springboot集成flowable工作流
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、工作流是如加载自定义流程的?
- 二、集成flowable
-
- 1.引入依赖以及jdbc/mybatis
- 2.配置字体,防止乱码
- 3.连接好数据库
- 4.启动项目
- 5.开始编码
- 总结
前言
工作流flowable更加的方便:
工作流中的表说明:
1、Flowable的所有数据库表都以ACT_开头。第二部分是说明表用途的两字符标示符。服务API的命名也大略符合这个规则。
2、ACT_RE_: 'RE’代表repository。带有这个前缀的表包含“静态”信息,例如流程定义与流程资源(图片、规则等)。
3、ACT_RU_: 'RU’代表runtime。这些表存储运行时信息,例如流程实例(process instance)、用户任务(user task)、变量(variable)、作业(job)等。Flowable只在流程实例运行中保存运行时数据,并在流程实例结束时删除记录。这样保证运行时表小和快。
4、ACT_HI_: 'HI’代表history。这些表存储历史数据,例如已完成的流程实例、变量、任务等。
5、ACT_GE_: 通用数据。在多处使用。
这些表无需手动建立,集成后,第一次启动,自动生成
一、工作流是如加载自定义流程的?
可以在 flowable-spring-boot-autoconfigure的包下中,发现配置文件中的如下这段
{
"sourceType": "org.flowable.spring.boot.FlowableProperties",
"defaultValue": "classpath*:\/processes\/",
"name": "flowable.process-definition-location-prefix",
"description": "The folder in which processes need to be searched for auto deployment.",
"type": "java.lang.String"
}
这也就是为什么,我们在 /resources/processes/ 中建立好一个流程文件后,就可以被工作流识别并加载到表中的原因;
二、集成flowable
1.引入依赖以及jdbc/mybatis
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
mysql
mysql-connector-java
runtime
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.flowable
flowable-spring-boot-starter
6.3.0
2.配置字体,防止乱码
增加一个配置类
@Configuration
public class FlowableConfig implements EngineConfigurationConfigurer<SpringProcessEngineConfiguration> {
@Override
public void configure(SpringProcessEngineConfiguration engineConfiguration) {
engineConfiguration.setActivityFontName("宋体");
engineConfiguration.setLabelFontName("宋体");
engineConfiguration.setAnnotationFontName("宋体");
}
}
3.连接好数据库
yml配置
server:
port: 8080
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/flowable-spring-boot?characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useTimezone=true
username: root
password:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
数据库名称无所谓,只需对应即可,需要手动创建数据库,配置好用户名密码
4.启动项目
- 右键启动后,项目会自动生成链接库中对应的所有工作流flowable中的表
- 安装插件
Flowable BPMN visualizer - 在 /resource 目录下创建 processes 文件夹
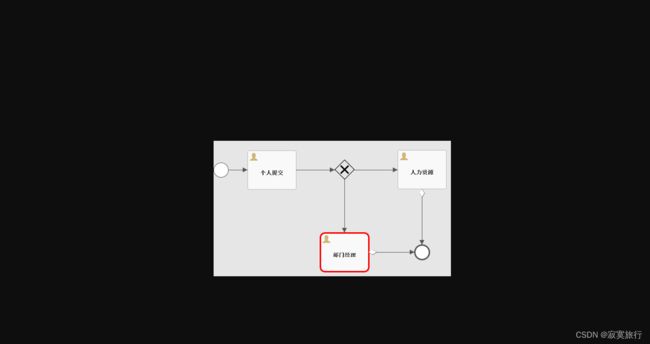
- 新建 类型为: bpmn20.xml 的文件, 例如名称为: qingjia
- 右键该新建文件,绘制流程图
5.开始编码
至此,准备工作全部完毕,开始编码;
- 新增工作流
- 审批任务
- 驳回任务
- 任务查询
- 流程图获取
import org.flowable.bpmn.model.BpmnModel;
import org.flowable.engine.*;
import org.flowable.engine.runtime.Execution;
import org.flowable.engine.runtime.ProcessInstance;
import org.flowable.image.ProcessDiagramGenerator;
import org.flowable.task.api.Task;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "common")
public class CommonController {
@Autowired
private RuntimeService runtimeService;
@Autowired
private TaskService taskService;
@Autowired
private RepositoryService repositoryService;
@Autowired
private ProcessEngine processEngine;
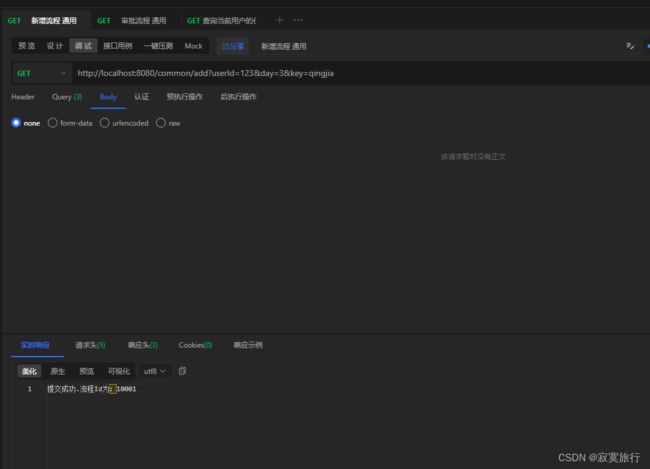
@RequestMapping(value = "add")
@ResponseBody
public String addExpense(String userId, Integer day, String key) {
//启动流程
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("user", userId);
