部署kvm虚拟化
一.虚拟化介绍
虚拟化是云计算的基础。简单的说,虚拟化使得在一台物理的服务器上可以跑多台虚拟机,虚拟机共享物理机的 CPU、内存、IO 硬件资源,但逻辑上虚拟机之间是相互隔离的。
物理机我们一般称为宿主机(Host),宿主机上面的虚拟机称为客户机(Guest)。
那么 Host 是如何将自己的硬件资源虚拟化,并提供给 Guest 使用的呢?
这个主要是通过一个叫做 Hypervisor 的程序实现的。
根据 Hypervisor 的实现方式和所处的位置,虚拟化又分为两种:
- 全虚拟化
- 半虚拟化
全虚拟化:
Hypervisor 直接安装在物理机上,多个虚拟机在 Hypervisor 上运行。Hypervisor 实现方式一般是一个特殊定制的 Linux 系统。Xen 和 VMWare 的 ESXi 都属于这个类型
半虚拟化:
物理机上首先安装常规的操作系统,比如 Redhat、Ubuntu 和 Windows。Hypervisor 作为 OS 上的一个程序模块运行,并对管理虚拟机进行管理。KVM、VirtualBox 和 VMWare Workstation 都属于这个类型
理论上讲:
全虚拟化一般对硬件虚拟化功能进行了特别优化,性能上比半虚拟化要高;
半虚拟化因为基于普通的操作系统,会比较灵活,比如支持虚拟机嵌套。嵌套意味着可以在KVM虚拟机中再运行KVM
二.kvm介绍
kVM 全称是 Kernel-Based Virtual Machine。也就是说 KVM 是基于 Linux 内核实现的。
KVM有一个内核模块叫 kvm.ko,只用于管理虚拟 CPU 和内存。
那 IO 的虚拟化,比如存储和网络设备则是由 Linux 内核与Qemu来实现。
作为一个 Hypervisor,KVM 本身只关注虚拟机调度和内存管理这两个方面。IO 外设的任务交给 Linux 内核和 Qemu。
大家在网上看 KVM 相关文章的时候肯定经常会看到 Libvirt 这个东西。
Libvirt 就是 KVM 的管理工具。
其实,Libvirt 除了能管理 KVM 这种 Hypervisor,还能管理 Xen,VirtualBox 等。
Libvirt 包含 3 个东西:后台 daemon 程序 libvirtd、API 库和命令行工具 virsh
- libvirtd是服务程序,接收和处理 API 请求;
- API 库使得其他人可以开发基于 Libvirt 的高级工具,比如 virt-manager,这是个图形化的 KVM 管理工具;
- virsh 是我们经常要用的 KVM 命令行工具
三.kvm部署
实验环境:
系统类型——centos7
主机ip——192.168.80.143
1.kvm安装
部署前请确保你的CPU虚拟化功能已开启。分为两种情况:
- 虚拟机要关机设置CPU虚拟化
- 物理机要在BIOS里开启CPU虚拟化
关闭虚拟机打开虚拟机设置,开启虚拟化引擎(全部勾选)
无论两项还是三项均无影响,全部勾选即可
ps:虚拟机硬盘内存要给大一些,因为稍后要导入iso镜像,以防导入失败
配置网络源,并且安装依赖包以及相关命令
//配置网络源
[root@192 ~]# curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS7-Base-163.repo http://mirrors.163.com/.help/CentOS7-Base-163.repo
[root@192 ~]# sed -i 's/\$releasever/7/g' /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS7-Base-163.repo
[root@192 ~]# sed -i 's/^enabled=.*/enabled=1/g' /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS7-Base-163.repo
//安装依赖包,和命令
[root@192 ~]# yum -y install epel-release vim wget net-tools unzip zip gcc gcc-c++
关闭防火墙,并且验证cpu是否支持虚拟化
ps:出现vmx(inter)或者svm(amd)字样说明支持虚拟化(出现几个代表cpu具有几个核心)
//关闭防火墙
[root@192 ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/firewalld.service.
