JAVA 定时任务实现方式
1、JDK自带定时任务
1.1、Timer
java自带的java.util.Timer类,这个类允许你调度一个java.util.TimerTask任务。使用这种方式可以让你的程序按照某一个频度执行,但不能在指定时间运行。一般用的较少。
public class TestTimer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TimerTask timerTask = new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("task run:"+ new Date());
}
};
Timer timer = new Timer();
//安排指定的任务在指定的时间开始进行重复的固定延迟执行。这里是每3秒执行一次
timer.schedule(timerTask,10,3000);
}
}
1.2、ScheduledExecutorService(JDK)
jdk自带的一个类;是基于线程池设计的定时任务类,每个调度任务都会分配到线程池中的一个线程去执行,也就是说,任务是并发执行,互不影响。
public class MyScheduledExecutorService {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建任务队列 10 为线程数量
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService =
Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10);
// 执行任务
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
System.out.println("打印当前时间:" + new Date());
}, 1, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 1s 后开始执行,每 3s 执行一次
}
}2、spring 支持定时任务
2.1、Spring Task
Spring3.0系列框架中Spring Framework自带的定时任务,可以将它看成一个轻量级的Quartz,而且使用起来比Quartz简单许多。
org.springframework
spring-context
@EnableScheduling
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplicationBuilder(Application.class).web(WebApplicationType.SERVLET).run(args);
}
}sue.spring.task.cron=*/10 * * * * ?
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component // 把此类托管给 Spring,不能省略
public class TaskUtils {
@Scheduled(cron = "${sue.spring.task.cron}")
public void fun() {
System.out.println("doSomething");
}
// 添加定时任务
@Scheduled(cron = "30 40 23 0 0 5") // cron表达式:每周一 23:40:30 执行
public void doTask(){
System.out.println("我是定时任务~");
}
/**fixedRate:上一次开始执行时间点之后5秒再执行*/
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000)
public void run1() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(6000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=====>>>>>使用fixedRate {}"+(System.currentTimeMillis()/1000));
}
/**fixedDelay:上一次执行完毕时间点之后5秒再执行*/
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 5000)
public void run2() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(7000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=====>>>>>使用fixedDelay {}"+(System.currentTimeMillis()/1000));
}
/**第一次延迟2秒后执行,之后按fixedDelay的规则每5秒执行一次*/
@Scheduled(initialDelay = 2000, fixedDelay = 5000)
public void run3(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=====>>>>>使用initialDelay {}"+(System.currentTimeMillis()/1000));
}
}多线程执行(在类或方法上加@Async)
@Configuration
@EnableAsync //开启异步事件的支持
public class AsyncConfig {
/*
此处成员变量应该使用@Value从配置中读取
*/
private int corePoolSize = 10;
private int maxPoolSize = 200;
private int queueCapacity = 10;
@Bean
public Executor taskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize);
executor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}cron常用表达式
0 0 0 1 * ?每月1号零点执行0 0 2 * * ?每天凌晨2点执行0 0 2 * * ?每天凌晨2点执行0 0/5 11 * * ?每天11点-11点55分,每隔5分钟执行一次0 0 18 ? * WED每周三下午6点执行- 每隔5秒执行一次:*/5 ** ?
- 每隔1分钟执行一次:0 */1 *?
