C语言代码审计项目——编辑器、高亮、查找替换、选词跳转(下)
前置知识
抽象语法树
基本介绍
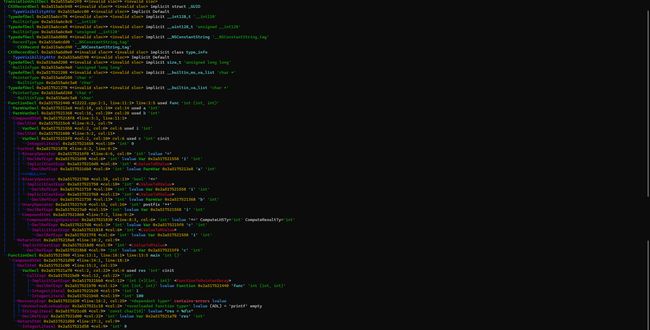
AST(Abstract Syntax Tree)抽象语法树,当你有一段源代码的时候,是用于表示该源代码的抽象语法结构的树状图。对于不同的语言,有不同的抽象语法树结构,比如说C语言或者C++所使用的抽象语法树就和python的不一样。
类似于如果有这样一段源码:
#include用树状图分析:
用clang工具直接忽略标准头文件分析:
clang -Xclang -ast-dump -fsyntax-only -nostdinc test.c
用法
得到的树状图上有很多信息,标识了函数的类型,参数和参数类型,变量,变量类型等(有些只有一点信息,所以需要利用不同的分析工具来对比效果)。
这些数据可以用来分析函数结构、跳转函数、函数漏洞具体分析等。
LLVM
基本介绍
这里我直接拿来一个知乎答案:
LLVM是一个编译器框架。LLVM作为编译器框架,是需要各种功能模块支撑起来的,你可以将clang和lld都看做是LLVM的组成部分,框架的意思是,你可以基于LLVM提供的功能开发自己的模块,并集成在LLVM系统上,增加它的功能,或者就单纯自己开发软件工具,而利用LLVM来支撑底层实现。LLVM由一些库和工具组成,正因为它的这种设计思想,使它可以很容易和IDE集成(因为IDE软件可以直接调用库来实现一些如静态检查这些功能),也很容易构建生成各种功能的工具(因为新的工具只需要调用需要的库就行)。
这里是具体介绍。
因为我们需要使用它的接口,所以需要提前安装它和与python的第三方接口库。
整包安装方式
从这个网址上直接下载windows64版本,因为我用的win11。
并且把这个路径加入环境变量里面:???/???/bin/libclang.dll
python接口
pip install clang
正式开始
一般使用
词法分析
这里可以直接用于一般词法分析,就是把每个词分出来,但并不会生成行和类型分析。
from clang.cindex import Index, Config, CursorKind, TypeKind
libclangPath = r"???\???\LLVM\bin\libclang.dll"
#这个路径需要自己先在笔记本上安装
Config.set_library_file(libclangPath)
file_path_ = r"your_file_path"
index = Index.create()
tu = index.parse(file_path_)
AST_root_node = tu.cursor #cursor根节点
# 词法分析
cursor_content = ""
for token in AST_root_node.get_tokens():
# 针对根节点,调用get_tokens方法。
print(token.spelling)# 相当于分离这个节点上的spelling属性 就是它的内容
这里只是最基础的分析,并没有涉及到复杂属性的筛选和区分,所以很简单,就是用于讲解的,真正的分词,可以使用定制化工具ctags来分析变量和函数,这样不仅可以知道函数的类型和变量的类型,还能知道它们所位于源代码里的具体位置,并且能告知是否是全局还是局部属性。
json生成
这里是筛选了比较多的节点上的属性,并且把它们整合到一个json文件里,如果它们是空,则代表它们可能是操作运算符或者某些关键字。
import json
from clang.cindex import Index, Config, CursorKind
class AST_Tree_json:
def __init__(self, absolute_path):
self.absolute_path = absolute_path
self.clang_path = r'??\???\LLVM\bin\libclang.dll'
Config.set_library_file(self.clang_path)
self.AST_Root = Index.create().parse(absolute_path).cursor
def serialize_node(self, cursor):
node_dict = {
"kind": str(cursor.kind),
"location": [cursor.extent.start.line, cursor.extent.start.column,
cursor.extent.end.line, cursor.extent.end.column],
"children": []
}
if cursor.spelling:
node_dict["spelling"] = cursor.spelling
print('keywords: ', cursor.spelling)
print('location: ', cursor.extent.start.line, cursor.extent.start.column,
cursor.extent.end.line, cursor.extent.end.column)
for child in cursor.get_children():
child_dict = self.serialize_node(child)
node_dict["children"].append(child_dict)
return node_dict
def start(self):
string_res = self.serialize_node(self.AST_Root)
serialized_json = json.dumps(string_res, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False)
import time
local_time = time.localtime()
date_time = time.strftime("%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S", local_time)
with open('./res_{}.json'.format(date_time),'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(serialized_json)
file.close()
