树与二叉树——练习题
深度优先遍历(借用栈)
前序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
中序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
后序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
广度优先遍历(借用队列)
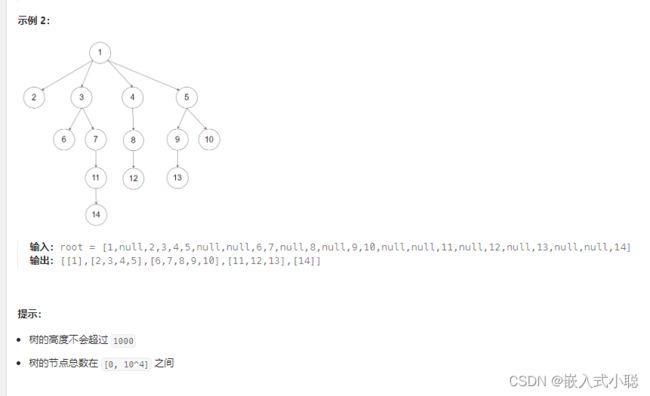
层次遍历(迭代法)
递归三步曲:
- 「确定递归函数的参数和返回值:」确定哪些参数是递归的过程中需要处理的,那么就在递归函数里加上这个参数, 并且还要明确每次递归的返回值是什么进而确定递归函数的返回类型
- 「确定终止条件:」写完了递归算法, 运行的时候,经常会遇到栈溢出的错误,就是没写终止条件或者终止条件写的不对,操作系统也是用一个栈的结构来保存每一层递归的信息,如果递归没有终止,操作系统的内存栈必然就会溢出
- 「确定单层递归的逻辑:」确定每一层递归需要处理的信息。在这里也就会重复调用自己来实现递归的过程
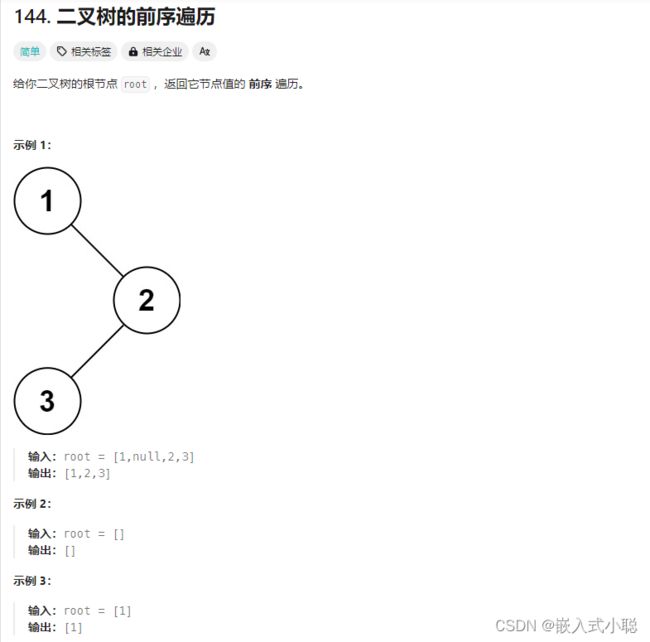
1. ✌二叉树的前序遍历
代码实现:递归 + 迭代
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ #define MAX_NODE 100 // 递归 void pre_order1(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* returnSize) { if (root == NULL) { // 终止条件 return ; } res[(*returnSize)++] = root->val; pre_order1(root->left, res, returnSize); pre_order1(root->right, res, returnSize); } // 迭代(非递归) 深度优先搜索---借用栈 void pre_order2(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* returnSize) { if (root == NULL) { return ; } struct TreeNode* stack[MAX_NODE]; // 创建一个栈 int top = -1; // 栈顶 stack[++top] = root; while (top != -1) { // 栈不为空则执行while循环 struct TreeNode* node = stack[top]; // 记录栈顶 res[(*returnSize)++] = node->val; top--; if (node->right) { // 右子树先进栈 stack[++top] = node->right; } if (node->left) { stack[++top] = node->left; } } } int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) { int* res = malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX_NODE); *returnSize = 0; pre_order1(root, res, returnSize); pre_order2(root, res, returnSize); return res; }
2. ✌二叉树的中序遍历
代码实现:递归 + 迭代
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ #define MAX_NODE 100 // 递归 void mid_order1(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* returnSize) { if (root == NULL) { // 终止条件 return ; } mid_order1(root->left, res, returnSize); res[(*returnSize)++] = root->val; mid_order1(root->right, res, returnSize); } // 迭代(非递归) 深度优先搜索---借用栈 void mid_order2(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* returnSize) { if (root == NULL) { return ; } struct TreeNode* stack[MAX_NODE]; // 创建一个栈 int top = -1; // 栈顶 struct TreeNode* p = root; struct TreeNode* q = NULL; while (p || top != -1) { if (p) { stack[++top] = p; p = p->left; } else { q = stack[top]; res[(*returnSize)++] = q->val; top--; p = q->right; } } } int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) { int* res = malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX_NODE); *returnSize = 0; mid_order1(root, res, returnSize); mid_order2(root, res, returnSize); return res; }
3. 二叉树的后序遍历
代码实现:递归 + 两种迭代方法
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ #define MAX_NODE 100 // 递归 void post_order1(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* returnSize) { if (root == NULL) { // 终止条件 return ; } post_order1(root->left, res, returnSize); post_order1(root->right, res, returnSize); res[(*returnSize)++] = root->val; } // 迭代(非递归) 深度优先搜索---借用栈 /* 第一种方法: 先序遍历是 中左右 --->调整代码左右循序--->中右左--->反转result数组--->左右中 后序遍历是 左右中 */ void post_order2(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* returnSize) { if (root == NULL) { return ; } struct TreeNode* stack[MAX_NODE]; // 创建一个栈 int top = -1; // 栈顶 stack[++top] = root; while (top != -1) { // 栈不为空则执行while循环 struct TreeNode* node = stack[top]; // 记录栈顶 res[(*returnSize)++] = node->val; top--; if (node->right) { // 右子树先进栈 stack[++top] = node->right; } if (node->left) { stack[++top] = node->left; } } // 反转res数组 int i = 0, j = *returnSize - 1; while (i < j) { int temp = res[i]; res[i] = res[j]; res[j] = temp; i++; j--; } } /* 第二种方法: 1、沿着根的左孩子,依次入栈,直到左孩子为空; 2、读栈顶元素进行判定,若右孩子不空且未被访问,将右孩子执行第一步; 3、栈顶元素出栈。 */ struct TreeNode* stack[MAX_NODE]; // 定义一个栈 int top = -1; // 栈顶 void post_order3(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* returnSize) { struct TreeNode *p = root, *r = NULL; // r标记最近访问过的结点 while (p || top != -1) { if (p) { stack[++top] = p; p = p->left; } else { p = stack[top]; // 获取栈顶元素赋值给p // ❤case one❤ if (p->right && p->right != r) { // 若右孩子存在且未被访问 p = p->right; // 就让右孩子 stack[++top] = p; // 入栈 p = p->left; // 让右孩子向左 // 上面三句意思就是让右孩子的左孩子一直入栈,一直向左走 } else { // ❤case two❤ res[(*returnSize)++] = stack[top--]->val; // 右孩子为空或未被访问过,就出栈 r = p; // r标记最近访问结点 p = NULL; // r置空 // 置空原因:因为这个结点已经出栈了 } } } } int* postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) { int* res = malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX_NODE); *returnSize = 0; post_order1(root, res, returnSize); post_order2(root, res, returnSize); post_order3(root, res, returnSize); return res; }
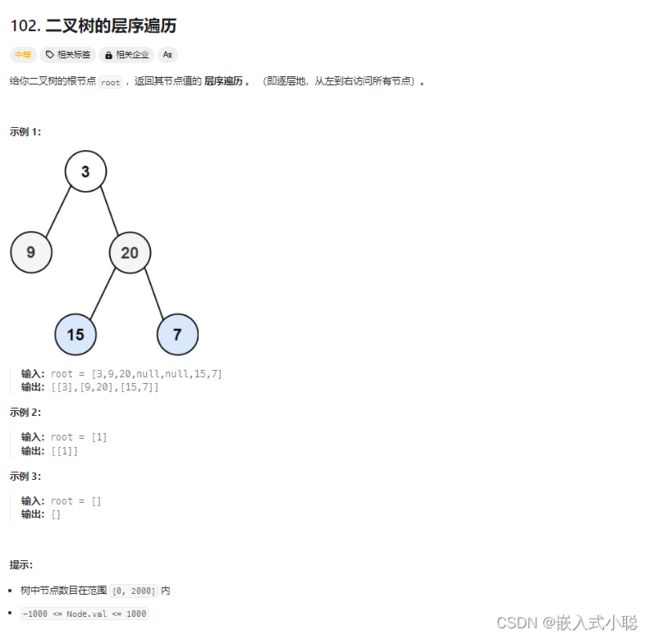
4. 二叉树的层序遍历
代码实现:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize. * The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array. * Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ // returnColumnSizes:用于存储每个数组中元素个数 int** levelOrder(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes) { *returnSize = 0; if (root == NULL) { return NULL; } int** res = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * 2000); *returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2000); struct TreeNode* queue[2001]; // 创建一个队列 注意:队头不放元素,长度须+1 int head = 0; // 队头 int tail = 0; // 队尾 queue[++tail] = root; //head:不存放数据,tail:存放数据 while (head < tail) { int colSize = 0, last = tail; res[*returnSize] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (last - head)); while (head < last) { struct TreeNode* node = queue[++head]; res[*returnSize][colSize++] = node->val; if (node->left != NULL) { queue[++tail] = node->left; } if (node->right != NULL) { queue[++tail] = node->right; } } (*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize] = colSize; (*returnSize)++; } return res; }
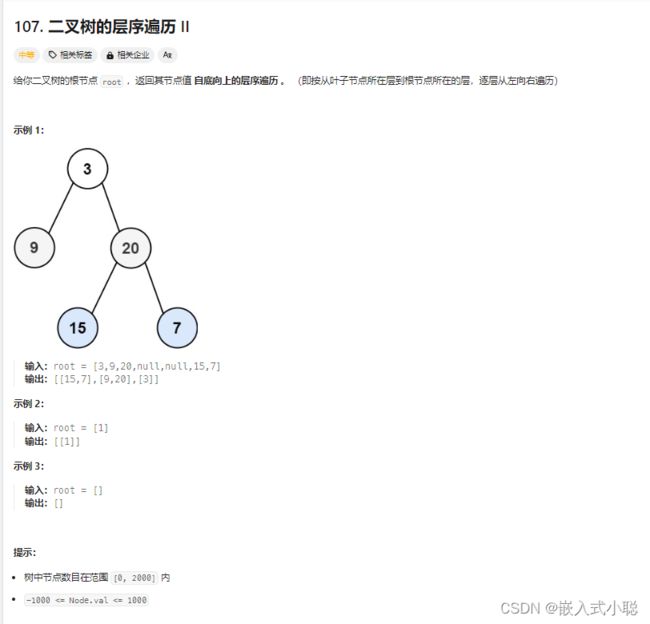
5. 二叉树的层序遍历||
思路:相对于102.二叉树的层序遍历,就是最后把res数组反转一下就可以了
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize. * The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array. * Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ // returnColumnSizes:用于存储每个数组中元素个数 int** levelOrderBottom(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes) { *returnSize = 0; if (root == NULL) { return NULL; } int** res = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * 2000); *returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2000); struct TreeNode* queue[2001]; // 创建一个队列 注意:队头不放元素,长度须+1 int head = 0; // 队头 int tail = 0; // 队尾 queue[++tail] = root; //head:不存放数据,tail:存放数据 while (head < tail) { int colSize = 0, last = tail; res[*returnSize] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (last - head)); while (head < last) { struct TreeNode* node = queue[++head]; res[*returnSize][colSize++] = node->val; if (node->left) { queue[++tail] = node->left; } if (node->right) { queue[++tail] = node->right; } } (*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize] = colSize; (*returnSize)++; } // 反转res数组 int** ret = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * (*returnSize)); int nums[*returnSize]; for (int i = 0; i < *returnSize; i++) { nums[i] = (*returnColumnSizes)[i]; } for (int i = 0; i < *returnSize; i++) { (*returnColumnSizes)[i] = nums[*returnSize - i - 1]; } for (int i = 0; i < *returnSize; i++) { ret[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * nums[*returnSize - i - 1]); for (int j = 0; j < nums[*returnSize - i - 1]; j++) { ret[i][j] = res[*returnSize - i - 1][j]; } } free(res); return ret; }
6. 二叉树的右视图
思路:层序遍历的时候,判断是否遍历到单层的最后一个元素,如果是,就放进result数组中,随后返回result就可以了
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ int* rightSideView(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) { int* ret = malloc(sizeof(int) * 100); memset(ret, 0, sizeof(int) * 100); *returnSize = 0; if (root == NULL) { return ret; } struct TreeNode* queue[101]; // 创建一个队列 int head = 0; // 对头 int tail = 0; // 队尾 queue[++tail] = root; //head:不存放数据,tail:存放数据 while (head < tail) { int last = tail; while (head < last) { struct TreeNode* node = queue[++head]; if (head == last) { ret[(*returnSize)++] = node->val; } if (node->left) { queue[++tail] = node->left; } if (node->right) { queue[++tail] = node->right; } } } return ret; }
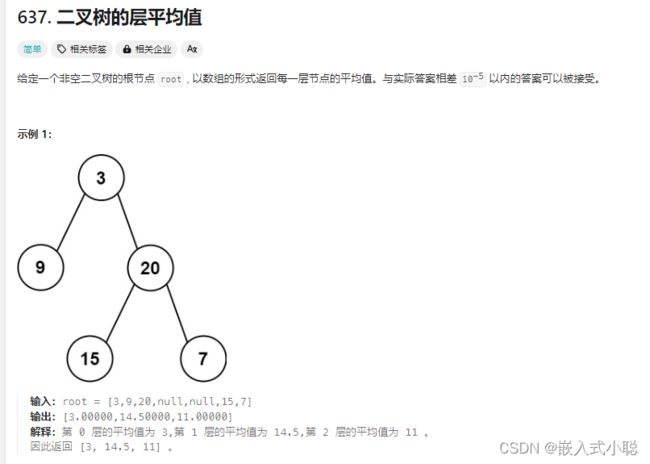
7. 二叉树的层平均值
代码实现:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ double* averageOfLevels(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) { double* ret = malloc(sizeof(double) * 10000); memset(ret, 0, sizeof(int) * 10000); *returnSize = 0; if (root == NULL) { return ret; } struct TreeNode* queue[10001]; // 创建一个队列 int head = 0; // 对头 int tail = 0; // 队尾 queue[++tail] = root; //head:不存放数据,tail:存放数据 while (head < tail) { int last = tail; double sum = 0; int size = tail - head; // 每层结点个数 while (head < last) { struct TreeNode* node = queue[++head]; sum += node->val; if (node->left) { queue[++tail] = node->left; } if (node->right) { queue[++tail] = node->right; } } ret[(*returnSize)++] = sum / size; } return ret; }
8. N叉树的前序遍历
9. 在每个树行中找最大值 515
10. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 116
11. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针|| 117
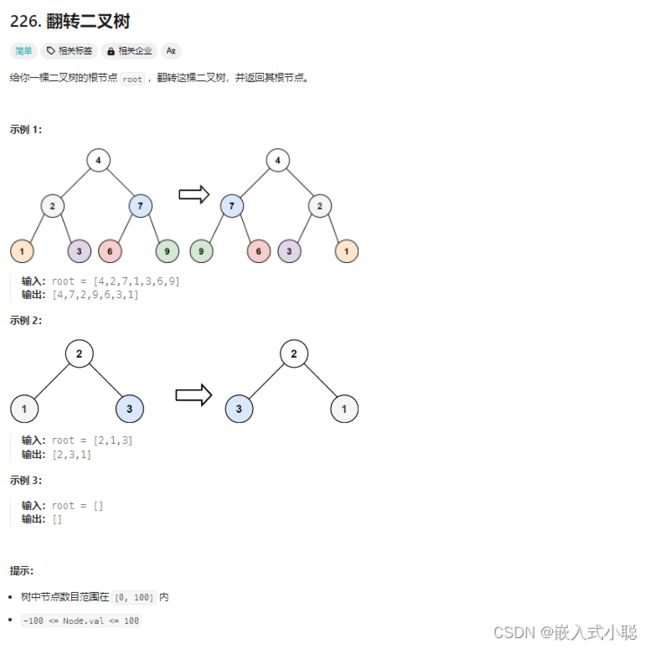
12. 翻转二叉树
思路:
- 在翻转时,需要从根节点往下先交换左右子树,然后再递归到左右子树进行相同的操作
(前序遍历 and 层序遍历)
- 在翻转时,需要从下往上先交换左右子树,然后再递归到父节点进行交换(后序遍历)
- 中序遍历不可以(原因:先翻转左子树, 然后左右子树交换,这时候再翻转的右子树是之前的左子树)
层序遍历:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ // 交换左右子树 void swap(struct TreeNode* root) { struct TreeNode* l = root->left; struct TreeNode* r = root->right; root->left = r; root->right = l; } struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return root; } struct TreeNode* queue[101]; // 创建一个队列 int head = 0; // 队头 int tail = 0; // 队尾 queue[++tail] = root; // head:不存放数据,tail:存放数据 while (head < tail) { struct TreeNode* node = queue[++head]; swap(node); // 翻转 if (node->left) { queue[++tail] = node->left; } if (node->right) { queue[++tail] = node->right; } } return root; }前序遍历:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ // 交换左右子树 void swap(struct TreeNode* root) { struct TreeNode* l = root->left; struct TreeNode* r = root->right; root->left = r; root->right = l; } // 递归:先序遍历 void