大于 0 时,在最后面添加新节点
let currentNode = this.head;
// 当 currentNode.next 不为空时,
// 循序依次找最后一个节点,即节点的 next 为 null 时
while (currentNode.next !== null) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 最后一个节点的 next 指向新节点
currentNode.next = newNode;
}
// 3、追加完新节点后,链表长度 + 1
this.length++;
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
//1.创建LinkList
const list = new LinkedList();
//2.测试append方法
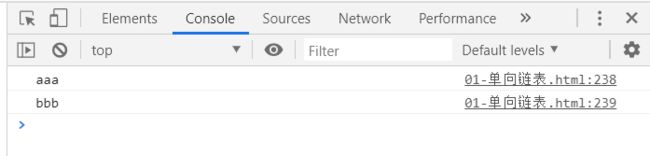
list.append('aaa');
list.append('bbb');
list.append('ccc');
console.log(list);
测试结果:
2. toString()
代码实现:
// 实现toString方法
LinkedList.prototype.toString = () => {
// 1.定义变量
let current = this.head;
let listString = "";
// 2.循环获取一个个的节点
while(current){
listString += current.data + " ";
current = current.next;//千万不要忘了拼接完一个节点数据之后,让current指向下一个节点
}
return listString;
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
//1.创建LinkList
let list = new LinkedList()
//2.插入数据
list.append('aaa')
list.append('bbb')
list.append('ccc')
//3.测试toString方法
console.log(list.toString());
测试结果:
3. insert(position,element)
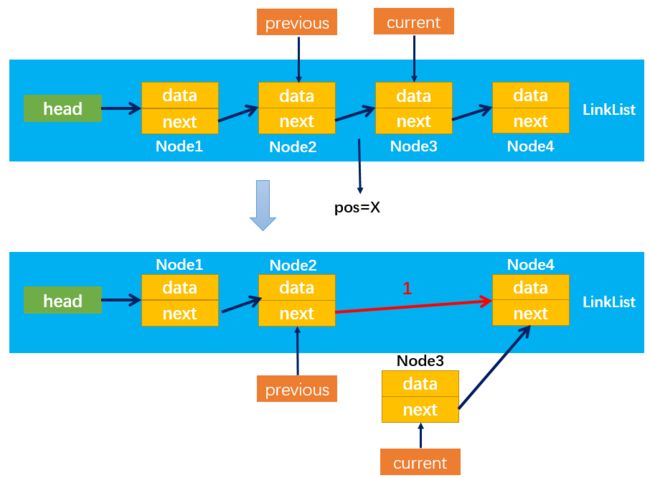
过程详解:
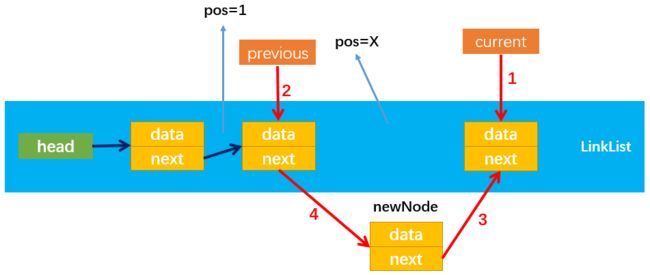
insert方法实现的过程:根据插入节点位置的不同可分为多种情况:
- 情况1:position = 0:
通过: newNode.next = this.head,建立连接1;
通过: this.head = newNode,建立连接2;(不能先建立连接2,否则this.head不再指向Node1)
- 情况2:position > 0:
首先定义两个变量previous和curent分别指向需要插入位置pos = X的前一个节点和后一个节点;
然后,通过:newNode.next = current,改变指向3;
最后,通过:previous.next = newNode,改变指向4;
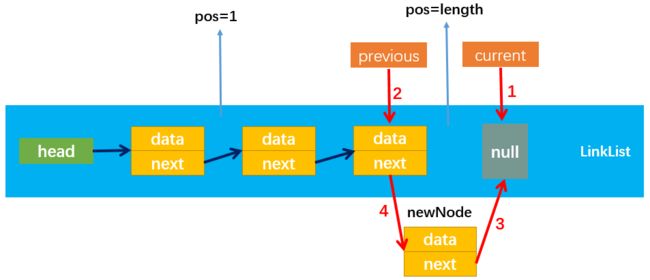
- 情况2的特殊情形:position = length:
情况2也包含了pos = length的情况,该情况下current和newNode.next都指向null;建立连接3和连接4的方式与情况2相同。
代码实现:
// 实现insert方法
LinkedList.prototype.insert = (position, data) => {
//理解positon的含义:position=0表示新界点插入后要成为第1个节点,position=2表示新界点插入后要成为第3个节点
//1.对position进行越界判断:要求传入的position不能是负数且不能超过LinkedList的length
if(position < 0 || position > this.length){
return false;
}
//2.根据data创建newNode
let newNode = new Node(data);
//3.插入新节点
//情况1:插入位置position=0
if(position == 0){
// 让新节点指向第一个节点
newNode.next = this.head;
// 让head指向新节点
this.head = newNode;
//情况2:插入位置position>0(该情况包含position=length)
} else{
let index = 0;
let previous = null;
let current = this.head;
//步骤1:通过while循环使变量current指向position位置的后一个节点(注意while循环的写法)
while(index++ < position){
//步骤2:在current指向下一个节点之前,让previous指向current当前指向的节点
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
// 步骤3:通过变量current(此时current已经指向position位置的后一个节点),使newNode指向position位置的后一个节点
newNode.next = current;
//步骤4:通过变量previous,使position位置的前一个节点指向newNode
previous.next = newNode;
/*
启示:
1.我们无法直接操作链表中的节点,但是可以通过变量指向这些节点,以此间接地操作节点(替身使者);
比如current指向节点3,想要节点3指向节点4只需要:current.next = 4即可。
2.两个节点间是双向的,想要节点2的前一个节点为节点1,可以通过:1.next=2,来实现;
*/
}
//4.新节点插入后要length+1
this.length += 1;
return true;
}
4. getData(position)
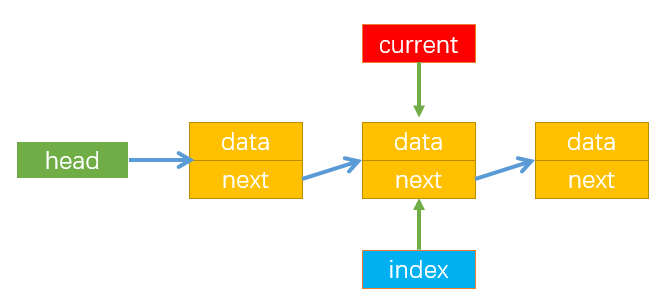
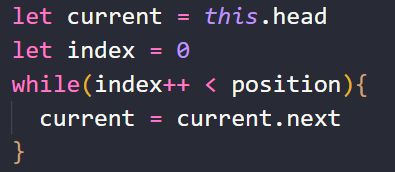
过程详解:
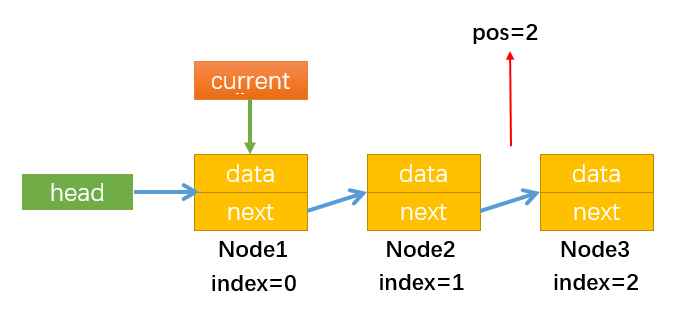
getData方法的实现过程:以获取position = 2为例,如下图所示:
- 首先使current指向第一个节点,此时index=0;
- 通过while循环使current循环指向下一个节点,注意循环终止的条件index++ < position,即当index=position时停止循环,此时循环了1次,current指向第二个节点(Node2),最后通过current.data返回Node2节点的数据;
代码实现:
//实现get方法
LinkedList.prototype.getData = (position) => {
//1.越界判断
// 当position = length时,取到的是null所以0 =< position < length
if(position < 0 || position >= this.length){
return null;
}
//2.获取指定的positon位置的后一个节点的data
//同样使用一个变量间接操作节点
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while(index++ < position){
current = current.next;
}
return current.data;
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
//1.创建LinkedList
let list = new LinkedList();
//2.插入数据
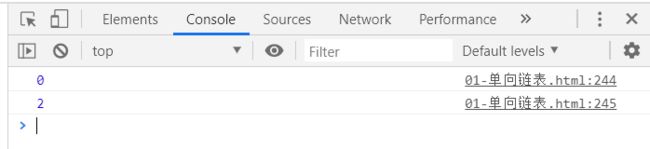
list.append('aaa');
list.append('bbb');
list.append('ccc');
//3.测试get方法
console.log(list.get(0));
console.log(list.get(1));
测试结果:
5. indexOf(element)
过程详解:
indexOf方法的实现过程:
- 使用变量current记录当前指向的节点,使用变量index记录当前节点的索引值(注意index = node数-1):
代码实现:
//实现indexOf方法
LinkedList.prototype.indexOf = (data) => {
//1.定义变量
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
//2.开始查找:只要current不指向null就一直循环
while(current){
if(current.data == data){
return index;
}
current = current.next;
index += 1;
}
//3.遍历完链表没有找到,返回-1
return -1;