- 0/2 * * * * ? 表示每2秒 执行任务
- 0 0/2 * * * ? 表示每2分钟 执行任务
- 0 0 2 1 * ? 表示在每月的1日的凌晨2点调整任务
- 0 15 10 ? * MON-FRI 表示周一到周五每天上午10:15执行作业
- 0 15 10 ? 6L 2002-2006 表示2002-2006年的每个月的最后一个星期五上午10:15执行作
- 0 0 10,14,16 * * ? 每天上午10点,下午2点,4点
- 0 0/30 9-17 * * ? 朝九晚五工作时间内每半小时
- 0 0 12 ? * WED 表示每个星期三中午12点
- 0 0 12 * * ? 每天中午12点触发
- 0 15 10 ? * * 每天上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 * * ? 每天上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 * * ? 每天上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 * * ? 2005 2005年的每天上午10:15触发
- 0 * 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:59期间的每1分钟触发
- 0 0/5 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:55期间的每5分钟触发
- 0 0/5 14,18 * * ? 在每天下午2点到2:55期间和下午6点到6:55期间的每5分钟触发
- 0 0-5 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:05期间的每1分钟触发
- 0 10,44 14 ? 3 WED 每年三月的星期三的下午2:10和2:44触发
- 0 15 10 ? * MON-FRI 周一至周五的上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 15 * ? 每月15日上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 L * ? 每月最后一日的上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 ? * 6L 每月的最后一个星期五上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 ? * 6L 2002-2005 2002年至2005年的每月的最后一个星期五上午10:15触发
- 0 15 10 ? * 6#3 每月的第三个星期五上午10:15触发
2.2、Spring Quartz
quartz主要接口:
-
Scheduler代表调度容器,一个调度容器中可以注册多个JobDetail和Trigger。 -
Job代表工作,即要执行的具体内容。 -
JobDetail代表具体的可执行的调度程序,Job是这个可执行程调度程序所要执行的内容。 -
JobBuilder用于定义或构建JobDetail实例。 -
Trigger代表调度触发器,决定什么时候去调。 -
TriggerBuilder用于定义或构建触发器。 -
JobStore用于存储作业和任务调度期间的状态。
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-quartz
- 定时任务执行类继承
QuartzJobBean
public class QuartzTestJob extends QuartzJobBean {
@Override
protected void executeInternal(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException {
String userName = (String) context.getJobDetail().getJobDataMap().get("userName");
System.out.println("userName:" + userName);
}
}- 创建调度程序
JobDetail和调度器Trigger
@Configuration
public class QuartzConfig {
@Value("${sue.spring.quartz.cron}")
private String testCron;
/**
* 创建定时任务
*/
@Bean
public JobDetail quartzTestDetail() {
JobDetail jobDetail = JobBuilder.newJob(QuartzTestJob.class)
.withIdentity("quartzTestDetail", "QUARTZ_TEST")
.usingJobData("userName", "susan")
.storeDurably()
.build();
return jobDetail;
}
/**
* 创建触发器
*/
@Bean
public Trigger quartzTestJobTrigger() {
//每隔5秒执行一次
CronScheduleBuilder cronScheduleBuilder = CronScheduleBuilder.cronSchedule(testCron);
//创建触发器
Trigger trigger = TriggerBuilder.newTrigger()
.forJob(quartzTestDetail())
.withIdentity("quartzTestJobTrigger", "QUARTZ_TEST_JOB_TRIGGER")
.withSchedule(cronScheduleBuilder)
.build();
return trigger;
}
}sue.spring.quartz.cron=*/5 * * * * ?
