Java学习苦旅(十)——链表的奥秘
本篇博客将详细讲解链表的知识。
文章目录
- 什么是链表
- 单向链表
-
- 穷举创建链表
- 打印链表
- 判断单链表中是否包含某数据
- 测量单链表的长度
- 头插法增加节点
- 尾插法增加节点
- 任意位置插入节点
- 删除某个第一次出现的数据
- 删除多个同一数据
- 清空链表
- 双向链表
-
- 什么是双链表
- 打印双向链表
- 测量双链表的长度
- 判断双向链表中是否包含某数据
- 头插法增加节点
- 尾插法增加节点
- 任意位置增加节点
- 删除某个节点
- 删除多个数值相同的节点
- 清空链表
- 顺序表与链表的区别
-
- 对数据的组织方式
- 对数据的操作方式
- 结尾
什么是链表
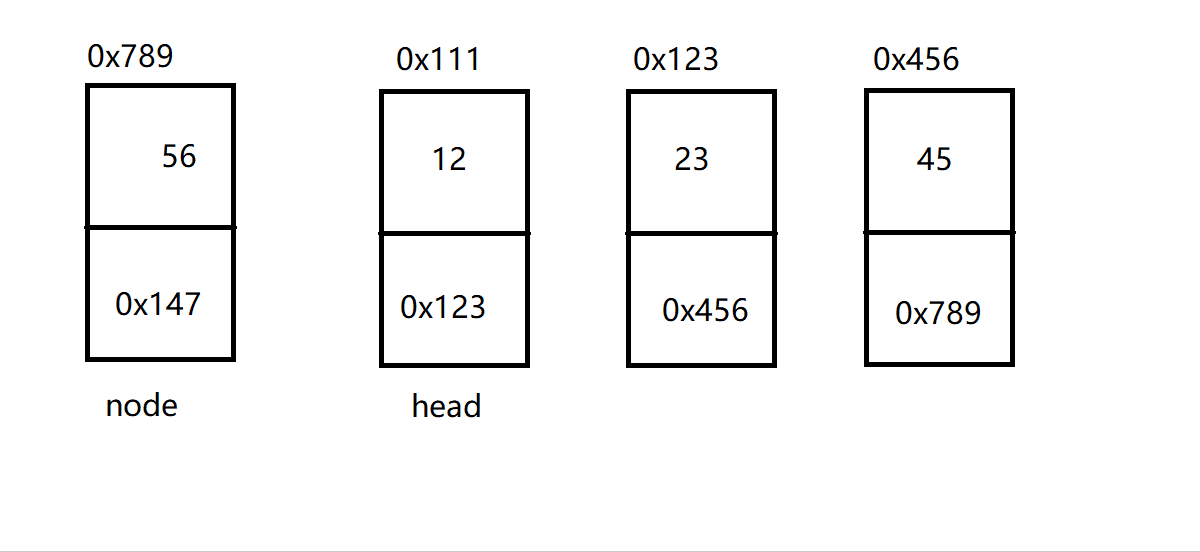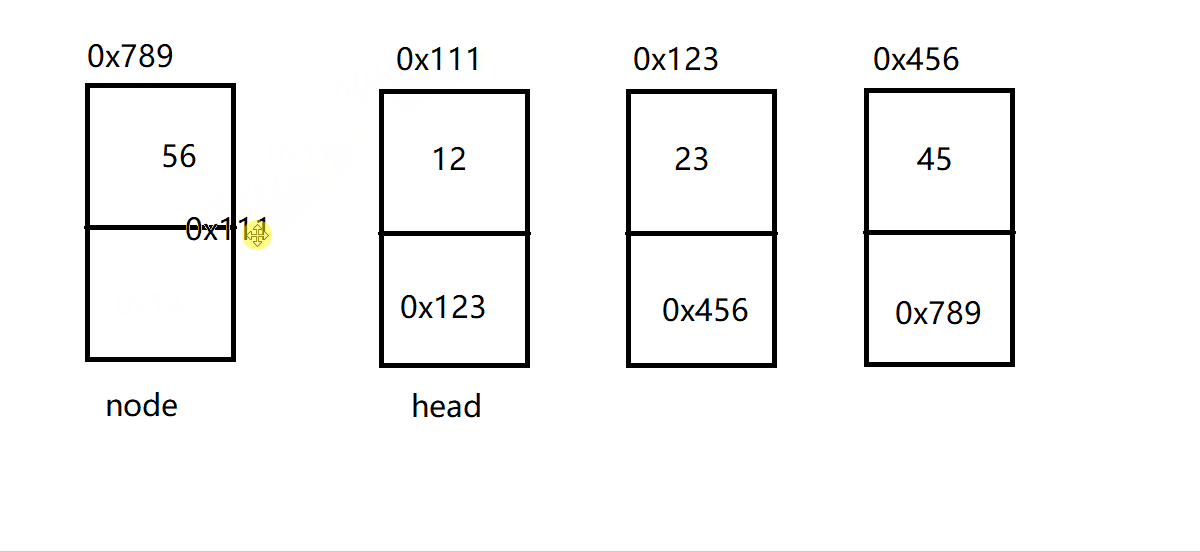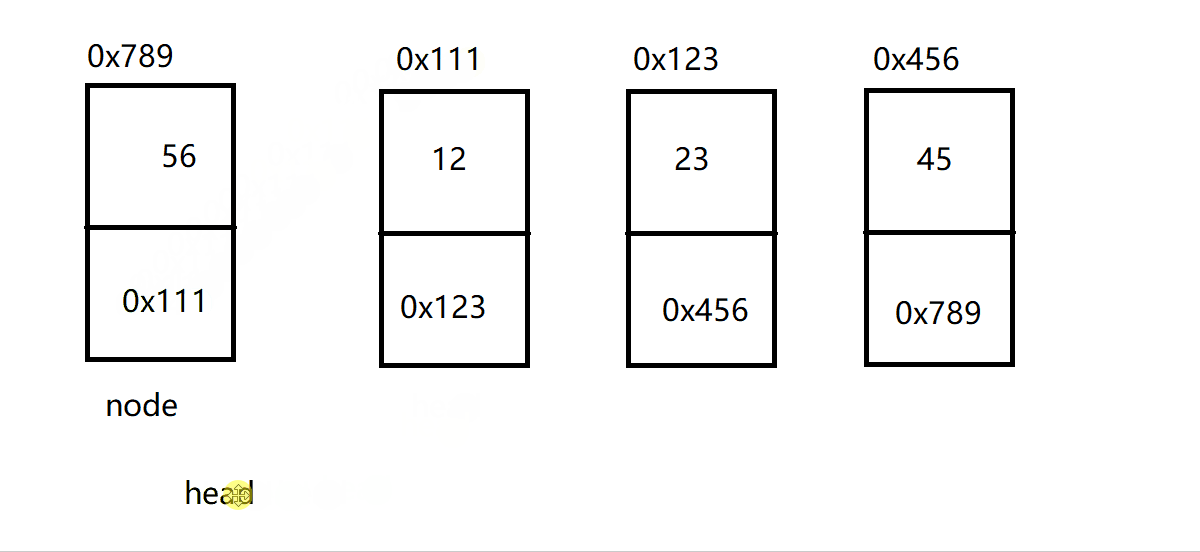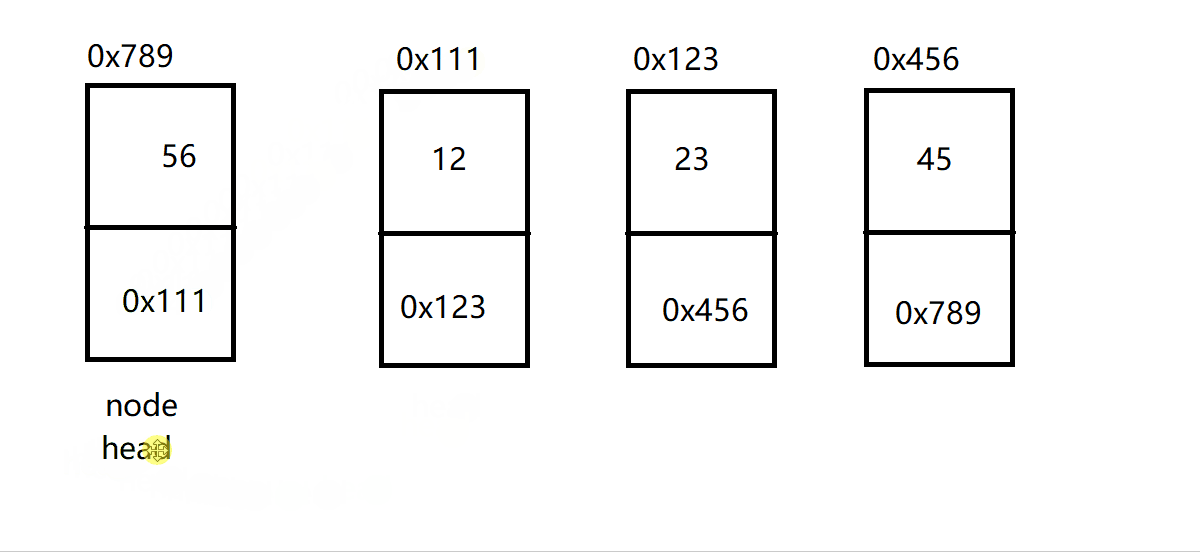
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的。通俗地说,链表是由一个个节点组合而成的。而节点,是用数据域和下一个节点地址构成的,如:
链表即为:
而上面这个链表,也被成为 单向不带头非循环链表 。
那么什么是带头呢?
带头的意思是存在头节点,也叫做傀儡节点,例如:
这个就是 单向带头非循环链表 。除此之外,还有双向链表,循环链表,这些都会在之后介绍的。
单向链表
穷举创建链表
为了让读者更好地理解链表,我先用穷举的方法创建链表。代码如下:
class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}//代表一个节点