# 虽然但是它能识别[]{};+-=,不能获取它们的标识符....而且获取不到值....
# print(serialized_json)
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = r'your_file_path'
ast_obj = AST_Tree_json(path)
ast_obj.start()
虽然能够生成json文件,但是仍然能力有限,对于特殊字符的过滤并没有过滤出来。但是基本已经能生成较为详细的json文件内容,包含有内容的扫出来的所有属性的节点以及它们的所在的具体位置。
(start_line, start_column, end_line, end_column)指的是出现的(起始行, 起始列, 结束行,结束列)的位置。想要出具体位置的字符,则可能需要读取源代码片段并取它们的位置,并记录。
定制化使用
针对函数分析:
- 函数语句类型(声明、定义、调用)
- 函数具体位置
- 函数声明、定义、调用内容
- 函数参数和返回值的内容和类型
- 函数所在文件绝对路径
函数信息类设计
我分别写了几个类用于承接过滤出来的信息。
FunctionDeclaration:函数声明信息类FunctionDefinition:函数定义信息类FunctionCallExpress:函数调用信息类FunctionDump:函数数据包装类DefinitionCallExpressCombiner:函数定义调用拼接类SourceInfo:函数数据类FunctionPreprocessor预处理器类
源码部分:
1.FunctionDeclaration类
class FunctionDeclaration:
def __init__(self, function_name=None, declared_location=None, declared_contents=None, return_types=None,
parameter_types=None):
self.function_name = function_name
self.declared_location = declared_location
self.declared_contents = declared_contents
self.return_types = return_types
self.parameter_types = parameter_types
self.kind = 'FUNCTION_DELCARATION'
def __repr__(self):
return f"函数名字: {self.function_name}\n函数语句类别: {self.kind}\n函数声明位置: {self.declared_location}\n" \
f"函数参数类型: {self.parameter_types}\n函数返回值类型: {self.return_types}\n"
2.FunctionDefinition类
class FunctionDefinition:
def __init__(self, function_name=None, definition_location=None, definition_contents=None):
self.function_name = function_name
self.definition_location = definition_location
self.definition_contents = definition_contents
self.kind = 'FUNCTION_DEFINITION'
def __repr__(self):
return f"函数名字: {self.function_name}\n函数语句类别: {self.kind}\n" \
f"函数定义位置: {self.definition_location}\n函数定义内容: {self.definition_contents}\n"
3.FunctionCallExpress类
class FunctionCallExpress:
def __init__(self, function_name=None, call_express_location=None, call_express_contents=None):
self.function_name = function_name
self.call_express_location = call_express_location
self.call_express_contents = call_express_contents
self.kind = 'FUNCTION_CALLEXPRESS'
def __repr__(self):
return f"函数名字: {self.function_name}\n函数语句类别: {self.kind}\n" \
f"函数调用位置: {self.call_express_location}\n函数调用内容: {self.call_express_contents}\n"
4.FunctionDump类
class FunctionDump:
def __init__(self, source_path):
self.index = Index.create()
self.translation_unit = self.index.parse(source_path)
self.root_cursor = self.translation_unit.cursor
self.function_declaration_list = []
self.function_definition_list = []
self.function_callexpress_list = []
self.source_path = source_path
# 启动函数
def analyseLauncher(self):
self.analyseRunner(self.root_cursor)
# 实施函数
def analyseRunner(self, cursor):
if cursor.kind == CursorKind.FUNCTION_DECL or cursor.kind == CursorKind.CXX_METHOD:
if not cursor.is_definition():
name = cursor.spelling
location = (
cursor.extent.start.line, cursor.extent.start.column, cursor.extent.end.line,
cursor.extent.end.column)
parameter_types = self.get_parameter_types(cursor)
return_type = self.get_return_type(cursor)
function_declaration = FunctionDeclaration(function_name=name, declared_location=location,
declared_contents=self.get_node_contents(cursor),
return_types=return_type,
parameter_types=parameter_types)
self.function_declaration_list.append(function_declaration)
definition_cursor = cursor.get_definition()
if definition_cursor:
definition_location = (definition_cursor.extent.start.line, definition_cursor.extent.start.column,
definition_cursor.extent.end.line, definition_cursor.extent.end.column)
definition_contents = self.get_node_contents(definition_cursor)