-
优点:默认是多线程异步执行,单个任务时,在上一个调度未完成时,下一个调度时间到时,会另起一个线程开始新的调度,多个任务之间互不影响。支持复杂的
cron表达式,它能被集群实例化,支持分布式部署。 -
缺点:相对于spring task实现定时任务成本更高,需要手动配置
QuartzJobBean、JobDetail和Trigger等。需要引入了第三方的quartz包,有一定的学习成本。不支持并行调度,不支持失败处理策略和动态分片的策略等。
3、分布式定时任务
3.1、xxl-job
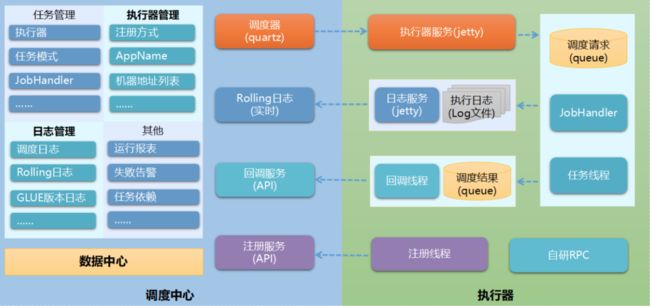
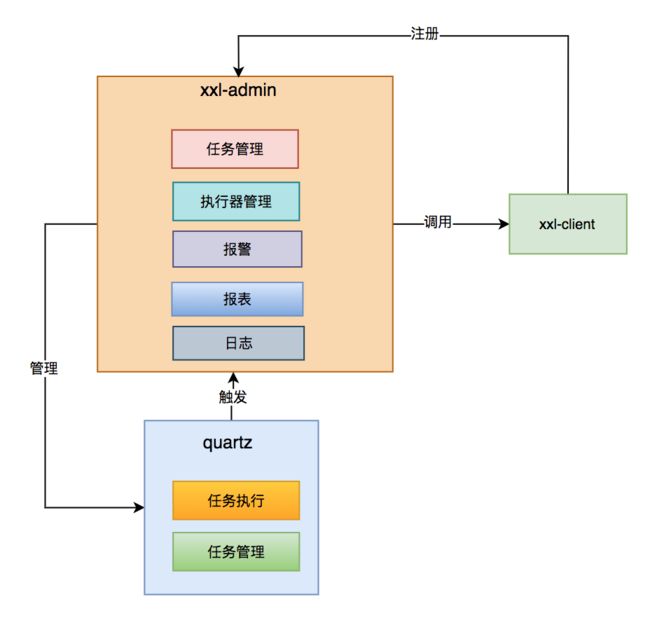
xxl-job框架对quartz进行了扩展,使用mysql数据库存储数据,并且内置jetty作为RPC服务调用。
-
有界面维护定时任务和触发规则,非常容易管理。
-
能动态启动或停止任务
-
支持弹性扩容缩容
-
支持任务失败报警
-
支持动态分片
-
支持故障转移
-
Rolling实时日志
-
支持用户和权限管理
管理界面:
quartz架构图 :
部署xxl-job-admin:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/fa7186bea84b
xxl-job使用1:
- pom.xml文件中引入
xxl-job相关依赖
com.xuxueli
xxl-job-core
applicationContext.properties文件中配置参数
#调度中心部署跟地址
xxl.job.admin.address: http://localhost:8088/xxl-job-admin/
xxl.job.executor.appname: xxl-job-executor-sample
xxl.job.executor.port: 8888
xxl.job.executor.logpath: /data/applogs/xxl-job/- 创建HelloJobHandler类继承
IJobHandler类
package com.tp.athena.jobhandler;
import com.xxl.job.core.biz.model.ReturnT;
import com.xxl.job.core.handler.IJobHandler;
import com.xxl.job.core.handler.annotation.JobHandler;
import com.xxl.job.core.log.XxlJobLogger;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.sound.midi.Soundbank;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 任务Handler示例(Bean模式)
*
* 开发步骤:
* 1、继承"IJobHandler":“com.xxl.job.core.handler.IJobHandler”;
* 2、注册到Spring容器:添加“@Component”注解,被Spring容器扫描为Bean实例;
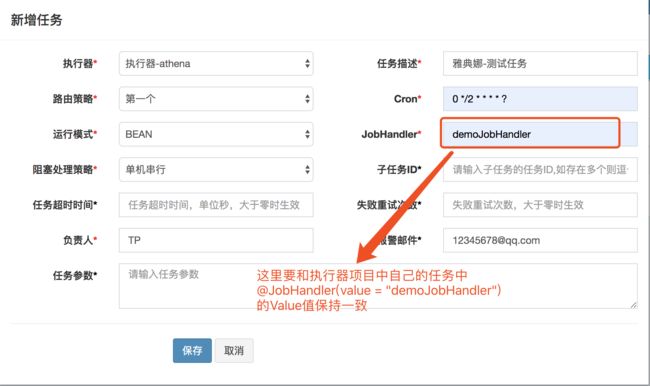
* 3、注册到执行器工厂:添加“@JobHandler(value="自定义jobhandler名称")”注解,注解value值对应的是调度中心新建任务的JobHandler属性的值。
* 4、执行日志:需要通过 "XxlJobLogger.log" 打印执行日志;
*
*/
@JobHandler(value = "demoJobHandler")
@Component
public class DemoJobHandler extends IJobHandler {
@Override
public ReturnT execute(String param) throws Exception {
System.out.println("XXL-JOB Hello World");
return SUCCESS;
}
}
xxl-job使用2:
- 添加依赖
// 添加依赖
com.xuxueli
xxl-job-core
2.2.0
- 添加配置
// 添加配置
xxl.job.admin.addresses=http://http://172.37.40.42/xxl-job-admin
xxl.job.accessToken=
xxl.job.executor.appname=monitor-ms
xxl.job.executor.address=
xxl.job.executor.ip=
xxl.job.executor.port=9999
xxl.job.executor.logpath=/tmp/i6000logs/monitor-ms/job/xxl-job/jobhandler
xxl.job.executor.logretentiondays=30- 启动加载xxl配置参数
package com.nrxt.nms.monitor.ms.utils;
import com.xxl.job.core.executor.impl.XxlJobSpringExecutor;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class XxlJobConfig {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(XxlJobConfig.class);
@Value("${xxl.job.admin.addresses}")
private String adminAddresses;
@Value("${xxl.job.accessToken}")
