算法学习系列(十):用数组模拟链表、双链表、栈、队列、单调栈、单调队列
目录
- 引言
- 一、数组模拟链表
-
- 1.模板
- 2.例题
- 3.测试
- 二、数组模拟双链表
-
- 1.模板
- 2.例题
- 3.测试
- 三、数组模拟栈
-
- 1.模板
- 2.例题
- 3.测试
- 四、数组模拟队列
-
- 1.模板
- 2.例题
- 3.测试
- 五、数组模拟单调栈
-
- 1.例题+模板
- 2.测试
- 六、数组模拟单调队列
-
- 1.例题+模板
- 2.测试
引言
首先说一下为什么要拿数组来模拟,最主要的原因是为了快,因为如果用stl库里的容器的话,在算法竞赛中,一般是不会给你开O2优化或者臭氧优化的,然后所以在一些时间卡的非常紧的情况下,还是推荐用数组来模拟会比较好,然后开始吧。
一、数组模拟链表
1.模板
const int N = 100010;
//head为头节点所在的下标,e[i]代表下标为i的值,ne[i]代表下标为i的下一个下标,idx代表当前可用的下标
int head, e[N], ne[N], idx;
void init()
{
head = -1;
idx = 0;
}
void add_to_head(int x)
{
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = head, head = idx++;
}
void add(int k, int x) //插到下标为k的后面
{
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k], ne[k] = idx++;
}
void remove(int k) //删掉下标为k的后一个元素
{
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
2.例题
实现一个单链表,链表初始为空,支持三种操作:
向链表头插入一个数;
删除第 k 个插入的数后面的数;
在第 k 个插入的数后插入一个数。
现在要对该链表进行 M 次操作,进行完所有操作后,从头到尾输出整个链表。注意:题目中第 k 个插入的数并不是指当前链表的第 k 个数。例如操作过程中一共插入了 n 个数,则按照插入的时间顺序,这 n 个数依次为:第 1 个插入的数,第 2 个插入的数,…第 n 个插入的数。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 M,表示操作次数。接下来 M 行,每行包含一个操作命令,操作命令可能为以下几种:H x,表示向链表头插入一个数 x。D k,表示删除第 k 个插入的数后面的数(当 k 为 0 时,表示删除头结点)。I k x,表示在第 k 个插入的数后面插入一个数 x(此操作中 k 均大于 0)。
输出格式
共一行,将整个链表从头到尾输出。数据范围1≤M≤100000所有操作保证合法。
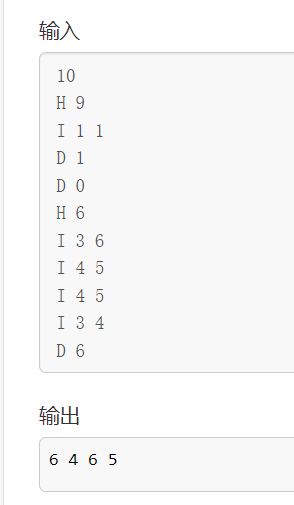
输入样例:
10
H 9
I 1 1
D 1
D 0
H 6
I 3 6
I 4 5
I 4 5
I 3 4
D 6
输出样例:
6 4 6 5
#include 3.测试
二、数组模拟双链表
1.模板
const int N = 100010;
int e[N], l[N], r[N], idx;
void init() //0代表左端点 1代表右端点
{
r[0] = 1, l[1] = 0, idx = 2;
}
void insert(int k, int x) //在结点k的右边插入一个数x
{
e[idx] = x;
r[idx] = r[k], l[idx] = k;
l[r[k]] = idx, r[k] = idx++;
}
void remove(int k) //删除结点k
{
r[l[k]] = r[k];
l[r[k]] = l[k];
}
2.例题
实现一个双链表,双链表初始为空,支持 5 种操作:
在最左侧插入一个数;
在最右侧插入一个数;
将第 k 个插入的数删除;
在第 k 个插入的数左侧插入一个数;
在第 k 个插入的数右侧插入一个数
现在要对该链表进行 M 次操作,进行完所有操作后,从左到右输出整个链表。
注意:题目中第 k 个插入的数并不是指当前链表的第 k 个数。例如操作过程中一共插入了 n 个数,则按照插入的时间顺序,这 n 个数依次为:第 1 个插入的数,第 2 个插入的数,…第 n 个插入的数。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 M,表示操作次数。接下来 M 行,每行包含一个操作命令,操作命令可能为以下几种:L x,表示在链表的最左端插入数 x。R x,表示在链表的最右端插入数 x。D k,表示将第 k 个插入的数删除。IL k x,表示在第 k 个插入的数左侧插入一个数。IR k x,表示在第 k 个插入的数右侧插入一个数。
输出格式
共一行,将整个链表从左到右输出。数据范围1≤M≤100000所有操作保证合法。
输入样例:
10
R 7
D 1
L 3
IL 2 10
D 3
IL 2 7
L 8
R 9
IL 4 7
IR 2 2
输出样例:
8 7 7 3 2 9
#include 3.测试
三、数组模拟栈
1.模板
const int N = 100010;
int stk[N], tt;
void push(int x)
{
stk[++tt] = x;
}
bool empty()
{