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
//1.创建LinkList
let list = new LinkedList()
//2.插入数据
list.append('aaa')
list.append('bbb')
list.append('ccc')
//3.测试indexOf方法
console.log(list.indexOf('aaa'));
console.log(list.indexOf('ccc'));
测试结果:
6. update(position,element)
代码实现:
//实现update方法
LinkedList.prototype.update = (position, newData) => {
//1.越界判断
//因为被修改的节点不能为null,所以position不能等于length
if(position < 0 || position >= this.length){
return false;
}
//2.查找正确的节点
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while(index++ < position){
current = current.next;
}
//3.将position位置的后一个节点的data修改成newData
current.data = newData;
//返回true表示修改成功
return true;
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
//1.创建LinkList
let list = new LinkedList()
//2.插入数据
list.append('aaa')
list.append('bbb')
list.append('ccc')
//3.测试update方法
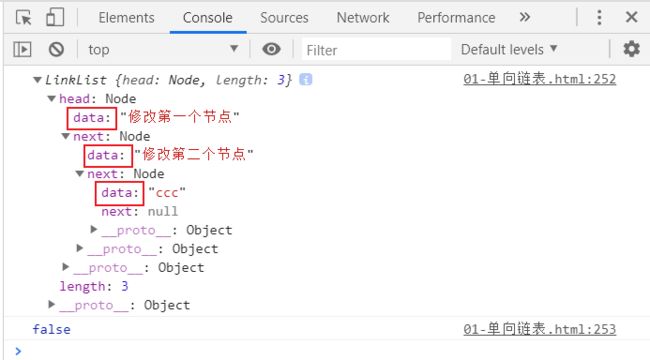
list.update(0, '修改第一个节点')
list.update(1, '修改第二个节点')
console.log(list);
console.log(list.update(3, '能修改么'));
测试结果:
7. removeAt(position)
过程详解:
removeAt方法的实现过程:删除节点时存在多种情况:
- 情况1:position = 0,即移除第一个节点(Node1)。
通过:this.head = this.head.next,改变指向1即可;
虽然Node1的next仍指向Node2,但是没有引用指向Node1,则Node1会被垃圾回收器自动回收,所以不用处理Node1指向Node2的引用next。
- 情况2:positon > 0,比如pos = 2即移除第三个节点(Node3)。
**注意:**position = length时position后一个节点为null不能删除,因此position != length;
首先,定义两个变量previous和curent分别指向需要删除位置pos = x的前一个节点和后一个节点;
然后,通过:previous.next = current.next,改变指向1即可;
随后,没有引用指向Node3,Node3就会被自动回收,至此成功删除Node3 。
代码实现:
//实现removeAt方法
LinkedList.prototype.removeAt = (position) => {
//1.越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) {
return null;
}
//2.删除元素
//情况1:position = 0时(删除第一个节点)
let current = this.head;
if (position ==0 ) {
//情况2:position > 0时
this.head = this.head.next;
}else{
let index = 0;
let previous = null;
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
//循环结束后,current指向position后一个节点,previous指向current前一个节点
//再使前一个节点的next指向current的next即可
previous.next = current.next;
}
//3.length-1;
this.length -= 1;
//返回被删除节点的data,为此current定义在最上面
return current.data;
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
//1.创建LinkedList
let list = new LinkedList()
//2.插入数据
list.append('aaa')
list.append('bbb')
list.append('ccc')
//3.测试removeAt方法
console.log(list.removeAt(0));
console.log(list.removeAt(0));
console.log(list);
测试结果:
8. 其他方法
其他方法包括:remove(element)、isEmpty()、size()
代码实现:
/*-------------其他方法的实现--------------*/
//一.实现remove方法
LinkedList.prototype.remove = (data) => {
//1.获取data在列表中的位置
let position = this.indexOf(data);
//2.根据位置信息,删除结点
return this.removeAt(position);
}
//二.实现isEmpty方法
LinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = () => {
return this.length == 0;
}
//三.实现size方法
LinkedList.prototype.size = () => {
return this.length;
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
//1.创建LinkList
let list = new LinkedList()
//2.插入数据
list.append('aaa');
list.append('bbb');
list.append('ccc');
/*---------------其他方法测试----------------*/
//remove方法
console.log(list.remove('aaa'));
console.log(list);
//isEmpty方法
console.log(list.isEmpty());
//size方法
console.log(list.size());
测试结果:
9. 完整实现
1) 构造函数实现
function LinkedList(){
//内部类
function Node(data){
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
//一.append方法
LinkedList.prototype.append = data => {
let newNode = new Node(data);
if(this.length == 0){
this.head = newNode;
}else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next){
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
}
this.length += 1;
}
//二.toString方法
LinkedList.prototype.toString = () => {
let current = this.head;
let listString = "";
while(current){
listString += current.data + " ";
current = current.next;
}
return listString;
}
//三.insert方法
LinkedList.prototype.insert = (position, data) => {
if(position < 0 || position > this.length){
return false;
}
let newNode = new Node(data);
if(position == 0){
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode
} else{
let index = 0;
let previous = null;
let current = this.head;
while(index++ < position){
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
newNode.next = current;
previous.next = newNode;
}
this.length += 1;