public class MyLinkList {
public ListNode head;//链表的头引用
public void creatList() {
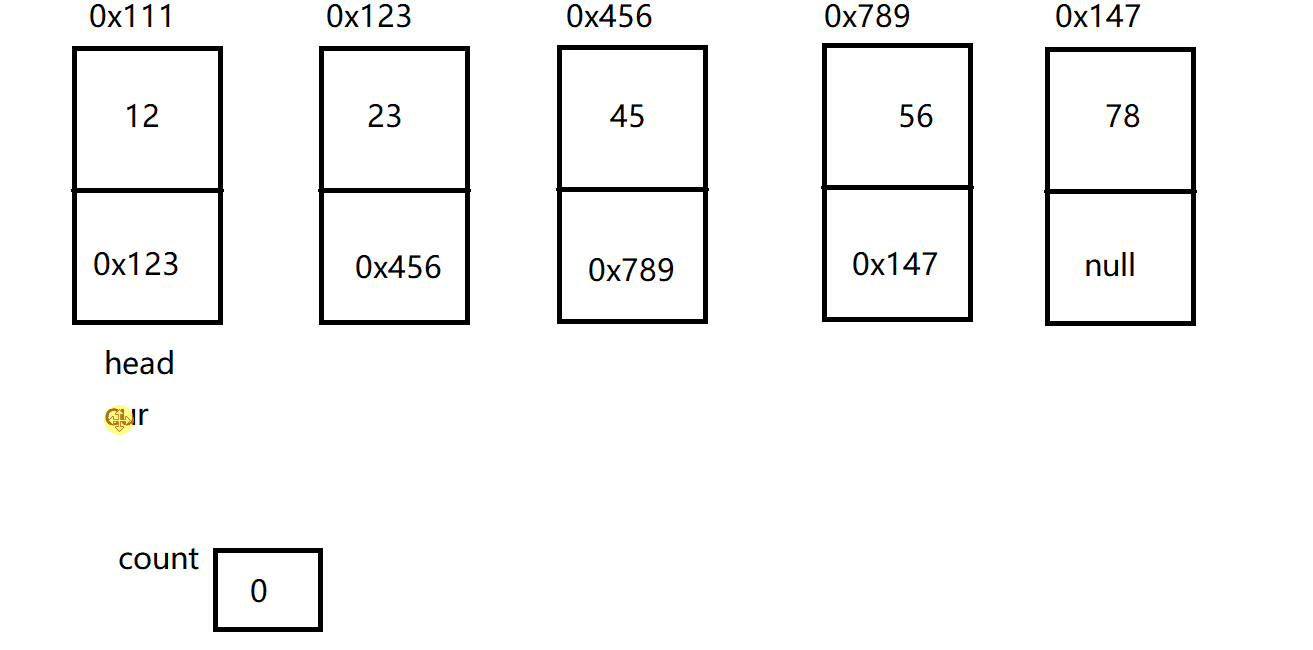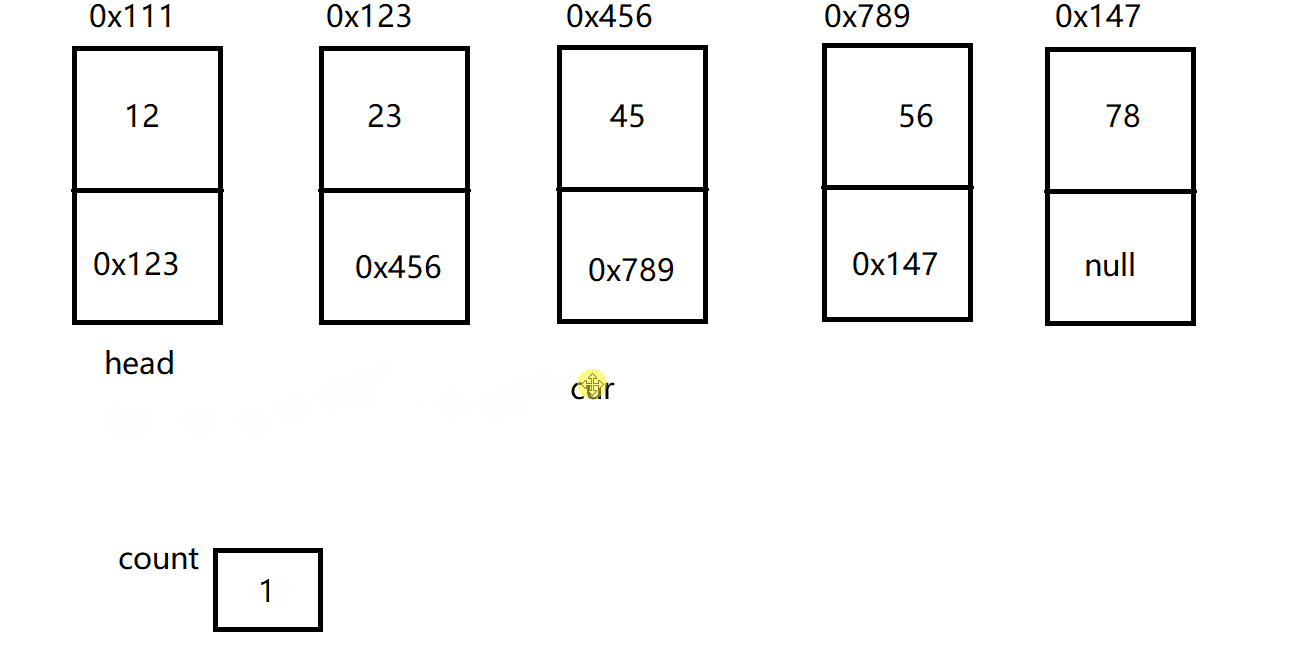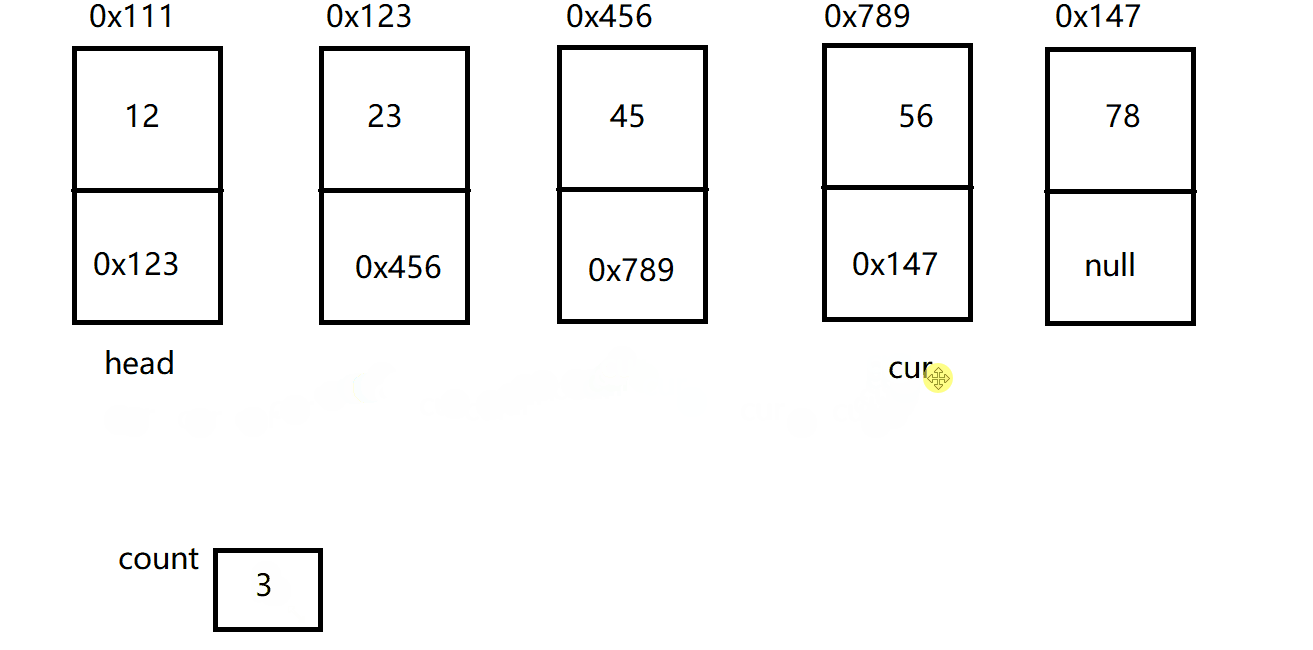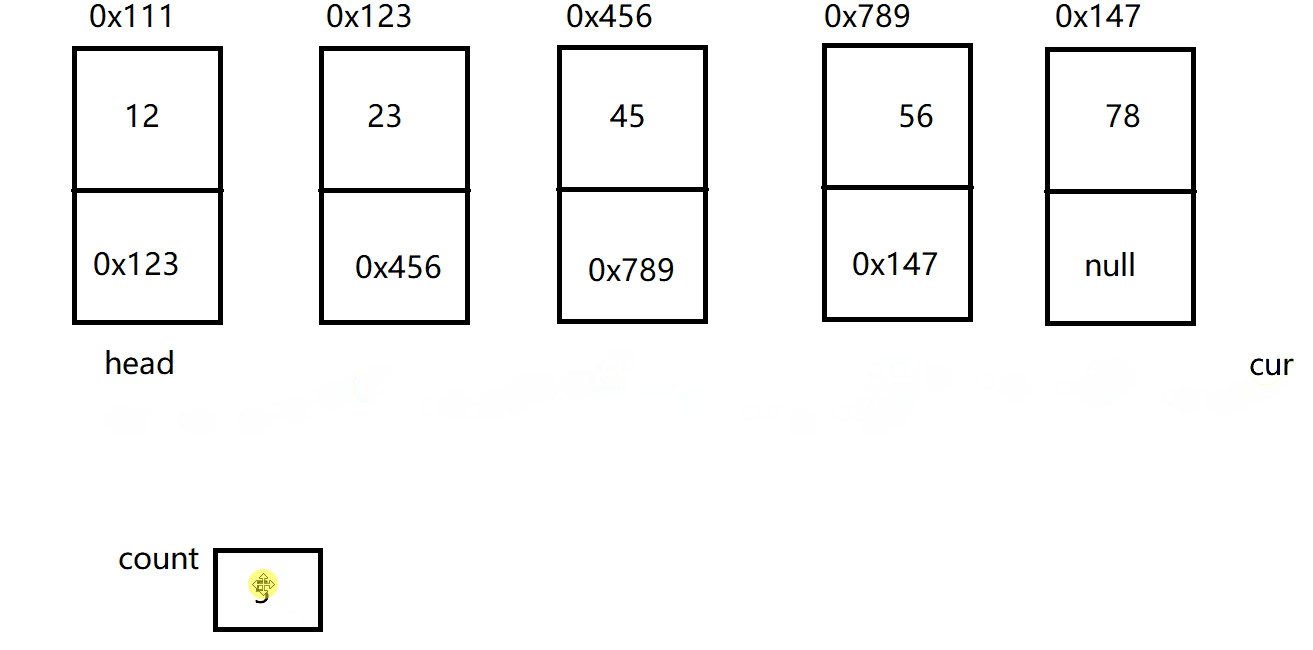
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(34);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(45);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(56);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
this.head = listNode1;
}
}
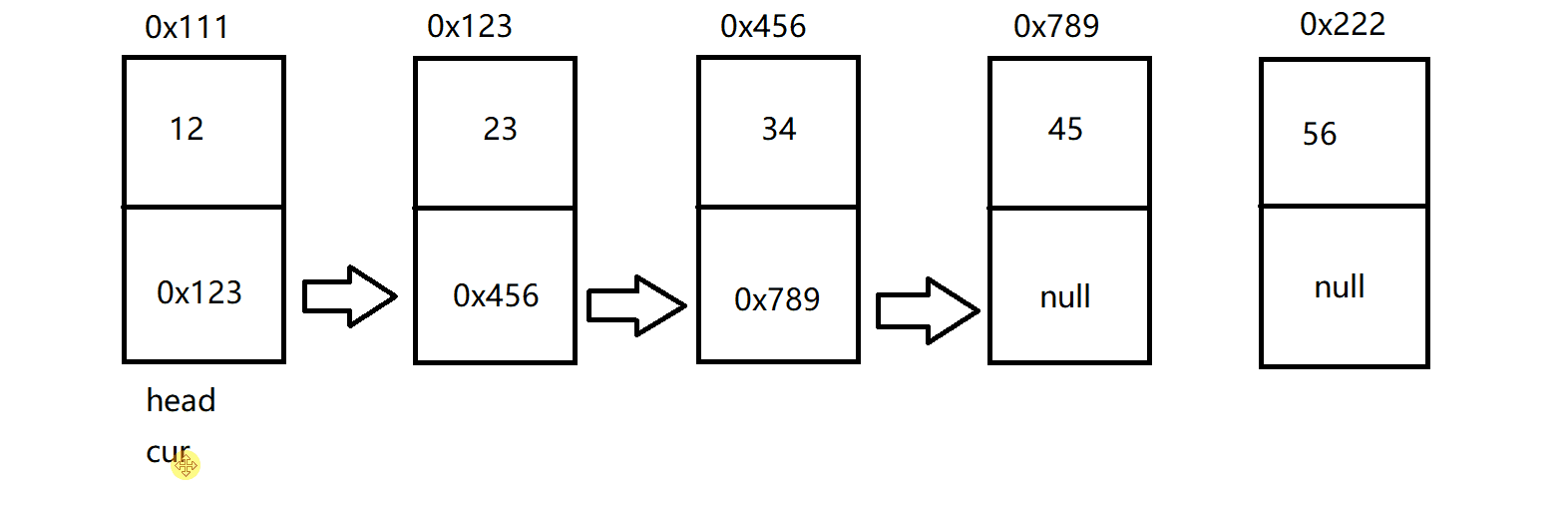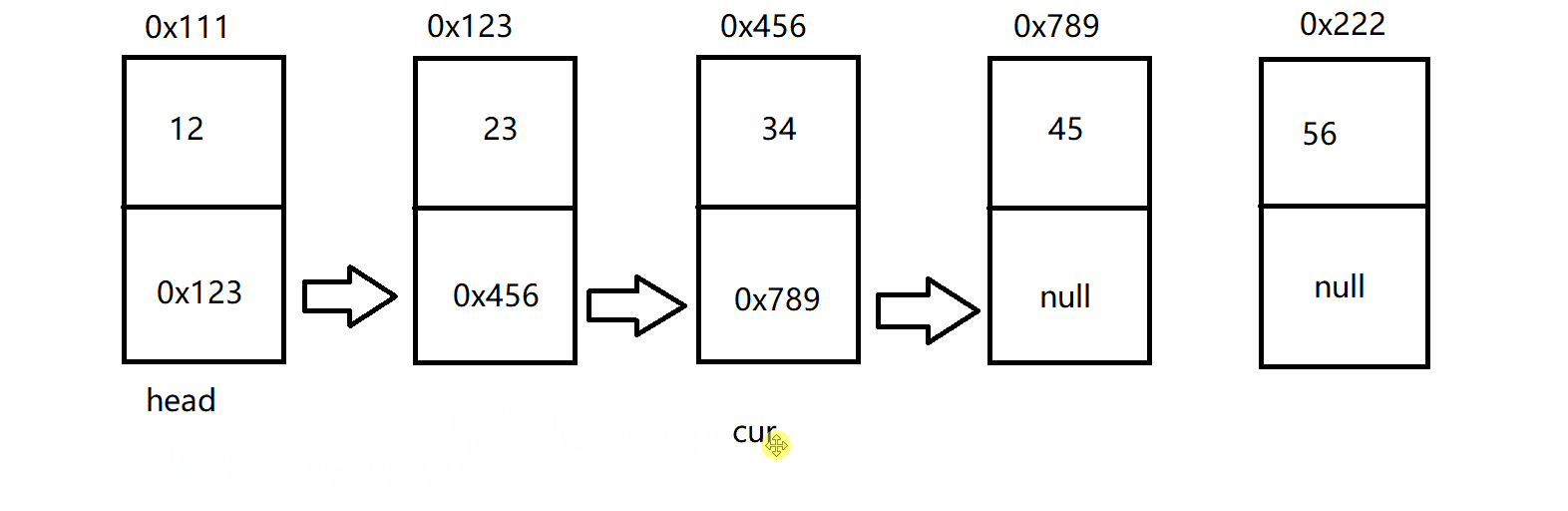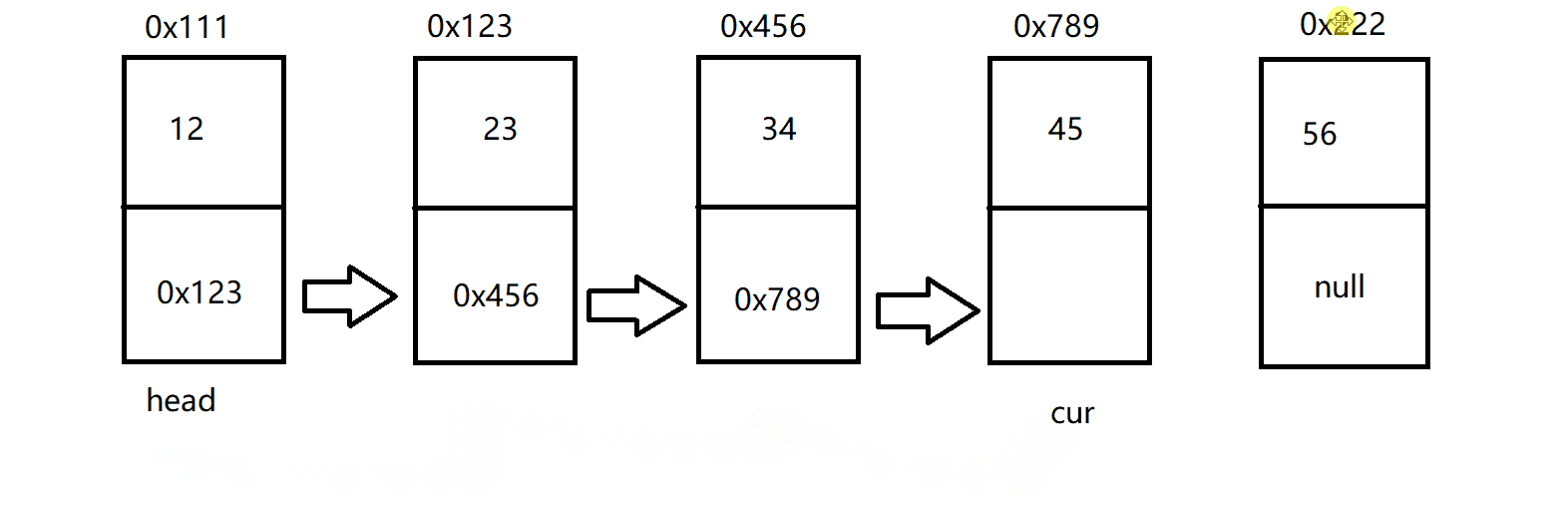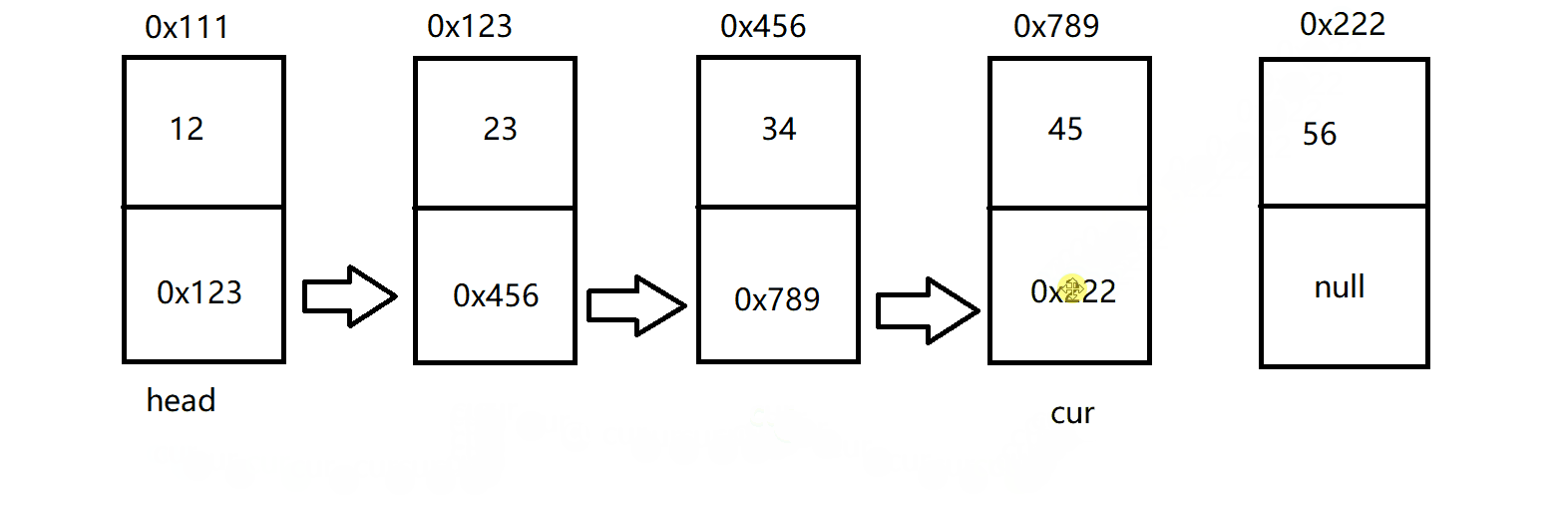
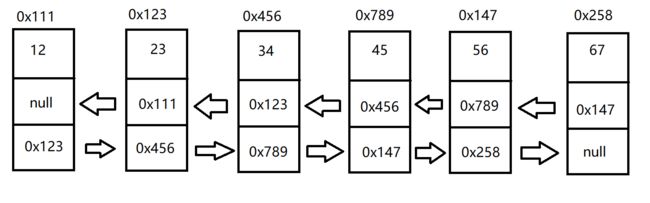
因此,这也就创建了这样的一个链表:
打印链表
打印链表和打印顺序表的方法是类似的,只不过打印顺序表是下标++,而打印链表需要引用下一个节点的地址。具体代码如下:
public void display() {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
