C语言—链表
文章目录
一,链表的概念
二,静态创建链表和动态遍历
三,统计链表节点个数及链表查找
四,链表的插入
1,从指定节点后方插入新节点
2,从指定节点前方插入新节点
五,链表删除指定节点
六,动态创建链表
1,头插法:
2,尾插法:
一,链表的概念
1,什么是链表?
链表是一种数据结构,是一种数据存放的思想;
2,链表和数组的区别
数组的特点:
- 数组中的每一个元素都属于同一数据类型的;
- 数组是一组有序数据的集合;
- 数组是在内存中开辟一段连续的地址空间用来存放一组数据,可以用数组名加下标来访问数组中的元素;
链表的特点:
- 动态地进行存储分配的一种结构;
- 链表中的各节点在内存中的地址都是不连续的;
- 链表是由一个个节点组成,像一条链子一样;
- 链表中的节点一般包括两个部分(1)用户要用的数据(2)下一个节点的地址;
*两者对比:
- 一个数组只能存放同一种类型的数据,而链表中就可以存放不同的数据类型;
- 数组中的元素地址是连续的,想删除或添加一个新的元素,十分的麻烦不灵活,而且用数组存放数据是都要先定义好数组的大小(即元素的个数),如果在定义数组时,定义小了,内存不够用,定义大了,显然会浪费内存;而链表就可以很好的解决这些问题,链表中每一项都是一个结构体,链表中各节点在内存中的地址可以是不连续的,所以你想删除或添加一个新的节点很简单和方便,直接把节点中存放的的地址拿去修改就ok了(具体怎么添加或删除放在后用代码详细讲),因为链表是一种动态结构,所以链表在建立的时候并不用像数组一样需要提前定义大小和位置(具体怎么创建也放在后面用代码详细讲)。
二,静态创建链表和动态遍历
#include
struct Test//声明结构体类型
{
int data;//定义数据域
struct Test *next;//定义指针域
};
//遍历链表
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *p = head;//使p指向链表头
while(p != NULL){//p现在是链表头,会一直遍历链表尾NULL时,循环结束
printf("%d ",p->data);//输出当前节点中data的值
p = p->next;//使p指向下一个节点
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
struct Test* head;
//定义结构体变量,作为节点,给节点赋值
struct Test t1 = {1,NULL};//对节点t1的data和next赋值
struct Test t2 = {2,NULL};//对节点t2的data和next赋值
struct Test t3 = {3,NULL};//对节点t3的data和next赋值
struct Test t4 = {4,NULL};//对节点t4的data和next赋值
struct Test t5 = {5,NULL};//对节点t5的data和next赋值
head = &t1;//将节点t1的起始地址赋给头指针head
t1.next = &t2;//将节点t2的起始地址赋给t1节点中的next
t2.next = &t3;//将节点t3的起始地址赋给t2节点中的next
t3.next = &t4;//将节点t4的起始地址赋给t3节点中的next
t4.next = &t5;//将节点t5的起始地址赋给t4节点中的next
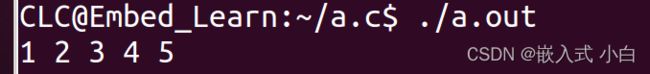
printLink(head);//把链表头传到函数printLink中
return 0;
} 三,统计链表节点个数及链表查找
#include
struct Test//声明结构体类型
{
int data;//定义数据域
struct Test *next;//定义指针域
};
//遍历链表
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *p = head;//使p指向链表头
while(p != NULL){//p现在是链表头,会一直遍历链表尾NULL时,循环停止
printf("%d ",p->data);//输出当前节点中data的值
p = p->next;//使p指向下一个节点
}
}
//统计节点的个数
int getNodeSum(struct Test *head)
{
int sum = 0;
struct Test *p = head;//使p指向链表头