return true;
}
//四.getData方法
LinkedList.prototype.getData = (position) => {
if(position < 0 || position >= this.length){
return null;
}
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while(index++ < position){
current = current.next;
}
return current.data;
}
//五.indexOf方法
LinkedList.prototype.indexOf = data => {
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while(current){
if(current.data == data){
return index;
}
current = current.next;
index += 1;
}
return -1;
}
//六.update方法
LinkedList.prototype.update = (position, newData) => {
if(position < 0 || position >= this.length){
return false;
}
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while(index++ < position){
current = current.next;
}
current.data = newData;
return true;
}
//七.removeAt方法
LinkedList.prototype.removeAt = position => {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) {
return null;
}
let current = this.head;
if (position ==0 ) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}else{
let index = 0;
let previous = null;
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.length -= 1;
return current.data;
}
//八.remove方法
LinkedList.prototype.remove = (data) => {
let position = this.indexOf(data);
return this.removeAt(position);
}
//九.isEmpty方法
LinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = () => {
return this.length == 0;
}
//十.size方法
LinkedList.prototype.size = () => {
return this.length;
}
}
2) class类实现
class LinkedList {
// 初始链表长度为 0
length = 0;
// 初始 head 为 null,head 指向链表的第一个节点
head = null;
// 内部类(链表里的节点 Node)
Node = class {
data;
next = null;
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
}
};
// ------------ 链表的常见操作 ------------ //
// append() 往链表尾部追加数据
append(data) {
// 1、创建新节点
const newNode = new this.Node(data);
// 2、追加新节点
if (this.length === 0) {
// 链表长度为 0 时,即只有 head 的时候
this.head = newNode;
} else {
// 链表长度大于 0 时,在最后面添加新节点
let currentNode = this.head;
// 当 currentNode.next 不为空时,
// 循序依次找最后一个节点,即节点的 next 为 null 时
while (currentNode.next !== null) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 最后一个节点的 next 指向新节点
currentNode.next = newNode;
}
// 3、追加完新节点后,链表长度 + 1
this.length++;
}
// insert() 在指定位置(position)插入节点
insert(position, data) {
// position 新插入节点的位置
// position = 0 表示新插入后是第一个节点
// position = 1 表示新插入后是第二个节点,以此类推
// 1、对 position 进行越界判断,不能小于 0 或大于链表长度
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
// 2、创建新节点
const newNode = new this.Node(data);
// 3、插入节点
if (position === 0) {
// position = 0 的情况
// 让新节点的 next 指向 原来的第一个节点,即 head
newNode.next = this.head;
// head 赋值为 newNode
this.head = newNode;
} else {
// 0 < position <= length 的情况
// 初始化一些变量
let currentNode = this.head; // 当前节点初始化为 head
let previousNode = null; // head 的 上一节点为 null
let index = 0; // head 的 index 为 0
// 在 0 ~ position 之间遍历,不断地更新 currentNode 和 previousNode
// 直到找到要插入的位置
while (index++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 在当前节点和当前节点的上一节点之间插入新节点,即它们的改变指向
newNode.next = currentNode;
previousNode.next = newNode;
}
// 更新链表长度
this.length++;
return newNode;
}
// getData() 获取指定位置的 data
getData(position) {
// 1、position 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
// 2、获取指定 position 节点的 data
let currentNode = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (index++ < position) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 3、返回 data
return currentNode.data;
}
// indexOf() 返回指定 data 的 index,如果没有,返回 -1。
indexOf(data) {
let currentNode = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode.data === data) {
return index;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
index++;
}
return -1;
}
// update() 修改指定位置节点的 data
update(position, data) {
// 涉及到 position 都要进行越界判断
// 1、position 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return false;
// 2、痛过循环遍历,找到指定 position 的节点
let currentNode = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (index++ < position) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 3、修改节点 data
currentNode.data = data;
return currentNode;
}
// removeAt() 删除指定位置的节点
removeAt(position) {
// 1、position 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
// 2、删除指定 position 节点
