【webpack插件篇】webpack-plugin-mock 一款mockjs的webpack插件,配置简单、易用
背景
现在前后端分离的项目很常见,当服务端接口在开发中时,前端要怎么调试接口尼,为了解决这个问题,模拟服务端接口应运而生,webapck-plugin-mock 就是一个模拟服务端接口的webpack插件,配置起来简单,容易上手,且mock数据支持多种格式
如何编写webpack插件
Webpack 通过 Plugin 机制让其更加灵活,在 Webpack 运行的生命周期中会挂许多钩子函数,Plugin 通过这些钩子函数来改变webpack输出的结果。
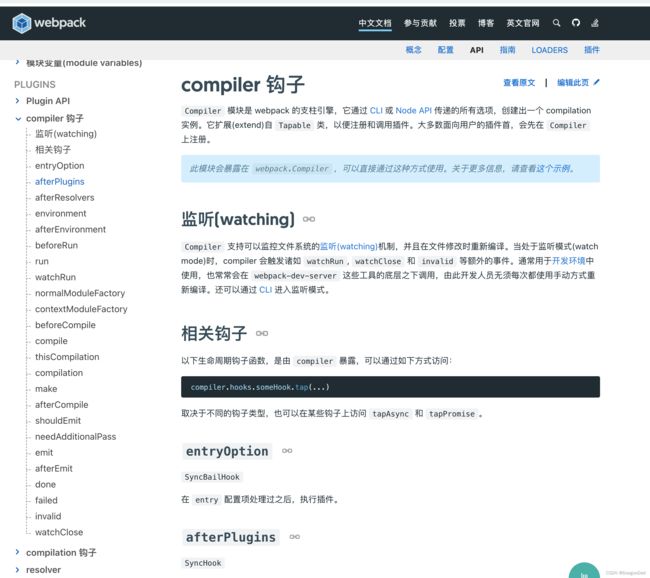
钩子如下图
最简单的 Plugin 的代码是这样的
class BasicPlugin{
// 在构造函数中获取用户给该插件传入的配置
constructor(options){
}
// Webpack 会调用 BasicPlugin 实例的 apply 方法给插件实例传入 compiler 对象
apply(compiler){
compiler.plugin('compilation',function(compilation) {
})
}
}
// 导出 Plugin
module.exports = BasicPlugin;
使用这个 Plugin 时,相关配置代码如下:
const BasicPlugin = require('./BasicPlugin.js');
module.export = {
plugins:[
new BasicPlugin(options),
]
}
Webpack 启动后,在读取配置的过程中会先执行 new BasicPlugin(options) 初始化一个 BasicPlugin 获得其实例。 在初始化 compiler 对象后,再调用 basicPlugin.apply(compiler) 给插件实例传入 compiler 对象。 插件实例在获取到 compiler 对象后,就可以通过 compiler.plugin(事件名称, 回调函数) 监听到 Webpack 广播出来的事件。 并且可以通过 compiler 对象去操作 Webpack
开始编写插件WebpackPluginMock
class WebpackPluginMock {
private readonly config: MockServerConfig
constructor(config: MockServerConfig) {
this.config = config
}
apply() {
serve(this.config)
}
}
module.exports = WebpackPluginMock
const serve = async (config: MockServerConfig) => {
const app = new Koa();
const router = new Router();
// const upload = multer();
const __DEV__ = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development';
const publicBasePath = path.resolve(__dirname, '../public');
__DEV__ && console.log('[mock] config', config);
jsonp(app, {
callback: 'callback',
limit: 50,
});
/**
* logger 最外层调用
* json pretty 次外层,方便格式化 response
* cors 次次外层,收到请求优先处理 CORS
* 先调用 koa-body 再调用 koa-router
*/
app.use(logger());
if (config.pretty) {
app.use(
json({
pretty: true,
spaces: 2,
})
);
}
app.use(
cors({
credentials: true,
})
);
app.use(
koaBody({
multipart: true,
})
);
app.use(router.routes());
app.use(router.allowedMethods());
app.use(koaStatic(publicBasePath));
addInternalRoutes(router);
try {
// 自动扫描 apis 文件夹下 JS、JSON,添加为 route
const { jsPaths, jsonPaths } = await scanRoutes(config.apiBasePath);
registerRoutes(router, {
rootPath: config.apiBasePath,
jsPaths,
jsonPaths,
});
} catch (err) {
logError(err);
}
/**