while(p != NULL){//遍历链表,直到链表尾NULL时停止
sum++;//统计链表节点的个数
p = p->next;//使p指向下一个节点
}
return sum;//把统计的节点的个数return回去
}
//链表查询
int searchLink(struct Test *head,int n)
{
while(head != NULL){//遍历链表,直到链表尾NULL时停止
if(head->data == n){//判断当前节点中的data(数据域)和要查询的是否相同
return 1;//相同的话return 1
}
head = head->next;//使head指向下一个节点
}
return 0;//不相同return 0
}
int main()
{
int ret;
struct Test* head;
//定义结构体变量,作为节点,给节点赋值
struct Test t1 = {1,NULL};//对节点t1的data和next赋值
struct Test t2 = {2,NULL};//对节点t2的data和next赋值
struct Test t3 = {3,NULL};//对节点t3的data和next赋值
struct Test t4 = {4,NULL};//对节点t4的data和next赋值
struct Test t5 = {5,NULL};//对节点t5的data和next赋值
head = &t1;//将节点t1的起始地址赋给头指针head
t1.next = &t2;//将节点t2的起始地址赋给t1节点中的next
t2.next = &t3;//将节点t3的起始地址赋给t2节点中的next
t3.next = &t4;//将节点t4的起始地址赋给t3节点中的next
t4.next = &t5;//将节点t5的起始地址赋给t4节点中的next
printLink(head);//把链表头传到函数printLink中
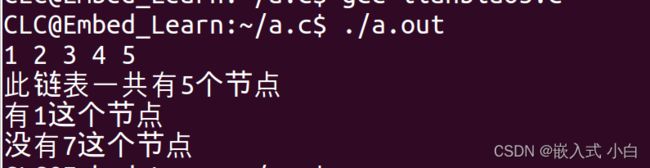
ret = getNodeSum(head);
printf("此链表一共有%d个节点\n",ret);
ret = searchLink(head,2);
if(ret == 1){//判断return回来的值
printf("有1这个节点\n");
}
else{
printf("没有1这个节点\n");
}
ret = searchLink(head,7);
if(ret == 1){//判断return回来的值
printf("有7这个节点\n");
}
else{
printf("没有7这个节点\n");
}
return 0;
}
四,链表的插入
插入一个新节点有两种方法:
- 在指定节点后
- 在指定节点前
1,从指定节点后方插入新节点
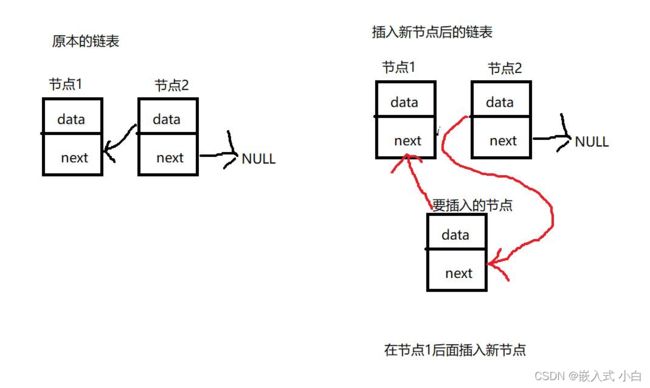
找到指定节点,把新节点节点的下一个节点放在要新节点的next(指针域)中,再把新节点放在指定节点的next(指针域)中
#include
struct Test//声明结构体类型
{
int data;//定义数据域
struct Test *next;//定义指针域
};
//遍历链表
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *p = head;
while(p != NULL){//p现在是链表头,会一直遍历链表尾NULL时停止
printf("%d ",p->data);//输出p节点中data的值
p = p->next;//使p指向下一节点
}
printf("\n");
}
//从指定节点后方插入新节点
void insertFromBehind(struct Test *head,int n,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
while(p != NULL){
if(p->data == n){//判断当前节点是不是指定节点
new->next = p->next;//把新节点的next(指针域)指向指定节点的下一个节点(这边要注意顺序不能换,否则链表会断掉)
p->next = new;//再把指定节点的next(指针域)指向新节点
}
p = p->next;//使p指向下一节点
}
}
int main()
{
struct Test* head;
//定义结构体变量,作为节点,给节点赋值
