操作系统课设(优先数调度算法&&最先适应算法)
一.设计目的:
1. 模拟实现计算机的处理机调度。帮助学生理解计算机的处理机调度的工作原理和实现过程。
2. 模拟实现计算机的主存储器空间的分配与回收.帮助学生理解计算机主存储器空间的分配与回收
的工作原理和实现过程。
二.设计内容:
1. 设计一个按优先数调度算法实现处理机调度的程序。
2. 设计一个在可变分区管理方式下采用最先适应算法实现主存的分配与回收的程序。
三.设计要求:
a) 完成程序调试和运行。
b) 完成课程设计报告书
c) 课程设计报告书含数据结构、符号说明、流程图、源程序并附注解
四.设计思路:
(一)按优先数调度算法实现处理机调度
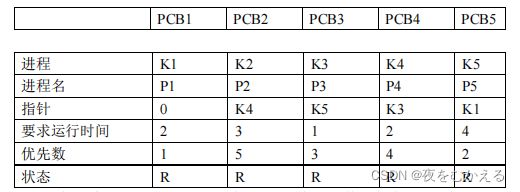
说明:系统假设 5 个进程,进程控制块 PCB 的格式为:(用结构体描述)
进程名-----作为进程的标识,5 个进程的进程名分别为 P1,P2,P3,P4,P5。
指针 -----按优先数大小把 5 个进程连成队列,用指针针出下一个进程的进程控制块 PCB 的首地址,
最后一个进程的指针为”0”.
要求运行时间-----进程需要运行的单位时间数。
优先数------进程的优先数,调度时按优先数大的进程先执行。
状态---------假设有两种状态,”就绪”状态和”结束”状态 。5 个进程的初始状态为”就绪”状态,用“R”
表示,”结束”状态用“E”表示。
1)功能说明
①在每次运行你所设计的处理器调度程序之前,为每个进程任意确定它的“优先数”和“要求运行时间”。
②为了调度方便,把五个进程按给定的优先数从大到小连成队列。用一单元指出队首进程,用指针指出队列的连接情况。例如:用next代替指针指向下一个节点。
③处理器调度总是选队首进程运行。采用动态改变优先数的办法,进程每运行一次优先数就减“1”。由于本实习是模拟处理器调度,所以,对被选中的进程并不实际的启动运行,而是执行:
优先数-1
要求运行时间-1
来模拟进程的一次运行。
④ 进程运行一次后,若要求运行时间!=0,则再将它加入队列(按优先数大小插入,且置队首标志);若要求运行时间=0,则把它的状态修改成“结束”(E),且退出队列。
⑤若“就绪”状态的进程队列不为空,则重复上面(4)和(5)的步骤,直到所有进程都成为“结束”状态。
⑥ 在所设计的程序中应有显示或打印语句,能显示或打印每次被选中进程的进程名以及运行一次后进程队列的变化。
⑦为五个进程任意确定一组“优先数”和“要求运行时间”,启动所设计的处理器调度程序,显示或打印逐次被选中进程的进程名以及进程控制块的动态变化过程。
即实现:按优先数调度算法实现处理机调度
2)相关类的定义(结构)
进程控制块PCB
public class PCB {
public String pcbName;//进程名
public PCB next;//指针
public int time;//运行时间
public int priority;//优先数
public char statue = 'R';//进程的状态,初始化为就绪态
//构造方法
public PCB(String pcbName, int time, int priority) {
this.pcbName = pcbName;
this.time = time;
this.priority = priority;
}}
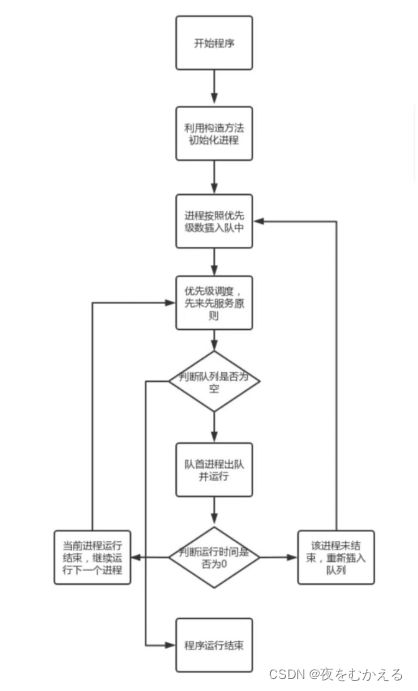
3)流程图
4)源程序代码
package hh;
// 定义进程控制块PCB
public class PCB {
public String pcbName;//进程名
public PCB next;//指针
public int time;//运行时间
public int priority;//优先数
public char statue = 'R';//进程的状态,初始化为就绪态
//构造方法
public PCB(String pcbName, int time, int priority) {
this.pcbName = pcbName;
this.time = time;
this.priority = priority;
}
//重写toString方法
public String toString() {
return "进程名='" + pcbName + '\'' +
", 要求运行时间=" + time +
", 优先级数=" + priority +
", 状态=" + statue;
}
}
/*按优先数调度算法模拟实现处理器调度
*/
class ProcessScheduling {
private PCB head;
/**
* PCB对象插入操作,根据每一个进程的优先级数进行插入
* 如果优先级数相等,则按先来先服务原则进行插入
*/
public void addPCB(PCB node) {
//若要求运行时间=0,则把它的状态修改成“结束”(E),且退出队列
if(node.time == 0) {
node.statue = 'E';
System.out.println(node.pcbName + "退出进程队列");
System.out.println(node + "\n");
return;
}
//若头结点为空
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
return;
}
//边插入边按优先级进行排序
//如果node的优先级比头结点大
if(node.priority > this.head.priority) {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
return;
}
//如果node的优先级与头结点相等,按先来先服务原则