let currentNode = this.head;
if (position === 0) {
// position = 0 的情况
this.head = this.head.next;
} else {
// position > 0 的情况
// 通过循环遍历,找到指定 position 的节点,赋值到 currentNode
let previousNode = null;
let index = 0;
while (index++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 巧妙之处,让上一节点的 next 指向到当前的节点的 next,相当于删除了当前节点。
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
}
// 3、更新链表长度 -1
this.length--;
return currentNode;
}
// remove() 删除指定 data 的节点
remove(data) {
this.removeAt(this.indexOf(data));
}
// isEmpty() 判断链表是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
// size() 获取链表的长度
size() {
return this.length;
}
// toString() 链表数据以字符串形式返回
toString() {
let currentNode = this.head;
let result = "";
// 遍历所有的节点,拼接为字符串,直到节点为 null
while (currentNode) {
result += currentNode.data + " ";
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return result;
}
}
双向链表
单向链表和双向链表
单向链表
- 只能从头遍历到尾或者从尾遍历到头(一般从头到尾)。
- 链表相连的过程是单向的,实现原理是上一个节点中有指向下一个节点的引用。
- 单向链表有一个比较明显的缺点:可以轻松到达下一个节点,但回到前一个节点很难,在实际开发中, 经常会遇到需要回到上一个节点的情况。
双向链表
- 既可以从头遍历到尾,也可以从尾遍历到头。
- 链表相连的过程是双向的。实现原理是一个节点既有向前连接的引用,也有一个向后连接的引用。
- 双向链表可以有效的解决单向链表存在的问题。
- 双向链表缺点:
- 每次在插入或删除某个节点时,都需要处理四个引用,而不是两个,实现起来会困难些。
- 相对于单向链表,所占内存空间更大一些。
- 但是,相对于双向链表的便利性而言,这些缺点微不足道。
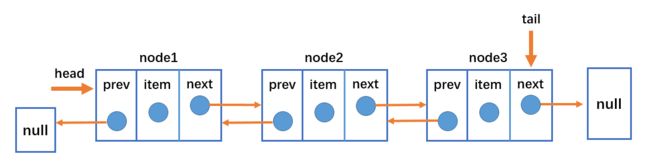
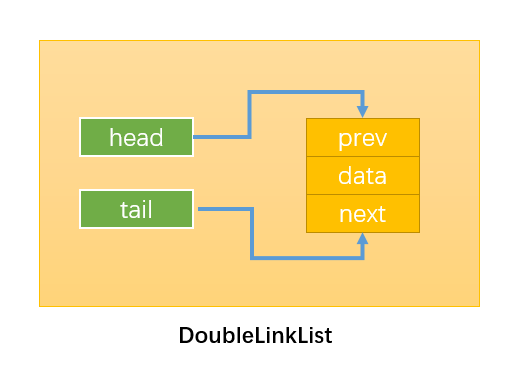
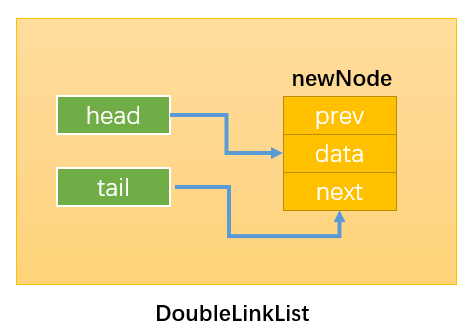
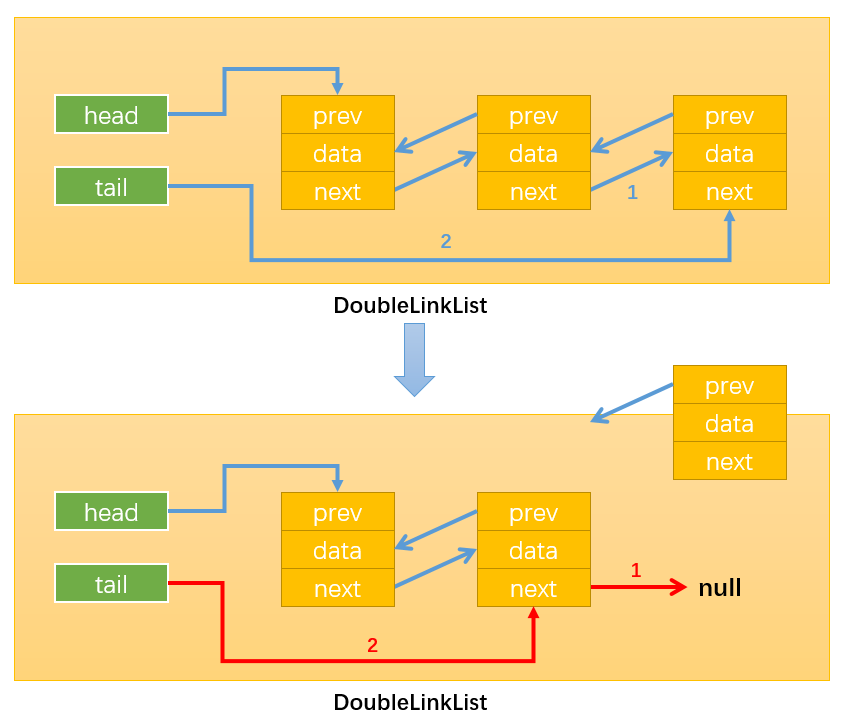
双向链表结构
- 双向链表不仅有 head 指针指向第一个节点,而且有 tail 指针指向最后一个节点。
- 每一个节点由三部分组成:item 储存数据、prev 指向前一个节点、next 指向后一个节点。
- 双向链表的第一个节点的 prev 指向 null。
- 双向链表的最后一个节点的 next 指向 null。
双向链表常见的操作
append(element)向链表尾部追加一个新元素。insert(position, element)向链表的指定位置插入一个新元素。getElement(position)获取指定位置的元素。indexOf(element)返回元素在链表中的索引。如果链表中没有该元素就返回 -1。update(position, element)修改指定位置上的元素。removeAt(position)从链表中的删除指定位置的元素。remove(element)从链表删除指定的元素。isEmpty()如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回 trun,如果链表长度大于 0 则返回 false。size()返回链表包含的元素个数,与数组的 length 属性类似。toString()由于链表项使用了 Node 类,就需要重写继承自 JavaScript 对象默认的 toString 方法,让其只输出元素的值。forwardString()返回正向遍历节点字符串形式。backwordString()返回反向遍历的节点的字符串形式。
封装双向链表类
注:此处仅贴出使用function实现的代码,使用class实现代码参考完整实现
0. 创建双向链表类
先创建双向链表类DoubleLinklist,并添加基本属性,再实现双向链表的常用方法:
//封装双向链表类
function DoubleLinklist(){
//封装内部类:节点类
function Node(data){
this.data = data;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
//属性
this.head = null;
this.tail ==null;
this.length = 0;
}
/*使用class类实现*/
// 双向链表的节点类(继承单向链表的节点类)
class DoublyNode extends Node {
constructor(element) {
super(element);
this.prev = null;
}
}
// 双向链表类继承单向链表类
class DoublyLinkList extends LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
this.tail = null;
}
1. append(element)
过程详解:
添加节点时分为多种情况:
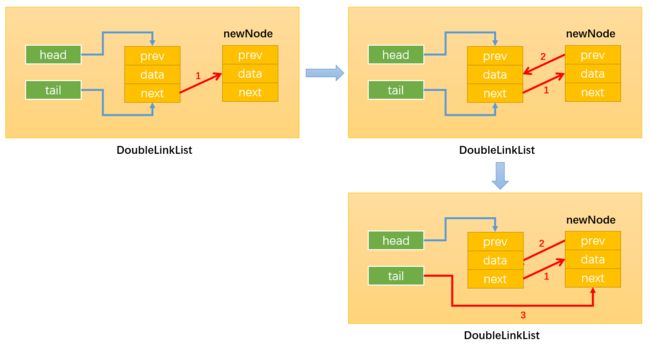
- 情况1:添加的是第一个节点:只需要让head和tail都指向新节点即可;
-
情况2:添加的不是第一个节点,如下图所示:只需要改变相关引用的指向即可。
- 通过:
newNode.prev = this.tail, 建立指向1; - 通过:
this.tail.next = newNode, 建立指向2; - 通过:
this.tail = newNode, 建立指向3
要注意改变变量指向的顺序,最后修改tail指向,这样未修改前tail始终指向原链表的最后一个节点。
- 通过:
代码实现:
//append方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.append = (data) => {
//1.根据data创建新节点
let newNode = new Node(data);
//2.添加节点
//情况1:添加的是第一个节点
if (this.length == 0) {
this.tail = newNode;
this.head = newNode ;
}
//情况2:添加的不是第一个节点
else {
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
//3.length+1
this.length += 1;
}
测试代码:
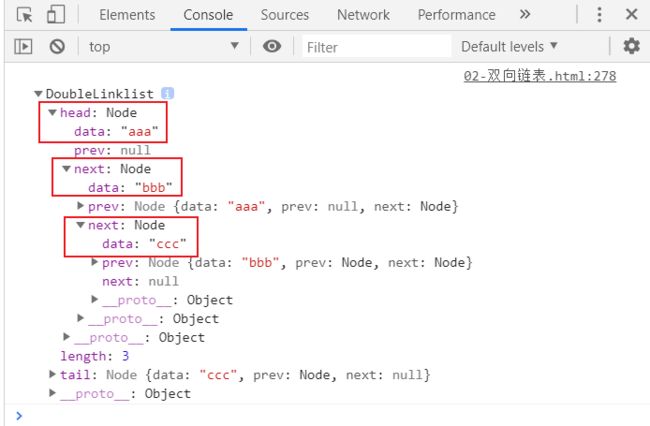
//测试代码
//1.创建双向链表
let list = new DoubleLinklist();
//2.测试append方法
list.append('aaa');
list.append('bbb');
list.append('ccc');
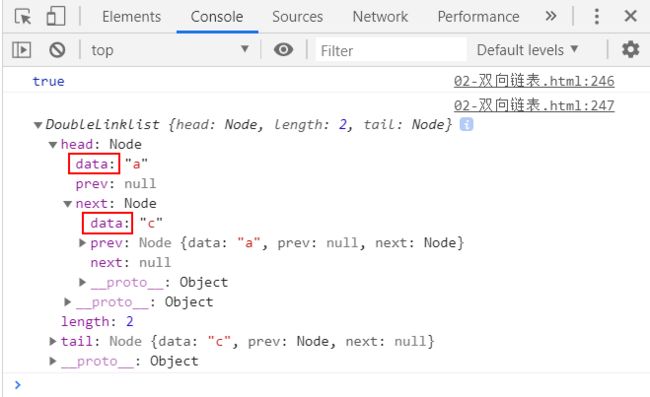
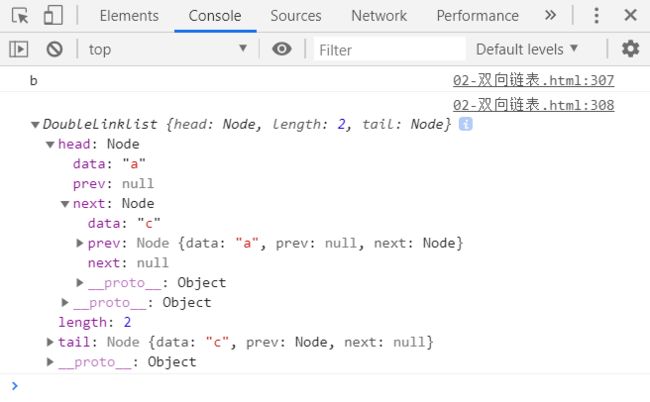
console.log(list);
测试结果:
- next方向:
- prev方向:
2. toString()
过程详解:
三种获取字符串的方法:toString()、forwardString()、**backwardString()**实现原理相似,仅以backWardString方法为例:
- 定义current变量记录当前指向的节点。首先让current指向第一个节点,然后通过
current = current.next依次向后遍历。在while循环中以(current)作为条件遍历链表,只要current != null就一直遍历,由此可获取链表所有节点的数据。
代码实现:
//将链表转变为字符串形式
//一.toString方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.toString = () => {
return this.backwardString();
}
//二.forwardString方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.forwardString = () => {
//1.定义变量
let current =this.tail;