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service.
[root@192 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@192 ~]# vim /etc/selinux/config
SELINUX=disabled
[root@192 ~]# reboot
//验证cpu是否支持虚拟化,如果出现vmx(Intel)或svm(AMD)的字样说明支持
[root@192 ~]# egrep -o 'vmx|svm' /proc/cpuinfo
vmx
vmx
vmx
vmx安装kvm
//安装kvm
[root@192 ~]# yum -y install qemu-kvm qemu-kvm-tools qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python libvirt-client virt-install virt-viewer bridge-utils libguestfs-tools
因为我们要与生产环境中的其他服务器是同一个网段,所以要把kvm服务器的网卡配置为桥接模式
这样的话kvm创建的虚拟机就可以通过该桥接网卡和生产环境内部的其他服务器保持在同一个网段
//修改网卡为桥接模式
[root@192 ~]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
[root@192 network-scripts]# cp ifcfg-ens33 ifcfg-br0
[root@192 network-scripts]# vim ifcfg-br0
[root@192 network-scripts]# cat ifcfg-br0
TYPE=Bridge
BOOTPROTO=static
DEFROUTE="yes"
NAME=br0
DEVICE=br0
ONBOOT=yes
IPADDR=192.168.80.142
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=192.168.80.2
DNS1=192.168.80.2
[root@192 network-scripts]# vim ifcfg-ens33
[root@192 network-scripts]# cat ifcfg-ens33
OTPROTO="static"
DEFROUTE="yes"
NAME="ens33"
DEVICE="ens33"
ONBOOT="yes"
BRIDGE=br0
//重启网卡并且查看
[root@192 network-scripts]# systemctl restart network
[root@192 network-scripts]# ip a
1: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens33: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master br0 state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:4a:0a:17 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: br0: mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:4a:0a:17 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.80.142/24 brd 192.168.80.255 scope global noprefixroute br0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::c66:d2ff:fecc:bac9/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
启动服务并且加入开机自启
//启动服务,并且加入开机自启
[root@192 ~]# systemctl enable --now libvirtd验证并且测试安装结果
//验证安装结果
[root@192 ~]# lsmod | grep kvm
kvm_intel 188740 0
kvm 637515 1 kvm_intel
irqbypass 13503 1 kvm
//测试并验证安装结果
[root@192 ~]# virsh -c qemu:///system list
Id 名称 状态
----------------------------------------------------
[root@192 ~]# virsh --version
4.5.0
[root@192 ~]# virt-install --version
1.5.0
[root@192 ~]# ln -s /usr/libexec/qemu-kvm /usr/bin/qemu-kvm
[root@192 ~]# ll /usr/bin/qemu-kvm
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 21 8月 21 23:01 /usr/bin/qemu-kvm -> /usr/libexec/qemu-kvm
[root@192 ~]# lsmod |grep kvm
kvm_intel 188740 0
kvm 637515 1 kvm_intel
irqbypass 13503 1 kvm查看网桥信息
//查看网桥信息
[root@192 ~]# brctl show
bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces
br0 8000.000c294a0a17 no ens33
virbr0 8000.525400280fd0 yes virbr0-nic2.kvm web管理界面安装
//安装依赖包
[root@192 ~]# yum -y install git python-pip libvirt-python libxml2-python python-websockify supervisor nginx python-devel
//从GitHub上下载webvirtmgr
[root@192 ~]# cd /usr/local/src/
[root@192 src]# git clone git://github.com/retspen/webvirtmgr.git
正克隆到 'webvirtmgr'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 5614, done.
remote: Total 5614 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 5614
接收对象中: 100% (5614/5614), 2.97 MiB | 794.00 KiB/s, done.
处理 delta 中: 100% (3606/3606), done.
