Android 13 - Media框架(28)- MediaCodec(三)
上一节我们了解到 ACodec 执行完 start 流程后,会把所有的 input buffer 都提交给 MediaCodec 层,MediaCodec 是如何处理传上来的 buffer 呢?这一节我们就来了解一下这部分内容。
1、ACodecBufferChannel::fillThisBuffer
ACodec 通过调用 ACodecBufferChannel::fillThisBuffer 把input buffer传递给 MediaCodc,传入参数为 buffer id:
void ACodecBufferChannel::fillThisBuffer(IOMX::buffer_id bufferId) {
ALOGV("fillThisBuffer #%d", bufferId);
std::shared_ptr<const std::vector<const BufferInfo>> array(
std::atomic_load(&mInputBuffers));
// 遍历buffer数组,查找对应ACodecBufferChannel::BufferInfo
BufferInfoIterator it = findBufferId(array, bufferId);
if (it == array->end()) {
ALOGE("fillThisBuffer: unrecognized buffer #%d", bufferId);
return;
}
// 如果存在解密/解扰,那么需要设置input format
if (it->mClientBuffer != it->mCodecBuffer) {
it->mClientBuffer->setFormat(it->mCodecBuffer->format());
}
// 调用callback
mCallback->onInputBufferAvailable(
std::distance(array->begin(), it),
it->mClientBuffer);
}
fillThisBuffer 很简单,主要步骤如下:
- 遍历buffer数组,根据bufferid查找对应ACodecBufferChannel::BufferInfo,从而获得mClientBuffer;我们这里再回顾一下,在不用解密/解扰的模式下,mClientBuffer和mCodecBuffer其实是指向同一个MediaCodecBuffer的,解密/解扰的模式那么mClientBuffer和mCodecBuffer指向的则不是同一块MediaCodecBuffer了;
- 如果mClientBuffer和mCodecBuffer不是指向同一块MediaCodecBuffer,那么需要给 mClientBuffer 设置默认的 input format;
- 调用 onInputBufferAvailable 将消息回传给 MediaCodec;
这里有一点很容易让人忽略,为什么调用onInputBufferAvailable时,传递的index要用std::distance来计算呢?
std::distance应该计算的是 ACodecBufferChannel::BufferInfo 在数组中的位置,也就是数组索引,所以传递给 MediaCodec 用的 index 其实是 ACodecBufferChannel 的buffer数组索引,它和buffer id是两码事。
2、BufferCallback::onInputBufferAvailable
void BufferCallback::onInputBufferAvailable(
size_t index, const sp<MediaCodecBuffer> &buffer) {
sp<AMessage> notify(mNotify->dup());
notify->setInt32("what", kWhatFillThisBuffer);
notify->setSize("index", index);
notify->setObject("buffer", buffer);
notify->post();
}
onInputBufferAvailable 会把回传的数组索引 以及 MediaCodecBuffer 重新封装到 AMessage中,最后交由 MediaCodec Handler 处理。
2、kWhatFillThisBuffer
case kWhatFillThisBuffer:
{
// 将拿到的 MediaCodec 加入到列表当中
/* size_t index = */updateBuffers(kPortIndexInput, msg);
// 如果正在处理以下事件,则直接将所有的buffer返回给Codec
if (mState == FLUSHING
|| mState == STOPPING
|| mState == RELEASING) {
returnBuffersToCodecOnPort(kPortIndexInput);
break;
}
// 如果 csd buffer 不为空,则先写入csd buffer
if (!mCSD.empty()) {
ssize_t index = dequeuePortBuffer(kPortIndexInput);
CHECK_GE(index, 0);
// If codec specific data had been specified as
// part of the format in the call to configure and
// if there's more csd left, we submit it here
// clients only get access to input buffers once
// this data has been exhausted.
