详解线上gitlab服务搭建(字数2w+)
目录
一、GitLab是什么?
1.GitLab的功能
2.GitLab和Git区别
3.GitLab的优势
二、GitLab安装1.环境配置
2.环境要求
#系统层
#Ruby versions
#硬件要求
#CPU
#Memory
#Unicorn Workers(进程数)
#Database
#PostgreSQL要求
#Redis and Sidekiq
#Prometheus and its exporters
#Node exporter
#Redis exporter
#Postgres exporter
#GitLab monitor exporter
#Supported web browsers
3.安装
2、关闭firewall
3、同步时间
4、配置gitlab-ce yum源
5、Gitlab安装方式
6、修改下配置文件
7、启动Gitlab服务
8、登录
9、卸载
4.汉化
#查看版本
#8版本下载汉化包并汉化
5.GitLab命令操作
6.GitLab配置
#修改web端口
#修改Prometheus端口
#修改项目工程数量
#关闭注册功能
#关闭监控
7.GitLab安全
#Custom password length limits
#Rack attack
#Information exclusivity
#How to reset your root password
#User email confirmation at sign-up
8.GitLab集群
9.GitLab Runner构建任务
#简介
#Requirements
#Features
#安装
#gitlab-runner使用
10.测试-http客户端
11.测试-ssh客户端
12.测试-GitLab Runner
一、GitLab是什么?
GitHub是2008年由Ruby on Rails编写而成,与业界闻名的Github类似;但要将代码上传到 GitHub上面,而且将项目设为私有还要收费。GitLab 是一个用于仓库管理系统的开源项目,使用Git作为代码管理工具,可通过Web界面进行访问公开的或者私人项目,非常适合在团队内部使用。在gitlab中有三个版本,分别是CE(社区版)、EE(企业版)、OM(RPM包完整版,里面包括nginx、redis等其它软件,比较大)。这里的编译安装版,是指CE版的源码安装。
1.GitLab的功能
- 代码托管服务
- 访问权限控制
- 问题跟踪,bug的记录和讨论
- 代码审查,可以查看、评论代码
- 社区版基于 MIT License 开源完全免费
2.GitLab和Git区别
Github和Git是两回事。Git是版本控制系统,Github是在线的基于Git的代码托管服务。
3.GitLab的优势
公司的项目,因为商业层面的原因,需要把代码托管到自有的服务器上,并且服务器很有可能是放在企业内网中,不对公网开放。出于安全性的考虑,暂时没有使用国内的Git服务平台的计划。GitHub和BitBucket,GitLab,由于服务商是在国外,受地域的影响,因此在网络访问上会迟。现有的服务商,对于免费的套餐都有一定的限制,比如GitHub只允许建立免费的开repository,不允许建立私有的仓库。BitBucket允许建立无限制的私有项目,不过对于项目中参与的开发人员是有人数限制的。当团队中开发者规模达到一定数量后,需要付费购买相应的套餐。
二、GitLab安装
1.环境配置
| 硬件: | redhat-7.x系列_x86_64 Mem建议2G |
| 软件: | gitlab-ce.x86_64 0:8.8.0-ce git-2.11.0 ruby2.1(至少是2.1) |
2.环境要求
#系统层
Ubuntu Debian CentOS 不支持win
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (please use the CentOS packages and instructions)
Scientific Linux (please use the CentOS packages and instructions)
Oracle Linux (please use the CentOS packages and instructions)
#Ruby versions
GitLab需要Ruby(MRI)2.3。支持低于2.3(2.1,2.2)的Ruby版本将停止与GitLab 8.13
#硬件要求
必要的硬盘驱动器空间很大程度上取决于您要存储在GitLab中的存档的大小,但是根据经验,您应该至少拥有与所有存档组合相同的可用空间。如果你希望在将来考虑使用LVM来安装硬盘驱动器空间方面具有灵活性,那么您可以在需要时添加更多的硬盘驱动器。除本地硬盘驱动器外,你还可以安装支持网络文件系统(NFS)协议的卷。此卷可能位于文件服务器,网络连接存储(NAS)设备,存储区域网络(SAN)或Amazon Web Services(AWS)弹性块存储(EBS)卷上。 如果你有足够的RAM内存和最近的CPU,则GitLab的速度主要受硬盘搜索时间的限制。快速驱动(7200 RPM或更高)或固态硬盘(SSD)将提高GitLab的响应速度
#CPU
1核心的CPU,基本上可以满足需求,大概支撑100个左右的用户,不过在运行GitLab网站的同时,还需要运行多个worker以及后台job,显得有点捉襟见肘了。
两核心的CPU是推荐的配置,大概能支撑500个用户.
