【小家Spring】聊聊Spring中的数据转换:Converter、ConversionService、TypeConverter、PropertyEditor
每篇一句
表像大都这样:出力的不挣钱,挣钱的不出力
前言
前面聊了HttpMessageConverter,它的名称叫消息转换器,所以它面向的是消息体,和Http强相关,所以该接口所在的包为:org.springframework.http.converter
数据转换,顾名思义就是数据类型之间的转换,但是对于数据转换,有的是可以进行转化的,例如字符串转整型,但是有些数据类型之间是不能进行转换的,例如从“aaa”字符串到整型的转换。
不同的框架,肯定都有自己的数据转换的实现,比如MyBatis、Hibernate等这些转换器都是必备的。然后作为这么强大的Spring,它肯定也缺席不了。org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter它位于核心包中,所以它不仅仅运用于Spring MVC等web环境,比如spring-jdbc等都是有使用到的~
数据转换在框架设计中是非常重要的一环,它能让你的框架更普适,更通用,更自动化,解决的问题更多,所以我个人认为,了解Spring数据转换的设计思想,以及它的常用实现是非常有必要的。
若是源生Servlet开发,你能想象到那种低下的开发效率吗以及漫天遍地的“垃圾代码”吗?
关于Spring中的数据转换,首先需要了解两大主要分支:
Converter:是Spring中最为简单的一个接口。位于包:org.springframework.core.convert.converter。 相关的顶层接口(类)有:ConditionalConverter、GenericConverter、ConverterFactory、ConvertingComparator、ConverterRegistryConversionService:用于类型转换的服务接口。这是进入转换系统的入口点。位于包:org.springframework.core.convert。相关的顶层接口(类)有:ConversionService、FormattingConversionService、DefaultConversionService、ConversionServiceFactoryBean、FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean…
注意各子接口,实现类不一定都是core包里,可能在context包、web包等等~。他俩体系都是@since 3.0
Converter
Spring的Converter是可以将一种类型转换成另一种类型的一个对象,它的接口定义非常的的简单。
// 实现此接口的 大都会实现ConditionalConverter
// 请保持线程安全~~
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Converter<S, T> {
// 把S转成T
@Nullable
T convert(S source);
}
Spring提供了3种converter接口,分别是Converter、ConverterFactory和GenericConverter.一般用于1:1, 1:N, N:N的source->target类型转化。
Converter接口 :使用最简单,最不灵活;
ConverterFactory接口 :使用较复杂,比较灵活;
GenericConverter接口 :使用最复杂,也最灵活;
Converter
Converter的实现类举例:该接口Spring内部的实现也非常多,大多数都是以内部类的形式实现(因为它是一个@FunctionalInterface嘛)
// ObjectToStringConverter
final class ObjectToStringConverter implements Converter<Object, String> {
@Override
public String convert(Object source) {
return source.toString();
}
}
// StringToCharsetConverter @since 4.2
@Override
public Charset convert(String source) {
return Charset.forName(source);
}
// StringToPropertiesConverter
@Override
public Properties convert(String source) {
try {
Properties props = new Properties();
// Must use the ISO-8859-1 encoding because Properties.load(stream) expects it.
props.load(new ByteArrayInputStream(source.getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1)));
return props;
}catch (Exception ex) {
// Should never happen.