private String accessToken;
@Value("${xxl.job.executor.appname}")
private String appName ;
@Value("${xxl.job.executor.address}")
private String address;
@Value("${xxl.job.executor.ip}")
private String ip;
@Value("${xxl.job.executor.port}")
private int port;
@Value("${xxl.job.executor.logpath}")
private String logPath;
@Value("${xxl.job.executor.logretentiondays}")
private int logRetentionDays;
@Bean
public XxlJobSpringExecutor xxlJobExecutor() {
XxlJobSpringExecutor xxlJobSpringExecutor = new XxlJobSpringExecutor();
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setAdminAddresses(adminAddresses);
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setAppname(appName);
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setAddress(address);
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setIp(ip);
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setPort(port);
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setAccessToken(accessToken);
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setLogPath(logPath);
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setLogRetentionDays(logRetentionDays);
return xxlJobSpringExecutor;
}
}- 加载任务执行器
package com.nrxt.nms.collect.syncCmdbSubCi.xxljob;
import com.nrxt.nms.collect.syncCmdbSubCi.service.SyncCmdbSubCiService;
import com.xxl.job.core.biz.model.ReturnT;
import com.xxl.job.core.handler.annotation.XxlJob;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
@Component
public class SyncCmdbSubCiJob {
@Autowired
SyncCmdbSubCiService syncCmdbSubCiService;
static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(SyncCmdbSubCiJob.class);
@XxlJob("syncCmdbSubCiAll")
public ReturnT syncCmdbSubCiAllJob(String param) {
String jobTime = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmss").format(new Date());
syncCmdbSubCiService.syncCmdbSubCi(jobTime, false);
return ReturnT.SUCCESS;
}
}
使用xxl-job的优缺点:
-
优点:有界面管理定时任务,支持弹性扩容缩容、动态分片、故障转移、失败报警等功能。它的功能非常强大,很多大厂在用,可以满足绝大多数业务场景。
-
缺点:和
quartz一样,通过数据库分布式锁,来控制任务不能重复执行。在任务非常多的情况下,有一些性能问题。
3.2、elastic-job
elastic-job是当当网开发的弹性分布式任务调度系统,功能丰富强大,采用zookeeper实现分布式协调,实现任务高可用以及分片。它是专门为高并发和复杂业务场景开发。
elastic-job目前是apache的shardingsphere项目下的一个子项目,官网地址:http://shardingsphere.apache.org/elasticjob/。
elastic-job在2.x之后,出了两个产品线:Elastic-Job-Lite和Elastic-Job-Cloud,而我们一般使用Elastic-Job-Lite就能够满足需求。Elastic-Job-Lite定位为轻量级无中心化解决方案,使用jar包的形式提供分布式任务的协调服务,外部仅依赖于Zookeeper。
-
分布式调度协调
-
弹性扩容缩容
-
失效转移
-
错过执行作业重触发
-
作业分片一致性,保证同一分片在分布式环境中仅一个执行实例
-
自诊断并修复分布式不稳定造成的问题
-
支持并行调度
整体架构:
- pom.xml文件中引入
elastic-job相关依赖
com.dangdang
elastic-job-lite-core
com.dangdang
elastic-job-lite-spring