4核心的CPU能支撑 2,000 个用户.
8核心的CPU能支撑 5,000 个用户.
16核心的CPU能支撑 10,000 个用户.
32核心的CPU能支撑 20,000 个用户.
64核心的CPU能支持多达 40,000 个用户.
#Memory
你需要至少4GB的可寻址内存(RAM交换)来安装和使用GitLab!操作系统和任何其他正在运行的应用程序也将使用内存,因此请记住,在运行GitLab之前,您至少需要4GB的可用空间。使用更少的内存GitLab将在重新配置运行期间给出奇怪的错误,并在使用过程中发生500个错误.
1GB RAM + 3GB of swap is the absolute minimum but we strongly advise against this amount of memory. See the unicorn worker section below for more advice.
2GB RAM + 2GB swap supports up to 100 users but it will be very slow
4GB RAM is the recommended memory size for all installations and supports up to 100 users
8GB RAM supports up to 1,000 users
16GB RAM supports up to 2,000 users
32GB RAM supports up to 4,000 users
64GB RAM supports up to 8,000 users
128GB RAM supports up to 16,000 users
256GB RAM supports up to 32,000 users
建议服务器上至少有2GB的交换,即使您目前拥有足够的可用RAM。如果可用的内存更改,交换将有助于减少错误发生的机会。
#Unicorn Workers(进程数)
可以增加独角兽工人的数量,这通常有助于减少应用程序的响应时间,并增加处理并行请求的能力.
对于大多数情况,我们建议使用:CPU内核1 =独角兽工人。所以对于一个有2个核心的机器,3个独角兽工人是理想的。
对于所有拥有2GB及以上的机器,我们建议至少三名独角兽工人。如果您有1GB机器,我们建议只配置两个Unicorn工作人员以防止过度的交换.
#Database
PostgreSQL
MySQL/MariaDB
强烈推荐使用PostgreSQL而不是MySQL / MariaDB,因为GitLab的所有功能都不能与MySQL / MariaDB一起使用。例如,MySQL没有正确的功能来以有效的方式支持嵌套组.
运行数据库的服务器应至少有5-10 GB的可用存储空间,尽管具体要求取决于GitLab安装的大小
#PostgreSQL要求
从GitLab 9.0起,PostgreSQL 9.2或更新版本是必需的,不支持早期版本。
#Redis and Sidekiq
Redis存储所有用户会话和后台任务队列。Redis的存储要求最低,每个用户大约25kB。
Sidekiq使用多线程进程处理后台作业。这个过程从整个Rails堆栈(200MB)开始,但是由于内存泄漏,它可以随着时间的推移而增长。在非常活跃的服务器(10,000个活跃用户)上,Sidekiq进程可以使用1GB的内存。
#Prometheus and its exporters
从Omnibus GitLab 9.0开始,默认情况下,Prometheus及其相关出口商启用,可以轻松,深入地监控GitLab。这些进程将使用大约200MB的内存,具有默认设置。这个还可以监控k8s
#Node exporter
节点导出器允许您测量各种机器资源,如内存,磁盘和CPU利用率。默认端口9100
#Redis exporter
Redis出口商允许您测量各种Redis指标。
#Postgres exporter
Postgres导出器允许您测量各种PostgreSQL度量。
#GitLab monitor exporter
GitLab监视器导出器允许您测量各种GitLab指标。
#Supported web browsers
支持Firefox,Chrome / Chromium,Safari和Microsoft浏览器(Microsoft Edge和Internet Explorer 11)的当前和之前的主要版本。
3.安装
1、关闭SELinux
#下面的命令实现永久关闭SELinux
[root@git ~]# sed -i 's/^SELINUX=.*/#&/;s/^SELINUXTYPE=.*/#&/;/SELINUX=.*/a SELINUX=disabled' /etc/sysconfig/selinux
#下面的命令实现临时关闭SELinux
[root@git ~]# setenforce 0
setenforce: SELinux is disabled
#永久修改下主机名,需要重启系统之后生效
Redhat6中修改
[root@git ~]# vi /etc/sysconfig/network
NETWORKING=yes
HOSTNAME=git.server.com #修改成你自己的主机名
Redhat7中修改
[root@noede1 ~]# vi /etc/hostname
gitlab.server.com
#永久修改
[root@git ~]#hostnamectl set-hostname gitlab.server.com
#添加域名
[root@git ~]#cat /etc/hosts
192.168.201.131 gitlab.server.com
2、关闭firewall
#临时关闭
[root@git yum.repos.d]# iptables -F
或者