判断单链表中是否包含某数据
在链表的使用过程中,我们需要判断某数据是否存在于链表中,假设该数据为key,具体代码如下:
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
测量单链表的长度
在使用单链表的过程中,我们需要知道单链表的长度。
实现该功能的代码如下:
public int size() {
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
头插法增加节点
使用头插法增加节点是单链表中增加数据的常见方法。
具体代码如下:
public void addFirst(int data) {
LisrNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
尾插法增加节点
尾插法增加节点也是一个较为常见的增加数据的方法
具体代码如下:
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
}else {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}
任意位置插入节点
在单链表的使用过程中,往往需要在指定位置增加数据,例如:
假设在index位置插入data数据,具体代码如下:
public void addIndex(int index,int data) {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
System.out.println("index位置不合法");
return;
}
if(index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
public ListNode findIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(index - 1 != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
删除某个第一次出现的数据
在单链表中,我们要删除某个第一次出现的数据,假设该数据为key,具体代码如下:
public void remove(int key) {
if(this.head == null) {
System.out.println("单链表为空");
return;
}
if(this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = searchPrev(key);
if (cur == null) {
System.out.println("没有你要删除的节点!");
return;
}
ListNode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
}
public ListNode searchPrev(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
删除多个同一数据
上面这段代码只能删除某个第一次出现的数据,如果一个数据在链表中出现多次,那么想删除的话,上面这段代码就不适用。因此,我们需要更改一下思路,假设要删除多个key,具体代码如下:
public ListNode removeAllkey(int key) {
if(this.head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode prev = this.head;
