ServletConfig和ServletContext对象
目录
1.ServletConfig对象
1.1ServletConfig对象是什么
1.2ServletConfig对象里的方法
1.3ServletConfig的配置方式
1.4ServletConfig实现步骤
2. ServletContext对象
2.1ServletContext对象是什么
2.2ServletContext对象里的方法
2.3ServletContext对象的配置方式
2.4ServletContext对象的实现步骤
3.ServletConfig和ServletContext对象的区别
1.ServletConfig对象
1.1ServletConfig对象是什么
ServletContext是javax.servlet包下的一个接口,又称上下文对象,是配置对象也是一个域对象;
当服务器启动时,会为服务器中的每一个web应用程序创建一个ServletContext对象;
在web应用中的servlet要想实现资源的共享,可以通过ServletContext来完成;
1.2ServletConfig对象里的方法
getInitParameter() //获取指定参数名称的全局参数值
getRealPath(String path) //获得当前项目的服务器磁盘路径
getContextPath() //获取项目的根路径
getAttribute(String parameterName) //获取ServletContext域中指定名称的参数值;
setAttribute(String paramterName,Object parameterValue) //存储参数到ServletContext域中;
removeAttribute(String parameterNam) //将ServletContext域中指定名称的参数移除;1.3ServletConfig的配置方式
在
1.
2.
username
root
password
root456
1.4ServletConfig实现步骤
- 定义一个类,继承HttpServlet。
- 重写doGet()和doPost()方法。
- 在web.xml进行配置。
- 在请求方法中通过请求对象获取到ServletConfig对象。
- 然后再通过getInitParameter()方法获取到配置的初始化参数。
- 部署并启动项目。
- 通过浏览器测试。
代码实现:
package com.by.servlet;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
public class ServletConfigServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest,
ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException {
//1.获取ServletConfig对象
ServletConfig servletConfig = getServletConfig();
//2.获取Servlet中的初始化参数
String username = servletConfig.getInitParameter("username");
System.out.println(username);
String password = servletConfig.getInitParameter("password");
System.out.println(password);
//3.获取ServletContext对象(域对象)
ServletContext servletContext = servletConfig.getServletContext();
}
}param参数不可以在另外的Servlet中获取
public class ServletConfigServlet2 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void goGet(ServletRequest servletRequest,
ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException {
//1.获取ServletConfig对象
ServletConfig servletConfig = getServletConfig();
//2.获取Servlet中的初始化参数
String username = servletConfig.getInitParameter("username");//不能获取
System.out.println(username);
String password = servletConfig.getInitParameter("password");//不能获取
System.out.println(password);
//3.获取ServletContext对象(域对象)
ServletContext servletContext = servletConfig.getServletContext();
}
}2. ServletContext对象
2.1ServletContext对象是什么
ServletContext是javax.servlet包下的一个接口,又称上下文对象,是配置对象也是一个域对象;
当服务器启动时,会为服务器中的每一个web应用程序创建一个ServletContext对象;
在web应用中的servlet要想实现资源的共享,可以通过ServletContext来完成;
2.2ServletContext对象里的方法
getInitParameter() //获取指定参数名称的全局参数值
getRealPath(String path) //获得当前项目的服务器磁盘路径
getContextPath() //获取项目的根路径
getAttribute(String parameterName) //获取ServletContext域中指定名称的参数值;
setAttribute(String paramterName,Object parameterValue) //存储参数到ServletContext域中;
removeAttribute(String parameterNam) //将ServletContext域中指定名称的参数移除;2.3ServletContext对象的配置方式
ServletContext不像ServletConfig接口在Servlet标签里配置,而是针对于整个应用的配置,也叫全局的初始化参数;
在
1.
2.
username
root
password
root456
该代码是直接放在
2.4ServletContext对象的实现步骤
ServletContext 实现步骤:
1.定义一个类,继承HttpServlet。
2.重写 doGet和 doPost 方法。
3.在web.xml文件中配置Servlet和ServletContext。
4.获取 ServletContext 对象。
5.测试相关方法的使用。
6.部署并启动项目。
7.通过浏览器测试。
代码实现:
public class ServletContextServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//一个web应用只有一个serveletContext对象,能实现共享
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
String username = servletContext.getInitParameter("username");
String password = servletContext.getInitParameter("password");
System.out.println(username+"---------"+password);
//往servletContext对象添加属性:继承了map
servletContext.setAttribute("msg", "sb");
}
}
param参数可以在另外的Servlet中获取
在写两个分别用来测试:
public class ServletContextServlet2 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//一个web应用只有一个serveletContext对象,能实现共享
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
String username = servletContext.getInitParameter("username");
String password = servletContext.getInitParameter("password");
System.out.println(username+"---------"+password);
Object msg = servletContext.getAttribute("msg");
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
public class ServletContextServlet3 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
//删除servletContext对象中的属性
servletContext.removeAttribute("msg");
}
}web.xml中的配置:
context1
com.by.servlet.ServletContextServlet
context1
/context1
context2
com.by.servlet.ServletContextServlet2
context2
/context2
context3
com.by.servlet.ServletContextServlet3
context3
/context3
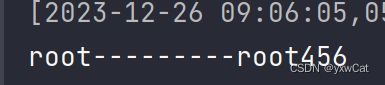
先访问context1:
再访问context2;
可以接收到msg。
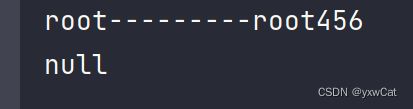
再访问context3,此时msg已被删除,再次访问context2,此时msg为空。
3.ServletConfig和ServletContext对象的区别
ServletConfig 是针对单个servlet 而言的,在servlet 被创建时初被容器创建,用来存储servlet 初始化参数。Servlet 可以通过 getServletConfig()方法获取ServletConfig 对象。
ServletContext 是针对整个web 应用而言的,在web 应用启动时被容器创建,用来存储应用级别的信息,例如应用名称、上下文路径等。所有servlet 可以通过 getServletContext()方法获取Servle etContext 对象。