[root@git gitlab_pack]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
#永久关闭,需要下次重启系统之后生效
[root@git gitlab_pack]# systemctl disable firewalld.service
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service.
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/basic.target.wants/firewalld.service.
#线上开启防火墙
[root@gitlab ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
success
[root@gitlab ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
Success
[root@gitlab ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
#重新加载配置
[root@gitlab ~]#systemctl reload firewalld
3、同步时间
[root@git yum.repos.d]# ntpdate time.nist.gov
10 Apr 11:00:04 ntpdate[40122]: step time server 216.229.0.179 offset 53747.856066 sec
4、配置gitlab-ce yum源
[root@git yum.repos.d]# cat gitlab.repo
[gitlab-ce]
name=gitlab-ce
baseurl=http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/gitlab-ce/yum/el7
repo_gpgcheck=0
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://packages.gitlab.com/gpg.key
注解:如果想要在centos6系列上安装,只需把el7修改成el6
5、Gitlab安装方式
Gitlab两种安装方式
编译安装
优点:可定制性强。数据库既可以选择MySQL,也可以选择PostgreSQL;服务器既可以选择Apache,也可以选择Nginx。
缺点:国外的源不稳定,被墙时,依赖软件包难以下载。配置流程繁琐、复杂,容易出现各种各样的问题。依赖关系多,不容易管理,卸载GitLab相对麻烦。
rpm包安装
优点:安装过程简单,安装速度快。采用rpm包安装方式,安装的软件包便于管理。
缺点:数据库默认采用PostgreSQL,服务器默认采用Nginx,不容易定制。
gitlab安装
1,下载
Download and install GitLab|GitLab
2,安装
#官方地址
https://about.gitlab.com/downloads/#centos7
#如果想查看rpm中内容,默认安装的位置
[root@gitlab gitlab_pack]# rpm2cpio gitlab-ce-8.8.0-ce.0.el6.x86_64.rpm | cpio -ivd
[root@git yum.repos.d]# yum install curl openssh-server openssh-clients postfix -y
[root@git yum.repos.d]# yum install gitlab-ce-8.8.0 -y
#这里为了节省时间,直接rpm安装
[root@git gitlab_pack]# rpm -ivh gitlab-ce-8.8.0-ce.0.el6.x86_64.rpm
Preparing... ################################# [100%]
Updating / installing...
1:gitlab-ce-8.8.0-ce.0.el6 ################################# [100%]
gitlab: Thank you for installing GitLab!
gitlab: To configure and start GitLab, RUN THE FOLLOWING COMMAND:
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
gitlab: GitLab should be reachable at http://localhost
gitlab: Otherwise configure GitLab for your system by editing /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb file
gitlab: And running reconfigure again.
gitlab:
gitlab: For a comprehensive list of configuration options please see the Omnibus GitLab readme
gitlab: https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/omnibus-gitlab/blob/master/README.md
gitlab:
It looks like GitLab has not been configured yet; skipping the upgrade script.