status_t err = queueCSDInputBuffer(index);
if (err != OK) {
ALOGE("queueCSDInputBuffer failed w/ error %d",
err);
setStickyError(err);
postActivityNotificationIfPossible();
cancelPendingDequeueOperations();
}
break;
}
// CCodec 使用的,暂时略过
if (!mLeftover.empty()) {
ssize_t index = dequeuePortBuffer(kPortIndexInput);
CHECK_GE(index, 0);
status_t err = handleLeftover(index);
if (err != OK) {
setStickyError(err);
postActivityNotificationIfPossible();
cancelPendingDequeueOperations();
}
break;
}
// 如果使用的是异步模式
if (mFlags & kFlagIsAsync) {
// 并且输入不是surface,输入是surface的情况我们暂时不看
if (!mHaveInputSurface) {
// 状态是 flushed,则暂时不处理该input buffer,等待重新启动
if (mState == FLUSHED) {
mHavePendingInputBuffers = true;
} else {
// 调用onInputBufferAvailable将input buffer返回给上层
onInputBufferAvailable();
}
}
} else if (mFlags & kFlagDequeueInputPending) {
// 如果是同步模式,并且处在阻塞等待的状态,收到input buffer,发送消息结束阻塞
CHECK(handleDequeueInputBuffer(mDequeueInputReplyID));
// 增加阻塞等待计数,使得kWhatDequeueInputTimedOut无效
++mDequeueInputTimeoutGeneration;
mFlags &= ~kFlagDequeueInputPending;
mDequeueInputReplyID = 0;
} else {
postActivityNotificationIfPossible();
}
break;
}
kWhatFillThisBuffer 消息处理流程中的内容稍有一点多,我们有选择的对内容进行展开:
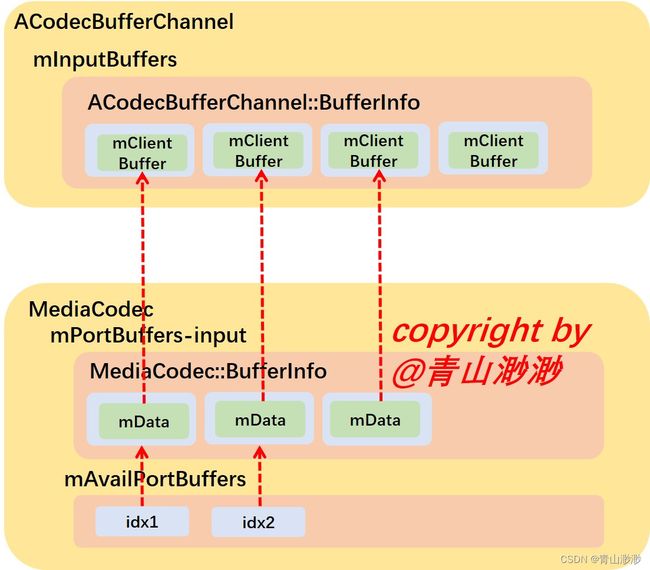
- 将拿到的 MediaCodec 加入到列表当中,这里的列表有两个,一个是用来记录 ACodecBufferChannel 中所有的 buffer(分为input / output 两个数组)
mPortBuffers;第二个列表是用来记录可用的input/output buffer的mAvailPortBuffers,同样分为input / output 两个数组,这里面记录的是可用的索引。
size_t MediaCodec::updateBuffers(
int32_t portIndex, const sp<AMessage> &msg) {
CHECK(portIndex == kPortIndexInput || portIndex == kPortIndexOutput);
size_t index;
CHECK(msg->findSize("index", &index));
sp<RefBase> obj;
CHECK(msg->findObject("buffer", &obj));
sp<MediaCodecBuffer> buffer = static_cast<MediaCodecBuffer *>(obj.get());
{
Mutex::Autolock al(mBufferLock);
if (mPortBuffers[portIndex].size() <= index) {
mPortBuffers[portIndex].resize(align(index + 1, kNumBuffersAlign));
}
mPortBuffers[portIndex][index].mData = buffer;
}
mAvailPortBuffers[portIndex].push_back(index);
return index;
}
- ==这里有一点非常重要,如果没看懂很容易对接下来的内容产生疑惑:==将传来的MediaCodecBuffer记录到 mPortBuffers 中时,这里会有一个隐式转换,用 MediaCodecBuffer 创建了一个 MediaCodec::BufferInfo,好家伙,人手一个bufferinfo是吧。
struct BufferInfo {
BufferInfo();
sp<MediaCodecBuffer> mData;
bool mOwnedByClient;
};
MediaCodec::BufferInfo::BufferInfo() : mOwnedByClient(false) {}
- 如果正在处理release/stop/release,则直接将所有的buffer返回给Codec,MediaCodec 不会持有任何 buffer;
void MediaCodec::returnBuffersToCodecOnPort(int32_t portIndex, bool isReclaim) {
CHECK(portIndex == kPortIndexInput || portIndex == kPortIndexOutput);
Mutex::Autolock al(mBufferLock);
if (portIndex == kPortIndexInput) {
mLeftover.clear();
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < mPortBuffers[portIndex].size(); ++i) {
BufferInfo *info = &mPortBuffers[portIndex][i];
if (info->mData != nullptr) {
sp<MediaCodecBuffer> buffer = info->mData;
if (isReclaim && info->mOwnedByClient) {
ALOGD("port %d buffer %zu still owned by client when codec is reclaimed",
portIndex, i);
} else {
info->mOwnedByClient = false;
info->mData.clear();
}
mBufferChannel->discardBuffer(buffer);
}
}
mAvailPortBuffers[portIndex].clear();
}
- returnBuffersToCodecOnPort 会遍历所有 MediaCodec 记录的 BufferChannel 中的 buffer,这里之所以要遍历记录的buffer,是因为可能刚开始解码,还有buffer没有传给MediaCodec流程就结束了;MediaCodecBuffer 的 mOwnedByClient 指的是 buffer 是否被上层 app 所持有;