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Failed to parse [" + source + "] into Properties", ex);
}
}
// StringToTimeZoneConverter @since 4.2
@Override
public TimeZone convert(String source) {
return StringUtils.parseTimeZoneString(source);
}
//ZoneIdToTimeZoneConverter @since 4.0
@Override
public TimeZone convert(ZoneId source) {
return TimeZone.getTimeZone(source);
}
// StringToBooleanConverter 这个转换器很有意思 哪些代表true,哪些代表fasle算是业界的一个规范了
// 这就是为什么,我们给传值1也会被当作true来封装进Boolean类型的根本原因所在~
static {
trueValues.add("true");
trueValues.add("on");
trueValues.add("yes");
trueValues.add("1");
falseValues.add("false");
falseValues.add("off");
falseValues.add("no");
falseValues.add("0");
}
// StringToUUIDConverter @since 3.2
@Override
public UUID convert(String source) {
return (StringUtils.hasLength(source) ? UUID.fromString(source.trim()) : null);
}
// StringToLocaleConverter
@Override
@Nullable
public Locale convert(String source) {
return StringUtils.parseLocale(source);
}
// SerializingConverter:把任意一个对象,转换成byte[]数组,唯独这一个是public的,其它的都是Spring内置的
public class SerializingConverter implements Converter<Object, byte[]> {
// 序列化器:DefaultSerializer 就是new ObjectOutputStream(outputStream).writeObject(object)
// 就是简单的把对象写到输出流里~~
private final Serializer<Object> serializer;
public SerializingConverter() {
this.serializer = new DefaultSerializer();
}
public SerializingConverter(Serializer<Object> serializer) { // 自己亦可指定实现。
Assert.notNull(serializer, "Serializer must not be null");
this.serializer = serializer;
}
@Override
public byte[] convert(Object source) {
ByteArrayOutputStream byteStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(1024);
try {
this.serializer.serialize(source, byteStream);
// 把此输出流转为byte[]数组~~~~~~
return byteStream.toByteArray();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new SerializationFailedException("Failed to serialize object using " +
this.serializer.getClass().getSimpleName(), ex);
}
}
}
Converter接口非常的简单,所以除了SerializingConverter一个是外部类,我们可以拿来使用外,其余的都是Spring内部自己使用的。从此可以看出:此接口一般也用于我们自己去实现,即:自定义数据转换器。
自定义转换器的一个Demo:
// 把形如这样的字符串: "fsx:18" 转换为Person对象
public class PersonConverter implements Converter<String, Person> {
@Override
public Person convert(String source) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(source)) {
return null;
}
String[] strings = StringUtils.delimitedListToStringArray(source, ":");
Person person = new Person();
person.setName(strings[0]);
person.setAge(Integer.valueOf(strings[1]));
return person;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PersonConverter personConverter = new PersonConverter();
System.out.println(personConverter.convert("fsx:18")); //Person{name='fsx', age=18}
}
}
备注:在Spring内部消息转换器的注册、使用一般都结合
ConversionService这个接口
ConditionalConverter
根据source和target来做条件判断,从而可以判断哪个转换器生效,哪个不生效之类的。
// @since 3.2 出现稍微较晚
public interface ConditionalConverter {
boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
}
org.springframework.core.convert.TypeDescriptor也是一个Spring的基础类(类似ResolvableType)这种,若有需要我们平时也可以使用它。 它能够把基础类型、MethodParameter、Field、org.springframework.core.convert.Property、Class等都描述进来。并且提供如下非常方便方法:
// @since 3.0
public class TypeDescriptor implements Serializable {
public Class<?> getType() {
return this.type;
}
public ResolvableType getResolvableType() {
return this.resolvableType;
}
public Object getSource() {
return this.resolvableType.getSource();
}
public String getName();
public boolean isPrimitive();
public Annotation[] getAnnotations();
public boolean hasAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType);
public <T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationType);
public boolean isAssignableTo(TypeDescriptor typeDescriptor);
public boolean isCollection();
public boolean isArray();
public boolean isMap();
public TypeDescriptor getMapKeyTypeDescriptor();
public TypeDescriptor getMapValueTypeDescriptor()
// 静态方法:可吧基础类型、任意一个class类型转为这个描述类型 依赖于下面的valueOf方法 source为null 返回null
public static TypeDescriptor forObject(@Nullable Object source);
public static TypeDescriptor valueOf(@Nullable Class<?> type);
// 把集合转为描述类型~
public static TypeDescriptor collection(Class<?> collectionType, @Nullable TypeDescriptor elementTypeDescriptor)
public static TypeDescriptor map(Class<?> mapType, @Nullable TypeDescriptor keyTypeDescriptor, @Nullable TypeDescriptor valueTypeDescriptor);