map.put("day", day);
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey(key, map);
return "提交成功.流程Id为:" + processInstance.getId();
}
/**
* 获取列表
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/list")
@ResponseBody
public Object list(String userId) {
List<Task> tasks = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskAssignee(userId).orderByTaskCreateTime().desc().list();
for (Task task : tasks) {
System.out.println(task.toString());
}
return tasks.toArray().toString();
}
/**
* 批准
*
* @param taskId 任务ID
*/
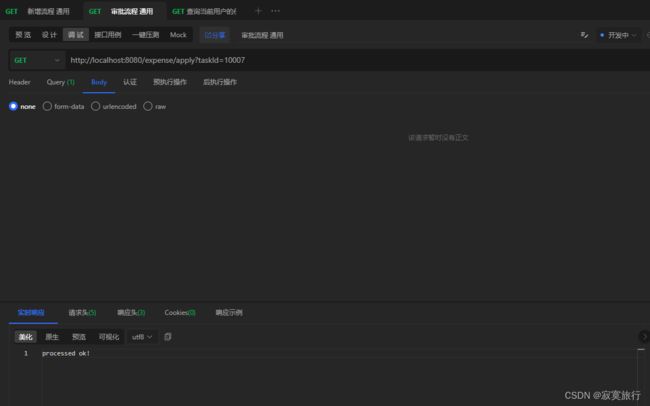
@RequestMapping(value = "apply")
@ResponseBody
public String apply(String taskId) {
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskId(taskId).singleResult();
if (task == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("流程不存在");
}
//通过审核
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("yijian", "tongyi");
taskService.complete(taskId, map);
return "processed ok!";
}
/**
* 拒绝
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "reject")
public String reject(String taskId) {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("outcome", "驳回");
taskService.complete(taskId, map);
return "reject";
}
/**
* 生成流程图
*
* @param processId 任务ID
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "processDiagram")
public void genProcessDiagram(HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, String processId) throws Exception {
ProcessInstance pi = runtimeService.createProcessInstanceQuery().processInstanceId(processId).singleResult();
//流程走完的不显示图
if (pi == null) {
return;
}
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().processInstanceId(pi.getId()).singleResult();
//使用流程实例ID,查询正在执行的执行对象表,返回流程实例对象
String InstanceId = task.getProcessInstanceId();
List<Execution> executions = runtimeService
.createExecutionQuery()
.processInstanceId(InstanceId)
.list();
//得到正在执行的Activity的Id
List<String> activityIds = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> flows = new ArrayList<>();
for (Execution exe : executions) {
List<String> ids = runtimeService.getActiveActivityIds(exe.getId());
activityIds.addAll(ids);
}
//获取流程图
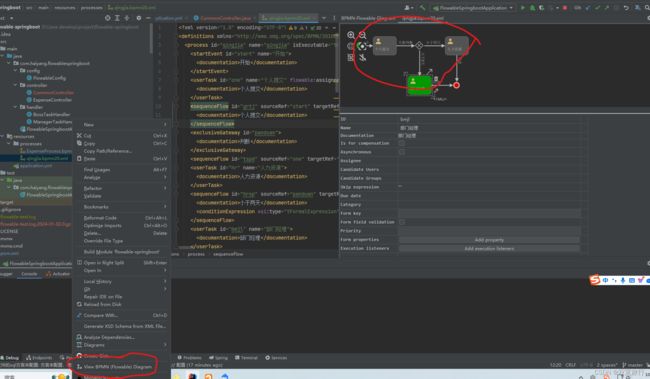
BpmnModel bpmnModel = repositoryService.getBpmnModel(pi.getProcessDefinitionId());
ProcessEngineConfiguration engconf = processEngine.getProcessEngineConfiguration();
ProcessDiagramGenerator diagramGenerator = engconf.getProcessDiagramGenerator();
InputStream in = diagramGenerator.generateDiagram(bpmnModel, "png", activityIds, flows, engconf.getActivityFontName(), engconf.getLabelFontName(), engconf.getAnnotationFontName(), engconf.getClassLoader(), 1.0);
OutputStream out = null;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int legth = 0;
try {
out = httpServletResponse.getOutputStream();
while ((legth = in.read(buf)) != -1) {
out.write(buf, 0, legth);
}
} finally {
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
}
开始测试:
总结
涉及的所有代码,源码地址: flowable-springboot