//安装webvirtmgr
[root@192 webvirtmgr]# pwd
/usr/local/src/webvirtmgr
[root@192 webvirtmgr]# pip install -r requirements.txt
//检查sqlite3是否安装
[root@192 webvirtmgr]# python
Python 2.7.5 (default, Jun 28 2022, 15:30:04)
[GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44)] on linux2
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import sqlite3
>>> exit()
报错处理
报错?
在上方从GitHub上下载webvirtmgr,如果直接下载,出现以下报错
[root@192 src]# git clone git://github.com/retspen/webvirtmgr.git
正克隆到 'webvirtmgr'...
fatal: unable to connect to github.com:
github.com[0: 20.205.243.166]: errno=????
问题解决:
输入以下代码即可解决
[root@192 src]# git config --global url."https://".insteadOf git://初始化账号信息
[root@192 webvirtmgr]# python manage.py syncdb
WARNING:root:No local_settings file found.
Creating tables ...
Creating table auth_permission
Creating table auth_group_permissions
Creating table auth_group
Creating table auth_user_groups
Creating table auth_user_user_permissions
Creating table auth_user
Creating table django_content_type
Creating table django_session
Creating table django_site
Creating table servers_compute
Creating table instance_instance
Creating table create_flavor
You just installed Django's auth system, which means you don't have any superusers defined.
Would you like to create one now? (yes/no): yes //是否创建超级管理员
Username (leave blank to use 'root'): //指定超级管理员用户名,默认为root
Email address: [email protected] //设置超级管理员邮箱
Password: //设置密码
Password (again): //再次输入
Superuser created successfully.
Installing custom SQL ...
Installing indexes ...
Installed 6 object(s) from 1 fixture(s)拷贝web网页至指定目录,并且生成密钥
//拷贝web页面
[root@192 src]# pwd
/usr/local/src
[root@192 src]# mkdir /var/www
[root@192 src]# cp -r /usr/local/src/webvirtmgr /var/www/
[root@192 src]# chown -R nginx.nginx /var/www/webvirtmgr/
//生成密钥
[root@192 src]# ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:zQgzp8bNK0B6s01uT85K8yZzIrw0R77lHPbVPWInlhA [email protected]
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| |
| |
| . + . E |
| o . O + . |
| . + * S o. |
| . @ . .... |
| .+ X * .*.o.|
| .o=+#oo .o + .|
| .ooBB . |
+----[SHA256]-----+
//由于webvirtmgr和kvm服务器部署在同一台机器,所以这里本地信任。如果kvm部署在其他他机器,那么这个是它的IP
[root@192 src]# ssh-copy-id 192.168.80.143
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.80.143 (192.168.80.143)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:4chrcHbdbZVo7uwRz3irhBqBcZz6qZcQgaA5T1rJAd4.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:b5:52:6f:c8:f9:09:f7:87:58:0a:9d:0a:d5:a8:47:b7.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
[email protected]'s password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh '192.168.80.143'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.配置端口转发
[root@192 src]# ssh 192.168.80.143 -L localhost:8000:localhost:8000 -L localhost:6080:localhost:60
Last login: Sun Aug 21 23:51:53 2022 from 192.168.80.1
[root@192 ~]# ss -anlt
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 5 192.168.122.1:53 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6080 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:8000 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:6080 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:8000 [::]:*配置nginx
[root@192 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
[root@192 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
# For more information on configuration, see:
# * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
# * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/doc/nginx/README.dynamic.
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /404.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
# Settings for a TLS enabled server.
#
# server {
# listen 443 ssl http2;
# listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
# server_name _;
# root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#
# ssl_certificate "/etc/pki/nginx/server.crt";
# ssl_certificate_key "/etc/pki/nginx/private/server.key";
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 10m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
