MySql数据库语法命令大全
基本操作
github:https://github.com/IsConor/C_and_C_plus.git
数据库的CURD
创建数据库:
Create database mydb1;
创建一个使用utf-8字符集的mydb2数据库
Create database mydb2 character set utf8;
创建一个使用utf-8字符集,并带校对规则的mydb3数据库,会对存入数据进行检查
Create database mydb3 character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;
查看数据库
显示所有数据库
show databases;
显示创建数据库的语句信息
show create database mydb2;
“ ` ”(ESC下面的按键),表示反引号,默认情况下,反引号括起来的字符串区分大小写
show create database mydb1;
修改数据库
修改mydb1的字符集为utf8(不能修改数据库名)
alter database mydb1 character set utf8;
删除数据库
drop database mydb3;
表的CURD
对表本身进行操作:创建create、查看show、修改、删除drop
创建表
use databasename;
create table employee (id int, name varchar(20));
mysql表中的数据类型
分类 数据类型 说明
数值类型 INT 2的32次方
文本/二进制 CHAR 固定长度字符串
文本/二进制 VARCHAR 可变长度字符串
时间日期 DATE/DATETIME YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
Bit 1位 可以指定位数,如bit(3);
查看当前使用的是哪个库:
Status 或者 select database() from dual;
查看当前选择的数据库中的表
Show tables;
查看表:
查看表的结构: desc tablename;
查看指定表的创建语句: show create table employee;
修改表:
更改表名: rename table employee to worker;
增加一个字段: alter table employee add column height double;
修改一个字段: alter table employee modify column height float;
删除一个字段: alter table employee drop column height;
修改表的字符集:alter table employee character set gbk;
删除表:
drop table worker;
表数据的CURD
1 创建一个员工表,新建employee表并向表中添加一些记录:
Create table employee(
id int,
Name varchar(20),
Sex int,
Birthday date,
Salary double,
Entry_date date,
Resume text
);
插入一些数据
Insert into employee values(1, ‘张三’, 1, ‘1983-04-27’, 15000, ‘2012-06-24’, ‘一个大牛’);
Insert into employee (id, name, sex, birthday, salary, entry_date, resume) values (2, ‘李四’, 1, ‘1984-02-22’, 10000, ‘2012-02-01’, ‘一个小牛’);
Insert into employee (id, name, sex, birthday, salary, entry_date, resume) values (3, ‘王五’, 0, ‘1985-09-12’, 7000, ‘2012-08-24’, ‘一个小虾’);
Select * from employee; 查看一下,如果行太长可以加\G参数
查询id大于1的所有员工的信息:
select id, name as 名字, salary as 月薪, salary*12 as 年薪 from employee where id >= 2;
2 update数据
---将所有员工薪水增加500元
update employee set salary=salary +500;
---将王五的员工薪水修改为10000元,resume改为也是一个中牛
update employee set salary = 10000, resume = '也是一个中牛' where name='王五';
delete数据
Delete from employee where name = ‘王五’;
Delete * from employee;
综合练习:
查询表中所有学生信息:
Select * from student;
查询表中所有学生的姓名和对应的英语成绩
select name, english from student;
过滤表中重复数据:
Select english from student;
Select DISTINCT english from student;
Select DISTINCT english, name from student;
Select name, english+chinese+math as 总分 from student;
让所有学生英语分数加上10分特长分
Select name, english+10 from student;(查询时临时加10)
Update student set english = english + 10;(永久加10, 改变了数据库的真实值)
统计每个学生的总分并按从大到小排序
select name, english+chinese+math as 总分 from student order by 总分 desc;
统计一个班级有多少学生
select count(*) from student;
统计数学成绩大于90分的学生有多少个
select count(*) from student where math>90;
统计一个班级数学的总成绩
select sum(math) from student;
统计一个班级语文、英语、数学的成绩总和
select sum(chinese+english+math) from student;
统计一个班级的数学平均分
select avg(math) from student;
统计一个班级总平均分
select avg(chinese+english+math) from student;
统计一个班级最高分和最低分
select max(chinese+english+math) as 最高分, min(chinese+english+math) as 最低分 from student;
Top-N 问题:
按math成绩从小到大排序,求math成绩在5-8名之间的
select * from student order by math limit 4,4;
分组数据:
为学生表,增加一个班级列,练习分组查询
Alter table student add column class_id int;
更新表:
Update student set class_id=1 where id<=5;
-----查出各个班级的总分和最高分
select class_id, sum(english+chinese+math) as 总分, max(chinese+english+math) as
最高分 from student group by class_id;
-----查出各个班级英语的平均分
select class_id, avg(english) from student group by class_id;
-----查出班级总分大于1300的班级id
select class_id, sum(english+chinese+math) as 总分 from student group by class_id having 总分>1300;
**注意:在mysql中,having后面可以使用别名,若是中文不要加””
时间日期函数