至此gitlab安装成功
注意:rpm 安装Gitlab的默认位置在/opt下
6、修改下配置文件
#修改url,供外部访问
[root@gitlab ~]# vi /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
external_url 'http://gitlab.server.com'
external_url 修改成自己的ip或者域名
#修改配置文件之后,需要重新是配置文件生效下,初始化下
[root@gitlab ~]#gitlab-ctl reconfigure #这里会花费一定的时间(1-10min),如果这里内存小,将会花费大量时间
Recipe: gitlab::gitlab-rails
* execute[clear the gitlab-rails cache] action run
- execute /opt/gitlab/bin/gitlab-rake cache:clear
* execute[clear the gitlab-rails cache] action run
- execute /opt/gitlab/bin/gitlab-rake cache:clear
Recipe: gitlab::unicorn
* service[unicorn] action restart
- restart service service[unicorn]
Recipe: gitlab::redis
* ruby_block[reload redis svlogd configuration] action create
- execute the ruby block reload redis svlogd configuration
Recipe: gitlab::postgresql
* ruby_block[reload postgresql svlogd configuration] action create
- execute the ruby block reload postgresql svlogd configuration
Recipe: gitlab::unicorn
* ruby_block[reload unicorn svlogd configuration] action create
- execute the ruby block reload unicorn svlogd configuration
Recipe: gitlab::sidekiq
* ruby_block[reload sidekiq svlogd configuration] action create
- execute the ruby block reload sidekiq svlogd configuration
Recipe: gitlab::gitlab-workhorse
* service[gitlab-workhorse] action restart
- restart service service[gitlab-workhorse]
* ruby_block[reload gitlab-workhorse svlogd configuration] action create
- execute the ruby block reload gitlab-workhorse svlogd configuration
Recipe: gitlab::gitlab-workhorse
* service[gitlab-workhorse] action restart
- restart service service[gitlab-workhorse]
* ruby_block[reload gitlab-workhorse svlogd configuration] action create
- execute the ruby block reload gitlab-workhorse svlogd configuration
Recipe: gitlab::nginx
* ruby_block[reload nginx svlogd configuration] action create
- execute the ruby block reload nginx svlogd configuration
Recipe: gitlab::logrotate
* ruby_block[reload logrotate svlogd configuration] action create
- execute the ruby block reload logrotate svlogd configuration
Running handlers:
Running handlers complete
Chef Client finished, 222/309 resources updated in 02 minutes 50 seconds
gitlab Reconfigured!#如果在此期间没有出现error,证明成功
7、启动Gitlab服务
[root@gitlab ~]# gitlab-ctl start
ok: down: gitaly: 0s, normally up
ok: down: gitlab-monitor: 1s, normally up
ok: down: gitlab-workhorse: 0s, normally up
ok: down: logrotate: 0s, normally up
ok: down: nginx: 0s, normally up
ok: down: node-exporter: 0s, normally up
ok: down: postgres-exporter: 1s, normally up
ok: down: postgresql: 0s, normally up
ok: down: prometheus: 1s, normally up
ok: down: redis: 0s, normally up
ok: down: redis-exporter: 0s, normally up
ok: down: sidekiq: 0s, normally up
ok: down: unicorn: 1s, normally up
注解:
- gitlab-workhorse这个“工作马”,就是gitlab-Git-http-server(GitlabV8.0出现,V8.2名称变更为Gitlab-workhorse)
- sidekiq 多线程启动
- unicorn是ruby的http server,可以通过http://localhost:8080端口访问, 默认端口是8080
- nginx作为方向代理,代理到unicorn,nginx默认端口是80
- postgresql作为数据库,默认端口是5432
- redis作为一个队列(NoSql), 用于存储用户session和任务,任务包括新建仓库、发送邮件等等,默认端口是6379
- logrotate 切割日志
- prometheus 监控,默认端口9090
- gitlab-monitor 默认端口9168
注:
(可选)如果系统资源不足,可以通过以下命令关闭Sidekiq来释放一部分内存
[root@gitlab ~]# gitlab-ctl stop sidekiq
ok: down: sidekiq: 0s, normally up
7.1 RPM安装模式下的启动、停止、重启
#初次配置服务
# gitlab-ctl reconfigure
#启动服务
# gitlab-ctl start
#停止服务
# gitlab-ctl stop
#重启服务
# gitlab-ctl restart
#状态
#gitlab-ctl status
#监控
#gitlab-ctl tail unicorn 监控unicorn日志
#gitlab-ctl tail
8、登录
访问地址http://ip
由于第一次登陆,需要设置密码,登录
9、卸载
重新安装清理
1,卸载
[root@git Gitlab-cn]# rpm -e gitlab-ce
2,删除文件
[root@git Gitlab-cn]#rm -rf /etc/gitlab/* /var/log/gitlab/ /var/opt/gitlab/ /opt/gitlab/
4.汉化
#查看版本
[root@git .ssh]# cat /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/VERSION9.1.2
#8版本下载汉化包并汉化
[root@git hanhua]# git clone https://gitlab.com/larryli/gitlab.git Gitlab-cn && cd Gitlab-cn
#备份/opt/gitlab/embedded/service目录下的gitlab-rails目录,该目录下的内容主要是web应用部分
#备份
[root@git Gitlab-cn]#\cp -rf /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails{,.ori}
#关闭gitlab这个服务
[root@git Gitlab-cn]#gitlab-ctl stop
#开始汉化
[root@git gitlab_pack]# \cp -rf Gitlab-cn/* /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/
测试是否汉化成功
[root@git ~]# gitlab-ctl start
ok: run: gitlab-workhorse: (pid 1407) 263s
ok: run: logrotate: (pid 1403) 263s
ok: run: nginx: (pid 1404) 263s
ok: run: postgresql: (pid 1405) 263s
ok: run: redis: (pid 1402) 263s
ok: run: sidekiq: (pid 1400) 263s
ok: run: unicorn: (pid 1401) 263s
登录
http://192.168.201.131/users/sign_in
5.GitLab命令操作
语法:
gitlab-ctl command (subcommand)
| Service Management Commands |
|
| start |
启动所有服务 |
| stop |
关闭所有服务 |
| restart |
重启所有服务 |
| status |
查看所有服务状态 |
| tail |
查看日志信息 |
| service-list |
列举所有启动服务 |
| graceful-kill |
平稳停止一个服务 |
例子:
#启动所有服务
[root@gitlab ~]# gitlab-ctl start
#启动单独一个服务
[root@gitlab ~]# gitlab-ctl start nginx
#查看日志,查看所有日志
[root@gitlab ~]# gitlab-ctl tail
#查看具体一个日志,类似tail -f
[root@gitlab ~]# gitlab-ctl tail nginx
| General Commands |
|
| help |
帮助 |
| reconfigure |
修改配置文件之后,需要重新加载下 |
| show-config |
查看所有服务配置文件信息 |
| uninstall |
卸载这个软件 |
| cleanse |
删除gitlab数据,重新白手起家 |
例子:
#显示所有服务配置文件
[root@gitlab ~]#gitlab-ctl show-config
#卸载gitlab
[root@gitlab ~]#gitlab-ctl uninstall
Database Commands(慎重使用)
| Database Commands |
|
| pg-upgrade |
更新postgresql版本 |
| revert-pg-upgrade |
还远先前的(离现在正在使用靠近的版本)一个数据库版本 |
例子:
#升级数据库
[root@gitlab ~]# gitlab-ctl pg-upgrade
Checking for an omnibus managed postgresql: OK
Checking if we already upgraded: OK
The latest version 9.6.1 is already running, nothing to do
#降级数据库版本
[root@gitlab ~]# gitlab-ctl revert-pg-upgrade
Toggling deploy page:cp /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/public/deploy.html /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/public/index.html
Toggling deploy page: OK
Toggling services:ok: down: gitaly: 129s, normally up
ok: down: gitlab-monitor: 128s, normally up
ok: down: logrotate: 127s, normally up
ok: down: node-exporter: 127s, normally up
ok: down: postgres-exporter: 126s, normally up
ok: down: prometheus: 125s, normally up
ok: down: redis-exporter: 125s, normally up
ok: down: sidekiq: 123s, normally up
Toggling services: OK
Checking if we need to downgrade: NOT OK
/var/opt/gitlab/postgresql/data.9.2.18 does not exist, cannot revert data
Will proceed with reverting the running program version only, unless you interrupt
Reverting database to 9.2.18 in 5 seconds
=== WARNING ===
This will revert the database to what it was before you upgraded, including the data.