- 增加ZKConfig类,配置
zookeeper
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnExpression("'${zk.serverList}'.length() > 0")
public class ZKConfig {
@Bean
public ZookeeperRegistryCenter registry(@Value("${zk.serverList}") String serverList,
@Value("${zk.namespace}") String namespace) {
return new ZookeeperRegistryCenter(new ZookeeperConfiguration(serverList, namespace));
}
}- 定义一个类实现
SimpleJob接口
public class TestJob implements SimpleJob {
@Override
public void execute(ShardingContext shardingContext){
System.out.println("ShardingTotalCount:"+shardingContext.getShardingTotalCount());
System.out.println("ShardingItem:"+shardingContext.getShardingItem());
}
}- 增加JobConfig配置任务
-
cron:cron表达式,定义触发规则。
-
shardingTotalCount:定义作业分片总数
-
shardingItemParameters:定义分配项参数,一般用分片序列号和参数用等号分隔,多个键值对用逗号分隔,分片序列号从0开始,不可大于或等于作业分片总数。
-
jobParameters:作业自定义参数
@Configuration
public class JobConfig {
@Value("${sue.spring.elatisc.cron}")
private String testCron;
@Value("${sue.spring.elatisc.itemParameters}")
private String shardingItemParameters;
@Value("${sue.spring.elatisc.jobParameters}")
private String jobParameters =;
@Value("${sue.spring.elatisc.shardingTotalCount}")
private int shardingTotalCount;
@Autowired
private ZookeeperRegistryCenter registryCenter;
@Bean
public SimpleJob testJob() {
return new TestJob();
}
@Bean
public JobScheduler simpleJobScheduler(final SimpleJob simpleJob) {
return new SpringJobScheduler(simpleJob, registryCenter, getConfiguration(simpleJob.getClass(),
cron, shardingTotalCount, shardingItemParameters, jobParameters));
}
private geConfiguration getConfiguration(Class jobClass,String cron,int shardingTotalCount,String shardingItemParameters,String jobParameters) {
JobCoreConfiguration simpleCoreConfig = JobCoreConfiguration.newBuilder(jobClass.getName(), testCron, shardingTotalCount).
shardingItemParameters(shardingItemParameters).jobParameter(jobParameters).build();
SimpleJobConfiguration simpleJobConfig = new SimpleJobConfiguration(simpleCoreConfig, jobClass.getCanonicalName());
LiteJobConfiguration jobConfig = LiteJobConfiguration.newBuilder(simpleJobConfig).overwrite(true).build();
return jobConfig;
}
}applicationContext.properties文件中配置参数
spring.application.name=elasticjobDemo
zk.serverList=localhost:2181
zk.namespace=elasticjobDemo
sue.spring.elatisc.cron=0/5 * * * * ?
sue.spring.elatisc.itemParameters=0=A,1=B,2=C,3=D
sue.spring.elatisc.jobParameters=test
sue.spring.elatisc.shardingTotalCount=4使用elastic-job的优缺点:
-
优点:支持分布式调度协调,支持分片,适合高并发,和一些业务相对来说较复杂的场景。
-
缺点:需要依赖于zookeeper,实现定时任务相对于
xxl-job要复杂一些,要对分片规则非常熟悉。