ListNode cur = this.head.next;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
return this.head;
}
清空链表
清空链表的具体代码如下:
public void clear() {
while(this.head != null) {
ListNode curNext = head.next;
this.head.next = null;
this.head = curNext;
}
}
双向链表
还记得开头所提到的双向链表吗?
下面将介绍双向链表的相关特性。
什么是双链表
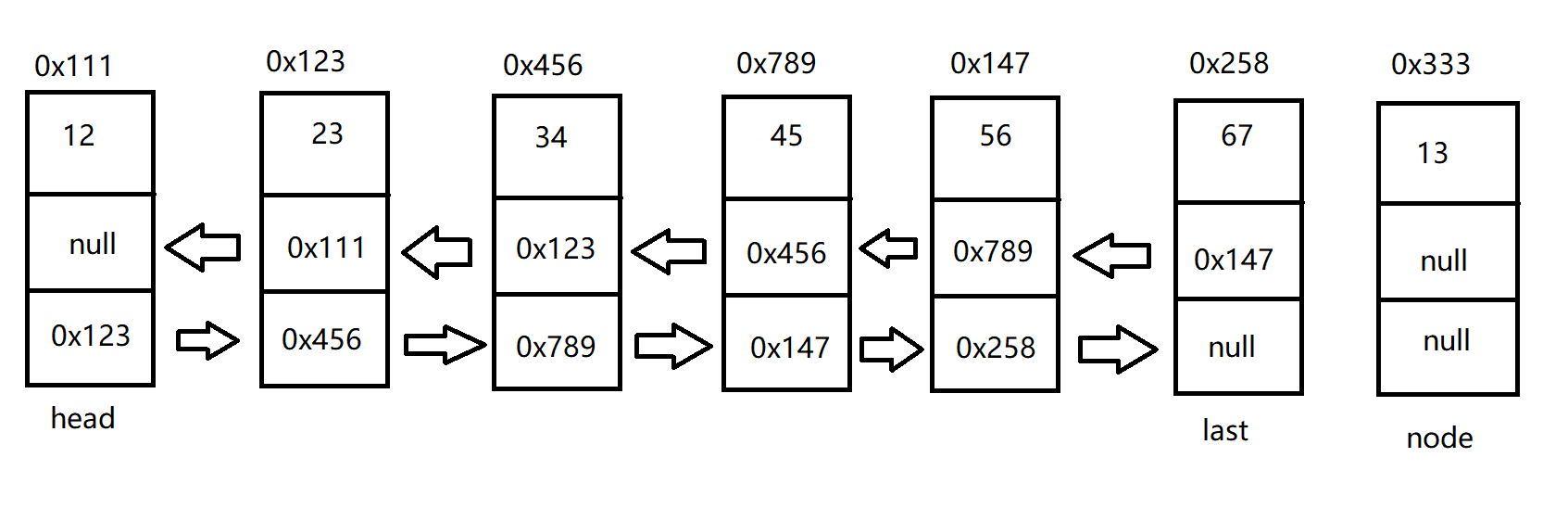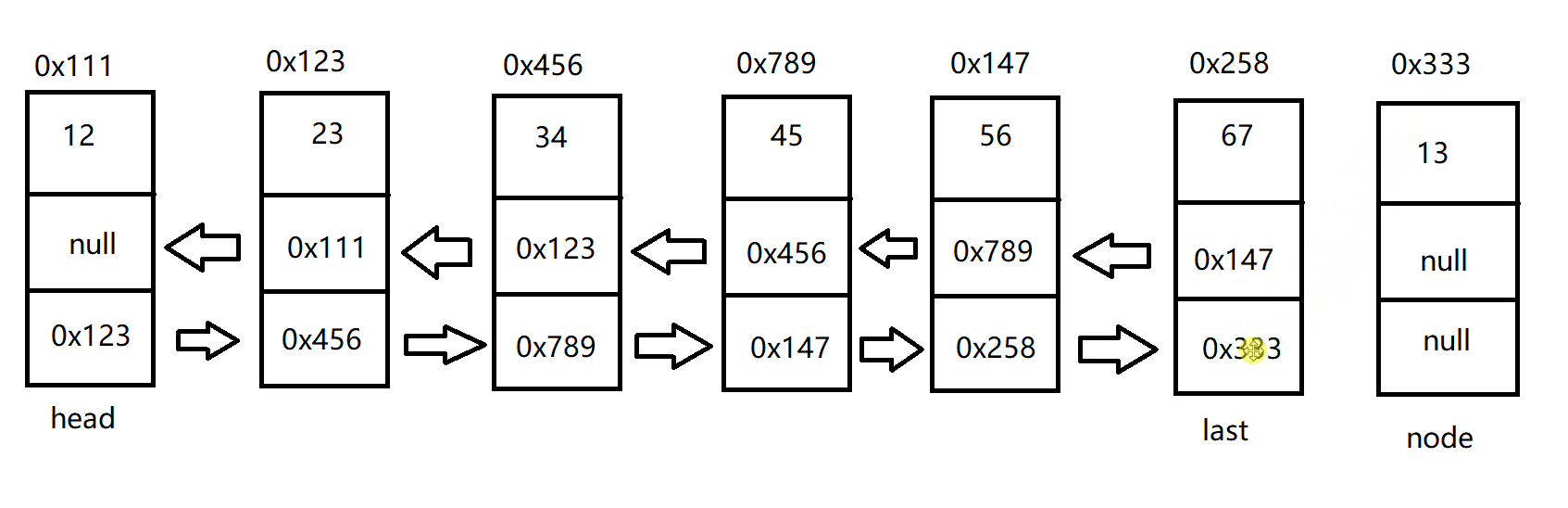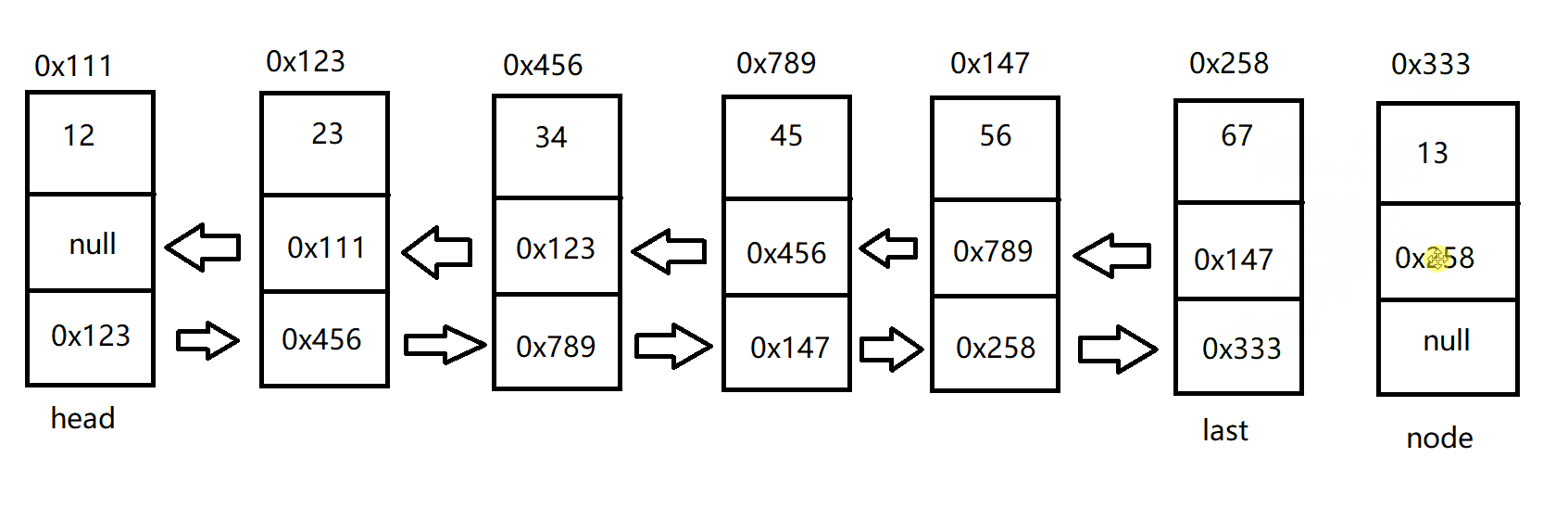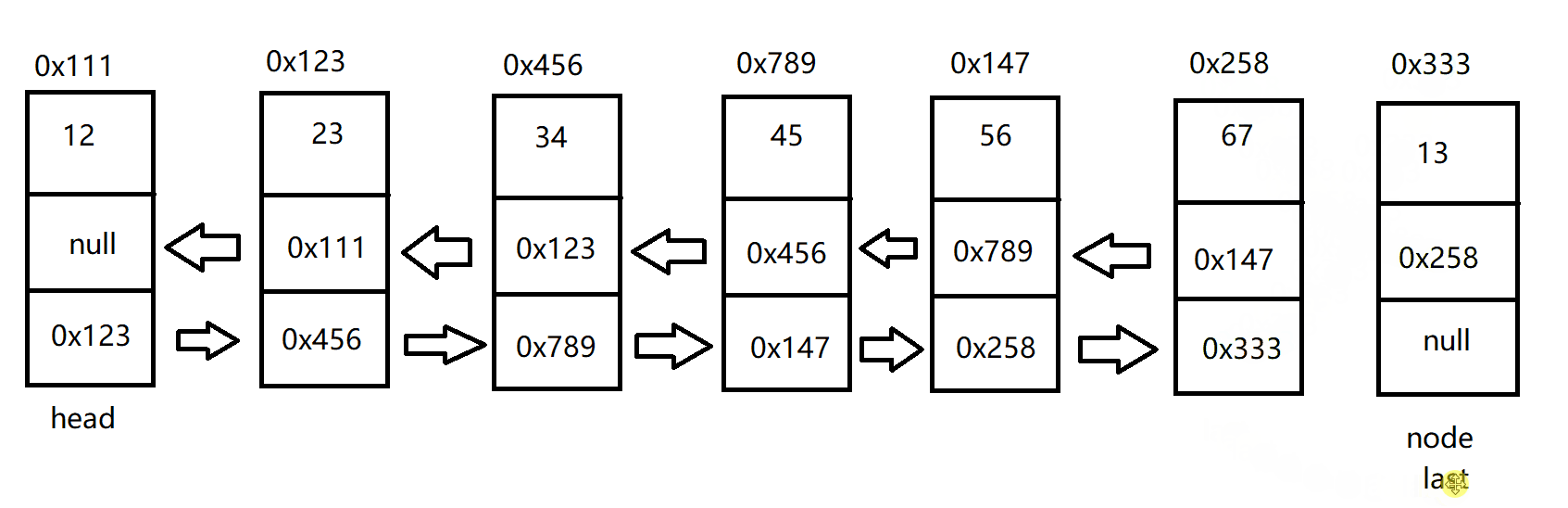
单链表中的节点是由一个数据域和下一节点的地址所构成的,双链表的节点是在单链表的基础上,存放前一个节点的地址。例如:
class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode prev;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
单链表有头节点,双向既有头节点,也有尾节点。代码实现如下:
public class MyLinkedList {
public ListNode head;//指向双向链表的头节点
public ListNode last;//指向双向链表的尾节点
}
打印双向链表
打印双向链表的方法与打印单链表的方法相同,具体代码如下:
public void display() {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