let resultString = "";
//2.依次向前遍历,获取每一个节点
while (current) {
resultString += current.data + "--";
current = current.prev;
}
return resultString;
}
//三.backwardString方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.backwardString = () => {
//1.定义变量
let current = this.head;
let resultString = "";
//2.依次向后遍历,获取每一个节点
while (current) {
resultString += current.data + "--";
current = current.next;
}
return resultString;
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
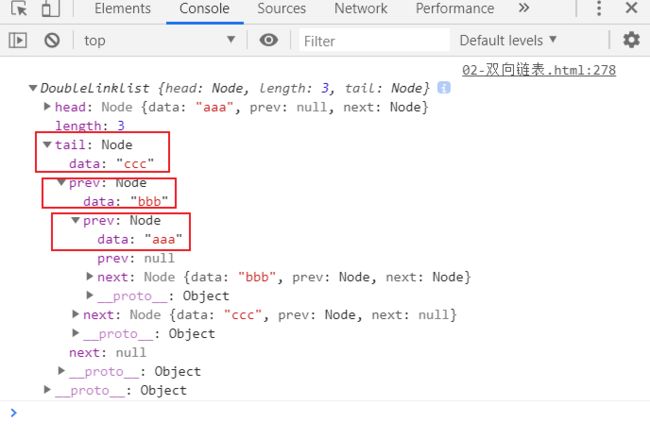
//1.创建双向链表
let list = new DoubleLinklist();
//2.测试字符串方法
list.append('aaa');
list.append('bbb');
list.append('ccc');
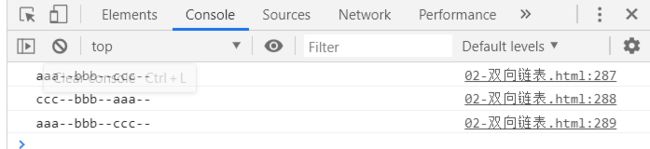
console.log(list.toString());
console.log(list.forwardString());
console.log(list.backwardString());
测试结果:
3. insert(position,element)
程详解:
插入节点可分为多种情况:
当原链表为空时:
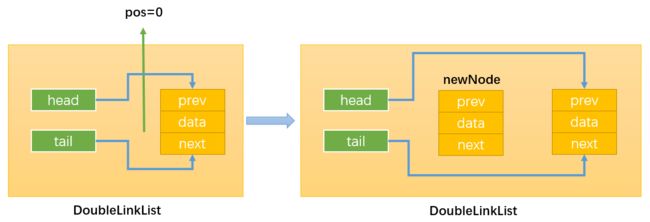
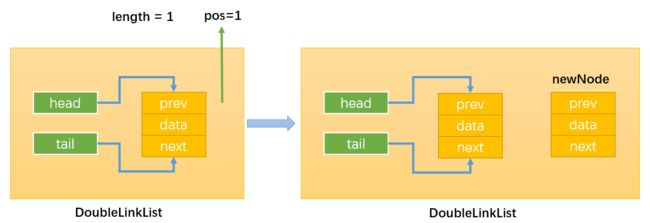
- 情况1:插入的新节点是链表的第一个节点;只需要让head和tail都指向newNode即可。
当原链表不为空时:
- 情况2:当position == 0,即在链表的首部添加节点:如下图所示:
首先,通过:this.head.prev = newNode,改变指向1;
然后,通过:newNode.next = this.head,改变指向2;
最后,通过:this.head = newNode,改变指向3;
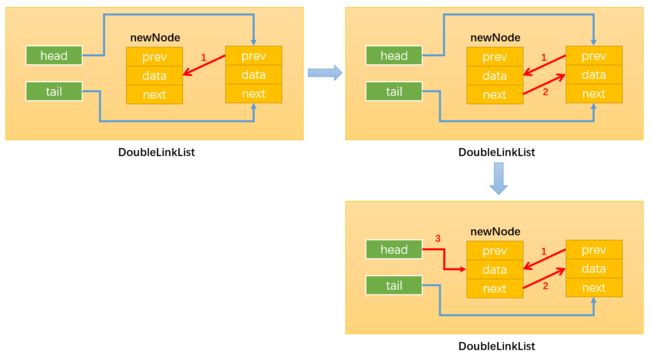
- 情况3:
position == this.length,即在链表的尾部添加节点,如下图所示:
首先,通过:this.tail.next = newNode,改变指向1;(注意这里使用this.tail指向原链表最后一个节点,而不是this.head。因为当length>1时,this.head != this.tail。)
然后,通过:newNode.prev = this.tail,改变指向2;
最后,通过:this.tail = newNode,改变指向3;
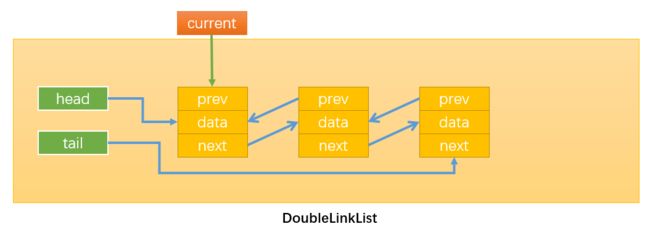
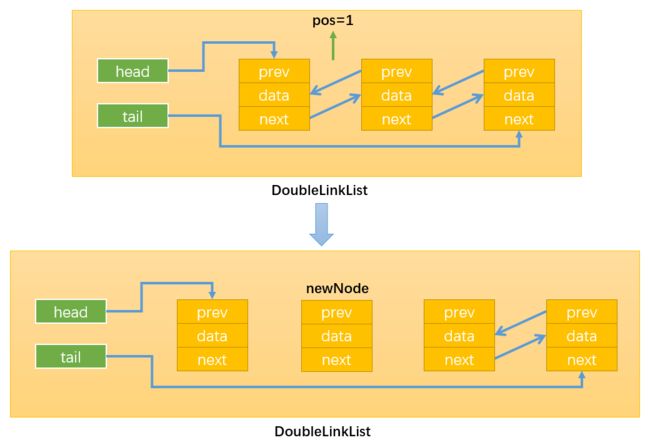
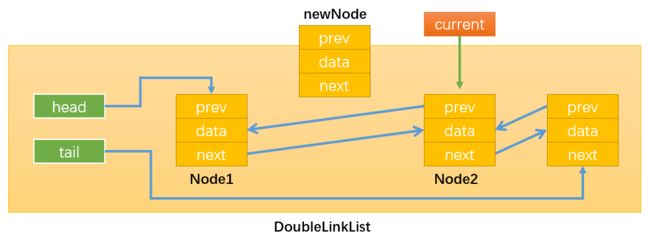
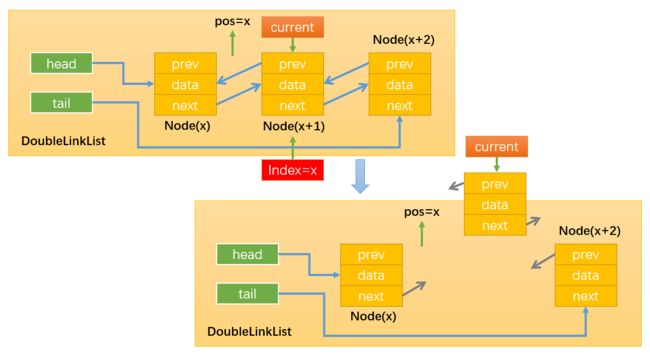
- 情况4:0 < position < this.length,即在链表的中间插入新节点,假设在position = 1的位置插入,如下图所示:
首先,需要定义变量current按照之前的思路,通过while循环找到position位置的后一个节点,循环结束后index = position
如下图所示:当position = 1时,current就指向了Node2。这样操作current就等同于间接地操作Node2,还可以通过current.prev间接获取Node1。得到了newNode的前一个节点和后一个节点就可以通过改变它们的prev和next变量的指向来插入newNode了。
通过:newNode.next = current,改变指向1;
通过:newNode.prev = current.prev,改变指向2;
通过:current.prev.next = newNode,改变指向3;
注意必须最后才修改current.prev的指向,不然就无法通过current.prev获取需要操作的Node1了。
通过:current.prev = current,改变指向4;
代码实现:
//insert方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.insert = (position, data) => {
//1.越界判断
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
//2.根据data创建新的节点
let newNode = new Node(data);
//3.插入新节点
//原链表为空
//情况1:插入的newNode是第一个节点
if (this.length == 0) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
//原链表不为空
}else {
//情况2:position == 0
if (position == 0) {
this.head.prev = newNode;
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
//情况3:position == this.length
} else if(position == this.length){
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
//情况4:0 < position < this.length
}else{
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while(index++ < position){
current = current.next;
}
//修改pos位置前后节点变量的指向
newNode.next = current;
newNode.prev = current.prev;
current.prev.next = newNode;
current.prev = newNode;
}
}
//4.length+1
this.length += 1;
return true//返回true表示插入成功
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
//1.创建双向链表
let list = new DoubleLinklist();
//2.测试insert方法
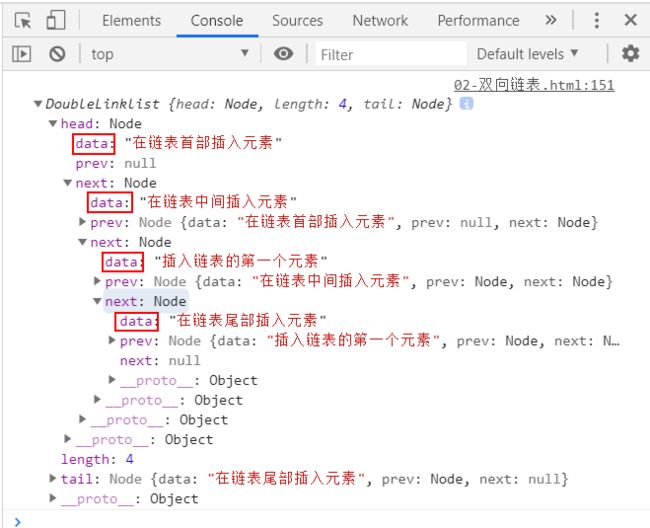
list.insert(0, '插入链表的第一个元素');
list.insert(0, '在链表首部插入元素');
list.insert(1, '在链表中间插入元素');
list.insert(3, '在链表尾部插入元素');
console.log(list);
测试结果:
4. get(position)
过程详解:
定义两个变量current和index,按照之前的思路通过while循环遍历分别获取当前节点和对应的索引值index,直到找到需要获取的position位置后的一个节点,此时index = position =x,然后 return current.data 即可。
如果链表的节点数量很多时,这种查找方式效率不高,改进方法为:
一定要通过this.length来获取链表的节点数否则就会报错。
- 当this.length / 2 > position:从头(head)开始遍历;
- 当this.length / 2 < position:从尾(tail)开始遍历;
代码实现:
//get方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.get = (position) => {
//1.越界判断
//获取元素时position不能等于length
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
//2.获取元素
let current = null;
let index = 0;
//this.length / 2 > position:从头开始遍历
if ((this.length / 2) > position) {
current = this.head;
while(index++ < position){
current = current.next;
}
//this.length / 2 =< position:从尾开始遍历
}else{
current = this.tail;
index = this.length - 1;
while(index-- > position){
current = current.prev;
}
}