if(node.priority == this.head.priority) {
node.next = this.head.next;
this.head.next = node;
return;
}
//如果node的优先级不比头结点大,也不与头结点相等
PCB cur = this.head;
while(cur.next != null) {
if(cur.next.priority < node.priority) {
PCB curNext = cur.next;
node.next = curNext;
cur.next = node;
return;
}
//如果node的优先级与头结点相等,按先来先服务原则
if(cur.next.priority == node.priority) {
PCB curNext = cur.next;
node.next = curNext.next;
curNext.next = node;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
//此时如果还未结束,则node应该直接插入到队尾
cur.next = node;
node.next = null;
}
/**
* 优先数调度算法模拟实现处理器调度的运行
* 每一次运行优先级数最高的一个进程,运行结束后再将其插入到队列中
*/
public void runPCB() {
while(this.head != null) {
//运行优先级最高的第一个进程
PCB cur = this.head;
this.head = this.head.next;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("开始执行" + cur.pcbName + "进程");
System.out.println(cur);
//cur的运行优先级数-1
cur.priority -= 1;
//cur的运行时间-1
cur.time -= 1;
System.out.println(cur.pcbName + "进程执行完毕");
System.out.println();
//再将cur插入进程队列
addPCB(cur);
//打印每次被选中进程的进程运行一次后进程队列的变化。
if(this.head == null) {
System.out.println("所有的线程执行完毕");
return;
}
System.out.println("=====================");
System.out.println("此时进程队列的所有进程信息");
display();
System.out.println("=====================");
}
}
//打印进程队列
public void display() {
for(PCB pcb = this.head; pcb != null; pcb = pcb.next) {
System.out.println(pcb);
}
}
}
package hh;
public class TestPCB {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PCB[] pcbs = new PCB[5];
pcbs[0] = new PCB("P1",2,1);
pcbs[1] = new PCB("P2",3,5);
pcbs[2] = new PCB("P3",1,3);
pcbs[3] = new PCB("P4",2,4);
pcbs[4] = new PCB("P5",4,2);
ProcessScheduling p = new ProcessScheduling();
for(PCB pcb : pcbs) {
p.addPCB(pcb);
}
p.runPCB();
}
}5)实验结果
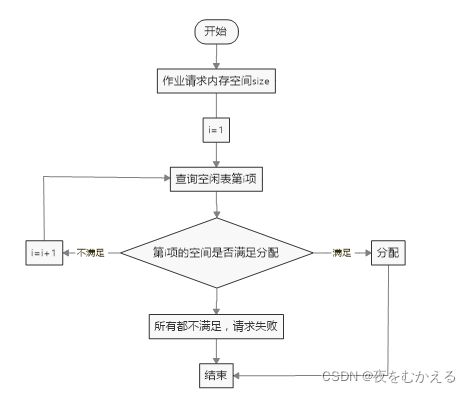
(二)可变分区管理方式下采用最先适应算法实现主存的分配与回收
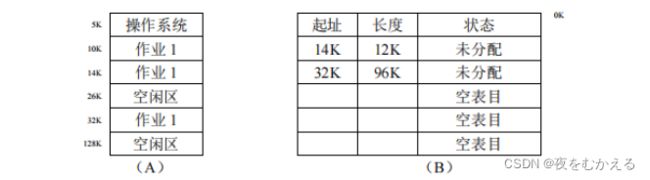
可变分区方式是按作业需要的主存空间大小来分割分区的。当要装人一个作业时;根据作业需要 的主存量查看是否有足够的空闲空间,若有,则按需要量分割一个分区分配给该作业;若无,则作业不能 装入。随着作业的装入、撤离、主存空间被分成许多个分区。有的分区被作业占用,而有的分区是空闲的。
如图(A)所示.为了说明哪些区是空闲的, 可以用来装入新作业,必须要有一张空闲区说明表,格式如图(B)所示:
起址:指出一个空闲区的主存起始地址。
长度:指出从起始地址开始的一个连续空闲区的长度。
状态:有两种状态。一种是“未分配”状态,指出对应的由起始地址接线员出的某个长度的区域是空闲区;另一种是“空表目”状态,表示表中对应的登记项目是空白(无效),可用来登记新的空闲区(例如,作业撤消后,它所占用的区域就成了空闲区位。应找一个“空表目”栏登记归还区的起址和长度且修改状态)。由于分区的个数不定,所以空闲区说明表中应有适量的状态为“空表目”的登记栏目,否则造成表格溢出无法登记。
1)功能说明
①当有一个新作业要求装入主存时,必须查空闲区说明表,从中找出一个足够大的空闲区。有时找 到的空闲区可能大于作业需要量。这时应把原来的空闲区分成两个部分:一部分分配给作业占用,另一部 分又成为一个较小的空闲区。为了尽量减少由于分割造成的“碎片”,采用二个措施:一是在作业装入时, 尽可能地利用主存的低地址部分的空闲区,而尽量保存高地址部分有较大的连续空间区域,以有利于大型作业的装入。
②采用最先适应法分配主存空间
按照作业的需要量,查空闲区说明表,找到第一个满足要求的空闲区.当空闲区大于作业量与选定常量之和时,一部分用来装入作业,另一部分仍为空闲区登记在空闲区说明表中。由于本实验是模拟主存的分配,所以当把主存区分配给作业后,并不实际启动装入作业,而用输出“分配情况”来代替。
③当一个作业执行结束撤离时,作业所占的区域归还,归还的区域如果与其它空闲区相邻,则应合成一个较大的空闲登记在空闲区说明表中。如果一个作业撤离,应归还所占主存区域时,应与上、下相邻的空闲区一起合并成一个大的空闲区后登记在空闲区说明表中。
2)相关类的定义(结构)
在编制程序时,可用一个链表结构分别放作业表和空闲区说明表。
class Node{
int start; //起始
int size; //大小
boolean state; //状态
int end; //结束地址
public Node(){
}
public Node(int size) { //作业申请节点
this.state=true;
this.size = size;
}
public Node(int start, int size, boolean state) { //空闲节点
this.start = start;
this.size = size;
this.state = state;
this.end=start+size;
}
3)流程图
4)源程序代码(附注解)
package abc;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
//1、初始化用户分区-》显示分区
//2、选择功能
//有以下功能:
//1)存储作业
//2)执行完显示分区
//3)回收作业
//4)执行完显示分区
public class MemoryManagement {
public static void main(String args[]) {
MainClass c = new MainClass();
c.execInstruction();
}
}
class MainClass{
static int SystemMemory = 500;//系统初始容量
//单个作业信息类
class Job{
String name;
int begin;
int lenth;
Job lastJob;
Job nextJob;
}
//空闲分区信息类
class freeSpace{
freeSpace lastSpace;//指向上一个空间
freeSpace nextSpace;//指向下一个空间
int begin;
int lenth;
}
//作业链表类
class JobLine{
Job firstJob;
boolean isFull = true;
}
//空闲区域链表类
class freeSpaceLine{
freeSpace firstSpace;
boolean isFull = true;
}
//定义一个选择菜单
public int getMenu() {
System.out.println("请你选择需要进行的操作:");
System.out.println("1:装入作业");
System.out.println("2:回收作业");
System.out.println("3:显示系统当前分区情况");
System.out.println("4:退出程序");
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int select = scan.nextInt();
if(1 == select) {
System.out.println("请你选择装入作业时要使用的算法:");
System.out.println("1:最先适应分配算法");
Scanner scan1 = new Scanner(System.in);
int select1 = scan1.nextInt();
if(1 == select1)
return 11;
else{
System.out.println("你想干嘛");
return -1;
}
}
else if(2 == select) {
return 2;
}
else if(3 == select) {
return 3;
}
else if(4 == select) {
return 0;
}
return -1;
}
//执行用户输入的命令
public void execInstruction() {
int select = getMenu();
initialFreeArea();
while(0 != select) {
if(11 == select)
storeHomework(select);
else if(2 == select) {
System.out.println("请输入要回收的作业的名称");
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String temp = in.next();
recycleJob(temp);
printSituation();
}
else if(3 == select){
printSituation();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
select = getMenu();
}
}
freeSpaceLine freeLineOne;
JobLine jobLine;
//初始化用户区
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
public void initialFreeArea() {
freeLineOne = new freeSpaceLine();
freeSpace first = new freeSpace();
freeLineOne.firstSpace = first;
freeLineOne.isFull = false;
first.begin = 0;
first.lenth = SystemMemory;
first.lastSpace = null;
first.nextSpace = null;
}
public void printSituation() {
System.out.println("********************************");
System.out.println(" 已分配分区表\n");
System.out.println("始址\t长度\t作业号\t");
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
Job temp = jobLine.firstJob;
while(temp != null) {
System.out.println(temp.begin + "\t" + temp.lenth + "\t" + temp.name + "\t");
temp = temp.nextJob;
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
System.out.println(" 空闲分区表\n");
System.out.println("始址\t长度\t标志位\t");
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
freeSpace temp2 = freeLineOne.firstSpace;
while(temp2 != null) {
System.out.println(temp2.begin + "\t" + temp2.lenth + "\t" + "未分配\t");
temp2 = temp2.nextSpace;
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
System.out.println("********************************");
System.out.println("\n\n\n\n");
}
//输入作业
//1、创建一个temp临时变量(job类)
//2、将信息输入经temp类
//3、在空闲用户区找合适的块
//4、如果找得到则将temp存进作业链表
//5、重置空闲区
//6、打印情况
public Job inputJob() {
Job tempJob = new Job();
Scanner scan1 = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入作业的名称");
tempJob.name = scan1.next();
System.out.println("请输入作业的长度");
tempJob.lenth = scan1.nextInt();
tempJob.nextJob = null;
tempJob.lastJob = null;
return tempJob;
}
//判断内存是否足够存入作业
public boolean lookForEnoughMemory(Job tempJob) {
if(freeLineOne != null) {
if(freeLineOne.isFull != true) {
freeSpace temp = freeLineOne.firstSpace;
while(temp != null) {
if(temp.lenth >= tempJob.lenth)
return true;
temp = temp.nextSpace;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//如果内存足够则存入作业
public void storeHomework(int selectArithmetic) {
Job tempJob = inputJob();
if(lookForEnoughMemory(tempJob) == true&&11 == selectArithmetic) {
{
freeSpace space = firstFit(tempJob);
apllicationSpace(tempJob,space);
insertJob(tempJob);
}
printSituation();
}
else
System.out.println("系统内存不足,请稍后再试");
}
public void apllicationSpace(Job tempJob,freeSpace space) {
int jobLenth = tempJob.lenth;
int spaceBegin = space.begin;
int spaceLenth = space.lenth;
tempJob.begin = spaceBegin;
space.begin = spaceBegin + jobLenth;
space.lenth = spaceLenth - jobLenth;
if(0 == space.lenth) {
if(space.lastSpace != null && space.nextSpace != null)
space.lastSpace.nextSpace = space.nextSpace;
if(space.nextSpace != null &&space.lastSpace != null)
space.nextSpace.lastSpace = space.lastSpace;
}
}
public void insertJob(Job tempJob) {
if(jobLine == null) {
jobLine = new JobLine();
jobLine.firstJob = tempJob;