public static TypeDescriptor array(@Nullable TypeDescriptor elementTypeDescriptor);
public static TypeDescriptor nested(MethodParameter methodParameter, int nestingLevel);
public static TypeDescriptor nested(Field field, int nestingLevel);
public static TypeDescriptor nested(Property property, int nestingLevel);
}
ConditionalConverter的继承树:
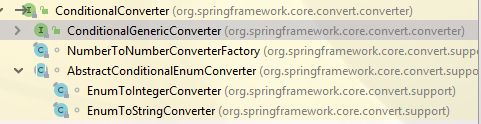
ConditionalGenericConverter这个子接口,就是把GenericConverter和ConditionalConverter联合起来了。而GenericConverter我们上面提到了,它一般用于处理N:N的转换,因此它的子类们放在下面讲会更合适~
NumberToNumberConverterFactory:它是个ConverterFactory,所以也放下面
AbstractConditionalEnumConverter:枚举类型的转换
// @since 4.3 也是只能Spring内部自己用的
abstract class AbstractConditionalEnumConverter implements ConditionalConverter {
// 它借助了ConversionService这个接口 需要外部自定义转换逻辑~~
private final ConversionService conversionService;
protected AbstractConditionalEnumConverter(ConversionService conversionService) {
this.conversionService = conversionService;
}
@Override
public boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
// 拿到source所有实现的接口 若没有实现任何接口,永远返回true
for (Class<?> interfaceType : ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(sourceType.getType())) {
// 最终是委托给conversionService去做这件事了~~~~
if (this.conversionService.canConvert(TypeDescriptor.valueOf(interfaceType), targetType)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
它的两个子类实现:EnumToIntegerConverter和EnumToStringConverter就是调用了source.ordinal()和source.name()。若你想要实现自己的枚举自定义属性的转换,其实是可以继承AbstractConditionalEnumConverter它的,但是Spring并没有公开它,so~~~你还是自己写吧
ConverterFactory
ConverterFactory:range范围转换器的工厂:可以将对象从S转换为R的子类型(1:N)
public interface ConverterFactory<S, R> {
//Get the converter to convert from S to target type T, where T is also an instance of R
<T extends R> Converter<S, T> getConverter(Class<T> targetType);
}
final class IntegerToEnumConverterFactory implements ConverterFactory<Integer, Enum> {
// ConversionUtils.getEnumType表示拿出枚举的class类型
@Override
public <T extends Enum> Converter<Integer, T> getConverter(Class<T> targetType) {
return new IntegerToEnum(ConversionUtils.getEnumType(targetType));
}
// 内部类的实现 把Integer转为Enum的子类型~~~ 相当于根据integer找到一个enum(注意此处根据角标来找的)
private class IntegerToEnum<T extends Enum> implements Converter<Integer, T> {
private final Class<T> enumType;
public IntegerToEnum(Class<T> enumType) {
this.enumType = enumType;
}
@Override
public T convert(Integer source) {
return this.enumType.getEnumConstants()[source];
}
}
}
// StringToEnumConverterFactory 大体同上 return (T) Enum.valueOf(this.enumType, source.trim())
...
该工厂就是用来创建一个converter,把目标类型转换成子类型,所以它是1->N的。注意:Spring内置的实现也都是外部不可访问的
GenericConverter
用于在两个或多个类型之间转换的通用转换器接口。这是最灵活的转换器SPI接口,也是最复杂的
灵活是因为它一个转换器就能转换多个s/t,所以它是N->N的。实现类们一般情况下也会实现接口:ConditionalConverter
1个GenericConverter支持转化的所有类型都写在了属性Set内
public interface GenericConverter {
@Nullable
Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes();
@Nullable
Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
/**
* Holder for a source-to-target class pair.
*/
// 包含有一对 s和t
final class ConvertiblePair {
private final Class<?> sourceType;
private final Class<?> targetType;
public ConvertiblePair(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType) {
Assert.notNull(sourceType, "Source type must not be null");
Assert.notNull(targetType, "Target type must not be null");
this.sourceType = sourceType;
this.targetType = targetType;
}
... // 去掉get/set方法 以及toString equals等基础方法
}
}
它的实现类都是子接口ConditionalGenericConverter的实现类(就是GenericConverter和ConditionalConverter的结合).
注意:Spring的所有内部实现,依旧全部未公开,因此本文只举例说明一下即可。
final class ArrayToObjectConverter implements ConditionalGenericConverter {
// 借助了ConversionService
private final ConversionService conversionService;
public ArrayToObjectConverter(ConversionService conversionService) {
this.conversionService = conversionService;
}
// 残暴:都是object
@Override
public Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes() {
return Collections.singleton(new ConvertiblePair(Object[].class, Object.class));
}
// 实现ConditionalConverter的方法,最终是委托给了ConversionService#canConvert方法
@Override
public boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
return ConversionUtils.canConvertElements(sourceType.getElementTypeDescriptor(), targetType, this.conversionService);
}
...