return current.data;
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
//1.创建双向链表
let list = new DoubleLinklist();
//2.测试get方法
list.append('a');
list.append('b');
list.append('b1');
list.append('b2');
list.append('b3');
list.append('b4');
list.append('b5');
list.append('b6');
list.append('b7');
console.log(list.get(0));
console.log(list.get(7));
测试结果:
5. indexOf(element)
过程详解:
以(current)作为条件,通过while循环遍历链表中的所有节点(停止条件为current = null)。在遍历每个节点时将current指向的当前节点的data和传入的data进行比较即可。
代码实现:
//indexOf方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.indexOf = (data) => {
//1.定义变量
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
//2.遍历链表,查找与data相同的节点
while(current){
if (current.data == data) {
return index;
}
current = current.next;
index += 1;
}
return -1;
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
//1.创建双向链表
let list = new DoubleLinklist();
//2.测试indexOf方法
list.append('a');
list.append('b');
list.append('c');
console.log(list.indexOf('a'));
console.log(list.indexOf('c'));
测试结果:
6. update(position,element)
过程详解:
以(index++ < position)为条件,通过while循环遍历链表中的节点(停止条件为index = position)。循环结束后,current指向需要修改的节点。
代码实现:
//update方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.update = (position, newData) => {
//1.越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return false;
//2.寻找正确的节点
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
//this.length / 2 > position:从头开始遍历
if (this.length / 2 > position) {
while(index++ < position){
current = current.next;
}
//this.length / 2 =< position:从尾开始遍历
}else{
current = this.tail;
index = this.length - 1;
while (index -- > position) {
current = current.prev;
}
}
//3.修改找到节点的data
current.data = newData;
return true;//表示成功修改
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
//1.创建双向链表
let list = new DoubleLinklist();
//2.测试update方法
list.append('a');
list.append('b');
console.log(list.update(1, 'c'));
console.log(list);
测试结果:
7. removeAt(position)
过程详解:
删除节点时有多种情况:
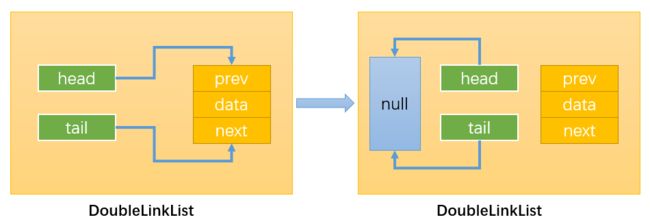
当链表的length = 1时:
- 情况1:删除链表中的所有节点:只需要让链表的head和tail指向null即可。
当链表的length > 1时:
-
情况2:删除链表中的第一个节点:
通过:
this.head.next.prev = null,改变指向1;通过:
this.head = this.head.next,改变指向2;虽然Node1有引用指向其它节点,但是没有引用指向Node1,那么Node1会被自动回收。
-
情况3:删除链表中的最后一个节点:
通过:
this.tail.prev.next = null,修改指向1;通过:
this.tail = this.tail.prev,修改指向2;
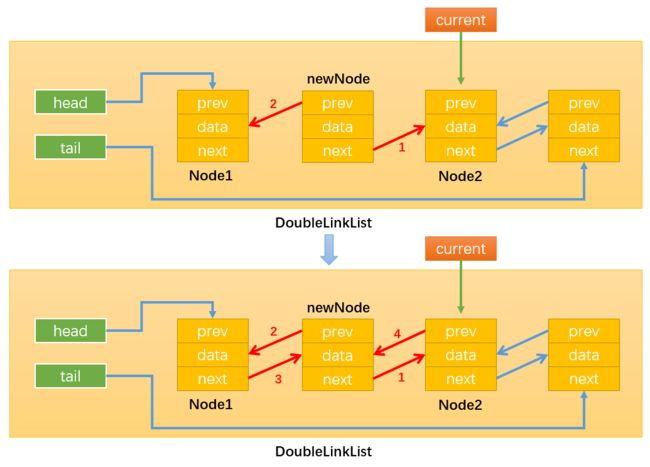
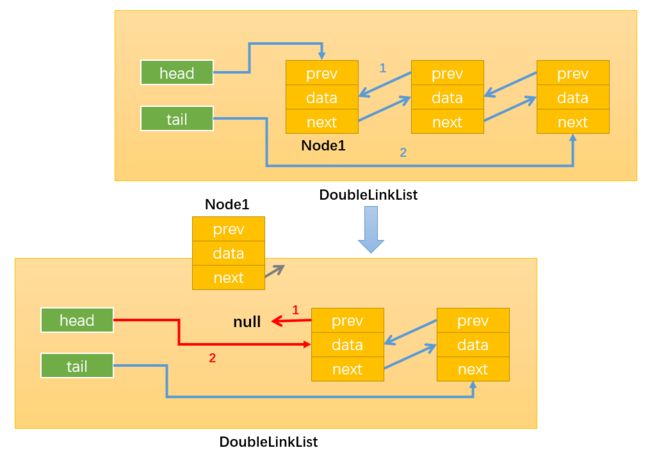
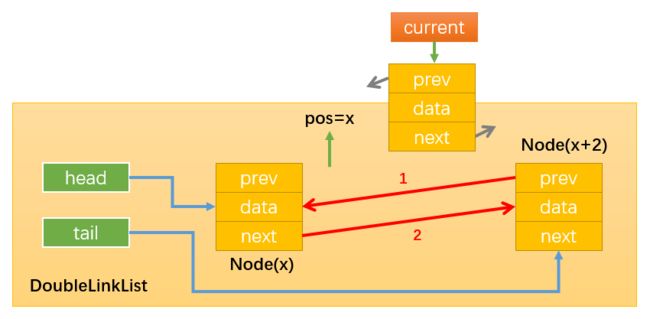
- 情况4:删除链表中间的节点:
通过while循环找到需要删除的节点,比如position = x,那么需要删除的节点就是Node(x+1),如下图所示:
通过:current.next.prev = current.prev,修改指向1;
通过:current.prev.next = current.next,修改指向2;
这样就没有引用指向Node(x+1)了(current虽指向Node(x+1),但current时临时变量,该方法执行完就会被销毁),随后Node(x+1)就会被自动删除。
代码实现:
//removeAt方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.removeAt = position => {
//1.越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
//2.删除节点
//当链表中length == 1
//情况1:链表只有一个节点
let current = this.head//定义在最上面方便以下各种情况返回current.data
if (this.length == 1) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
//当链表中length > 1
} else{
//情况2:删除第一个节点
if (position == 0) {
this.head.next.prev = null;
this.head = this.head.next;
//情况3:删除最后一个节点
}else if(position == this.length - 1){
current = this.tail;//该情况下返回被删除的最后一个节点
this.tail.prev.next = null;
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
}else{
//情况4:删除链表中间的节点
let index = 0
while(index++ < position){
current = current.next;
}
current.next.prev = current.prev;
current.prev.next = current.next;
}
}
//3.length -= 1;
this.length -= 1;
return current.data; //返回被删除节点的数据
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
//1.创建双向链表
let list = new DoubleLinklist();
//2.测试removeAt方法
list.append('a');
list.append('b');
list.append('c');
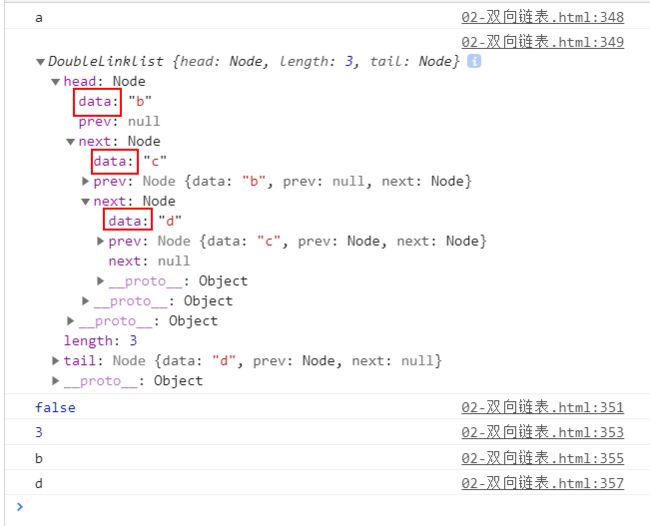
console.log(list.removeAt(1));
console.log(list);
测试结果:
8. 其他方法
其他方法包括:remove(element)、isEmpty()、size()、getHead()、getTail()
代码实现:
/*--------------------其他方法-------------------*/
//八.remove方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.remove = (data) => {
//1.根据data获取下标值
let index = this.indexOf(data);
//2.根据index删除对应位置的节点
return this.removeAt(index);
}