* apis 文件变化回调
*/
const onRoutesChange = async (filePath: string) => {
const { jsPaths, jsonPaths } = await scanRoutes(filePath);
const routePaths = [...jsPaths, ...jsonPaths];
routePaths.forEach(routePath => {
logWarning(
`[onRoutesChange] "${require.resolve(routePath)}" will be reload`
);
delete require.cache[require.resolve(routePath)];
});
registerRoutes(router, {
rootPath: config.apiBasePath,
jsPaths,
jsonPaths,
});
};
const onRoutesChangeDebounced = debounce(onRoutesChange, 1000);
// 监控 apis 文件变化
if (config.watch) {
logSuccess(`[mock] Watch "${config.apiBasePath}"`);
watchRoutes(config.apiBasePath, onRoutesChangeDebounced);
}
app.on('error', (err, ctx) => {
logError('[mock] server error', err, ctx);
});
app.listen(config.port);
logSuccess(`[mock] Mock server is running at ${config.port}`);
logSuccess(`[mock] LOCAL http://localhost:${config.port}`);
logSuccess(`[mock] LAN http://${address.ip()}:${config.port}`);
return {
app,
router,
};
};
export { serve }
安装
# npm
npm install webpack-plugin-mock -D
# yarn
yarn add webpack-plugin-mock -D
配置
new WebpackPluginMock({
apiBasePath: './mock',
watch: true,
pretty: true,
port: 8090
})
项目根目录建mock -> user -> list.json
{
"code": 0,
"msg": "",
"data": {
"dataList|10" :[
{
"id": "@id",
"name": "@cname",
"phone": "@pick([13913998972, 19941558406])",
"deptName": "前端开发部"
}
],
"totalCount": 20,
"totalPageCount": 2
}
}
启动项目
npm run dev
.....
[mock] Watch "./mock"
[mock] Mock server is running at 8090
[mock] LOCAL http://localhost:8090
[mock] LAN http://10.46.85.40:8090
[mock] api list http://10.46.85.40:8090/mock-api/list
....
webpack 5.72.1 compiled successfully in 10882 ms
效果

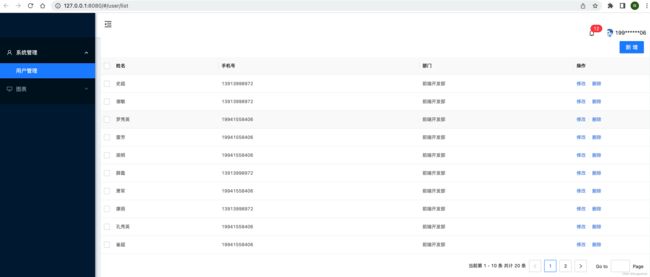
其实开发webpac插件有2个比较重要的对象Compiler 和 Compilation,虽然我们写WebpackPluginMock时没有用到,还是很有必要弄清楚
- Compiler 对象包含了 Webpack 环境所有的的配置信息,包含 options,loaders,plugins 这些信息,这个对象在 Webpack 启动时候被实例化,它是全局唯一的,可以简单地把它理解为 Webpack 实例;
- Compilation 对象包含了当前的模块资源、编译生成资源、变化的文件等。当 Webpack 以开发模式运行时,每当检测到一个文件变化,一次新的 Compilation 将被创建。Compilation 对象也提供了很多事件回调供插件做扩展。通过 Compilation 也能读取到 Compiler 对象。
Compiler 和 Compilation 的区别在于:Compiler 代表了整个 Webpack 从启动到关闭的生命周期,而 Compilation 只是代表了一次新的编译
源码地址
http://github.com/GuoguoDad/webpack-plugin-mock
结束语
如果文章对您有帮助,三连支持一下~O(∩_∩)O谢谢!