function_definition = FunctionDefinition(function_name=definition_cursor.spelling,
definition_location=definition_location,
definition_contents=definition_contents)
self.function_definition_list.append(function_definition)
self.check_function_calls(self.root_cursor, cursor.spelling) # 这句
for child in cursor.get_children():
self.analyseRunner(child)
def check_function_calls(self, cursor, function_name):
if cursor.kind == CursorKind.CALL_EXPR and cursor.spelling == function_name:
call_location = (
cursor.extent.start.line,
cursor.extent.start.column,
cursor.extent.end.line,
cursor.extent.end.column,
)
call_contents = self.get_node_contents(cursor) # 获取函数调用语句的内容
function_callexpress = FunctionCallExpress(function_name=function_name, call_express_location=call_location,
call_express_contents=call_contents)
self.function_callexpress_list.append(function_callexpress)
for child in cursor.get_children():
self.check_function_calls(child, function_name)
# 参数类型过滤
def get_parameter_types(self, cursor):
parameter_types = []
for arg in cursor.get_arguments():
arg_type = arg.type.spelling
parameter_types.append(arg_type)
if not parameter_types:
return ["void"] # 返回 "void" 字符串表示无参函数
return parameter_types
# 返回值过滤
def get_return_type(self, cursor):
result_type = cursor.type
if cursor.spelling == "main":
return "int"
elif result_type.kind == TypeKind.FUNCTIONPROTO: # 除了void以外的类型
return_type = result_type.get_result().spelling
return return_type
elif result_type.kind == TypeKind.FUNCTIONNOPROTO: # void
return_type = result_type.get_result().spelling
return return_type
return None
# 返回节点内容
def get_node_contents(self, cursor):
with open(self.source_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
contents = file.readlines()
start_line = cursor.extent.start.line - 1
start_column = cursor.extent.start.column - 1
end_line = cursor.extent.end.line - 1
end_column = cursor.extent.end.column - 1
cursor_contents = ""
for line in range(start_line, end_line + 1):
if line == start_line:
cursor_contents += contents[line][start_column:]
elif line == end_line:
cursor_contents += contents[line][:end_column + 1]
else:
cursor_contents += contents[line]
return cursor_contents
# 查找调用函数
def show_function_details(self):
### 函数声明
print('~~函数声明~~')
for item in self.function_declaration_list:
print(item)
print('~~函数定义~~')
for item in self.function_definition_list:
print(item)
print('~~函数调用~~')
for item in self.function_callexpress_list:
print(item)
5.DefinitionCallExpressCombiner组合器类
# 组合器
class DefinitionCallExpressCombiner:
def __init__(self, file_path):
self.file_path = file_path
self.main_sign = None
self.definition_contents = []
self.mix_contents = []
self.main_length = 0
self.offset_length = 0
def find_all_files(self, filepath):
directory, _ = os.path.split(filepath)
file_list = []
for root, _, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
if file.endswith('.c') or file.endswith('.cpp'):
file_list.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(root, file)))
return file_list
def find_all_headers(self, filepath):
directory, _ = os.path.split(filepath)
file_list = []
for root, _, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
if file.endswith('.h') or file.endswith('.hh'):
path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(root, file))
if self.is_defined(path):
file_list.append(path)
return file_list
def is_defined(self, file_path):
with open(file_path, "r") as file:
content = file.read()
return "{" in content or "}" in content
def has_main_function(self, file_path):
with open(file_path, "r") as file:
content = file.read()
return "int main(" in content
def getDefinitionCodes(self):
source_files = self.find_all_files(self.file_path)
for file_path in source_files:
with open(file_path, "r") as file:
content = file.readlines()
if self.has_main_function(file_path):
if self.main_sign is None:
self.main_sign = file_path
else:
pass
else:
if content:
last_line = content[-1]
pattern = r'.*\n'
if re.findall(pattern, last_line):
pass
else:
content[-1] = last_line + '\n'
self.definition_contents += content
def getDefinitionCodes_(self):
source_files = self.find_all_files(self.file_path)
header_files = self.find_all_headers(self.file_path)
for file_path in header_files:
with open(file_path, "r") as file:
content = file.readlines()
if content:
last_line = content[-1]
pattern = r'.*\n'
if re.findall(pattern, last_line):
pass
else:
content[-1] = last_line + '\n'
self.definition_contents += content
for file_path in source_files:
with open(file_path, "r") as file:
content = file.readlines()
if self.has_main_function(file_path):
if self.main_sign is None:
self.main_sign = file_path
else:
pass
else:
if content:
last_line = content[-1]
pattern = r'.*\n'
if re.findall(pattern, last_line):
pass
else:
content[-1] = last_line + '\n'
self.definition_contents += content
def Combiner_(self):
self.getDefinitionCodes_()
path, name = split(self.main_sign)
name = '._' + name
temp_path = os.path.join(path, name)
with open(self.main_sign, "r", encoding='utf-8') as main_file:
main_file_content = main_file.readlines()
self.main_length = len(main_file_content)
last_line = self.definition_contents[-1]
pattern = r'.*\n'
if re.findall(pattern, last_line):
pass
else:
self.definition_contents[-1] = last_line + '\n'
if main_file_content:
self.mix_contents = self.definition_contents + main_file_content
new_data = ["//" + line if line.startswith("#include") else line for line in self.mix_contents]
with open(temp_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as temp_obj:
temp_obj.writelines(new_data)
self.offset_length = len(new_data) - self.main_length
return temp_path
def Combiner(self):
self.getDefinitionCodes()
path, name = split(self.main_sign)
name = '.' + name
temp_path = os.path.join(path, name)
with open(self.main_sign, "r", encoding='utf-8') as main_file:
main_file_content = main_file.readlines()
self.main_length = len(main_file_content)
last_line = self.definition_contents[-1]
pattern = r'.*\n'
if re.findall(pattern, last_line):
pass
else:
self.definition_contents[-1] = last_line + '\n'
if main_file_content:
self.mix_contents = self.definition_contents + main_file_content
new_data = ["//" + line if line.startswith("#include") else line for line in self.mix_contents]
with open(temp_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as temp_obj:
temp_obj.writelines(new_data)
self.offset_length = len(new_data) - self.main_length
return temp_path
6.SourceInfo函数数据类
# 数据类
class SourceInfo:
def __init__(self, filepath, source_obj=None, headers_obj_list=None):
self.filepath = filepath
self.source_obj = source_obj
self.headers_obj_list = headers_obj_list
7.FunctionPreprocessor预处理器类
class FunctionPreprocessor:
def __init__(self, file_path, keyword=None):
self.file_path = file_path
self.target_function_name = keyword
self.headers_list = None
self.exclude_headers_list = None
self.main_flag = None
self.header_defined = False
# 产生除去头文件的临时文件XXX_.c/.cpp
def virtualTempFile(self, filename):
with open(filename, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
contents = file.readlines()
temp_contents = []
# 注释头文件....
for item in contents:
if item.startswith('#include'):
item = '//' + item # 在头文件行之前添加注释符号
temp_contents.append(item)
path, name = split(filename)
name = '.' + name
new_filename = os.path.join(path, name)
with open(new_filename, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.writelines(temp_contents)
return new_filename
# 获取源文件的所有头文件列表
def find_dependencies(self, filename):
with open(filename, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
contents = file.readlines()
headers = []
pattern = r'#include\s*["]\s*(\w+\.h)\s*["]'
for item in contents:
match = re.search(pattern, item)
if match:
dependency = match.group(1)
headers.append(dependency)
return headers
def find_all_headers(self, filepath):
directory, _ = os.path.split(filepath)
for root, _, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
if file.endswith('.h') or file.endswith('.hh'):
path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(root, file))
if self.is_defined(path):
self.header_defined = True
def is_defined(self, file_path):
with open(file_path, "r") as file:
content = file.read()
return "{" in content or "}" in content
# 遍历所有同类型文件
def find_all_files(self, filepath):
directory, _ = os.path.split(filepath)
file_list = []
for root, _, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
if file.endswith('.c') or file.endswith('.cpp'):
absolute_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(root, file))
file_list.append(absolute_path)
if self.has_main_function(absolute_path):
self.main_flag = absolute_path
return file_list
def has_main_function(self, file_path):
with open(file_path, "r") as file:
content = file.read()
return "int main(" in content
def multiCallExpressCombiner(self, filepath):
combiner = DefinitionCallExpressCombiner(filepath)
temp_filepath = combiner.Combiner()
call_analyzer = FunctionDump(temp_filepath)
call_analyzer.analyseLauncher()
os.remove(temp_filepath)
offset = combiner.offset_length
function_declaration_list = []
function_definition_list = []
function_call_express_list = []
for item in call_analyzer.function_declaration_list:
if item.declared_location[0] > offset:
start_line, start_index, end_line, end_index = item.declared_location
item.declared_location = (start_line - offset, start_index, end_line - offset, end_index)
function_declaration_list.append(item)
else:
continue
for item in call_analyzer.function_definition_list:
if item.definition_location[0] > offset:
start_line, start_index, end_line, end_index = item.definition_location
item.definition_location = (start_line - offset, start_index, end_line - offset, end_index)
function_definition_list.append(item)
else:
continue
for item in call_analyzer.function_callexpress_list:
if item.call_express_location[0] > offset:
start_line, start_index, end_line, end_index = item.call_express_location
item.call_express_location = (start_line - offset, start_index, end_line - offset, end_index)
function_call_express_list.append(item)
else:
continue
# 覆盖原文
call_analyzer.function_declaration_list = function_declaration_list
call_analyzer.function_definition_list = function_definition_list
call_analyzer.function_callexpress_list = function_call_express_list
return call_analyzer
def _multiCallExpressCombiner(self, filepath):
combiner = DefinitionCallExpressCombiner(filepath)
temp_filepath = combiner.Combiner_()
call_analyzer = FunctionDump(temp_filepath)
call_analyzer.analyseLauncher()
os.remove(temp_filepath)
offset = combiner.offset_length
function_declaration_list = []
function_definition_list = []
function_call_express_list = []
for item in call_analyzer.function_declaration_list:
if item.declared_location[0] > offset:
start_line, start_index, end_line, end_index = item.declared_location
item.declared_location = (start_line - offset, start_index, end_line - offset, end_index)
function_declaration_list.append(item)
else:
continue
for item in call_analyzer.function_definition_list:
if item.definition_location[0] > offset:
start_line, start_index, end_line, end_index = item.definition_location
item.definition_location = (start_line - offset, start_index, end_line - offset, end_index)
function_definition_list.append(item)
else:
continue
for item in call_analyzer.function_callexpress_list:
if item.call_express_location[0] > offset:
start_line, start_index, end_line, end_index = item.call_express_location