struct Test t1 = {1,NULL};//对节点t1的data和next赋值
struct Test t2 = {2,NULL};//对节点t2的data和next赋值
struct Test t3 = {3,NULL};//对节点t3的data和next赋值
struct Test t4 = {4,NULL};//对节点t4的data和next赋值
struct Test t5 = {5,NULL};//对节点t5的data和next赋值
head = &t1;//将节点t1的起始地址赋给头指针head
t1.next = &t2;//将节点t2的起始地址赋给t1节点中的next
t2.next = &t3;//将节点t3的起始地址赋给t2节点中的next
t3.next = &t4;//将节点t4的起始地址赋给t3节点中的next
t4.next = &t5;//将节点t5的起始地址赋给t4节点中的next
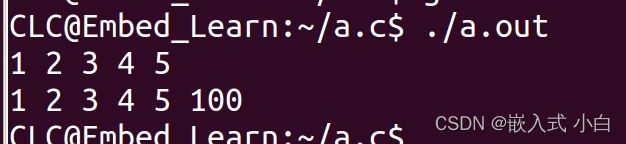
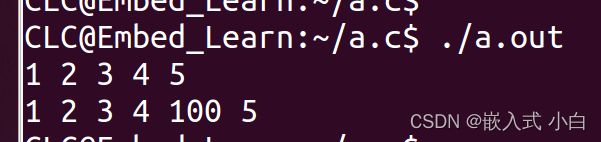
printLink(head);//把链表头传到函数printLink中
struct Test new = {100,NULL};//定义一个新节点
insertFromBehind(head,5,&new);//把链表头,要插入的位置,和新节点的地址传过去
printLink(head);//把链表头传过去,打印链表
return 0;
}
2,从指定节点前方插入新节点
要考虑两种情况:
- 在第一个节点前插入;
- 在中间节点插入;
#include
struct Test//声明结构体类型
{
int data;//定义数据域
struct Test *next;//定义指针域
};
//遍历链表
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *p = head;
while(p != NULL){//p现在是链表头,会一直遍历链表尾NULL时停止
printf("%d ",p->data);//输出p节点中data的值
p = p->next;//使p指向下一节点
}
printf("\n");
}
//从指定节点前方插入新节点
struct Test* insertFromfront(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test* p = head;
//在头节点插入(链表头会改变)
if(p->data == data){//判断指定的节点是不是头节点
new->next = p;//让新节点的next(指针域)指向p
return new;//现在new成为新的链表头了
}
//在中间节点插入
while(p->next != NULL){//因为这里是从中间节点插入,所以会从第二个节点开始遍历链表,直到链表尾NULL时停止
if(p->next->data == data){//判断当前节点是不是指定节点
new->next = p->next;//让要插入节点的next(指针域)指向p->next(就是当前节点的下一个节点)
p->next = new;//在让当前节点next(指针域)指向要插入的节点new
return head;//再把链表头给return回去
}
p = p->next;//使p指向下一节点
}
return head;
}
int main()
{
struct Test* head;
//定义结构体变量,作为节点,给节点赋值
struct Test t1 = {1,NULL};//对节点t1的data和next赋值
struct Test t2 = {2,NULL};//对节点t2的data和next赋值
struct Test t3 = {3,NULL};//对节点t3的data和next赋值
struct Test t4 = {4,NULL};//对节点t4的data和next赋值
struct Test t5 = {5,NULL};//对节点t5的data和next赋值
head = &t1;//将节点t1的起始地址赋给头指针head
t1.next = &t2;//将节点t2的起始地址赋给t1节点中的next
t2.next = &t3;//将节点t3的起始地址赋给t2节点中的next
t3.next = &t4;//将节点t4的起始地址赋给t3节点中的next
t4.next = &t5;//将节点t5的起始地址赋给t4节点中的next
printLink(head);//将头指针的地址传到函数printLink中
struct Test new = {100,NULL};//定义一个新节点
head = insertFromfront(head,5,&new);//把链表头,要插入的位置,和新节点的地址传过去
printLink(head);//把链表头传过去,打印链表
return 0;
} 五,链表删除指定节点
要考虑两种情况:
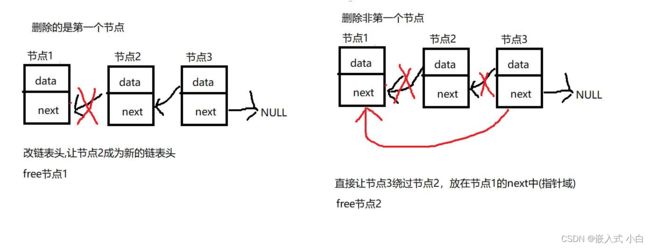
- 判断删除的节点是不是第一个节点,如果是第一个节点,直接改链表头,让第二个节点成为新的链表头
- 删除的节点如果非第一个节点的话:把要删除节点的前一个节点的next(指针域)越过要删除的节点,然后指向要删除节点的下一个节点;
*注意如果链表是动态创建的记得把删除的这个节点给free掉
#include
struct Test//声明结构体类型
{
int data;//定义数据域
struct Test *next;//定义指针域
};
//遍历链表
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *p = head;
while(p != NULL){//p现在是链表头,会一直遍历链表尾NULL时停止
printf("%d ",p->data);//输出p节点中data的值
p = p->next;//使p指向下一节点
}
printf("\n");
}
//删除指定节点
struct Test* deleteNode(struct Test *head,int data)
{
struct Test* p = head;
//删除第一个节点
if(p->data == data){//判断要删除的节点是不是头节点
head = head->next;//让p指向下一个节点
return head;//把新的链表头传回去
}
//删除非第一个节点
while(p->next != NULL){//从第二个节点开始遍历链表
if(p->next->data == data){//判断当前节点是不是要删除的节点
p->next = p->next->next;//把要删除节点的前一个节点的next(指针域)越过要删除的节点,然后指向要删除节点的下一个节点
return head;//把链表头传回去
}
p = p->next;//使p指向下一节点
}
return head;
}
int main()
{
struct Test* head;
//定义结构体变量,作为节点,给节点赋值
struct Test t1 = {1,NULL};//对节点t1的data和next赋值
struct Test t2 = {2,NULL};//对节点t2的data和next赋值
struct Test t3 = {3,NULL};//对节点t3的data和next赋值
struct Test t4 = {4,NULL};//对节点t4的data和next赋值
struct Test t5 = {5,NULL};//对节点t5的data和next赋值
head = &t1;//将节点t1的起始地址赋给头指针head
t1.next = &t2;//将节点t2的起始地址赋给t1节点中的next
t2.next = &t3;//将节点t3的起始地址赋给t2节点中的next
t3.next = &t4;//将节点t4的起始地址赋给t3节点中的next
t4.next = &t5;//将节点t5的起始地址赋给t4节点中的next
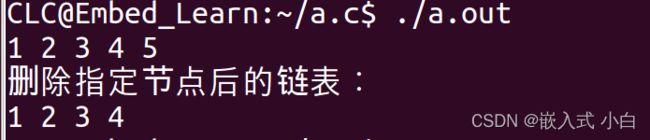
printLink(head);//将头指针的地址传到函数printLink中
printf("删除指定节点后的链表:\n");
head = deleteNode(head,5);//把链表头,和要删除第几个节点传过去
printLink(head);//把链表头传过去,打印链表
return 0;
} 六,动态创建链表
动态创建链表也是有两种方法:
1,头插法:
每一次创建的新节点插在之前的链表头之前,再让新节点做为新的链表头;
#include
#include
struct Test//声明结构体类型
{
int data;//定义数据域
struct Test *next;//定义指针域
};
//遍历链表
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *p = head;
while(p != NULL){//p现在是链表头,会一直遍历链表尾NULL时停止
printf("%d ",p->data);//输出p节点中data的值
p = p->next;//使p指向下一节点
}
printf("\n");
}
struct Test* insertFromHead(struct Test* head,struct Test* new)
{
if(head == NULL){//判断链表是否为空
head = new;//如果为空把创建的新节点当作链表头
}else{
new->next = head;//当链表不为空的时候,让新节点插在链表头的前面(称之为头插法)
head = new;//再让新节点成为链表头
}
return head;
}
//动态创建链表(头插法)
struct Test* creatLink(struct Test* head)
{
struct Test* new;
while(1){
new = (struct Test*)malloc(sizeof(struct Test));//开辟空间
new->next = NULL;
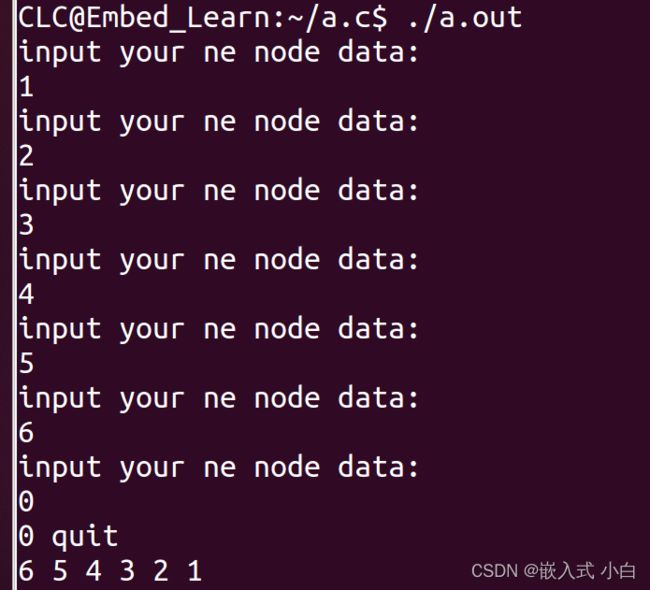
printf("input your ne node data:\n");
scanf("%d",&(new->data));//输入节点的数据域(data)
if(new->data == 0){//判断每次输入的值是否为0,如果为0,停止创建新节点
printf("0 quit\n");
return head;
}
head = insertFromHead(head,new);
}
return head;
}
int main()
{
struct Test* head = NULL;
head = creatLink(head);
printLink(head);
return 0;
} 2,尾插法:
如果链表为空,创建的第一个节点做为链表头,然后每一次创建的新节点插在链表最后一个节点的指针域(next)中;
#include
#include
struct Test//声明结构体类型
{
int data;//定义数据域
struct Test *next;//定义指针域
};
//遍历链表
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *p = head;
while(p != NULL){//p现在是链表头,会一直遍历链表尾NULL时停止
printf("%d ",p->data);//输出p节点中data的值
p = p->next;//使p指向下一节点
}
printf("\n");
}
struct Test* insertBehind(struct Test* head,struct Test* new)
{
struct Test* p = head;
if(p == NULL){//判断链表是否为空
return head = new;//如果为空把创建的新节点当作链表头
}
while(p->next != NULL){//遍历到最后一个节点
p = p->next;//使p指向下一节点
}
p->next = new;//把新节点插入最后一个节点的指针域(next)中
return head;//把链表头传回去
}
//动态创建链表(尾插法)
struct Test* creatLink(struct Test* head)
{
struct Test* new;
while(1){
new = (struct Test*)malloc(sizeof(struct Test));//开辟空间
new->next = NULL;
printf("input your ne node data:\n");
scanf("%d",&(new->data));//输入节点的数据域(data)
if(new->data == 0){//判断每次输入的值是否为0,如果为0,停止创建新节点
printf("0 quit\n");
return head;
}
head = insertBehind(head,new);
}
}
int main()
{
struct Test* head = NULL;
head = creatLink(head);
printLink(head);
} 写在最后:
博主是一位在校中专生,刚学不久,实力有限,内容仅供参考,有不对地方欢迎大神指出,一起讨论,一起进步