Spring Cloud Gateway学习
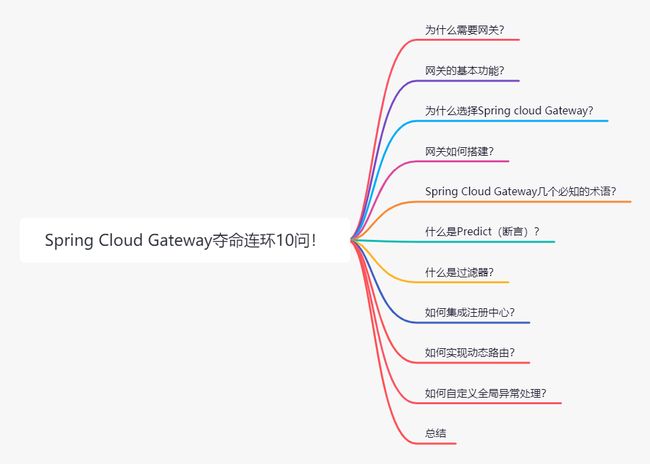
文章大纲
为什么需要网关?
传统的单体架构只有一个服务开放给客户端调用,但是在微服务架构体系中是将一个系统拆分成多个微服务,那么作为客户端如何去调用这些微服务呢?如果没有网关的存在,就只能在本地记录每个微服务的调用地址。
- 客户端多次请求不同的微服务,增加客户端代码或配置编写的复杂
- 认证复杂,每个服务都需要独立认证
- 存在跨域请求,在一定场景下处理相对复杂
网关的基本功能
- 路由转发
- 认证、鉴权
- 熔断
- 负载均衡
- 限流
- 日志监控
Spring Cloud Gateway 几个必知的术语?
1、路由(route)
gateway的基本构建模块。由ID、目标URI、断言集合和过滤器组成。如果断言结果为真,则匹配到该路由。
2、断言(Predicate)
参照Java8的特性Predicate,允许开发人员匹配HTTP请求中的任何内容,比如头或参数等。
3、过滤器(filter)
可以在返回请求之前或之后修改请求之前或之后修改请求和响应的内容。
网关如何搭建?
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gatewayartifactId>
dependency>
ps:一定要去除spring-boot-starter-web 依赖,否则启动报错。
什么是Predicate(断言)?
Predicate 来自于Java8的接口。Predicate 接收一个输入参数,返回一个布尔值结果。该接口包含多种默认方法来将Predicate组合成其他复杂的逻辑(比如:与、或、非)。
可以用于接口请求参数校验、判断新老数据是否有变化需要进行更新操作。
Spring Cloud Gateway 内置了许多Predict:
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
## 路由
routes:
## id只要唯一即可,名称任意
- id: gateway-provider_1
uri: http://localhost:9024
## 配置断言
predicates:
## Path Route Predicate Factory断言,满足/gateway/provider/**这个请求路径的都会被路由到http://localhost:9024这个uri中
- Path=/gateway/provider/**
## Weight Route Predicate Factory,同一分组按照权重进行分配流量,这里分配了80%
## 第一个group1是分组名,第二个参数是权重
- Weight=group1, 8
## id必须唯一
- id: gateway-provider_2
## 路由转发的uri
uri: http://localhost:9025
## 配置断言
predicates:
## Path Route Predicate Factory断言,满足/gateway/provider/**这个请求路径的都会被路由到http://localhost:9024这个uri中
- Path=/gateway/provider/**
## Weight Route Predicate Factory,同一分组按照权重进行分配流量,这里分配了20%
## 第一个group1是分组名,第二个参数是权重
- Weight=group1, 2
routes 下就是配置的路由策略,各个组件如下:
- id:路由的唯一id,名称任意
- uri:路由转发的uri
- predicates:断言配置,可以配置多个
Spring Cloud Gateway中的断言命名都是有规划的,格式:xxxRoutePredicateFactory。
比如权重的断言:WeightRoutePredicateFactory,那么配置时直接取前面的Weight。
默认的路由转发如果路由到了两个,则是的按照配置先后顺序转发,上面都配置了路径:Path=/gateway/provider/**,如果没有配置权重,则肯定是转发到http://localhost:9024。但是既然配置配置了权重并且相同的分组,则按照权重比例进行分配流量。
什么时过滤器?
Gateway过滤器的生命周期:
PRE:这个过滤器在请求被路由之前调用。我们可以利用这种过滤器实现身份验证、在集群中选择请求的微服务、记录调式信息等。POST:这种过滤器在路由到微服务以后执行。这种过滤器可以用来为响应添加标准的HTTP Header、收集统计信息和指标、将响应从微服务发送给客户端等。
Gateway 的Filter从作用范围可以分为两种:
GatewayFilter:应用到单个路由或者一个分组的路由上(需要在配置文件中配置)。GlobalFilter:应用到所有的路由上(无需配置,全局生效)。
GatewayFilter 局部过滤器
局部过滤器需要在指定路由配置才能生效,默认是不生效的。
以AddResponseHeaderGatewayFilterFactory 这个过滤器为例,为原始响应添加Header,配置如下:
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
## 路由
routes:
## id只要唯一即可,名称任意
- id: gateway-provider_1
uri: http://localhost:9024
## 配置断言
predicates:
## Path Route Predicate Factory断言,满足/gateway/provider/**这个请求路径的都会被路由到http://localhost:9024这个uri中
- Path=/gateway/provider/**
## 配置过滤器(局部)
filters:
- AddResponseHeader=X-Response-Foo, Bar
浏览器请求,发现响应头中已经有了X-Respongse-Foo=Bar 这个键值对,如下图:

注意: 过滤器的名称只需要写前缀,过滤器命名必须是xxxGatewayFilterFactory(包括自定义的局部过滤器)。
虽然内置的过滤器能够解决很多场景,但是难免有一些特殊的需求需要定制一个过滤器。
场景:模拟一个授权验证的过程,如果请求头或者请求参数中携带token 则放行,否则直接拦截返回401,代码如下:
/**
* 名称必须是xxxGatewayFilterFactory形式
* todo:模拟授权的验证,具体逻辑根据业务完善
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class AuthorizeGatewayFilterFactory extends AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<AuthorizeGatewayFilterFactory.Config> {
private static final String AUTHORIZE_TOKEN = "token";
//构造函数,加载Config
public AuthorizeGatewayFilterFactory() {
//固定写法,这里可以参过内置的局部过滤器的写法比如AddRequestGatewayFilter
super(AuthorizeGatewayFilterFactory.Config.class);
log.info("Loaded GatewayFilterFactory [Authorize]");
}
//读取配置文件中的参数 赋值到 配置类中
@Override
public List<String> shortcutFieldOrder() {
//Config.enabled
return Arrays.asList("enabled");
}
@Override
public GatewayFilter apply(AuthorizeGatewayFilterFactory.Config config) {
return (exchange, chain) -> {
//判断是否开启授权验证
if (!config.isEnabled()) {
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
HttpHeaders headers = request.getHeaders();
//从请求头中获取token
String token = headers.getFirst(AUTHORIZE_TOKEN);
if (token == null) {
//从请求头参数中获取token
token = request.getQueryParams().getFirst(AUTHORIZE_TOKEN);
}
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
//如果token为空,直接返回401,未授权
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) {
response.setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED);
//处理完成,直接拦截,不再进行下去
return response.setComplete();
}
/**
* todo chain.filter(exchange) 之前的都是过滤器的前置处理
*
* chain.filter().then(
* 过滤器的后置处理...........
* )
*/
//授权正常,继续下一个过滤器链的调用
return chain.filter(exchange);
};
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public static class Config {
// 控制是否开启认证
private boolean enabled;
}
}
局部过滤器需要在路由中配置才能生效,配置如下:
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
## 路由
routes:
## id只要唯一即可,名称任意
- id: gateway-provider_1
uri: http://localhost:9024
## 配置断言
predicates:
## Path Route Predicate Factory断言,满足/gateway/provider/**这个请求路径的都会被路由到http://localhost:9024这个uri中
- Path=/gateway/provider/**
## 配置过滤器(局部)
filters:
- AddResponseHeader=X-Response-Foo, Bar
## AuthorizeGatewayFilterFactory自定义过滤器配置,值为true需要验证授权,false不需要
- Authorize=true
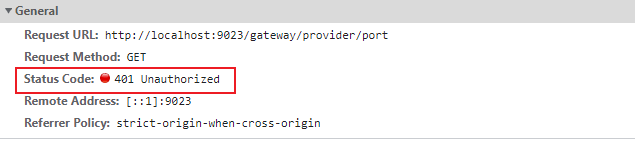
此时直接访问:http://localhost:9023/gateway/provider/port,不携带token,返回如下图:
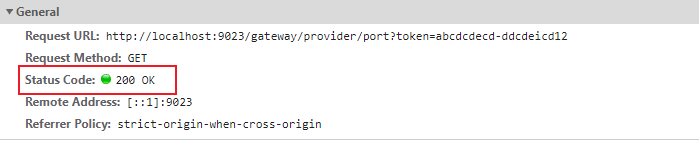
请求参数带上token:http://localhost:9023/gateway/provider/port?token=abcdcdecd-ddcdeicd12,成功返回,如下图:
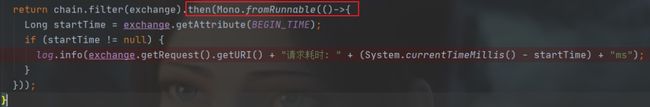
上述的AuthorizeGatewayFilterFactory只是涉及到了过滤器的前置处理,后置处理是在chain.filter().then()中的then()方法中完成的,具体可以看下项目源码中的TimeGatewayFilterFactory,代码就不再贴出来了,如下图:
GlobalFilter 全局过滤器
全局过滤器应用到全部路由上,无需开发者配置,Spring Cloud Gateway也内置了一些全局过滤器,如下图:

