React源码(二)
目录
context
1. 创建context的两种方式
2. createContext
ConcurrentMode(并发模式syncMode)
Supense + lazy(懒加载)
React.Children
1. React.Children.map
2. React.Children.forEach
3. React.Children.count
4. React.Children.only
5. React.Children.toArray
注意:react源码中的_DEV_是一个伪全局变量,它代表的是development模式,用于管理开发环境中需运行的代码块。
context
1. 创建context的两种方式
childContextType(目前已经被弃用了,但是之前被用的很多),这种方法会导致context中值方式生变化时,所有子组件都会更新,非常影响性能。
//用法
//父组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
class Parent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
childContext: 'xw'
}
}
//给context传入value
getChildContext() {
return { value: this.state.childContext, num: 111 }
}
render() {
return (
{this.props.children}
)
}
}
//子组件
class Son extends Component {
render() {
return (
我是Son:{this.context.value} //获取
)
}
}
/*这两个type定义很重要,一个child上层可能有很多个context,许多个context
会merge到一起,规定parent的contextTypes以及Son的contextTypes
才能确定取哪一个属性值*/
Son.contextTypes = {
value: PropTypes.string,
}
//context中的值都需要放在这里,不管用不用
Parent.childContextTypes = {
value: PropTypes.string,
num: PropTypes.number,
}
export default () => {
return 2. createContext
① 类组件需要用createContext 中的 Provider + static contextType = contextName接收;
import React, { Component, createContext } from 'react';
const sonContext = createContext('createContext');
const { Provider, Consumer } = sonContext;
class Parent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
childContext: 'xw'
}
}
render() {
return (
//传一个对象
{this.props.children}
)
}
}
//子组件
class Son extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
static contextType = sonContext; //接收context
render() {
console.log('context', this.context);
return (
我是Son:{this.context.content} //获取某个值
)
}
}
export default () => {
return ②-1 函数组件使用Consumer接收(用Consumer包裹用到context的具体位置,然后使用回调的形式拿到context);
//其他部分相同
function Son() {
return (
我是Son组件
{
context => {
return `我是Son:${context.content}`
}
}
)
}②-2 useContext(react hook)
上面函数组件获取context中的值也可以用useContext获取;
//其他部分相同
import React, { useContext } from 'react'
function Son() {
let { content } = useContext(contentContext); //获取context 不需要Consumer包裹
return (
我是Son:{content}
)
}
ConcurrentMode(并发模式syncMode)
它是实验性的,需要安装 @experimental 版本;
对react整体渲染过程进行优先级排比,并且渲染任务可以随时中断,随时重启;
被ConcurrentMode包裹的内部产生的所有更新(setState、动画)都是低优先级的;我们可以使用flashSync提高优先级。
用法:
import React, { ConcurrentMode } from 'react';
import { flushSync } from 'react-dom';
import React, { Component } from 'react'
class Parent extends Component {
render() {
return (
Parent
)
}
}
export default () => (
)
源码中,ConcurrentMode其实是一个Symbol标识。
//import { REACT_CONCURRENT_MODE_TYPE } from 'shared/ReactSymbols';
......
if (enableStableConcurrentModeAPIs) {
React.ConcurrentMode = REACT_CONCURRENT_MODE_TYPE; //
React.Profiler = REACT_PROFILER_TYPE;
} else {
React.unstable_ConcurrentMode = REACT_CONCURRENT_MODE_TYPE;
React.unstable_Profiler = REACT_PROFILER_TYPE;
}
//ReactSymbols.js
export const REACT_CONCURRENT_MODE_TYPE = hasSymbol
? Symbol.for('react.concurrent_mode')
: 0xeacf;Supense + lazy(懒加载)
Supense+React.lazy(callback) => 异步加载组件,但是需要等到
中所有的组件resolved,才会返回内容,否则一直显示fallback中的内容。
//Suspense的源码
Suspense: REACT_SUSPENSE_TYPE, //一个Symbol变量,一个标识
export const REACT_SUSPENSE_TYPE = hasSymbol
? Symbol.for('react.suspense')
: 0xead1;//lazy的源码
import type {LazyComponent, Thenable} from 'shared/ReactLazyComponent';
import {REACT_LAZY_TYPE} from 'shared/ReactSymbols';
//接受一个函数,函数返回一个带有.then函数的对象(例如promise),它也是懒加载组件
export function lazy(ctor: () => Thenable): LazyComponent {
return {
$$typeof: REACT_LAZY_TYPE,
_ctor: ctor, //传入的函数
// React uses these fields to store the result.