测量双链表的长度
测量双链表长度和单链表的方法也是一样的,具体代码如下:
public int size() {
ListNode cur = this.head;
int count = 0;
while(cur != null) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
判断双向链表中是否包含某数据
这个与单链表的方法一样,具体代码如下:
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
头插法增加节点
双向链表的头插法与单向链表的头插法略有不同
具体代码如下:
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
}else {
node.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
}
尾插法增加节点
双向链表的尾插法和双向链表的头插法类似
具体代码如下:
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
}else {
this.last.next = node;
node.prev = this.last;
this.last = node;
}
}
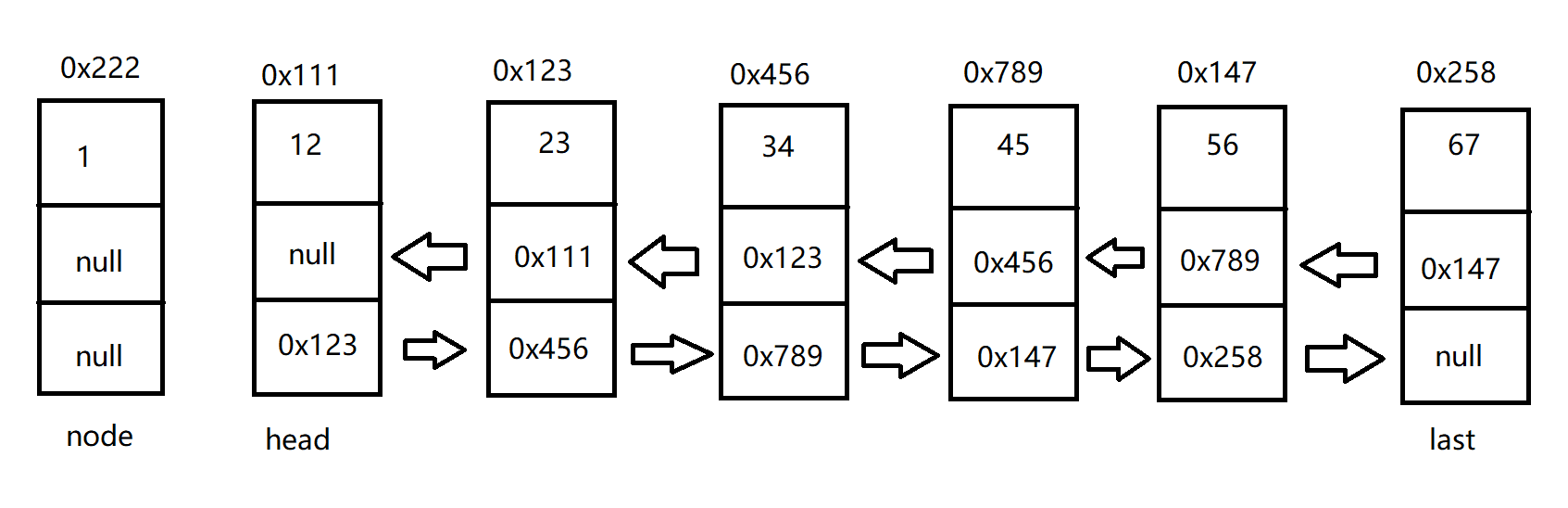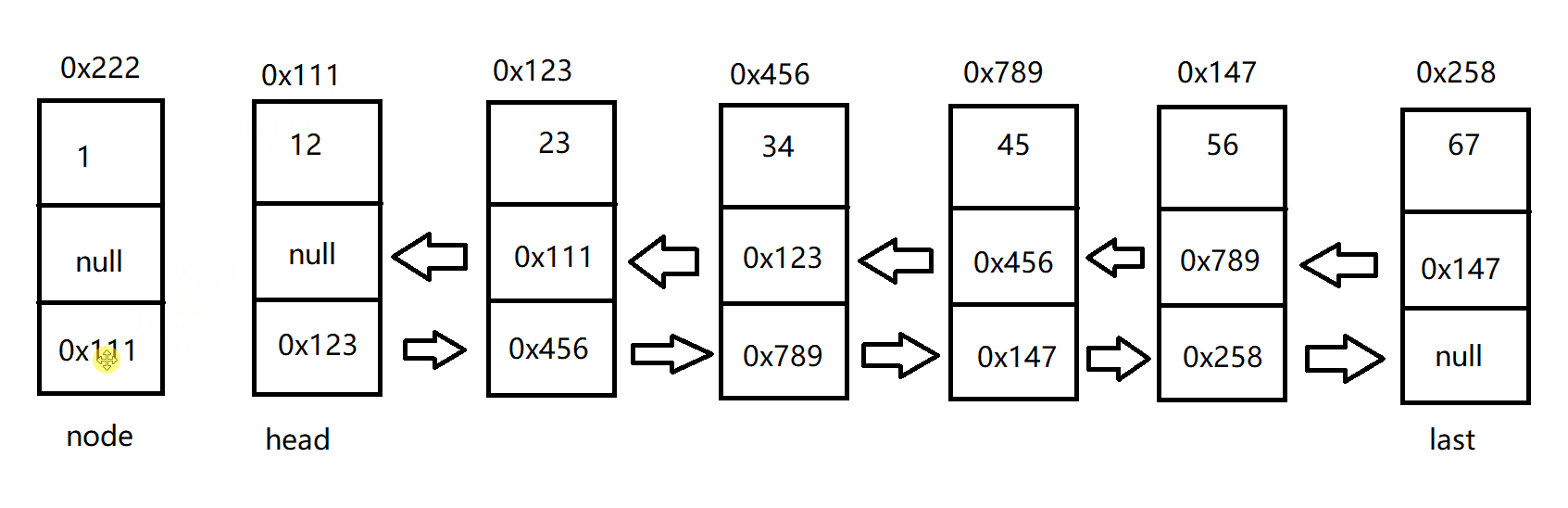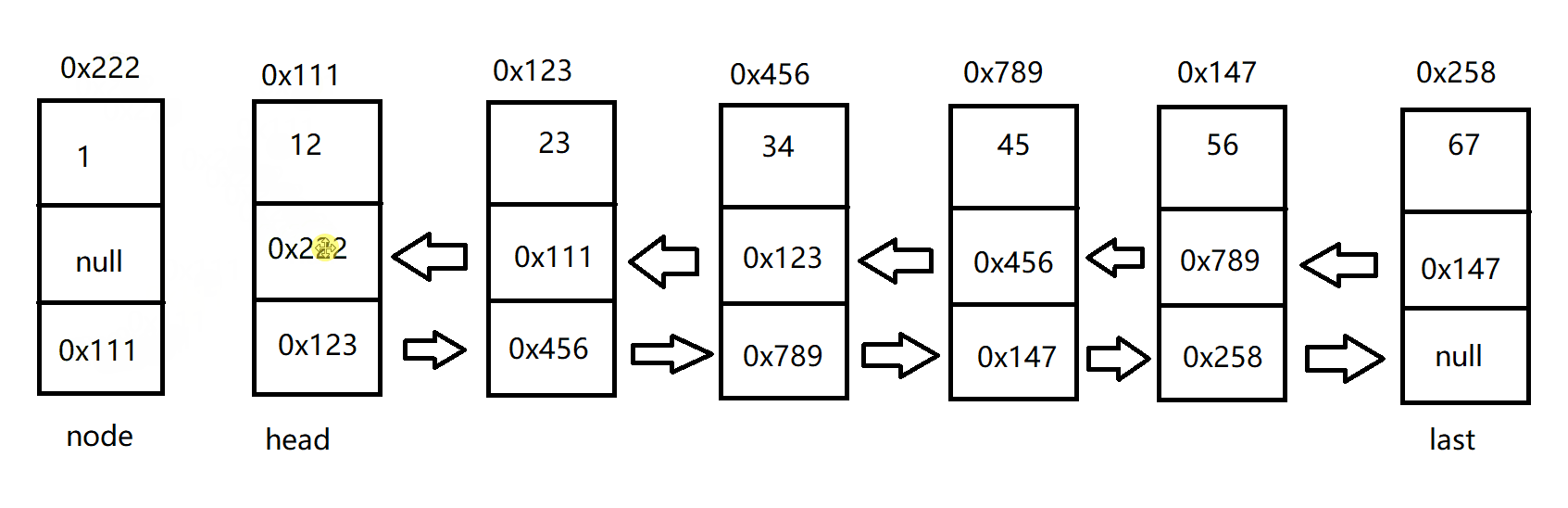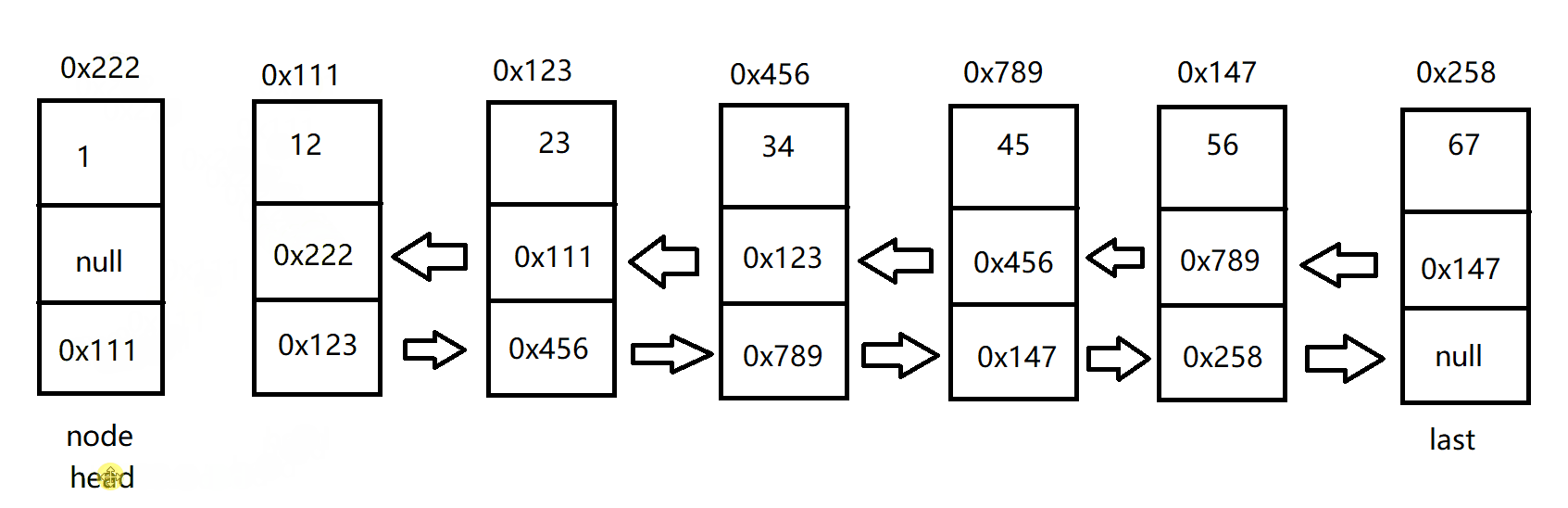
任意位置增加节点
双向链表任意位置增加节点和单向链表的方法类似,具体代码如下:
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
System.out.println("index位置不合法!");
return;
}
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = searchIndex(index);
node.next = cur.prev.next;
cur.prev.next = node;
node.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev = node;
}
public ListNode searchIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (index != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
删除某个节点
双向链表删除某个比单链表稍微复杂一点,不过也那么难。具体代码如下:
public void remove(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
if (cur == head) {
head = head.next;
if (head != null) {
head.prev = null;
}else {
last = null;
}
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}else {
last = last.prev;
}
}
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
删除多个数值相同的节点
双向链表中的删除多个数值相同的节点比单链表的要简单。如果明白了双向链表删除单个节点的原理的话,那么删除多个也就不成问题了。具体代码如下:
public void removeALLKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
if (cur == head) {
head = head.next;
if (head != null) {
head.prev = null;
}else {
last = null;
}
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}else {
last = last.prev;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
清空链表
清空双向链表需要一个节点一个节点地清空,具体代码如下:
public void clear() {
while (head != null) {
ListNode curNext = head.next;
head.next = null;
head.prev = null;
head = curNext;
}
last = null;
}
顺序表与链表的区别
对数据的组织方式
顺序表底层是一个数组,逻辑上和内存上都是连续的;链表是一个由若干个节点组成的一个数据结构,逻辑上是连续的,但内存上是不连续的。
对数据的操作方式
顺序表适合查找相关的操作,因为可以使用下标直接获取到某个位置的元素。
链表适合频繁的插入和删除操作。它无需像顺序表那样移动元素,它的插入只需要修改指向即可。
此外,顺序表满了之后还需要扩容,同时无法保证空间被充分利用,所以顺序表的空间利用率不高。
结尾
下一篇博客,将介绍java里的包。
上一篇博客:Java学习苦旅(九)——原来顺序表可以这么简单呀
下一篇博客:Java学习苦旅(十一)——你好,买“包”不?