pre_order(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return ; } swap(root); // 交换 if (root->left) { pre_order(root->left); } if (root->right) { pre_order(root->right); } } struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return root; } pre_order(root); return root; }后序遍历:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ // 交换左右子树 void swap(struct TreeNode* root) { struct TreeNode* l = root->left; struct TreeNode* r = root->right; root->left = r; root->right = l; } // 递归:后序遍历 void pre_order(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return ; } if (root->left) { pre_order(root->left); } if (root->right) { pre_order(root->right); } swap(root); // 交换 } struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return root; } pre_order(root); return root; }
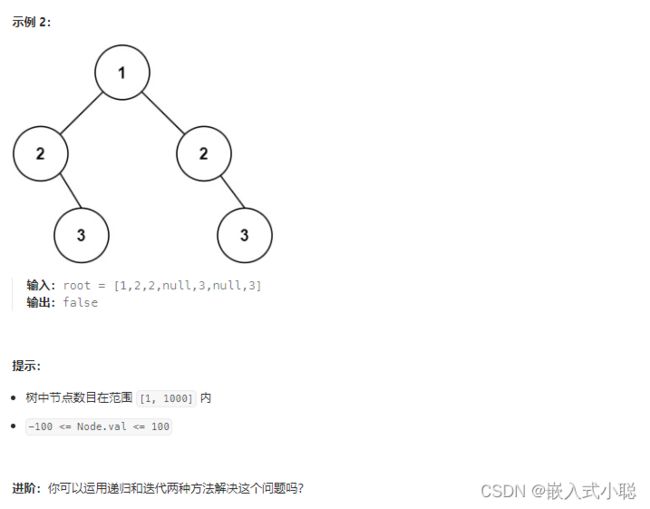
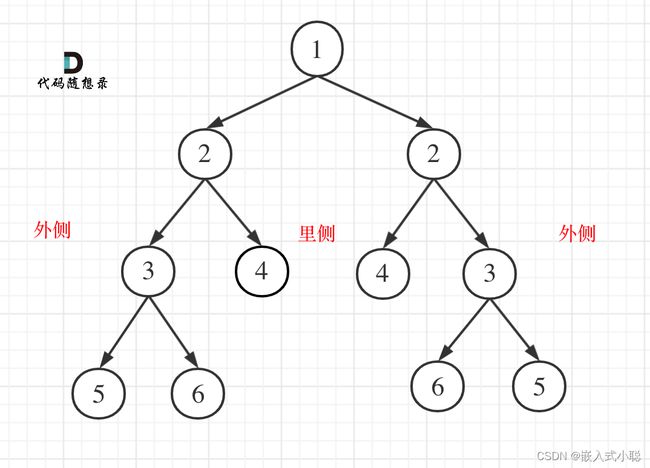
13. 对称二叉树
分析:比较的是两个子树的里侧和外侧的元素是否相等
本题遍历只能是“后序遍历”,因为我们要通过递归函数的返回值来判断两个子树的内侧节点和外侧节点是否相等
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ bool compare(struct TreeNode* l, struct TreeNode* r) { // 首先排除空节点的情况 if (l == NULL && r != NULL) { return false; } else if (l != NULL && r == NULL) { return false; } else if (l == NULL && r == NULL) { return true; } else if (l->val != r->val) { // 排除了空节点,再排除数值不相同的情况 return false; } // 此时就是:左右节点都不为空,且数值相同的情况 // 此时才做递归,做下一层的判断 return compare(l->left, r->right) && compare(l->right, r->left); } bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return true; } return compare(root->left, root->right); }
14. 二叉树的最大深度
后序遍历:通过递归函数的返回值做计算树的高度
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ #define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) int getDepth(struct TreeNode* node) { if (node == NULL) { return 0; } int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left); // 左 int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right); // 右 int depth = 1 + max(leftDepth, rightDepth); // 中 return depth; } int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root) { return getDepth(root); }精简代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ #define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return 0; } return 1 + max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)); }前序遍历:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ int result; void getDepth(struct TreeNode* node, int depth) { result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中 if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) { return ; } // 左 if (node->left) { depth++; // 深度+1 getDepth(node->left, depth); depth--; // 回溯,深度-1 } // 右 if (node->right) { depth++; // 深度+1 getDepth(node->right, depth); depth--; // 回溯,深度-1 } } int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root) { result = 0; if (root == NULL) { return result; } getDepth(root, 1); return result; }层序遍历:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return 0; } int depth = 0; struct TreeNode* queue[10001]; int head = 0; int tail = 0; queue[++tail] = root; //head:不存放数据,tail:存放数据 while (head < tail) { int last = tail; depth++; while (head < last) { struct TreeNode* node = queue[++head]; if (node->left) { queue[++tail] = node->left; } if (node->right) { queue[++tail] = node->right; } } } return depth; }
15. N叉树的最大深度
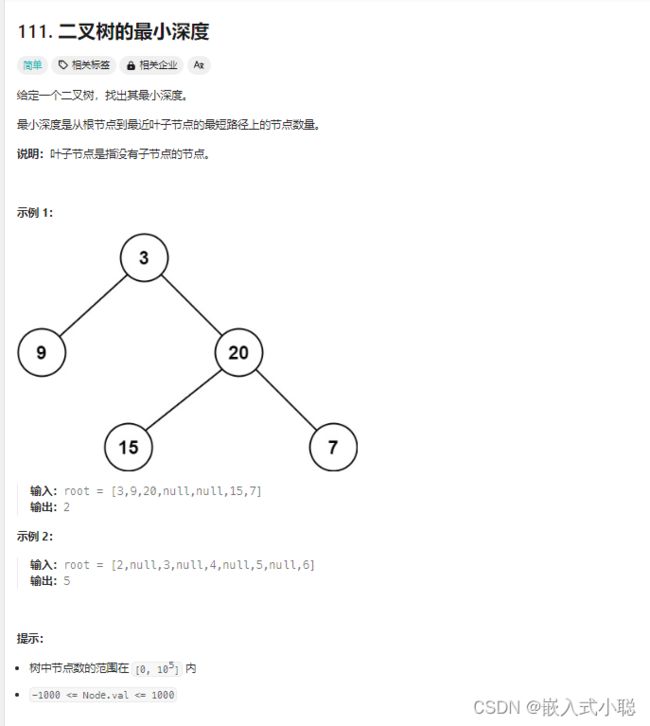
16. 二叉树的最小深度
注意:最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量(左右孩子都为空的节点才是叶子节点!)