item.call_express_location = (start_line - offset, start_index, end_line - offset, end_index)
function_call_express_list.append(item)
else:
continue
# 覆盖原文
call_analyzer.function_declaration_list = function_declaration_list
call_analyzer.function_definition_list = function_definition_list
call_analyzer.function_callexpress_list = function_call_express_list
return call_analyzer
def source_runner(self, init_filename):
filelist = self.find_all_files(init_filename)
self.find_all_headers(init_filename)
source_info_list = []
if len(filelist) < 2 and not self.header_defined:
for file in filelist:
headers_objs = []
# 源文件
source_path = self.virtualTempFile(file)
headers_path = self.find_dependencies(source_path)
path, name = split(source_path)
for header in headers_path:
header_path = path + '/' + header
source_path_ = self.virtualTempFile(header_path)
headers_analyzer = FunctionDump(source_path_)
headers_analyzer.analyseLauncher()
# headers_analyzer.show_function_details()
headers_objs.append((file, header_path, headers_analyzer))
os.remove(source_path_)
analyzer = FunctionDump(source_path)
analyzer.analyseLauncher()
os.remove(source_path)
# analyzer.show_function_details()
per_source_info = SourceInfo(filepath=file, source_obj=analyzer, headers_obj_list=headers_objs)
source_info_list.append(per_source_info)
elif len(filelist) >= 2 and not self.header_defined:
for file in filelist:
headers_objs = []
if file != self.main_flag:# 标记是不是main
# 源文件
source_path = self.virtualTempFile(file)
headers_path = self.find_dependencies(source_path)
path, name = split(source_path)
for header in headers_path:
header_path = path + '/' + header
source_path_ = self.virtualTempFile(header_path)
headers_analyzer = FunctionDump(source_path_)
headers_analyzer.analyseLauncher()
# headers_analyzer.show_function_details()
headers_objs.append((file, header_path, headers_analyzer))
os.remove(source_path_)
analyzer = FunctionDump(source_path)
analyzer.analyseLauncher()
os.remove(source_path)
else:
# 是main源文件 开始复杂拼装
analyzer = self.multiCallExpressCombiner(file)
per_source_info = SourceInfo(filepath=file, source_obj=analyzer, headers_obj_list=headers_objs)
source_info_list.append(per_source_info)
elif self.header_defined:
for file in filelist:
headers_objs = []
if file != self.main_flag:# 标记是不是main
# 源文件
source_path = self.virtualTempFile(file)
headers_path = self.find_dependencies(source_path)
path, name = split(source_path)
for header in headers_path:
header_path = path + '/' + header
source_path_ = self.virtualTempFile(header_path)
headers_analyzer = FunctionDump(source_path_)
headers_analyzer.analyseLauncher()
headers_objs.append((file, header_path, headers_analyzer))
os.remove(source_path_)
analyzer = FunctionDump(source_path)
analyzer.analyseLauncher()
os.remove(source_path)
else:
headers_path = self.find_dependencies(file)
path, name = split(file)
for header in headers_path:
header_path = path + '/' + header
source_path_ = self.virtualTempFile(header_path)
headers_analyzer = FunctionDump(source_path_)
headers_analyzer.analyseLauncher()
headers_objs.append((file, header_path, headers_analyzer))
os.remove(source_path_)
# 是main源文件 开始复杂拼装
analyzer = self._multiCallExpressCombiner(file)
per_source_info = SourceInfo(filepath=file, source_obj=analyzer, headers_obj_list=headers_objs)
source_info_list.append(per_source_info)
return source_info_list
函数跳转函数实现
- 过滤选中字符
selected_text - 函数跳转菜单
UI连接函数 - 三个函数跳转逻辑编写
gotoDeclaration:针对于右键转到声明的函数
gotoDefinition:针对右键转到定义的函数
gotoCallExpress:针对右键转到调用的函数 - 源数据的获取
getFuncAnalyzer:接口用于获取最新的函数分析数据,当文本编辑器里的内容发生过更改或者新建文件之后,刷新数据内容。
源代码
1.过滤选中字符串getSelectdFunctionName
def getSelectdFunctionName(self, input_string):
import re
pattern = r'\b(\w+)\s*\('
match = re.search(pattern, input_string)
if match:
return match.group(1)
words = re.findall(r'\b\w+\b', input_string) # 提取字符串中的单词列表
for word in words:
if re.match(r'^[a-zA-Z_][a-zA-Z0-9_]*$', word): # 判断单词是否符合函数名的命名规则
return word # 返回第一个符合要求的单词作为函数名
return None
2.右键菜单UI逻辑
def show_context_menu(self, point):
self.context_menu = self.__editor.createStandardContextMenu()
# 添加默认选项
self.context_menu.insertSeparator(self.context_menu.actions()[0])
ui_icon = self.config_ini['main_project']['project_name'] + self.config_ini['ui_img']['ui_turn_to']
action_goto_declaration = QAction("转到声明", self)
action_goto_declaration.setIcon(QIcon(ui_icon))
action_goto_declaration.triggered.connect(self.gotoDeclaration)