#
# # Load configuration files for the default server block.
# include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
#
# error_page 404 /404.html;
# location = /40x.html {
# }
#
# error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
# location = /50x.html {
# }
# }
}
[root@192 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/webvirtmgr.conf
[root@192 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/webvirtmgr.conf
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name $hostname;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/webvirtmgr_access_log;
location /static/ {
root /var/www/webvirtmgr/webvirtmgr;
expires max;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-for $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $host:$server_port;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $remote_addr;
proxy_connect_timeout 600;
proxy_read_timeout 600;
proxy_send_timeout 600;
client_max_body_size 1024M;
}
}
确保bind绑定的是本机8000端口,后重启nginx并且加入开机自启
//确保为8000端口
[root@192 ~]# vim /var/www/webvirtmgr/conf/gunicorn.conf.py
bind = '0.0.0.0:8000'
backlog = 2048
//重启nginx并且设置开机自启
[root@192 ~]# systemctl restart nginx.service
[root@192 ~]# systemctl enable --now nginx.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service.
[root@192 ~]# ps -ef | grep nginx
root 93078 1 0 00:53 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx
nginx 93079 93078 0 00:53 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 93080 93078 0 00:53 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 93081 93078 0 00:53 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 93082 93078 0 00:53 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
root 93401 69901 0 00:53 pts/2 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx配置supervisor,启动并且加入开机自启
[root@192 ~]# vim /etc/supervisord.conf
//在文件末尾添加以下内容
[program:webvirtmgr]
command=/usr/bin/python2 /var/www/webvirtmgr/manage.py run_gunicorn -c /var/www/webvirtmgr/conf/gunicorn.conf.py
directory=/var/www/webvirtmgr
autostart=true
autorestart=true
logfile=/var/log/supervisor/webvirtmgr.log
log_stderr=true
user=nginx
[program:webvirtmgr-console]
command=/usr/bin/python2 /var/www/webvirtmgr/console/webvirtmgr-console
directory=/var/www/webvirtmgr
autostart=true
autorestart=true
stdout_logfile=/var/log/supervisor/webvirtmgr-console.log
redirect_stderr=true
user=nginx
//启动并且设置开机自启
[root@192 ~]# systemctl enable --now supervisord.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/supervisord.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/supervisord.service.
[root@192 ~]# ss -anlt
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 *:80 *:*
LISTEN 0 5 192.168.122.1:53 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6080 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:8000 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:6080 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:8000 [::]:*配置nginx用户
[root@192 ~]# su - nginx -s /bin/bash
-bash-4.2$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/var/lib/nginx/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:IKbwuc6fvckwYnNDJn0Kd6M+MYWD9MiH+iHC52quhRY [email protected]
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| |
| . |
|.o =o.. |
| o===... |
|.E*.=o+ S |
|+ooOo= . |
|o+O.Bo |
|.*.*.B . |
|=o+.+.=. |
+----[SHA256]-----+
-bash-4.2$ touch ~/.ssh/config && echo -e "StrictHostKeyChecking=no\nUserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null" >> ~/.ssh/config
-bash-4.2$ chmod 0600 ~/.ssh/config
-bash-4.2$ ssh-copy-id [email protected]
/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.80.143' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
[email protected]'s password:
Permission denied, please try again.