_status: -1, //储存Thenable的状态,-1是pending,用于在渲染过程中通过分辨状态来选择处理的方法
_result: null, //储存Thenable的resolved返回的内容,也就是懒加载组件(Supense里面包裹的部分)
};
} React.Children
想要操作props.children时,可以通过这个api来处理,我们可以通过这个api拦截react默认的渲染结果。
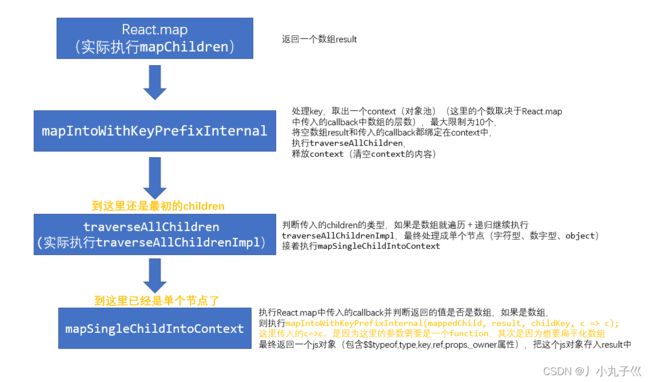
1. React.Children.map
React.Children.map处理过程:
//React.Children.map源码
function mapChildren(children, func, context) {
if (children == null) {
return children;
}
const result = [];
mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal(children, result, null, func, context);
return result;
}
function mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal(children, array, prefix, func, context) {
let escapedPrefix = '';
if (prefix != null) { //处理key
//key中的/是在这里加上的,只要最终的children不只有一层,就一定会走这里,加/
escapedPrefix = escapeUserProvidedKey(prefix) + '/';
}
//取出一个context
const traverseContext = getPooledTraverseContext(
array,
escapedPrefix,
func, //扁平化 func 就是x=>x
context,
);
//处理children
traverseAllChildren(children, mapSingleChildIntoContext, traverseContext);
//释放context
releaseTraverseContext(traverseContext);
}
//缓冲池context
const POOL_SIZE = 10;
const traverseContextPool = [];
function getPooledTraverseContext(
mapResult,
keyPrefix,
mapFunction,
mapContext,
) {
//如果里面有就删除一个再存
if (traverseContextPool.length) {
const traverseContext = traverseContextPool.pop();
traverseContext.result = mapResult;
traverseContext.keyPrefix = keyPrefix;
traverseContext.func = mapFunction;
traverseContext.context = mapContext;
traverseContext.count = 0;
return traverseContext;
} else {
return {
result: mapResult,
keyPrefix: keyPrefix,
func: mapFunction,
context: mapContext,
count: 0,
};
}
}
//释放context
function releaseTraverseContext(traverseContext) {
//清空context的内容
traverseContext.result = null;
traverseContext.keyPrefix = null;
traverseContext.func = null;
traverseContext.context = null;
traverseContext.count = 0;
//判断contextPool里面是否还可以存context,可以就存
if (traverseContextPool.length < POOL_SIZE) {
traverseContextPool.push(traverseContext);
}
}
function traverseAllChildren(children, callback, traverseContext) {
if (children == null) {
return 0;
}
return traverseAllChildrenImpl(children, '', callback, traverseContext);
}
//处理props.children
function traverseAllChildrenImpl(
children,
nameSoFar,
callback,
traverseContext,
) {
const type = typeof children;
if (type === 'undefined' || type === 'boolean') {
// All of the above are perceived as null.
children = null;
}
let invokeCallback = false;
if (children === null) {
invokeCallback = true;
} else {
switch (type) {
case 'string':
case 'number':
invokeCallback = true;
break;
case 'object':
switch (children.$$typeof) {
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE:
case REACT_PORTAL_TYPE:
invokeCallback = true;
}
}
}
//单个节点的时候走这个callback
if (invokeCallback) {
//map的时候callback是mapSingleChildIntoContext,forEach的时候callback是forEachSingleChild
callback(
traverseContext,
children,
// If it's the only child, treat the name as if it was wrapped in an array
// so that it's consistent if the number of children grows.
//SEPARATOR='.';
nameSoFar === '' ? SEPARATOR + getComponentKey(children, 0) : nameSoFar,
);
return 1;
}
let child;
let nextName;
let subtreeCount = 0; // Count of children found in the current subtree.