action_goto_definition = QAction("转到定义", self)
action_goto_definition.setIcon(QIcon(ui_icon))
action_goto_definition.triggered.connect(self.gotoDefinition)
action_goto_call_express = QAction("转到调用", self)
action_goto_call_express.setIcon(QIcon(ui_icon))
action_goto_call_express.triggered.connect(self.gotoCallExpress)
# 分隔符
self.context_menu.insertSeparator(self.context_menu.actions()[0])
self.context_menu.insertAction(self.context_menu.actions()[0], action_goto_declaration)
self.context_menu.insertAction(self.context_menu.actions()[1], action_goto_definition)
self.context_menu.insertAction(self.context_menu.actions()[2], action_goto_call_express)
# 应用
self.context_menu.exec_(self.__editor.mapToGlobal(point))
def gotoDeclaration(self):
self.gotoDeclarationSign.emit()
def gotoDefinition(self):
self.gotoDefinitionSign.emit()
def gotoCallExpress(self):
self.gotoCallExpressSign.emit()
text_editor_obj.gotoDeclarationSign.connect(lambda: self.gotoDeclaration(text_editor_obj))
text_editor_obj.gotoDefinitionSign.connect(lambda: self.gotoDefinition(text_editor_obj))
text_editor_obj.gotoCallExpressSign.connect(lambda: self.gotoCallExpress(text_editor_obj))
3.gotoDeclaration gotoDefinition gotoCallExpress
# 声明跳转
def gotoDeclaration(self, editor):
position, selected_text = editor.getSelected_Position_Content()
locations = []
absolute_path = editor.filepath + '/' + editor.filename
# 过滤选中的字符
selected_text = editor.getSelectdFunctionName(selected_text)
if self.source_data == None or self.current_source_path == None:
self.source_data = self.getFuncAnalyzer(editor=editor)
self.current_source_path = os.path.normpath(absolute_path)
if self.source_data and self.current_source_path == None:
self.current_source_path = os.path.normpath(absolute_path)
elif self.current_source_path and self.current_source_path != os.path.normpath(absolute_path):
self.current_source_path = os.path.normpath(absolute_path)
else:
pass
location = None
isSource = True
# 头文件跳源文件
if '.h' in editor.filename or '.hh' in editor.filename:
isSource = False
if self.source_data:
for data in self.source_data:
# 文件名
isFind = False
filename = data.filepath
# 声明
function_declaration_list = data.source_obj.function_declaration_list
# 头文件
headers_obj_list = data.headers_obj_list
# 查源文件...
for per_obj in function_declaration_list:
if selected_text == per_obj.function_name and per_obj.declared_contents:
location = per_obj.declared_location
isFind = True
break
if not isFind and location == None:
# 头文件遍历
current_editor = None
for per_obj in headers_obj_list:
filepath, header_path, item = per_obj
path, name = split(filepath)
path, name_ = split(header_path)
# 声明
for i in item.function_declaration_list:
if selected_text == i.function_name and i.declared_contents:
location = i.declared_location
if isSource:
self.create_new_open_tab(header_path)
current_editor = self.ui.text_editor.currentWidget()
else:# 关键!
current_editor = editor
break
if location is not None and current_editor is not None:
start_line = location[0] - 1
start_index = location[1] - 1
end_line = location[2] - 1
end_index = location[3] - 1
text_location = [(start_line, start_index, end_line, end_index)]
current_editor.highlight_function_declaration(text_location)
elif isFind and location is not None:
if location is not None:
start_line = location[0] - 1
start_index = location[1] - 1
end_line = location[2] - 1
end_index = location[3] - 1
text_location = [(start_line, start_index, end_line, end_index)]
editor.highlight_function_declaration(text_location)
# 定义跳转
def gotoDefinition(self, editor):
position, selected_text = editor.getSelected_Position_Content()
locations = []
absolute_path = editor.filepath + '/' + editor.filename
selected_text = editor.getSelectdFunctionName(selected_text)
if self.source_data == None or self.current_source_path == None:
self.source_data = self.getFuncAnalyzer(editor=editor)
self.current_source_path = os.path.normpath(absolute_path)
if self.source_data and self.current_source_path == None:
self.current_source_path = os.path.normpath(absolute_path)
elif self.current_source_path and self.current_source_path != os.path.normpath(absolute_path):
self.current_source_path = os.path.normpath(absolute_path)
else:
pass
location = None
isSource = True
if '.h' in editor.filename or '.hh' in editor.filename:
isSource = False
if self.source_data:
for data in self.source_data:
# 文件名
isFind = False
filename = data.filepath
# 定义
function_definition_list = data.source_obj.function_definition_list
# 头文件
headers_obj_list = data.headers_obj_list
# 查源文件...
for per_obj in function_definition_list:
if selected_text == per_obj.function_name and per_obj.definition_contents:
location = per_obj.definition_location
isFind = True
break
if not isFind and location == None:
# 头文件遍历
for per_obj in headers_obj_list:
filepath, header_path, item = per_obj
path, name = split(filepath)
path, name_ = split(header_path)
# 定义
for i in item.function_definition_list:
if selected_text == i.function_name and i.definition_contents:
location = i.definition_location
if isSource:
self.create_new_open_tab(header_path)
current_editor = self.ui.text_editor.currentWidget()
else:
current_editor = editor
break
if location is not None and current_editor is not None:
start_line = location[0] - 1
start_index = location[1] - 1
end_line = location[2] - 1
end_index = location[3] - 1
text_location = [(start_line, start_index, end_line, end_index)]
current_editor.highlight_function_definition(text_location)
elif isFind and location is not None:
another_editor = editor
if os.path.normpath(absolute_path) != os.path.normpath(filename):
self.create_new_open_tab(os.path.normpath(filename))
another_editor = self.ui.text_editor.currentWidget()
if location is not None:
start_line = location[0] - 1
start_index = location[1] - 1
end_line = location[2] - 1
end_index = location[3] - 1
text_location = [(start_line, start_index, end_line, end_index)]
another_editor.highlight_function_definition(text_location)
# 调用跳转
def gotoCallExpress(self, editor):
position, selected_text = editor.getSelected_Position_Content()
locations = []
absolute_path = editor.filepath + '/' + editor.filename
selected_text = editor.getSelectdFunctionName(selected_text)
if self.source_data == None or self.current_source_path == None:
self.source_data = self.getFuncAnalyzer(editor=editor)
self.current_source_path = os.path.normpath(absolute_path)
if self.source_data and self.current_source_path == None:
self.current_source_path = os.path.normpath(absolute_path)
elif self.current_source_path and self.current_source_path != os.path.normpath(absolute_path):
self.current_source_path = os.path.normpath(absolute_path)
else:
pass
isSource = True
if '.h' in editor.filename or '.hh' in editor.filename:
isSource = False
if self.source_data:
for data in self.source_data:
# 文件名
filename = data.filepath
# 调用
function_callexpress_list = data.source_obj.function_callexpress_list
# 记得清空 不然GG
locations = []
for per_obj in function_callexpress_list:
if selected_text == per_obj.function_name and per_obj.call_express_contents:
location = per_obj.call_express_location
start_line = location[0] - 1
start_index = location[1] - 1
end_line = location[2] - 1
end_index = location[3] - 1
text_location = (start_line, start_index, end_line, end_index)
locations.append(text_location)
if not isSource and locations != []:
self.create_new_open_tab(filename)
another_editor = self.ui.text_editor.currentWidget()
another_editor.highlight_function_call_express(locations)
elif isSource and locations != []:
if os.path.normpath(absolute_path) != os.path.normpath(filename):
self.create_new_open_tab(os.path.normpath(filename))
another_editor = self.ui.text_editor.currentWidget()
another_editor.highlight_function_call_express(locations)
else:
editor.highlight_function_call_express(locations)
4.getFuncAnalyzer
def getFuncAnalyzer(self, editor):
filename = editor.filename
filepath = editor.filepath
absolute_path = filepath + '/' + filename
func_dump = FunctionPreprocessor(absolute_path)
source_data = func_dump.source_runner(absolute_path)
return source_data
基本逻辑流程图
markdown画流程图真的是很难画啊,用飞书就是在救赎自己
奇淫技巧
由于我使用的接口分析信息的时候,会自动分析大量的头文件信息,导致我在分析过滤的时候会输出一大堆标准库里面的函数信息,这样会阻碍我对于自定义函数的分析和处理。
这个接口调用的方式是传入一个有内容的代码文件然后分析,如果能换成字符串那将会很好,但是不行,所以我选择手动注释掉文件里的头文件,然后把临时文件传入分析类里分析,但是保留原来文件的内容在文本编辑器上,分析结束之后立刻删除该临时文件,这样就能造成我读取的是源码分析的错觉。
演示效果
演示图
后面的碎碎念
起因
其实是实习的项目内容,但是我挑选了一部分(我觉得我在做的时候饱受折磨的)来展示。因为几乎没有得到明显的参考资料,大部分是自己手搓的,还有根据大爹chatgpt3.5的指点,虽然它的指点也很烂,写出来的代码还不如我手搓的。
给后辈的礼物
也许下一次他们这个还是写这个项目,可以拿来参考参考,但是跑不跑得通又是另一回事了。我果然有当老师的天赋吗,我修bug的能力一流…或者有些人被迫拿这个类来做文本编辑器…

源码
我放在github上了,但是配置文件是加密的,所以请仔细查看README里面的内容。
我的部分会详细说明,不是我的部分,自己参悟0-0!
源码在这里
上篇在这里