}
// 这里的转换器,都和数组、集合有关,比如:
// StringToCollectionConverter、CollectionToArrayConverter、CollectionToStringConverter
// StringToArrayConverter、StreamConverter、CollectionToArrayConverter等等
特别说一句:这里有一个非常有意思的转换器:IdToEntityConverter,SpringMVC默认给我们这已经注册进去了,在Spring MVC自定义常用的、通用的Controller的时候,我们会借助它实现通用方案,让controller异常的方便,好使~~~暂时可先参考:路由id转化为控制器Entity参数
ConverterRegistry
使用ConverterRegistry可以使我们对类型转换器做一个统一的注册。正如前言所说的,要实现自己的类型转换逻辑我们可以实现Converter接口、ConverterFactory接口和GenericConverter接口,ConverterRegistry接口就分别为这三种类型提供了对应的注册方法,至于里面的逻辑就可以发挥自己的设计能力进行设计实现了。
通过ConverterAdapter或者ConverterFactoryAdapter最后都会转化成GenericConverter,我想应该是因为这种converter是最通用的原因吧
一般而言:我们在实现
ConversionService接口的时候也会实现ConverterRegistry接口
// @since 3.0 Converter 注册处,用于存储 Converter 实例
public interface ConverterRegistry {
void addConverter(Converter<?, ?> converter);
// 添加一个 Converter 实例,并指定其源和目标类型
<S, T> void addConverter(Class<S> sourceType, Class<T> targetType, Converter<? super S, ? extends T> converter);
void addConverter(GenericConverter converter);
void addConverterFactory(ConverterFactory<?, ?> factory);
// 移除方法只有一个:它是面向s和t来做移除的~~~~ 删除所有匹配指定源和目标类型的 Converter
// Remove any converters from {@code sourceType} to {@code targetType}
void removeConvertible(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType);
}
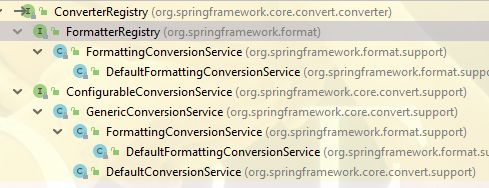
两大分支。FormatterRegistry用于注册格式化器,下面再说
ConfigurableConversionService:它就是把ConversionService和ConverterRegistry绑定在一起,自己并不提供新接口
// @since 3.1
public interface ConfigurableConversionService extends ConversionService, ConverterRegistry {
}
所以它的具体内容,放到ConversionService里描述吧。
ConversionService
用于类型转换的服务接口。这是转换系统的**入口点**。请保证它convert方法的线程安全,这个接口非常的重要。
举个例子,使用Environment的ConversionService来完成的。
// @since 3.0
public interface ConversionService {
// 特别说明:若是Map、集合、数组转换时。即使下面方法convert转换抛出了异常,这里也得返回true 因为Spring希望调用者处理这个异常:ConversionException
boolean canConvert(@Nullable Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType);
boolean canConvert(@Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
// 注意此处:转换的source都是对象,target只需要类型即可~~~
@Nullable
<T> T convert(@Nullable Object source, Class<T> targetType);
@Nullable
Object convert(@Nullable Object source, @Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
}
GenericConversionService
它也并不是一个抽象类,它是一个通用的处理。但是一般不会直接使用它,而是使用它的更具体的子类
// @since 3.0 实现了接口ConversionService和ConverterRegistry
public class GenericConversionService implements ConfigurableConversionService {
// 啥都不做,但是呢conversion is not required,相当于占位的意思
private static final GenericConverter NO_OP_CONVERTER = new NoOpConverter("NO_OP");
// 当转换器缓存中没有任何匹配时,它上场
// 请不要把它直接return,用null代替返回
private static final GenericConverter NO_MATCH = new NoOpConverter("NO_MATCH");
// 说明:Converter是一个静态内部类 它会Manages all converters registered with the service
private final Converters converters = new Converters();
// 缓存转换器。用的ConcurrentReferenceHashMap是Spring自己实现的一个软引用/弱引用的Map
private final Map<ConverterCacheKey, GenericConverter> converterCache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>(64);
// 仅有一个空构造函数,构造函数内啥都没做
@Override
public void addConverter(Converter<?, ?> converter) {
// 这个处理很有意思:getRequiredTypeInfo 拿到两个泛型参数类型(若没有指定泛型 返回的是null)