后序遍历:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ #define min(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (b) : (a)) int getDepth(struct TreeNode* node) { if (node == NULL) { return 0; } int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left); // 左 int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right); // 右 // 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点 if (node->left == NULL && node->right != NULL) { return 1 + rightDepth; } // 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点 if (node->left != NULL && node->right == NULL) { return 1 + leftDepth; } int result = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth); return result; } int minDepth(struct TreeNode* root) { return getDepth(root); }精简代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ #define min(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (b) : (a)) int minDepth(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return 0; } if (root->left == NULL && root->right != NULL) { return 1 + minDepth(root->right); } if (root->left != NULL && root->right == NULL) { return 1 + minDepth(root->left); } return 1 + min(minDepth(root->left), minDepth(root->right)); }层序遍历:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ #define min(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (b) : (a)) int minDepth(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return 0; } int depth = 0; struct TreeNode* queue[100001]; int head = 0; int tail = 0; queue[++tail] = root; //head:不存放数据,tail:存放数据 while (head < tail) { int last = tail; depth++; int flag = 0; while (head < last) { struct TreeNode* node = queue[++head]; if (node->left) { queue[++tail] = node->left; } if (node->right) { queue[++tail] = node->right; } if (!node->left && !node->right) { // 当左右孩子都为空的时候,说明是最低点的一层了,退出 flag = 1; break; } } if (flag == 1) { break; } } return depth; }
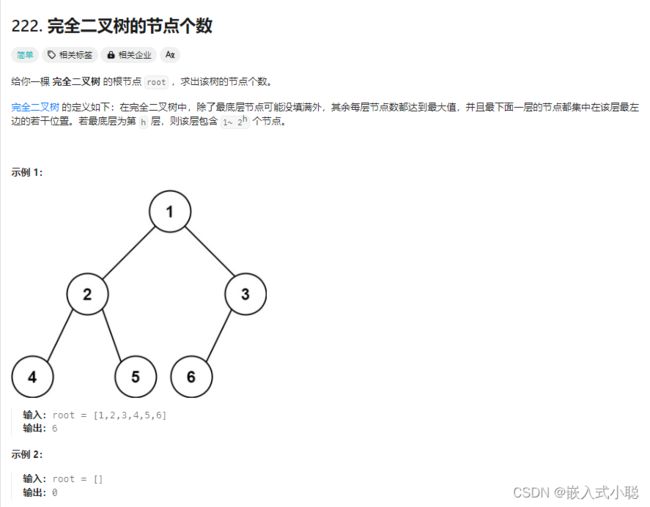
17. 完全二叉树的节点个数
后序遍历:
层序遍历:
18. 平衡二叉树
二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数
二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数
后序遍历:
层序遍历:
19. 二叉树的所有路径
前序遍历:让父节点指向孩子节点,找到对应的路径
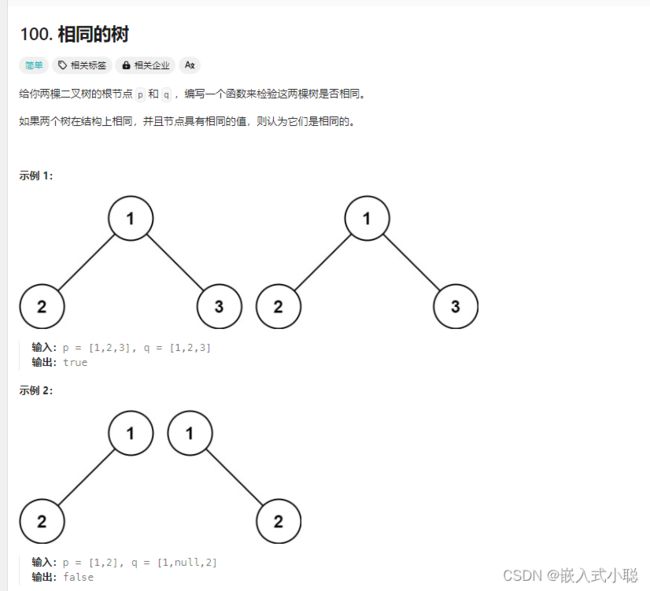
20. 相同的树
21. 左叶子之和
后序遍历(左右中):通过递归函数的返回值来累加求取左叶子数值之和
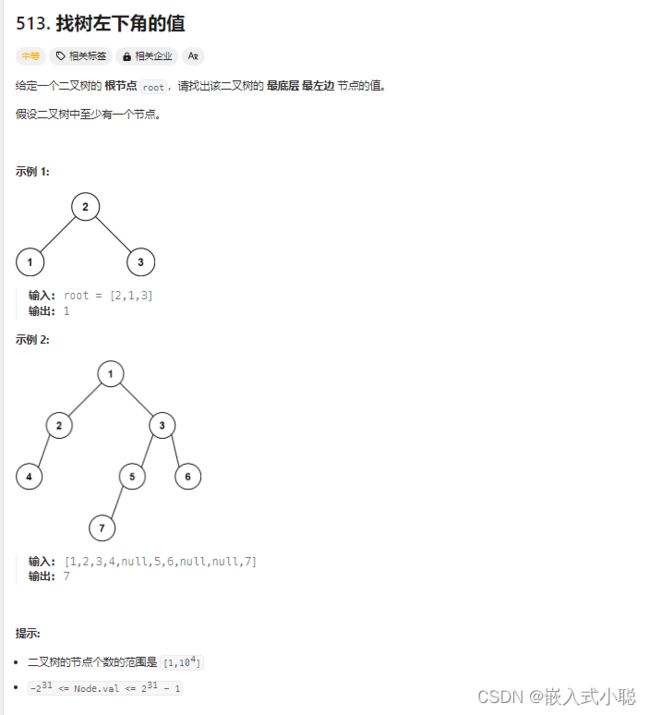
22. 找树左下角的值
层序遍历:
前序遍历:深度最大的叶子节点一定是最后一行,记录深度最大的叶子节点,此时就是树的最后一行最左边的值
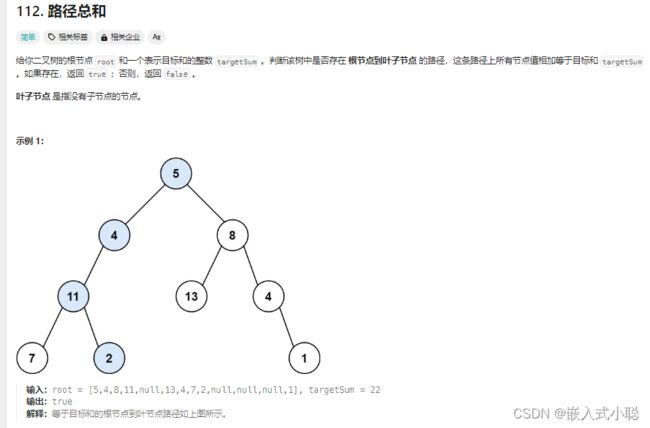
23. 路径总和
前序遍历:
中序遍历:
后序遍历:
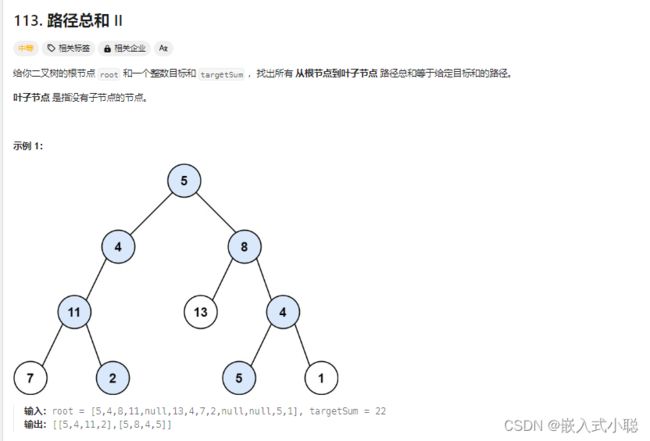
24. 路径总和||
前序遍历:
中序遍历:
后序遍历:
25. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
第一步:如果数组大小为零的话,说明是空节点了。
第二步:如果不为空,那么取后序数组最后一个元素作为节点元素。
第三步:找到后序数组最后一个元素在中序数组的位置,作为切割点
第四步:切割中序数组,切成中序左数组和中序右数组 (顺序别搞反了,一定是先切中 序数组)
第五步:切割后序数组,切成后序左数组和后序右数组
第六步:递归处理左区间和右区间
代码实现:
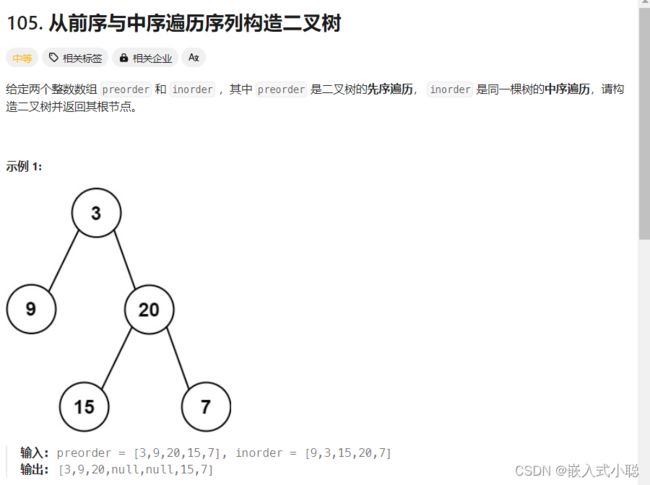
26. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
27. 最大二叉树
分析:构造树一般采用的是前序遍历,因为先构造中间节点,然后递归构造左子树和右子树
代码实现:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ struct TreeNode* construct(const int* nums, int l, int r) { if (l > r) { return NULL; } int best = l; // 最大值下标 for (int i = l + 1; i <= r; i++) { if (nums[i] > nums[best]) { best = i; } } struct TreeNode* node = (struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode)); node->val = nums[best]; node->left = construct(nums, l, best - 1); node->right = construct(nums, best + 1, r); return node; } struct TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(int* nums, int numsSize) { return construct(nums, 0, numsSize - 1); }
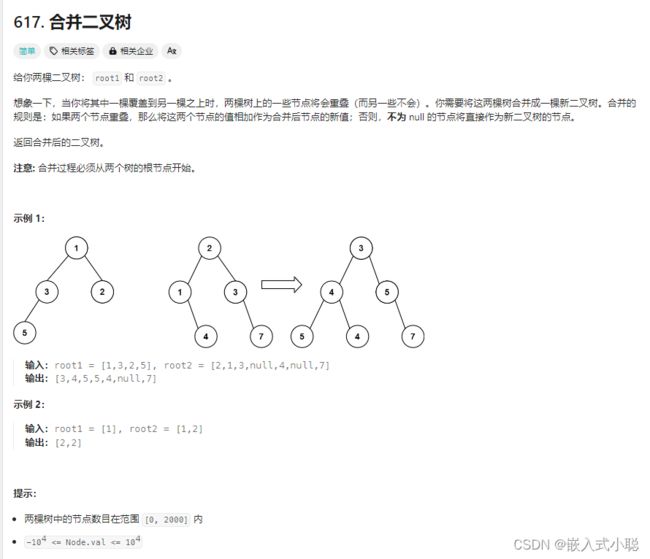
28. 合并两个二叉树
前序遍历:
中序遍历:
后序遍历:
层序遍历:
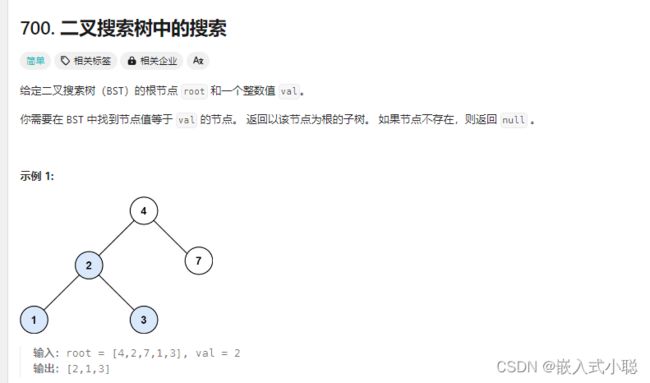
29. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
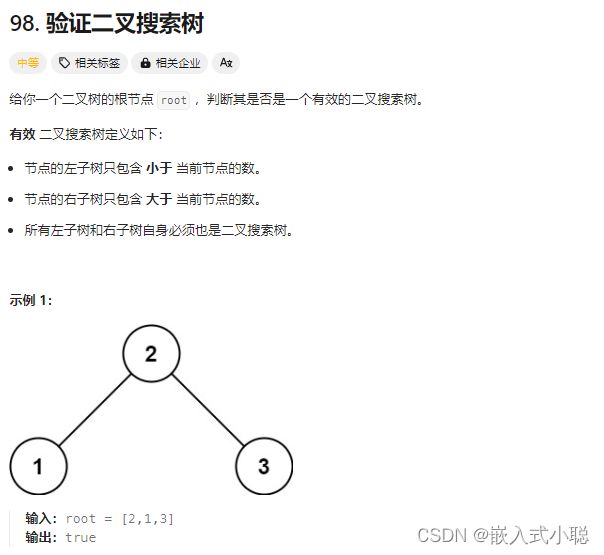
29. 验证二叉搜索树
代码实现:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ bool isValidBSTHelper(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* pre) { if (root == NULL) { return true; } // 检查左子树 bool left = isValidBSTHelper(root->left, pre); // 检查当前节点 if (pre != NULL && pre->val >= root->val) { return false; } // 记录前一个节点 pre = root; // 检查右子树 bool right = isValidBSTHelper(root->right, pre); return left && right; } bool isValidBST(struct TreeNode* root) { // 初始时前一个节点为空 return isValidBSTHelper(root, NULL); }
30. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
31. 二叉搜索树中的众数
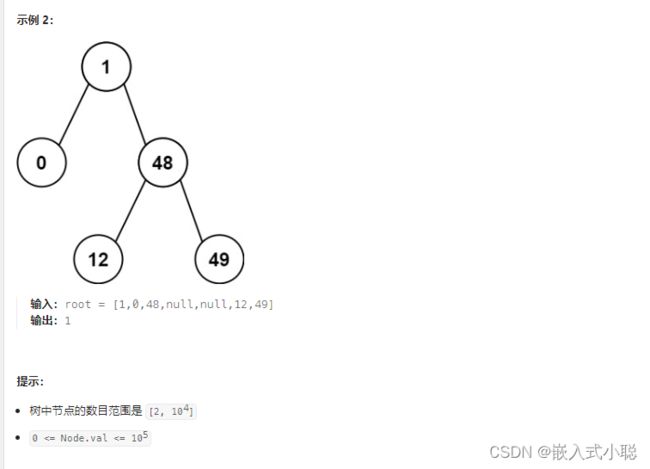
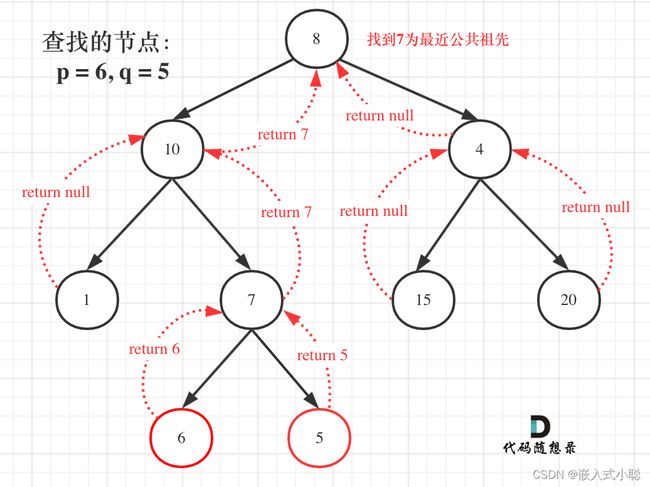
32. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
代码实现:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ struct TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) { if (root == q || root == p || root == NULL) { return root; } struct TreeNode* l = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q); struct TreeNode* r = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q); if (l != NULL && r != NULL) { return root; } if (l == NULL && r != NULL) { return r; } else if (l != NULL && r == NULL) { return l; } else { return NULL; } }精简代码:
33. 搜索树的公共祖先问题
递归:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ struct TreeNode* dfs(struct TreeNode* cur, struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) { if (cur == NULL) { return NULL; } if (cur->val > p->val && cur->val > q->val) { // 左 struct TreeNode* l = dfs(cur->left, p, q); if (l != NULL) { return l; } } if (cur->val < p->val && cur->val < q->val) { // 右 struct TreeNode* r = dfs(cur->right, p, q); if (r != NULL) { return r; } } return cur; } struct TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) { return dfs(root, p, q); }
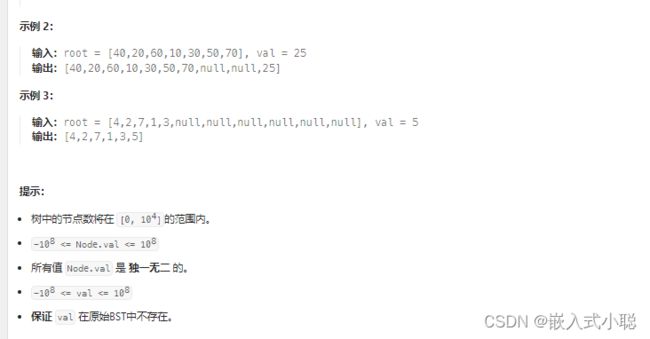
34. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
递归:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ struct TreeNode* insertIntoBST(struct TreeNode* root, int val) { if (root == NULL) { struct TreeNode* node = malloc(sizeof(*node)); node->left = node->right = NULL; node->val = val; return node; } if (root->val > val) { root->left = insertIntoBST(root->left, val); } if (root->val < val) { root->right = insertIntoBST(root->right, val); } return root; }
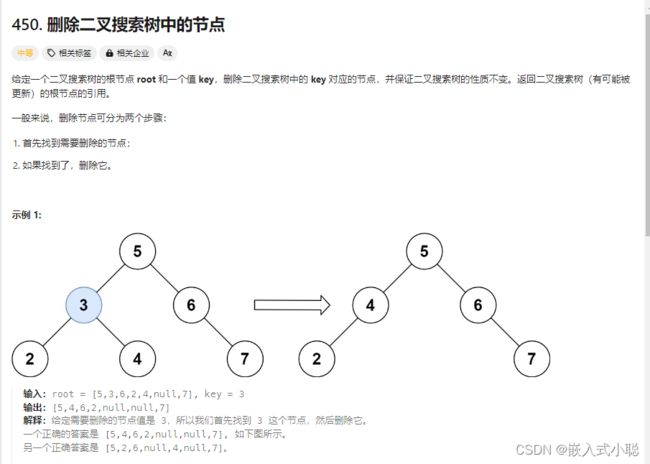
35. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
分析:
有以下五种情况:
第一种情况:没找到删除的节点,遍历到空节点直接返回了
找到删除的节点
第二种情况:左右孩子都为空(叶子节点),直接删除节点, 返回NULL为根节点
第三种情况:删除节点的左孩子为空,右孩子不为空,删除节点,右孩子补位,返回右孩子为根节点
第四种情况:删除节点的右孩子为空,左孩子不为空,删除节点,左孩子补位,返回左孩子为根节点
第五种情况:左右孩子节点都不为空,则将删除节点的左子树头结点(左孩子)放到删除节点的右子树的最左边节点的左孩子上,返回删除节点右孩子为新的根节点
递归:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ struct TreeNode* deleteNode(struct TreeNode* root, int key){ // 第一种情况:没找到删除的节点,遍历到空节点直接返回了 if (root == NULL) { return root; } if (root->val == key) { // 第二种情况:左右孩子都为空(叶子节点),直接删除节点, 返回NULL为根节点 // 第三种情况:其左孩子为空,右孩子不为空,删除节点,右孩子补位 ,返回右孩子为根节点 if (root->left == NULL) { return root->right; // 第四种情况:其右孩子为空,左孩子不为空,删除节点,左孩子补位,返回左孩子为根节点 } else if (root->right == NULL) { return root->left; // 第五种情况:左右孩子节点都不为空,则将删除节点的左子树放到删除节点的右子树的最左边节点的左孩子的位置 // 并返回删除节点右孩子为新的根节点 } else { struct TreeNode* node = root->right; // 找右子树最左边的节点 while (node->left != NULL) { node = node->left; } node->left = root->left; // 把要删除的节点(root)左子树放在cur的左孩子的位置 struct TreeNode* tmp = root; // 把root节点保存一下,下面来删除 root = root->right; // 返回旧root的右孩子作为新root free(tmp); // 释放节点内存 return root; } } if (root->val > key) { root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key); } if (root->val < key) { root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key); } return root; }迭代:
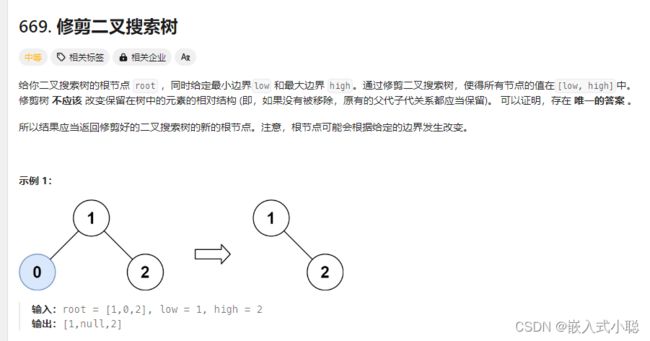
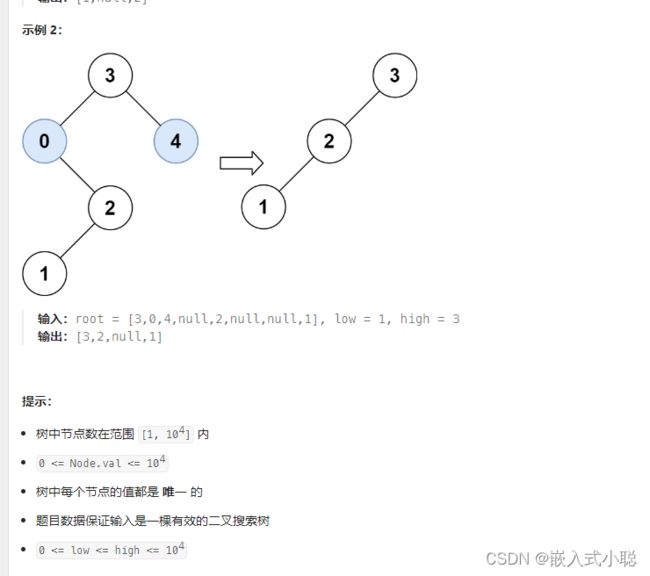
36. 修剪二叉搜索树
递归:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ struct TreeNode* trimBST(struct TreeNode* root, int low, int high) { if (root == NULL) { return NULL; } if (root->val < low) { // 寻找符合区间[low, high]的节点 return trimBST(root->right, low, high); } if (root->val > high) { // 寻找符合区间[low, high]的节点 return trimBST(root->left, low, high); } root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high); // root->left接入符合条件的左孩子 root->right = trimBST(root->right, low, high); // root->right接入符合条件的右孩子 return root; }
37. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
分析:分割数组中间位置的节点
递归:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ // 左闭右闭 struct TreeNode* pre_order(int* nums, int l, int r) { if (l > r) { return NULL; } int mid = (r + l) / 2; struct TreeNode* root = malloc(sizeof(*root)); root->left = root->right = NULL; root->val = nums[mid]; root->left = pre_order(nums, l, mid - 1); root->right = pre_order(nums, mid + 1, r); return root; } struct TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(int* nums, int numsSize) { return pre_order(nums, 0, numsSize - 1); }
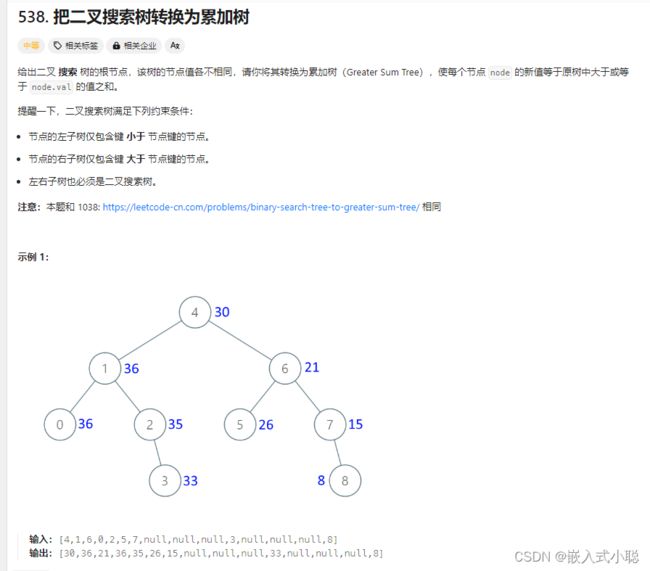
38. ✌把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
反中序遍历(递归):
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ int pre; // 记录前一个结点的数值 // 反中序遍历(右左中) 递归 void mid_order(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return ; } mid_order(root->right); root->val += pre; pre = root->val; mid_order(root->left); } struct TreeNode* convertBST(struct TreeNode* root) { pre = 0; mid_order(root); return root; }反中序遍历(迭代):
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ #define MAX_NODE 10000 int pre; // 记录前一个结点的数值 // 反中序遍历(右左中) 迭代 void mid_order(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return ; } struct TreeNode* stack[MAX_NODE]; // 创建一个栈 int top = -1; // 栈顶 struct TreeNode* p = root; struct TreeNode* q = NULL; while (p || top != -1) { if (p) { stack[++top] = p; p = p->right; // 右 } else { q = stack[top]; q->val += pre; pre = q->val; top--; p = q->left; // 左 } } } struct TreeNode* convertBST(struct TreeNode* root) { pre = 0; mid_order(root); return root; }