//九.isEmpty方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.isEmpty = () => {
return this.length == 0;
}
//十.size方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.size = () => {
return this.length;
}
//十一.getHead方法:获取链表的第一个元素
DoubleLinklist.prototype.getHead = () => {
return this.head.data;
}
//十二.getTail方法:获取链表的最后一个元素
DoubleLinklist.prototype.getTail = () => {
return this.tail.data;
}
测试代码:
//测试代码
//1.创建双向链表
let list = new DoubleLinklist();
/*------------其他方法的测试--------------*/
list.append('a');
list.append('b');
list.append('c');
list.append('d');
//remove方法
console.log(list.remove('a'));
console.log(list);
//isEmpty方法
console.log(list.isEmpty());
//size方法
console.log(list.size());
//getHead方法
console.log(list.getHead());
//getTead方法
console.log(list.getTail());
测试结果:
9. 完整实现
1) 构造函数实现
//封装双向链表
function DoubleLinklist(){
//封装内部类:节点类
function Node(data){
this.data = data;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
//属性
this.head = null;
this.tail ==null;
this.length = 0;
//一.append方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.append = data => {
let newNode = new Node(data);
if (this.length == 0) {
this.tail = newNode;
this.head = newNode ;
}else {
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length += 1;
}
//二.将链表转变为字符串形式
//2.1.toString方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.toString = () => {
return this.backwardString();
}
//2.2.forwardString方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.forwardString = () => {
let current =this.tail;
let resultString = "";
while (current) {
resultString += current.data + "--";
current = current.prev ;
}
return resultString;
}
//2.3.backwardString方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.backwardString = () => {
let current = this.head;
let resultString = "";
while (current) {
resultString += current.data + "--";
current = current.next;
}
return resultString;
}
//三.insert方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.insert = (position, data) => {
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
let newNode = new Node(data);
if (this.length == 0) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}else {
if (position == 0) {
this.head.prev = newNode;
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
} else if(position == this.length){
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}else{
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while(index++ < position){
current = current.next;
}
newNode.next = current;
newNode.prev = current.prev;
current.prev.next = newNode;
current.prev = newNode;
}
}
this.length += 1;
return true;
}
//四.get方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.get = position => {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
let current = null;
let index = 0;
if ((this.length / 2) > position) {
current = this.head;
while(index++ < position){
current = current.next;
}
}else{
current = this.tail;
index = this.length - 1;
while(index-- > position){
current = current.prev;
}
}
return current.data;
}
//五.indexOf方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.indexOf = data => {
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while(current){
if (current.data == data) {
return index;
}
current = current.next;
index += 1;
}
return -1;
}
//六.update方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.update = (position, newData) => {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return false;
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
if (this.length / 2 > position) {
while(index++ < position){
current = current.next;
}
}else{
current = this.tail;
index = this.length - 1;
while (index -- > position) {
current = current.prev;
}
}
current.data = newData;
return true;
}
//七.removeAt方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.removeAt = position => {
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) {
return null;
}
let current = this.head;
if (this.length == 1) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else{
if (position == 0) {
this.head.next.prev = null;
this.head = this.head.next;
}else if(position == this.length - 1){
current = this.tail;