MySQL里面的时间分为三类:时间、日期、时间戳(含有时分秒的sysdate)。
如:
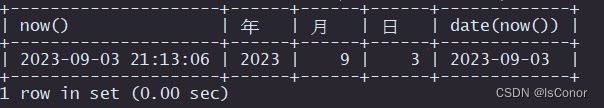
select now(), year(now()) 年, month(now()) 月, day(now()) 日, date(now());
select CURRENT_DATE(),CURRENT_TIME(), CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() from dual;
数学相关函数
ABS(number2) 绝对值
BIN(decimal_number) 十进制转二进制
CEILING(number2) 向上取整
CONV(number2, from_base, to_base); 进制转换
FLOOR(number2) 向下取整
FORMAT(number, decimal_places) 保留小数位数
HEX(decimalNumber) 转十六进制
LEAST(number, number2 [....]) 求最小值
MOD(numerator, denominator) 求余
多表查询
Sql脚本创建多个表并插入数据
1 交叉连接---相当于笛卡尔积
select e.*, d.* from emp e cross join dept d;
2 自连接:查询emp表和dept表的所有信息:
---SQL99:
Select e.ename, e.job, d.deptno, d.dname from emp e inner join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
其中inner可以省略
---oracle写法:
Select e.ename, e.job, d.deptno, d.dname from emp e, dept d where e.deptno=d.deptno;
3 外连接:
左外连接:
select e.ename, e.job, d.deptno, d.dname from emp e left outer join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
右外连接:
select e.ename, e.job, d.deptno, d.dname from emp e right outer join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
对比练习:
1 查询员工信息,员工号,姓名,月薪,部门名称
select e.ename, e.ename, e.sal, d.dname from emp e, dept d where e.deptno=d.deptno;
select e.empno, e.ename, e.sal, d.dname from emp e inner join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
2 统计各个部门员工总人数---要求显示部门名称
select d.deptno, d.dname, count(e.empno) from emp e, dept d where e.deptno=d.deptno group by d.deptno, d.dname;
(右外连接显示部门表里的数据)
select d.deptno, d.dname, count(e.empno) from emp e right outer join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno group by d.deptno, d.dname;
字符串相关函数
CHARSET(str) 返回字符串字符集
CONCAT(string2 [....]) 连接字串
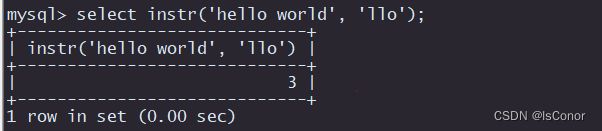
INSTR(string, substring) 返回substring在string中出现的位置,没有返回0
UCASE(string2) 转换成大写
LCASE(string2) 转换成小写
LEFT(string2, length) 从string2中的左边起取length个字符
LENGTH(string) string长度
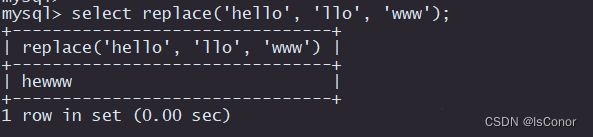
REPLACE(str, search_str, replace_str) 在str中用replace_str替换search_str
STRCMP(string1, string2) 比较两个字符串大小
SUBSTRING(str, position [length]) 从str的position开始,取length个字符
日期转字符串:
在mysql中没有to_date函数,进行日期转换需要使用date_format()来代替
Select date_format(‘2013-5-11’, ‘yyyy-mm-dd’) from dual;
Select date_format(now(), ‘%Y-%m-%d’) from dual;
字符串转日期:
select str_to_date(‘2013-6-04’, ‘%Y-%c-%d %h:%i:%s’) from dual;
Ifnull 函数 先当于oracle的nvl
select concat(e.ename, '的老板是', ifnull(b.ename, 'his wife')) from emp e left outer join emp b on e.mgr=b.empno;
表的约束:
*定义主键约束: primary key: 不允许为空,不允许重复
*定义主键自动增长:auto_increment
*定义唯一约束: unique
*定义非空约束: not null
*定义外键约束: constraint ordersid_FK foreign key(ordersid) references order
*删除主键: alter table tablename drop primary key ;
准备两个表:
Create table class(
id INT(11) primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) unique
);
Create table student(
id INT(11) primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) unique,
Passwd varchar(12) not null,
classid INT(11),
constraint stu_classid_FK foreign key(classid) references class(id)
);
向class表中插入两条数据:
Insert into class(name) values(‘音乐’);
Insert into class(name) values(‘美术’);
mysql> insert into student(id, name, passwd, classid) values(1, 'xiaoliu', 'xxxxx', 1)
mysql> insert into student(name, passwd, classid) values('xiaohong', 'xxxxx', 2);
mysql> insert into student(name, passwd, classid) values(null, 'xxxx', 2);
mysql的中文乱码问题:
两层因素:
因素1:MySQL自身的设计
步骤1
Show variables like ‘character%’; 查看所有应用的字符集
步骤2
$ mysql -uroot -p123456 -default_character_set=gbk 指定字符集登录数据库
Show variables like ‘character%’;
影响了与客户端相关联的3处(最外层)
在这种状态下执行use mydb2;
Select * from employee; 查看输出会出现乱码。
因素2:系统编码问题