return tt > 0 ? false : true;
}
void pop()
{
tt--;
}
int top()
{
return stk[tt];
}
2.例题
实现一个栈,栈初始为空,支持四种操作:
push x – 向栈顶插入一个数 x;
pop – 从栈顶弹出一个数;
empty – 判断栈是否为空;
query – 查询栈顶元素。
现在要对栈进行 M 个操作,其中的每个操作 3 和操作 4 都要输出相应的结果。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 M,表示操作次数。接下来 M 行,每行包含一个操作命令,操作命令为 push x,pop,empty,query 中的一种。
输出格式
对于每个 empty 和 query 操作都要输出一个查询结果,每个结果占一行。其中,empty 操作的查询结果为 YES 或 NO,query 操作的查询结果为一个整数,表示栈顶元素的值。
数据范围
1≤M≤100000,1≤x≤109所有操作保证合法。
输入样例:
10
push 5
query
push 6
pop
query
pop
empty
push 4
query
empty
输出样例:
5
5
YES
4
NO
#include 3.测试
四、数组模拟队列
1.模板
const int N = 100010;
int q[N], hh, tt = -1;
void push(int x)
{
q[++tt] = x;
}
int front()
{
return q[hh];
}
void pop()
{
hh++;
}
bool empty()
{
return hh <= tt ? false : true;
}
2.例题
实现一个队列,队列初始为空,支持四种操作:
push x – 向队尾插入一个数 x;
pop – 从队头弹出一个数;
empty – 判断队列是否为空;
query – 查询队头元素。
现在要对队列进行 M 个操作,其中的每个操作 3 和操作 4 都要输出相应的结果。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 M,表示操作次数。接下来 M 行,每行包含一个操作命令,操作命令为 push x,pop,empty,query 中的一种。
输出格式
对于每个 empty 和 query 操作都要输出一个查询结果,每个结果占一行。其中,empty 操作的查询结果为 YES 或 NO,query 操作的查询结果为一个整数,表示队头元素的值。
数据范围
1≤M≤100000,1≤x≤109,所有操作保证合法。
输入样例:
10
push 6
empty
query
pop
empty
push 3
push 4
pop
query
push 6
输出样例:
NO
6
YES
4
#include 3.测试
五、数组模拟单调栈
单调栈就是用来快速找当前下标左边第一个小于该数的数
1.例题+模板
给定一个长度为 N 的整数数列,输出每个数左边第一个比它小的数,如果不存在则输出 −1。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 N,表示数列长度。第二行包含 N 个整数,表示整数数列。
输出格式
共一行,包含 N 个整数,其中第 i 个数表示第 i 个数的左边第一个比它小的数,如果不存在则输出 −1。
数据范围
1≤N≤105,1≤数列中元素≤109
输入样例:
5
3 4 2 7 5
输出样例:
-1 3 -1 2 2
#include 2.测试
六、数组模拟单调队列
1.例题+模板
给定一个大小为 n≤106的数组。有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口,它从数组的最左边移动到最右边。你只能在窗口中看到 k 个数字。每次滑动窗口向右移动一个位置。以下是一个例子:
该数组为 [1 3 -1 -3 5 3 6 7],k 为 3。
窗口位置 最小值 最大值
[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 -1 3
1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 -3 3
1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 -3 5
1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 -3 5
1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 3 6
1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 3 7
你的任务是确定滑动窗口位于每个位置时,窗口中的最大值和最小值。
输入格式
输入包含两行。第一行包含两个整数 n 和 k,分别代表数组长度和滑动窗口的长度。第二行有 n 个整数,代表数组的具体数值。同行数据之间用空格隔开。
输出格式
输出包含两个。第一行输出,从左至右,每个位置滑动窗口中的最小值。第二行输出,从左至右,每个位置滑动窗口中的最大值。
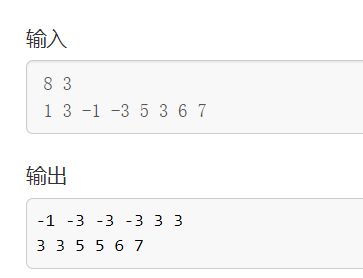
输入样例:
8 3
1 3 -1 -3 5 3 6 7
输出样例:
-1 -3 -3 -3 3 3
3 3 5 5 6 7
#include