GlobalFilter 的功能其实很和GatewayFilter 是相同的。只是GlobalFilter 的作用域是所有的路由配置,而不是绑定在指定路由配置上。多个GlobalFilter 可以通过@Order 或者getOrder() 方法指定每个GlobalFilter 的执行顺序,order值越小,GlobalFilter执行的优先级越高。
注意,由于过滤器有pre和post两种类型,pre类型过滤器如果order值越小,那么它就应该在pre过滤器链的顶层,post类型过滤器如果order值越小,那么它就应该在pre过滤器链的底层。示意图如下:

当然除了内置的全局过滤器,实际工作中还需要定制过滤器,下面来介绍一下如何自定义。
场景:模拟Nginx的Access Log 功能,记录每次请求的相关信息。代码如下:
/**
* 实现GlobalFilter
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
@Order(value = Integer.MIN_VALUE)
public class AccessLogGlobalFilter implements GlobalFilter {
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
//filter的前置处理
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
String path = request.getPath().pathWithinApplication().value();
InetSocketAddress remoteAddress = request.getRemoteAddress();
return chain
//继续调用filter
.filter(exchange)
//filter的后置处理
.then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> {
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
HttpStatus statusCode = response.getStatusCode();
log.info("请求路径:{},远程IP地址:{},响应码:{}", path, remoteAddress, statusCode);
}));
}
}
好了,全局过滤器不必在路由上配置,注入到IOC容器中即可全局生效。
此时发出一个请求,控制台打印信息如下:
请求路径:/gateway/provider/port,远程IP地址:/0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1:64114,响应码:200 OK
如何集成注册中心?
上述demo中并没有集成注册中心,每次路由配置都是指定固定的服务uri,如下图:

这样做有什么坏处呢?
- 服务的IP的地址一旦修改了,路由配置中的uri必须修改
- 服务集群中无法实现负载均衡
此时就需要集成的Nacos注册中心,使得网关能够从注册中心自动获取uri(负载均衡)。
pom文件中新增Nacos依赖,如下:
<!--nacos注册中心-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
启动类上开启注册中心功能,如下图:

配置文件中指定nacos注册中心的地址:
spring:
application:
## 指定服务名称,在nacos中的名字
name: cloud-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
# nacos的服务地址,nacos-server中IP地址:端口号
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
路由配置中唯一不同的就是路由的uri,格式:lb://service-name,这是固定写法:
- lb:固定格式,指的是从nacos中按照名称获取微服务,并遵循负载均衡策略
- service-name:nacos注册中心的服务名称,这里并不是IP地址形式的
集成Nacos注册中心完整的配置demo如下:
spring:
application:
## 指定服务名称,在nacos中的名字
name: cloud-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
# nacos的服务地址,nacos-server中IP地址:端口号
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
gateway:
## 路由
routes:
## id只要唯一即可,名称任意
- id: gateway-provider_1
## 使用了lb形式,从注册中心负载均衡的获取uri
uri: lb://gateway-provider
## 配置断言
predicates:
## Path Route Predicate Factory断言,满足/gateway/provider/**这个请求路径的都会被路由到http://localhost:9024这个uri中
- Path=/gateway/provider/**
## 配置过滤器(局部)
filters:
- AddResponseHeader=X-Response-Foo, Bar
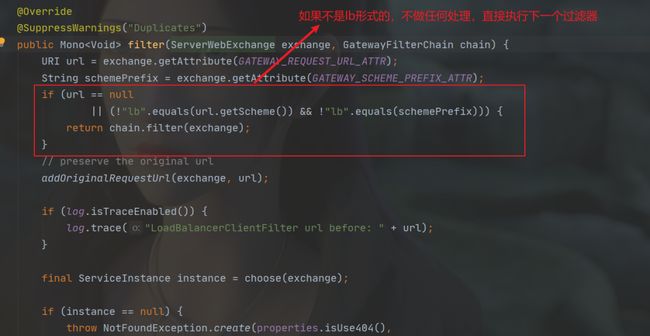
为什么指定了lb就可以开启负载均衡,前面说过全局过滤器LoadBalancerClientFilter就是负责路由寻址和负载均衡的,可以看到如下源码:
如何实现动态路由?
上述例子都是将网关的一系列配置写到项目的配置文件中,一旦路由发生改变必须要重新项目,这样维护成本很高。
其实我们可以将网关的配置存放到配置中心中,这样由配置中心统一管理,一旦路由发生改变,只需要在配置中心修改,这样便能达到一处修改,多出生效的目的。
这里当然要使用Nacos作为配置中心了,添加依赖如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-configartifactId>
dependency>
在bootstrap.yml文件中指定Nacos作为配置中心的一些相关配置:
spring:
application:
## 指定服务名称,在nacos中的名字
name: cloud-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
## todo 此处作为演示,仅仅配置了后缀,其他分组,命名空间根据需要自己配置
config:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
## 指定文件后缀未yaml
file-extension: yaml
在nacos中的public命名空间中创建dataId为cloud-gateway.yaml的配置(未指定环境),配置内容如下:

如何自定义全局异常处理?
通过前面的测试可以看到一个现象:一旦路由的微服务下线或者失联了,Spring Cloud Gateway直接返回了一个错误页面,如下图:

显然这种异常信息不友好,前后端分离架构中必须定制返回的异常信息。
传统的Spring Boot 服务中都是使用@ControllerAdvice来包装全局异常处理的,但是由于服务下线,请求并没有到达。
因此必须在网关中也要定制一层全局异常处理,这样才能更加友好的和客户端交互。
直接创建一个类GlobalErrorExceptionHandler,实现ErrorWebExceptionHandler,重写其中的handle方法,代码如下:
/**
* 用于网关的全局异常处理
* @Order(-1):优先级一定要比ResponseStatusExceptionHandler低
*/
@Slf4j
@Order(-1)
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class GlobalErrorExceptionHandler implements ErrorWebExceptionHandler {
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked", "NullableProblems"})
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange, Throwable ex) {
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
if (response.isCommitted()) {
return Mono.error(ex);
}
// JOSN格式返回
response.getHeaders().setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
if (ex instanceof ResponseStatusException) {
response.setStatusCode(((ResponseStatusException) ex).getStatus());
}
return response.writeWith(Mono.fromSupplier(() -> {
DataBufferFactory bufferFactory = response.bufferFactory();
try {
//todo 返回响应结果,根据业务需求,自己定制
CommonResponse resultMsg = new CommonResponse("500",ex.getMessage(),null);
return bufferFactory.wrap(objectMapper.writeValueAsBytes(resultMsg));
}
catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
log.error("Error writing response", ex);
return bufferFactory.wrap(new byte[0]);
}
}));
}
}
好了,全局异常处理已经定制完成了,在测试一下,此时正常返回JSON数据了,如下图: