软件测试/测试开发丨Pytest 参数化用例
参数化
- 通过参数的方式传递数据,从而实现数据和脚本分离。
- 并且可以实现用例的重复生成与执行。
参数化应用场景
-
测试登录场景
- 测试登录成功,登录失败(账号错误,密码错误)
- 创建多种账号: 中⽂文账号,英⽂文账号
-
普通测试用例方法
- Copy 多份代码 or 读⼊入参数?
- 一次性执⾏多个输⼊入参数
def test_param_login_ok():
# 登录成功
username = "right"
password = "right"
login(username,password)
def test_param_login_fail():
# 登录失败
username = "wrong"
password = "wrong"
login(username,password)
参数化实现方案
- pytest 参数化实现方法
- 装饰器:
@pytest.mark.parametrize
@pytest.mark.parametrize("username,password",[["right","right"], ["wrong","wrong"]])
def test_param(username,password):
login(username,password)
Mark:参数化测试函数使用
- 单参数
- 多参数
- 用例重命名
- 笛卡尔积
参数化:单参数情况
- 单参数,可以将数据放在列表中
search_list = ['appium','selenium','pytest']
# 参数化实现测试用例的动态生成,每一条测试数据都会生成一条测试用例
@pytest.mark.parametrize('name',search_list)
def test_search(name):
assert name in search_list
参数化:多参数情况
- 将数据放在列表嵌套元组中
- 将数据放在列表嵌套列表中
# 数据放在元组中
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected",[
("3+5",8),("2+5",7),("7+5",12)
])
def test_mark_more(test_input,expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected
# 数据放在列表中
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected",[
["3+5",8],["2+5",7],["7+5",12]
])
def test_mark_more(test_input,expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected
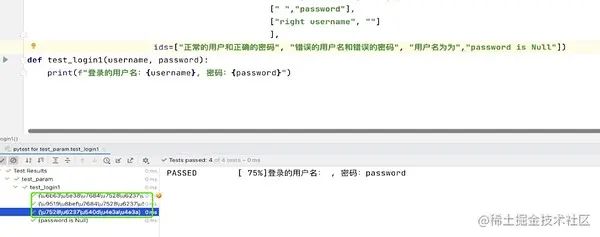
参数化:用例重命名-添加 ids 参数
- 通过ids参数,将别名放在列表中
# ids 为用例起个别名,ids 列表参数的个数要与参数值的个数一致
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected",[
("3+5",8),("2+5",7),("7+5",12)
],ids=['add_3+5=8','add_2+5=7','add_3+5=12'])
def test_mark_more(test_input,expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected
参数化:用例重命名-添加 ids 参数(中文)
pytest 不支持中文格式
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected",[
("3+5",8),("2+5",7),("7+5",12)
],ids=["3和5相加","2和5相加","7和5相加"])
def test_mark_more(test_input,expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected
# 创建conftest.py 文件 ,将下面内容添加进去,运行脚本
def pytest_collection_modifyitems(items):
"""
测试用例收集完成时,将收集到的用例名name和用例标识nodeid的中文信息显示在控制台上
"""
for i in items:
i.name=i.name.encode("utf-8").decode("unicode_escape")
i._nodeid=i.nodeid.encode("utf-8").decode("unicode_escape")
参数化:笛卡尔积
-
两组数据
- a=[1,2,3]
- b=[a,b,c]
-
对应有几种组合形势 ?
- (1,a),(1,b),(1,c)
- (2,a),(2,b),(2,c)
- (3,a),(3,b),(3,c)
# 装饰器方法,由近及远执行,先取a再依次取b
@pytest.mark.parametrize("b",["a","b","c"])
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a",[1,2,3])
def test_param1(a,b):
print(f"笛卡积形式的参数化中 a={a} , b={b}")
最后感谢每一个认真阅读我文章的人,礼尚往来总是要有的,虽然不是什么很值钱的东西,如果你用得到的话可以直接拿走:
这些资料,对于【软件测试】的朋友来说应该是最全面最完整的备战仓库,这个仓库也陪伴上万个测试工程师们走过最艰难的路程,希望也能帮助到你!
![]()