[email protected]'s password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh '[email protected]'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
-bash-4.2$ exit
登出
[root@192 ~]# vim /etc/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/50-libvirt-remote-access.pkla
[root@192 ~]# cat /etc/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/50-libvirt-remote-access.pkla
[Remote libvirt SSH access]
Identity=unix-user:root
Action=org.libvirt.unix.manage
ResultAny=yes
ResultInactive=yes
ResultActive=yes
[root@192 ~]# chown -R root.root /etc/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/50-libvirt-remote-access.pkla
[root@192 ~]# systemctl restart libvirtd
[root@192 ~]# systemctl restart nginx.service3.kvm web界面管理
第一次通过web访问kvm时可能会一直访问不了,一直转圈,而命令行界面一直报错(too many open files)
此时需要对nginx进行配置
[root@192 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
worker_rlimit_nofile 655350;
[root@192 ~]# systemctl restart nginx.service然后再对系统参数进行设置
[root@192 ~]# vim /etc/security/limits.conf
# End of file
* soft nofile 655350
* hard nofile 655350重启一下虚拟机即可正常访问
而后即可用ip访问kvm
用户名和密码为刚才设置的超级管理员用户和密码
创建ssh连接
点击添加
创建成功
选择目录类型卷,设置类型名称与路径,点击创建
进入储存池
[root@192 ~]# cd /var/lib/libvirt/images/
[root@192 images]# ls
[root@192 images]# ls
CentOS-Stream-8-x86_64-latest-dvd1.iso刷新页面,iso镜像即可显示,点击添加镜像
设置镜像名字,格式,容量后点击创建即可
创建后出现此画面则表示创建成功
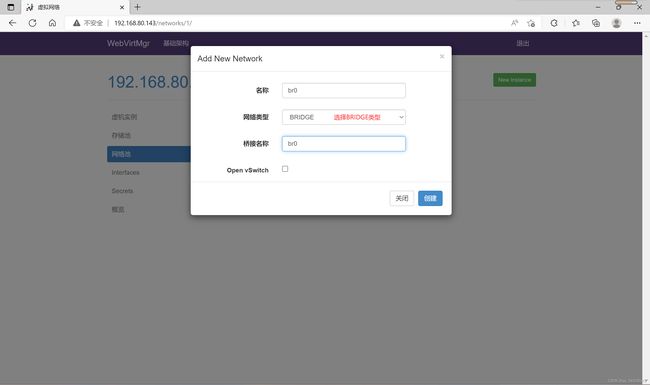
4.kvm网络管理
点击网络池,选择新建网络
设置好后点击创建
 5.管理实例(管理虚拟机)
5.管理实例(管理虚拟机)
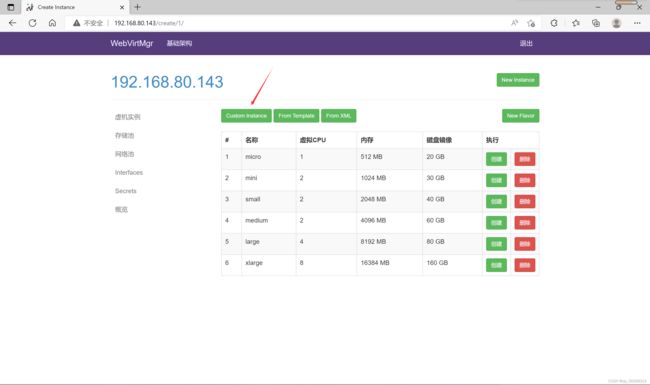
实例创建(虚拟机创建)
点击创建新虚拟机
点击Custon Instance定制虚拟机
设置好虚拟机后点击创建
虚拟机插入光盘
先点击设置,再点击media,最后点击连接插入虚拟机挂光盘
设置web上访问虚拟机的密码
先点击access,再点击console password,最后设置密码点击set password
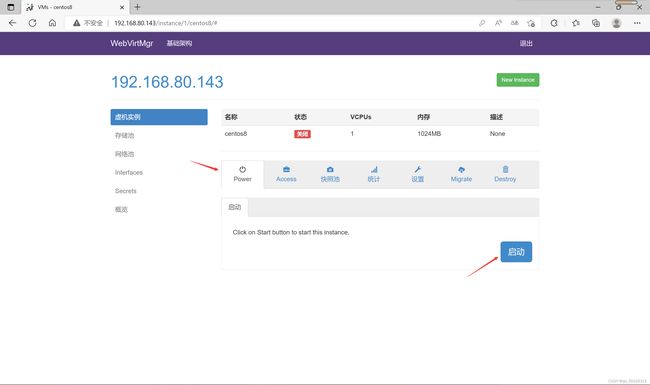
启动虚拟机