const nextNamePrefix =
nameSoFar === '' ? SEPARATOR : nameSoFar + SUBSEPARATOR; //SUBSEPARATOR=':'
//遍历两次还没出去key就会被加上:继续往后加index
//如果是数组就遍历递归
if (Array.isArray(children)) {
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
child = children[i];
//根据遍历的index给key取值,不论是children的map还是最后func返回的数组的map都会在这里给key取值
nextName = nextNamePrefix + getComponentKey(child, i);
subtreeCount += traverseAllChildrenImpl( //递归,最终都会从callback出去
child,
nextName,
callback,
traverseContext,
);
}
} else {
const iteratorFn = getIteratorFn(children);
if (typeof iteratorFn === 'function') {
if (__DEV__) {
// Warn about using Maps as children
if (iteratorFn === children.entries) {
warning(
didWarnAboutMaps,
'Using Maps as children is unsupported and will likely yield ' +
'unexpected results. Convert it to a sequence/iterable of keyed ' +
'ReactElements instead.',
);
didWarnAboutMaps = true;
}
}
const iterator = iteratorFn.call(children);
let step;
let ii = 0;
while (!(step = iterator.next()).done) {
child = step.value;
nextName = nextNamePrefix + getComponentKey(child, ii++);
subtreeCount += traverseAllChildrenImpl(
child,
nextName,
callback,
traverseContext,
);
}
} else if (type === 'object') {
let addendum = '';
if (__DEV__) {
addendum =
' If you meant to render a collection of children, use an array ' +
'instead.' +
ReactDebugCurrentFrame.getStackAddendum();
}
const childrenString = '' + children;
invariant(
false,
'Objects are not valid as a React child (found: %s).%s',
childrenString === '[object Object]'
? 'object with keys {' + Object.keys(children).join(', ') + '}'
: childrenString,
addendum,
);
}
}
return subtreeCount; //返回children的数量(长度)
}
//到这里的时候就是单个节点了
function mapSingleChildIntoContext(bookKeeping, child, childKey) {
const {result, keyPrefix, func, context} = bookKeeping;
//调用map中传入的func,并传入参数child, bookKeeping.count++
let mappedChild = func.call(context, child, bookKeeping.count++); //callback返回的值
if (Array.isArray(mappedChild)) {
mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal(mappedChild, result, childKey, c => c);
} else if (mappedChild != null) {
if (isValidElement(mappedChild)) {
mappedChild = cloneAndReplaceKey(
mappedChild,
// Keep both the (mapped) and old keys if they differ, just as
// traverseAllChildren used to do for objects as children
keyPrefix +
(mappedChild.key && (!child || child.key !== mappedChild.key)
? escapeUserProvidedKey(mappedChild.key) + '/'
: '') +
childKey,
);
}
result.push(mappedChild);
}
}
//key相关的函数
let didWarnAboutMaps = false;
const userProvidedKeyEscapeRegex = /\/+/g;
function escapeUserProvidedKey(text) {
return ('' + text).replace(userProvidedKeyEscapeRegex, '$&/');
}
function getComponentKey(component, index) {
//在这里做一些类型检查,因为我们是盲目调用的
// Do some typechecking here since we call this blindly. We want to ensure
// that we don't block potential future ES APIs.
if (
typeof component === 'object' &&
component !== null &&
component.key != null
) {
// Explicit key
return escape(component.key);
}
// Implicit key determined by the index in the set
return index.toString(36); //使用36进制,转换后为0-9 a-z组成
}
export {
mapChildren as map,
};//demo
import React from 'react'
function ChildrenDemo(props) {
console.log(props.children)
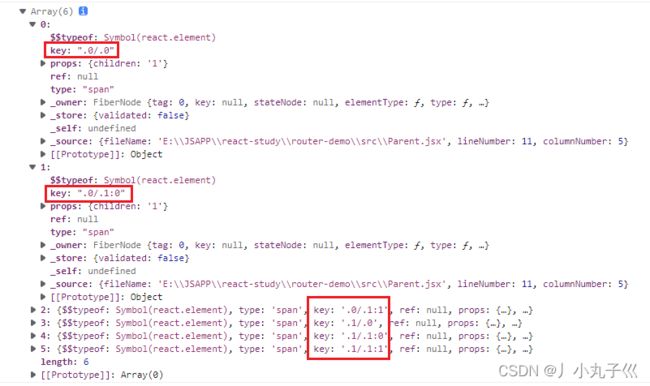
console.log(React.Children.map(props.children, c => [c, [c, c]])) //不管多少层都会被平铺
return props.children
}
export default () => (
1
2
)
2. React.Children.forEach
和React.Children.map一样,只是它没有返回值吗,是直接修改children
//其他部分一样
//可以从这里看出来forEach没有创建空的数组,没有返回值
function forEachChildren(children, forEachFunc, forEachContext) {
if (children == null) {
return children;
}
//获取一个context
const traverseContext = getPooledTraverseContext(
null,
null,
forEachFunc,
forEachContext,
);
//传入的是forEachSingleChild,与map不一样
traverseAllChildren(children, forEachSingleChild, traverseContext);
releaseTraverseContext(traverseContext);//清空context的内容
}
function forEachSingleChild(bookKeeping, child, name) {
const {func, context} = bookKeeping;
//调用forEach中传入的函数
func.call(context, child, bookKeeping.count++);
}
export {
forEachChildren as forEach,
};3. React.Children.count
返回传入的children的数量(长度)
function countChildren(children) {
//traverseAllChildren中traverseAllChildrenImpl返回的就是最终的children的长度
return traverseAllChildren(children, () => null, null);
}
export {
countChildren as count,
};4. React.Children.only
判断传入的children是不是只有一个,如果不是一个就报错
//isValidElement判断对象是不是react element
function onlyChild(children) {
//如果传入的children是react element,并且是一个child,就返回这个child
//如果传入的children是数组,就返回传入的error
invariant(
isValidElement(children),
'React.Children.only expected to receive a single React element child.',//传入的error
);
return children;
}
export {
onlyChild as only,
};5. React.Children.toArray
将传入的children转换成数组
function toArray(children) {
const result = [];
//因为mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal里面会调用traverseAllChildrenImpl,这里面会如果是数组会map,
//所以这里的回调传入child => child即可
mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal(children, result, null, child => child);
return result;
}
export {
toArray,
};