Netty网络编程
1.简介
Netty 是一个异步的、基于事件驱动的网络应用框架,用以快速开发高性能、高可靠性的网络 IO 程序。
Netty是基于NIO开发的,体系图如下。

2.BIO/NIO/AIO
-
BIO(blocking IO):同步阻塞IO,每次客户端发送请求,服务器都需要单独开一个线程去处理,每个线程对应着一个客户端。
-
NIO(non-blocking IO):同步非阻塞IO,使用selector作为多路复用器,channel连接buffer的结构,一个线程能够同时处理多个请求。

-
AIO(async IO):异步非阻塞IO,采用了 Proactor 模式,有效的请求才启动线程,它的特点是先由操作系统完成后才通知服务端程序启动线程去处理。
使用场景:
BIO适用于连接数目比较小且固定的架构
NIO 方式适用于连接数目多且连接比较短(轻操作)的架构,比如聊天服务器,弹幕系统,服务器间通讯等。
AIO 方式使用于连接数目多且连接比较长(重操作)的架构。
3.Channel与Buffer的关系
- 每个 Channel 都会对应一个 Buffer。 Selector 对应一个线程,一个线程对应多个 Channel(连接)。
- 该图反应了有三个 Channel 注册到该 Selector //程序 程序切换到哪个 Channel 是由事件决定的。
- Selector 会根据不同的事件,在各个通道上切换。
- Buffer 就是一个内存块,底层是有一个数组。
- 数据的读取写入是通过 Buffer,这个和 BIO是不同的,BIO 中要么是输入流,或者是输出流,不能双向,但是 NIO 的Buffer 是可以读也可以写,需要 flip 方法切换 Channel 是双向的,可以返回底层操作系统的情况。
4.Selector(多路复用器)
Selector 能够检测多个注册的通道上是否有事件发生(注意:多个 Channel 以事件的方式可以注册到同一个 Selector),如果有事件发生,便获取事件然后针对每个事件进行相应的处理。这样就可以只用一个单线程去管理多个通道,也就是管理多个连接和请求。
以下是TCP服务器的案例,综合使用Selector、Channel、Buffer。
服务端:
创建ServerSocketChannel用于接收TCP连接,并将其注册给Selector监听Accept事件。每次获取到连接后,将新连接的SocketChannel注册给Selector监听Read事件。
注册后的活跃事件由SelectionKey给出,一个SelectionKey对应着之前注册的Channel,也能通过SelectionKey反向获取Channel。
public class NIOServerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//初始化ServerSocketChannel作为TCP服务器
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",6666));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);//设置为非阻塞
Selector selector = Selector.open();//创建Selector
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //注册ACCEPT事件
System.out.println("等待连接加入");
while (true){
selector.select(1000);//检测Selector是否有事件发生,超过1s返回
//注册的Channel在Selector中由SelectionKey存储
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
//遍历SelectionKeys
while (keyIterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey selectionKey = keyIterator.next();
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
//如果有新的连接产生,则加入监听read事件
System.out.println("有新的连接加入,selectionKey="+selectionKey.toString());
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));//注册读事件并携带一个ByteBuffer
}else if(selectionKey.isReadable()){
//出现读事件,则打印读到的数据
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer)selectionKey.attachment();//获取携带的ByteBuffer
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)selectionKey.channel();//通过SelectionKey反向获取对应的Channel
int n = channel.read(buffer);
if(n==-1){//n为-1时表示客户端关闭连接
continue;
}
System.out.println("接收到消息:"+new String((buffer.array()))+" from"+channel.getRemoteAddress());
}
keyIterator.remove();//从集合中移除已经处理过的响应事件(selectionKey)
}
}
}
}
这里需要注意在轮询完后一定要记得keyIterator.remove();删除SelectionKey集合中的selectionKey,如果不删除,在下一次轮询时会将没有发生可读事件的Channel误判成发生了可读事件,造成重复判别。这个时候如果代码中对可读事件的channel进行了read操作,程序将阻塞。
客户端:简单的创建TCP连接,并向服务器发送hello world消息。
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 6666);
if(!socketChannel.connect(inetSocketAddress)){
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()){
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("正在连接,可以做些其他工作");
}
}
String str="hello world";
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());//将str包裹到buffer中去
System.out.println("向服务器发送消息");
socketChannel.write(buffer);
socketChannel.close();
System.in.read();
}
}
5.Reactor模式
使用IO复用器监听事件,收到事件后,将事件分发给某个线程进行事件处理。
Reactor:单独一个线程执行,负责监听和分发事件。
Handlers: 负责处理实际发生的事件。
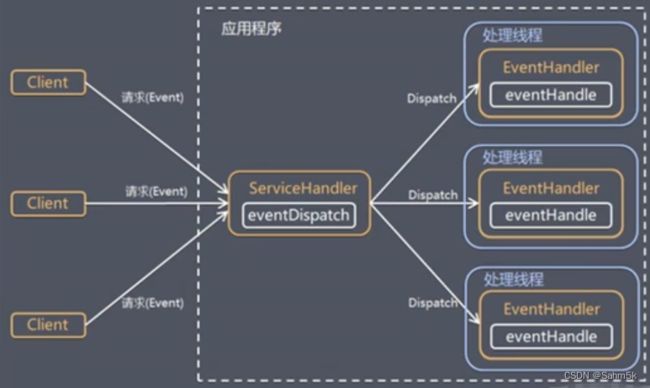
单Reactor模型
整个程序在一个线程中执行,实现简单没有多线程竞争问题,会出现性能问题。

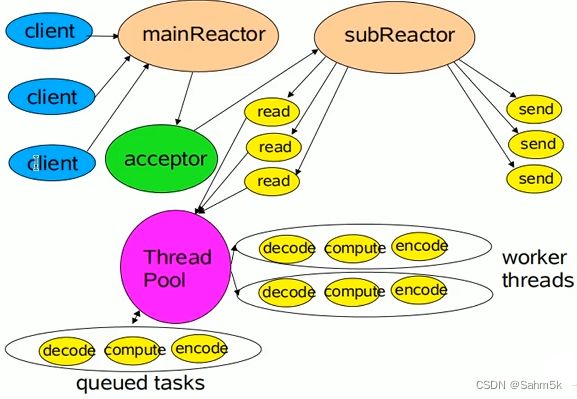
单Reactor多线程
请求分发给Handler后,Handler只做响应事件,不做具体的业务处理,业务处理交给Worker线程来执行,并将结果返回Handler。
单线程Reactor处理所有的事件和响应,容易在高并发场景出现性能瓶颈。

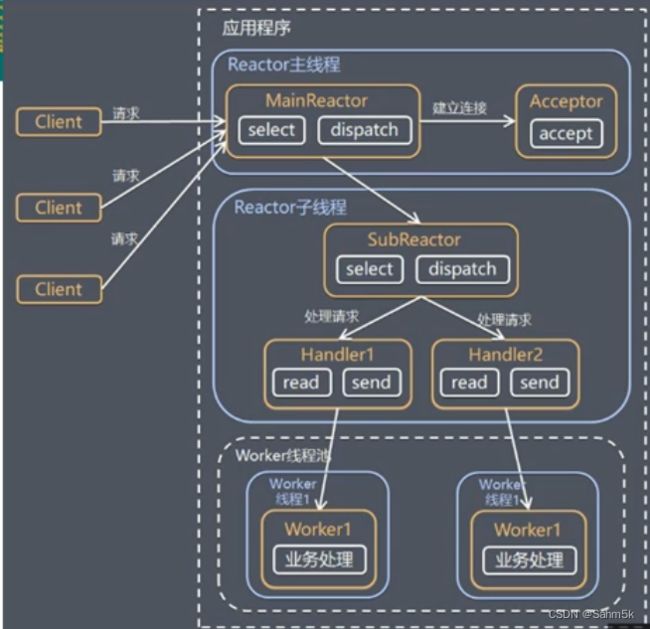
主从Reactor多线程(Netty)
将原先的Reactor分成一个MainReactor和多个SubReactor,MainReactor单线程负责监听连接事件,将连接分配给SubReactor。
多个SubReactor由多线程来执行监听连接事件,以及事件的分发(业务处理)。
Netty模型
分为BossGroup、WorkerGroup两部分,BossGroup多线程监听Accept事件,WorkerGroup对读写事件进行处理。
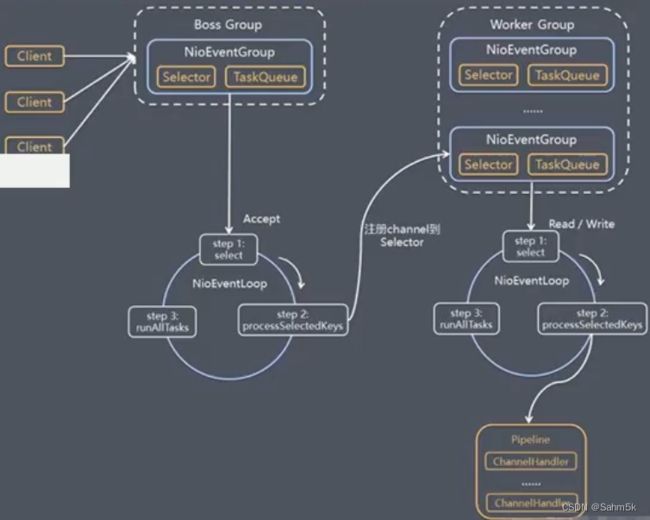
6.Netty使用
服务端:发送消息给客户端,并且打印客户端发送的消息
NettyServer.java
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) //设置两个线程组
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) //使用NioSocketChannel作为通道
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)//Channel最多能连接128个
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)//设置保持活动连接状态
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler());
}
});
//绑定端口并同步
ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.bind(6666).sync();
cf.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
NettyServerHandler.java
public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf=(ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("客户端发送消息:"+buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("客户端的地址"+ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
}
//数据读取完毕
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//对发送的数据进行编码
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,客户端 miao~",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
}
客户端:接收服务器消息,并发送消息给服务器
NettyClient.java
public class NettyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyClientHandler());
}
});
System.out.println("客户端 ok..");
ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 6666).sync();
cf.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
NettyClientHandler.java
public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
//通道就绪时触发
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("client "+ctx);
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello server miao~", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
//数据可读
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf =(ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("服务器回复的消息:"+buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("服务器的地址:"+ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