return;
}
else if(jobLine.firstJob == null) {
jobLine.firstJob = tempJob;
return;
}
Job temp = jobLine.firstJob;
while(temp.nextJob != null) {
temp = temp.nextJob;
}
temp.nextJob = tempJob;
tempJob.lastJob = temp;
}
//最先适应分配算法
public freeSpace firstFit(Job tempJob) {
freeSpace temp = freeLineOne.firstSpace;
while(temp != null) {
if(temp.lenth >= tempJob.lenth){
return temp;
}
temp = temp.nextSpace;
}
return null;
}
public void recycleJob(String name) {
//1、找到与输入相同的Job
Job address = jobLine.firstJob;
Job sameJob = null;
while(address != null) {
if(address.name.equalsIgnoreCase(name)) {
sameJob = address;
break;
}
address = address.nextJob;
}
//按顺序插入空闲区域队列
if(sameJob != null) {
//改变空闲区
freeSpace tempFree1 = freeLineOne.firstSpace;
freeSpace tempFree2 = new freeSpace();
tempFree2.begin = sameJob.begin;
tempFree2.lenth = sameJob.lenth;
while(tempFree1 != null) {
if( tempFree1.begin < sameJob.begin ) {
if(tempFree1.nextSpace == null) {
tempFree1.nextSpace = tempFree2;
tempFree2.lastSpace = tempFree1;
tempFree2.nextSpace = null;
defragmentation();
break;
}
else if(tempFree1.nextSpace != null && tempFree1.nextSpace.begin > sameJob.begin) {
freeSpace temp3 = tempFree1.nextSpace;
tempFree1.nextSpace = tempFree2;
tempFree2.nextSpace = temp3;
tempFree2.lastSpace = tempFree1;
temp3.lastSpace = tempFree2;
defragmentation();
break;
}
}
else if(tempFree1.begin > sameJob.begin){
tempFree2.lastSpace = null;
tempFree2.nextSpace = tempFree1;
tempFree1.lastSpace = tempFree2;
freeLineOne.firstSpace = tempFree2;
defragmentation();
break;
}
tempFree1 = tempFree1.nextSpace;
}
//改变作业区
if(sameJob.lastJob == null) {
if(sameJob.nextJob != null) {
jobLine.firstJob = sameJob.nextJob;
sameJob.nextJob.lastJob = null;
}
else {
jobLine.firstJob = null;
}
}
else if(sameJob.nextJob == null) {
sameJob.lastJob.nextJob = null;
}
else if(sameJob.nextJob != null) {
Job temp1 = sameJob.lastJob;
Job temp2 = sameJob.nextJob;
temp1.nextJob = temp2;
temp2.lastJob = temp1;
}
}
}
public void defragmentation() {
//回收的作业在空闲区的前方
freeSpace tempSpace1 = freeLineOne.firstSpace;
freeSpace tempSpace2;
boolean conbine = false;
while(tempSpace1.nextSpace != null) {
if(tempSpace1.begin + tempSpace1.lenth == tempSpace1.nextSpace.begin) {
tempSpace1.lenth += tempSpace1.nextSpace.lenth;
tempSpace2 = tempSpace1.nextSpace.nextSpace;
tempSpace1.nextSpace = tempSpace2;
if(tempSpace2 != null) {
tempSpace2.lastSpace = tempSpace1;
}
conbine = true;
}
tempSpace1 = tempSpace1.nextSpace;
if(conbine == true) {
tempSpace1 = freeLineOne.firstSpace;
conbine = false;
}
}
}
}