ResolvableType[] typeInfo = getRequiredTypeInfo(converter.getClass(), Converter.class);
// Decorate和Proxy模式的区别。Decorate模式可用于函数防抖 Proxy模式就是我们常用的代理模式
if (typeInfo == null && converter instanceof DecoratingProxy) {
typeInfo = getRequiredTypeInfo(((DecoratingProxy) converter).getDecoratedClass(), Converter.class);
}
// 由此可见这个转换器的泛型类型是必须的~~~
if (typeInfo == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to determine source type and target type for your " +
"Converter [" + converter.getClass().getName() + "]; does the class parameterize those types?");
}
// ConverterAdapter是个GenericConverter。由此课件最终都是转换成了GenericConverter类型
addConverter(new ConverterAdapter(converter, typeInfo[0], typeInfo[1]));
}
@Override
public <S, T> void addConverter(Class<S> sourceType, Class<T> targetType, Converter<? super S, ? extends T> converter) {
addConverter(new ConverterAdapter(converter, ResolvableType.forClass(sourceType), ResolvableType.forClass(targetType)));
}
// 最终都是转换成了GenericConverter 进行转换器的保存 全部放在Converters里保存着
@Override
public void addConverter(GenericConverter converter) {
this.converters.add(converter);
invalidateCache(); // 清空缓存
}
// 使用ConverterFactoryAdapter转换成GenericConverter
@Override
public void addConverterFactory(ConverterFactory<?, ?> factory) { ... }
// 注意ConvertiblePair是重写了equals方法和hash方法的
@Override
public void removeConvertible(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType) {
this.converters.remove(sourceType, targetType);
invalidateCache();
}
// 主要是getConverter() 方法 相当于只有有转换器匹配,就是能够被转换的
@Override
public boolean canConvert(@Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
Assert.notNull(targetType, "Target type to convert to cannot be null");
if (sourceType == null) {
return true;
}
GenericConverter converter = getConverter(sourceType, targetType);
return (converter != null);
}
@Nullable
protected GenericConverter getConverter(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
ConverterCacheKey key = new ConverterCacheKey(sourceType, targetType);
GenericConverter converter = this.converterCache.get(key);
// 这个处理:如果缓存有值 但是为NO_MATCH 那就返回null,而不是把No_Match直接return
if (converter != null) {
return (converter != NO_MATCH ? converter : null);
}
converter = this.converters.find(sourceType, targetType);
if (converter == null) {
converter = getDefaultConverter(sourceType, targetType);
}
// 如果默认的不为null 也可以return的
// NO_OP_CONVERTER还是可以return的~~~
if (converter != null) {
this.converterCache.put(key, converter);
return converter;
}
this.converterCache.put(key, NO_MATCH);
return null;
}
@Nullable
protected GenericConverter getDefaultConverter(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
return (sourceType.isAssignableTo(targetType) ? NO_OP_CONVERTER : null);
}
// 拿到泛型类型们
@Nullable
private ResolvableType[] getRequiredTypeInfo(Class<?> converterClass, Class<?> genericIfc) {
ResolvableType resolvableType = ResolvableType.forClass(converterClass).as(genericIfc);
ResolvableType[] generics = resolvableType.getGenerics();
if (generics.length < 2) {
return null;
}
Class<?> sourceType = generics[0].resolve();
Class<?> targetType = generics[1].resolve();
if (sourceType == null || targetType == null) {
return null;
}
return generics;
}
...