任务队列
在Handler中加入下面代码可以将pipeline中的耗时任务交由对应的Channel的Eventloop任务队列去执行。
ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//TODO 在channel对应的EventLoop任务队列中执行某些任务
try {
Thread.sleep(1000*5);
System.out.println("i am timing task");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
将任务交由ScheduleTaskQueue去执行定时任务
ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//TODO 在channel对应的EventLoop任务队列中执行某些任务
try {
Thread.sleep(1000*5);
System.out.println("i am timing task");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
},3, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
7.异步模型
Netty中的IO操作都是异步的,bind、write、Connect都会返回一个ChannelFuture,由ChannelFuture可以监控函数的处理过程,这就是Future-Listener机制。
//绑定端口并同步
ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.bind(6666).sync();
cf.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception {
if(channelFuture.isSuccess()){
System.out.println("绑定端口成功");
}else {
System.out.println("绑定端口失败");
}
}
});
8.Http服务器实现
TestServr.java
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) //设置两个线程组
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) //使用ServerSocketChannel作为channel实现类型
.childHandler(new TestServerInitializer());
//绑定端口并同步
ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.bind(6662).sync();
cf.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
TestServerInitializer.java
public class TestServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("MyHttpServerHandler",new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast("MyTestHttpServerHandler",new TestHttpServerHandler());
}
}
TestHttpServerHandler.java
public class TestHttpServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpObject> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, HttpObject httpObject) throws Exception {
//数据直接被封装成HttpObject类型
if(httpObject instanceof HttpRequest){
//过滤图标请求
HttpRequest httpRequest=(HttpRequest)httpObject;
URI uri = new URI(httpRequest.uri());
if("/favicon.ico".equals(uri.getPath())){
System.out.println("请求了favicion.ico,不做响应");
return;
}
//如果是Http请求
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,我是服务器", CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
//构造Http响应
DefaultFullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK,byteBuf);
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE,"text/plain");
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH,byteBuf.readableBytes());
channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
}
9.心跳检测实现
心跳检测主要分为:读空闲、写空闲、读写空闲,在空闲x秒后,会自动向客户端发送心跳包进行检测。
Server.java
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(boss,worker)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
//Netty内置状态检测Handler:3秒未出现读事件则发送心跳检测包检测连接是否断开,5s未出现写时间...,7s未出现读写事件...
//idleStateEvent事件触发后,会调用下一个handler的userEventTrigger
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(3,5,7, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
pipeline.addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(6666).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
ServerHandler.java
public class ServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
if(evt instanceof IdleStateEvent){
IdleStateEvent event=(IdleStateEvent) evt;
String eventType=null;
switch (event.state()){
case READER_IDLE:
eventType="读空闲";
break;
case WRITER_IDLE:
eventType="写空闲";
break;
case ALL_IDLE:
eventType="读写空闲";
break;
}
System.out.println( ctx.channel().remoteAddress()+"--超时时间---"+eventType);
}
}
}
10.websocket长连接实现
websocket是http协议的升级版,所以只要比http协议多几个handler就行。
Server.java
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(boss,worker)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
//基于HTTP协议,加入HTTP的编码器和解码器
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
//用块的方式写
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
//HTTP传输分段,将多个段聚合在一起
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(8192));
//将HTTP连接升级为Websocket协议,并设置请求uri
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/hello"));
//自定义handler
pipeline.addLast(new TextWebSocketFrameHandler()) ;
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(8888).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
TextWebSocketFrameHandler.java
传输的数据为TextWebSocketFrame,所以继承SimpleChannelInboundHandler< TextWebSocketFrame>
//TextWebSocketFrame表示文本帧
public class TextWebSocketFrameHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, TextWebSocketFrame textWebSocketFrame) throws Exception {
System.out.println("服务器收到消息"+textWebSocketFrame.text());
//回写消息
channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("服务器时间:"+ LocalDateTime.now()+" "+textWebSocketFrame.text()));
}
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("handleAdded被调用"+ctx.channel().id().asLongText());
System.out.println("handleAdded被调用"+ctx.channel().id().asShortText());
}
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("handleRemoved被调用"+ctx.channel().id().asLongText());
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("异常发生"+cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}
客户端:用网页来展示
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<script>
var socket;
if(window.WebSocket){
socket=new WebSocket("ws://127.0.0.1:8888/hello")
socket.onmessage=function (ev){
var rt = document.getElementById("responseText");
rt.value=rt.value+"\n"+ev.data;
}
socket.onopen=function (ev){
var rt=document.getElementById("responseText");
rt.value="连接开启"
}
socket.onclose=function (ev){
var rt=document.getElementById("responseText");
rt.value=rt.value+"\n"+"连接关闭了"
}
}else {
alert("浏览器不支持websocket")
}
function send(message){
if(!window.socket){
return;
}
if(socket.readyState===WebSocket.OPEN){
socket.send(message);
}else {
alert("连接没有开启");
}
}
script>
<body>
<form onsubmit="return false">
<textarea name="message" style="height: 300px; width: 300px">
textarea>
<input type="button" value="发送消息" onclick="send(this.form.message.value)" name="" id="">
<textarea id="responseText" style="height: 300px; width: 300px">textarea>
<input type="button" value="清空内容" onclick="document.getElementById('responseText').value=''">
form>
body>
html>
11.传输protobuf数据
首先要编写proto文件,指定要传输的对象内容。
Student.proto
syntax="proto3";
option java_outer_classname="StudentPOJO"; //外部的类名
//会在StudentPOJO生成内部类Student(真正传输的类)
//protoc.exe --java_out=. Student.proto
//编写proto文件 ——》 生成java类-》传输
message Student{
int32 id =1 ;//1是序号
string name =2 ;
}
再通过官网下载的protoc调用protoc.exe --java_out=. Student.proto,将proto文件转换为java类。
客户端、服务器分别加入相对应的编码器解码器的handler即可
pipeline.addLast(new ProtobufDecoder(StudentPOJO.Student.getDefaultInstance()));//解码器,用于接收protobuf数据
pipeline.addLast(new ProtobufEncoder());//编码器,用于发送protobuf数据,protobuf->二进制字节流
在自定义handle中进行数据发送
@Override
//channel激活时,即连接成功时。
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
StudentPOJO.Student kd = StudentPOJO.Student.newBuilder().setId(4).setName("kd").build();
ctx.writeAndFlush(kd);
}
传递多种protbuf数据
主要是proto文件的编写,设定一个枚举类型,用于标明message的类型。
syntax ="proto3";
option optimize_for=SPEED;
option java_outer_classname="MyDataInfo"; //指定外部类名
message MyMessage{
enum DataType{
studentType=0;
workerType=1;
}
DataType data_type=1;
oneof dataBody{ //只会出现一个 类似union
Student s=2;
Worker w=3;
}
}
message Student{
int32 id=1;
string name=2;
}
message Worker{
string name=1;
int32 age=2;
}
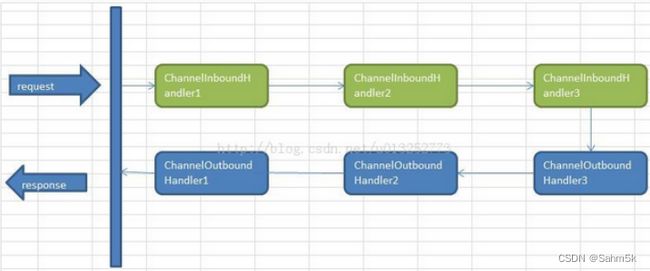
12.handler处理顺序
ChannelInboundHandler按照注册的先后顺序执行;
ChannelOutboundHandler按照注册的先后顺序逆序执行