this.tail.prev.next = null;
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
}else{
let index = 0;
while(index++ < position){
current = current.next;
}
current.next.prev = current.prev;
current.prev.next = current.next;
}
}
this.length -= 1;
return current.data;
}
//八.remove方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.remove = data => {
let index = this.indexOf(data);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
//九.isEmpty方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.isEmpty = () => {
return this.length == 0;
}
//十.size方法
DoubleLinklist.prototype.size = () => {
return this.length;
}
//十一.getHead方法:获取链表的第一个元素
DoubleLinklist.prototype.getHead = () => {
return this.head.data;
}
//十二.getTail方法:获取链表的最后一个元素
DoubleLinklist.prototype.getTail = () => {
return this.tail.data;
}
}
2) class类实现
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
this.tail = null;
}
// ------------ 链表的常见操作 ------------ //
// append(element) 往双向链表尾部追加一个新的元素
// 重写 append()
append(element) {
// 1、创建双向链表节点
const newNode = new DoublyNode(element);
// 2、追加元素
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
// !!跟单向链表不同,不用通过循环找到最后一个节点
// 巧妙之处
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length++;
}
// insert(position, data) 插入元素
// 重写 insert()
insert(position, element) {
// 1、position 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false;
// 2、创建新的双向链表节点
const newNode = new DoublyNode(element);
// 3、判断多种插入情况
if (position === 0) { // 在第 0 个位置插入
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
//== 巧妙之处:相处腾出 this.head 空间,留个 newNode 来赋值 ==//
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.perv = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
}
} else if (position === this.length) { // 在最后一个位置插入
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
} else { // 在 0 ~ this.length 位置中间插入
let targetIndex = 0;
let currentNode = this.head;
let previousNode = null;
// 找到要插入位置的节点
while (targetIndex++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 交换节点信息
previousNode.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = previousNode;
newNode.next = currentNode;
currentNode.prev = newNode;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
// getData() 继承单向链表
getData(position) {
return super.getData(position);
}
// indexOf() 继承单向链表
indexOf(data) {
return super.indexOf(data);
}
// removeAt() 删除指定位置的节点
// 重写 removeAt()
removeAt(position) {
// 1、position 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position > this.length - 1) return null;
// 2、根据不同情况删除元素
let currentNode = this.head;
if (position === 0) { // 删除第一个节点的情况
if (this.length === 1) { // 链表内只有一个节点的情况
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else { // 链表内有多个节点的情况
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.prev = null;
}
} else if (position === this.length - 1) { // 删除最后一个节点的情况
currentNode = this.tail;
this.tail.prev.next = null;
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
} else { // 删除 0 ~ this.length - 1 里面节点的情况
let targetIndex = 0;
let previousNode = null;
while (targetIndex++ < position) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
currentNode.next.perv = previousNode;
}
this.length--;
return currentNode.data;
}
// update(position, data) 修改指定位置的节点
// 重写 update()
update(position, data) {
// 1、删除 position 位置的节点
const result = this.removeAt(position);
// 2、在 position 位置插入元素
this.insert(position, data);
return result;
}
// remove(data) 删除指定 data 所在的节点(继承单向链表)
remove(data) {
return super.remove(data);
}
// isEmpty() 判断链表是否为空
isEmpty() {
return super.isEmpty();
}
// size() 获取链表的长度
size() {
return super.size();
}
// forwardToString() 链表数据从前往后以字符串形式返回
forwardToString() {
let currentNode = this.head;
let result = '';
// 遍历所有的节点,拼接为字符串,直到节点为 null
while (currentNode) {
result += currentNode.data + '--';
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return result;
}
// backwardString() 链表数据从后往前以字符串形式返回
backwardString() {
let currentNode = this.tail;
let result = '';
// 遍历所有的节点,拼接为字符串,直到节点为 null
while (currentNode) {
result += currentNode.data + '--';
currentNode = currentNode.prev;
}
return result;
}
}