}
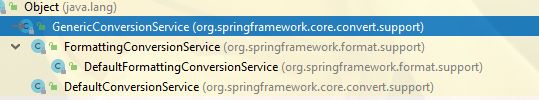
绝大多数情况下,我们不会直接使用GenericConversionService,而是使用它的子类DefaultConversionService
DefaultConversionService
它能适用于绝大多数的场景中。
// @since 3.1
public class DefaultConversionService extends GenericConversionService {
// @since 4.3.5 改变量出现得还是比较晚的
@Nullable
private static volatile DefaultConversionService sharedInstance;
// 空构造,那就注册到自己this身上~~~因为自己也是个ConverterRegistry
public DefaultConversionService() {
addDefaultConverters(this);
}
// 就是把sharedInstance返回出去~~~(永远不可能返回null)
public static ConversionService getSharedInstance() { ... }
// 默认情况下,这个ConversionService注册的转换器们~~~~ 几乎涵盖了所有~~~~
public static void addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
addScalarConverters(converterRegistry);
addCollectionConverters(converterRegistry);
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ByteBufferConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToTimeZoneConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ZoneIdToTimeZoneConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ZonedDateTimeToCalendarConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToObjectConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new IdToEntityConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new FallbackObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToOptionalConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
}
...
}
从源码可以看出,它几乎覆盖注册了所有的通用的类型转换,若涉及到自定义的对象的转换,亦可自己自定义转换器。
备注:
DefaultConversionService它在PropertyResolver、org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper、org.springframework.expression.TypeConverter…也就是properties、el表达式里、spring-jdbc数据封装的类型转换里都有应用
关于FormattingConversionService,它和格式化有关,所以放在Formatter章节里了,可参考:
【小家Spring】聊聊Spring中的格式化:Formatter、AnnotationFormatterFactory、DateFormatter以及@DateTimeFormat…
ConversionServiceFactoryBean
它是我们自定义转换器的一个入口。比如之前我们见过这么配置的自定义转换器:
<bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters">
<set>
<ref bean="userConverter"/>
set>
property>
bean>
这样,我们的自定义的转换器userConverter就被添加进去了。我们在Spring MVC中需要自定义转换器的时候,也是这么来弄的。(使用java配置的方式添加,此处省略)
它的源码比较简单:
public class ConversionServiceFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<ConversionService>, InitializingBean {
// 保存着我们diy set捡来的转换器们
@Nullable
private Set<?> converters;
// 最终是一个DefaultConversionService,然后向里添加自定义的转换器~
@Nullable
private GenericConversionService conversionService;
// Bean初始化结束后,注册自定义的转换器进去~~
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.conversionService = createConversionService();
ConversionServiceFactory.registerConverters(this.converters, this.conversionService);
}
protected GenericConversionService createConversionService() {
return new DefaultConversionService();
}
@Override
@Nullable
public ConversionService getObject() {
return this.conversionService;
}
// 最终是个GenericConversionService,实际是个DefaultConversionService
@Override
public Class<? extends ConversionService> getObjectType() {
return GenericConversionService.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
另外,如果你还需要格式化的功能,使用FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean代替即可
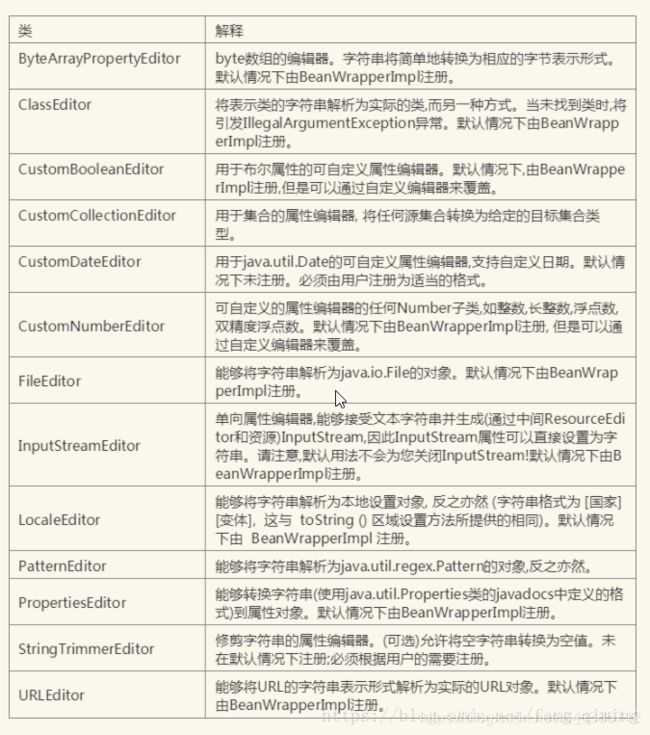
Spring中的PropertyEditor属性编辑器
在文末稍微介绍一下Spring中的PropertyEditor属性编辑器,因为它和类型转换器特别的像。
PropertyEditor是JavaBean规范定义的接口,这是java.beans中一个接口,其设计的意图是图形化编程上,方便对象与String之间的转换工作,而spring将其扩展,方便各种对象与String之间的转换工作。
Spring所有的扩展都是通过继承PropertyEditorSupport,因为它只聚焦于转换上,所以只需复写setAsText()、getAsText()以及构造方法即可实现扩展。
Spring 使用PropertyEditors的接口来实现对象和字符串之间的转换,比如将 2007-14-09转化为日期类型等,可以通过注册自定义编辑器来实现此功能
这些PropertyEditors都位于
org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors包中,大多是都是由BeanWrapperImpl注册,当属性编辑器以某种方式进行配置时,开发者仍可以注册自定义的变体用于覆盖默认的变量
应用的场景描述:
在基于xml的配置中,我们往往通过字面值为Bean各种类型的属性提供设置值:不管是double类型还是int类型,在配置文件中都对应字符串类型的字面值。
BeanWrapper填充Bean属性时如何将这个字面值转换为对应的double或int等内部类型呢?我们可以隐约地感觉到一定有一个转换器在其中起作用,这个转换器就是属性编辑器。
Spring MVC框架使用多种PropertyEditors分析HTTP请求的各种参数
有的小伙伴可能会问:既然有了PropertyEditor,那为何还需要有Converter呢?其实是因为Java原生的PropertyEditor存在以下两点不足:
- 只能用于字符串和Java对象的转换,不适用于任意两个Java类型之间的转换;
- 对源对象及目标对象所在的上下文信息(如注解、所在宿主类的结构等)不敏感,在类型转换时不能利用这些上下文信息实施高级转换逻辑。
鉴于此,Spring 3.0在核心模型中添加了一个通用的类型转换模块,类型转换模块位于org.springframework.core.convert包中。Spring希望用这个类型转换体系替换Java标准的PropertyEditor。但由于历史原因,Spring将同时支持两者。在Bean配置、Spring MVC处理方法入参绑定中使用它们。
Spring提供了PropertyEditorRegistry来注册自定义的Editor~ 提供了PropertyEditorRegistrar这个注册官来registerCustomEditors。它的实现类只有ResourceEditorRegistrar使用ResourceLoader来加载资源~默认注册了:Resource、InputStream、InputSource、File、Reader等等和资源先关的属性编辑器。
public interface PropertyEditorRegistry {
void registerCustomEditor(Class<?> requiredType, PropertyEditor propertyEditor);
// propertyPath可以是name,可以是person.name这种复合的~~~~
void registerCustomEditor(@Nullable Class<?> requiredType, @Nullable String propertyPath, PropertyEditor propertyEditor);
// 查找一个PropertyEditor
@Nullable
PropertyEditor findCustomEditor(@Nullable Class<?> requiredType, @Nullable String propertyPath);
}
Converter or PropertyEditor?
Spring有两种自动类型转换器,一种是Converter,一种是PropertyEditor。
Converter是类型转换成类型,Editor:从string类型转换为其他类型。
从某种程度上,Converter包含Editor。如果出现需要从string转换到其他类型。首选Editor。
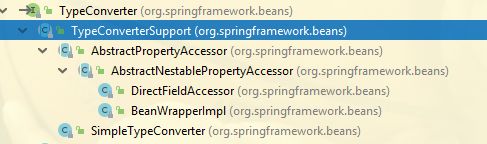
org.springframework.beans.TypeConverter
TypeConverter在org.springframework.expression包中还有一个,注意区分。
// @since 2.0
// 定义类型转换方法的接口。通常(但不一定)与PropertyEditorRegistry接口一起实现
// 通常接口TypeConverter的实现是基于非线程安全的PropertyEditors类,因此也不是线程安全的
public interface TypeConverter {
// 将参数中的value转换成requiredType类型
// 从String到任何类型的转换通常使用PropertyEditor类的setAsText方法或ConversionService中的Spring Converter
@Nullable
<T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType) throws TypeMismatchException;
// 意义同上,增加了作为转换目标的方法参数,主要用于分析泛型类型,可能是null
@Nullable
<T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable MethodParameter methodParam) throws TypeMismatchException;
// 意义同上,增加了转换目标的反射field
@Nullable
<T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Field field) throws TypeMismatchException;
// @since 5.1.4
@Nullable
default <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable TypeDescriptor typeDescriptor) throws TypeMismatchException {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("TypeDescriptor resolution not supported");
}
}
TypeConverterSupport
TypeConverter的基本实现类,同时也是BeanWrapperImpl类的依赖类。
public abstract class TypeConverterSupport extends PropertyEditorRegistrySupport implements TypeConverter {
@Nullable
TypeConverterDelegate typeConverterDelegate;
... //它所有的convertIfNecessary工作都是委托给了TypeConverterDelegate
}
TypeConverterDelegate
类型转换的委托类,所有类型转换的工作都由该类完成,即将属性转换为其他类型的Spring内部使用方法(内部实现: 先使用PropertyEditor转换器器转换,如果没找到对应的转换器器,会⽤ConversionService来进⾏行行对象转换。)
// @since 2.0
class TypeConverterDelegate {
// PropertyEditorRegistrySupport#findCustomEditor和getConversionService
// 就是处理这么一个基本逻辑的~~~~
private final PropertyEditorRegistrySupport propertyEditorRegistry;
private final Object targetObject;
// ......
}
所以从此处就可以看到,PropertyEditor和ConversionService的差别和联系。
SimpleTypeConverter
不在特定目标对象上运行的TypeConverter接口的简单实现。这是使用完整的BeanWrapperImpl实例来实现任意类型转换需求的替代方法,同时使用相同的转换算法(包括委托给PropertyEditor和ConversionService)。
public class SimpleTypeConverter extends TypeConverterSupport {
public SimpleTypeConverter() {
this.typeConverterDelegate = new TypeConverterDelegate(this);
registerDefaultEditors();
}
}
SimpleTypeConverter经常会被作为默认实现。
PropertyEditor用于字符串到其它对象的转换,由于其局限性,spring提供了converter接口,由ConversionService来调用对外提供服务,而TypeConverter综合了上述两种转换方式,交由TypeConverterDelegate来进行转换。
TypeConverterDelegater先使用PropertyEditor转换器器转换,如果没找到对应的转换器器,会⽤ConversionService来进⾏行行对象转换
总结
1.Spring使用ConversionService来convert各种类型.默认提供的是DefaultConversionService.同时它实现了ConverterRegistry接口,所以也可以添加你自定义的converter.
2.Spring提供了3种converter接口,分别是Converter,ConverterFactory和GenericConverter.一般用于1:1, 1:N, N:N的source->target类型转化.
3.在DefaultConversionService内部3种converter都会转化成GenericConverter放到静态内部类Converters中.
4.接口GenericConverter的内部类ConvertiblePair是source的class与target的Class的封装。GenericConversionService的静态内部类ConvertersForPair是多个converter对应的LinkedList的封装。。。GenericConversionService的静态内部类Converters中含有1个Map用来储存所有converter.
1个
GenericConverter可以对应N个ConvertiblePair,1个ConvertiblePair对应的ConvertersForPair中也可以有N个GenericConverter.
Convertible:可转换的
Spring为何要使用ConversionService替代PropertyEditor
此处总结三个原因,供给大家参考:
ConversionService功能更强大,支持的类型转换范围更广。
1. 相比PropertyEditor只提供String<->Object的转换,ConversionService能够提供任意Object<->Object的转换。ConverterFactory支持一整个class hierarchy的转换(也就是多态),PropertyEditor则不行- Java Bean这个规范最初是和Java GUI(Swing)一起诞生的,PropertyEditor接口里有大量和GUI相关的方法,显然已经过时了。
1. Java Bean和POJO不是一个概念,Java Bean不仅有getter、setter,还有一系列和Java GUI配套的东西。
关注A哥
| Author | A哥(YourBatman) |
|---|---|
| 个人站点 | www.yourbatman.cn |
| [email protected] | |
| 微 信 | fsx641385712 |
活跃平台 |
|
| 公众号 | BAT的乌托邦(ID:BAT-utopia) |
| 知识星球 | BAT的乌托邦 |
| 每日文章推荐 | 每日文章推荐 |