Please hit Ctrl-C now if this isn't what you were looking for
=== WARNING ===
== Reverting ==
ok: down: postgresql: 131s, normally up
ok: run: postgresql: (pid 12102) 0s
== Reverted ==
Toggling deploy page:rm -f /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/public/index.html
Toggling deploy page: OK
Toggling services:ok: run: gitaly: (pid 12107) 1s
ok: run: gitlab-monitor: (pid 12111) 0s
ok: run: logrotate: (pid 12115) 1s
ok: run: node-exporter: (pid 12121) 0s
ok: run: postgres-exporter: (pid 12125) 0s
ok: run: prometheus: (pid 12130) 1s
ok: run: redis-exporter: (pid 12139) 0s
ok: run: sidekiq: (pid 12144) 1s
Toggling services: OK
6.GitLab配置
| 名称 |
配置路径 |
| gitlab配置文件 |
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb |
| unicorn配置文件 |
/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/etc/unicorn.rb |
| nginx配置文件 |
/var/opt/gitlab/nginx/conf/gitlab-http.conf |
| gitlab仓库默认位置 |
/var/opt/gitlab/git-data/repositories |
#修改web端口
如果80和8080端口被占用可以修改
[root@gitlab gitlab_pack]# vi /var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/etc/unicorn.rb
listen "127.0.0.1:8080", :tcp_nopush => true #这一行端口修改为你要端口
#修改nginx端口
[root@gitlab gitlab_pack]# vi /var/opt/gitlab/nginx/conf/gitlab-http.conf
server { #这里的80端口修改为你所需要的端口
listen *:80;
注: 只要修改了配置文件一定要重新加载配置
#修改Prometheus端口
#Prometheus默认端口是9090
[root@gitlab gitlab_pack]# vi /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
#根据自己情况自行修改成自己需要的port
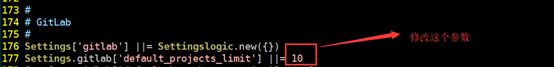
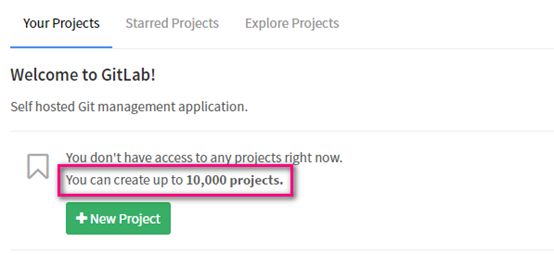
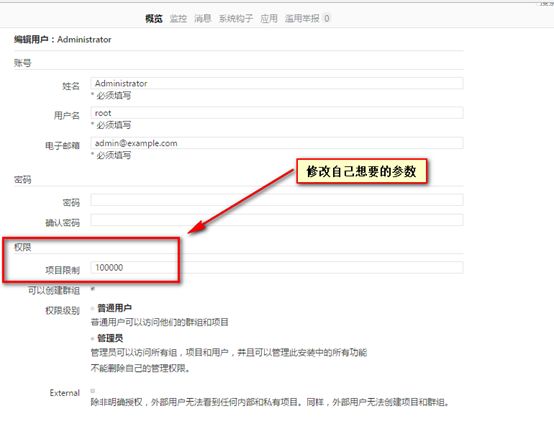
#修改项目工程数量
默认安装好,你能创建的项目,只能创建10个
#第一种方式修改
[root@gitlab gitlab_pack]# vi /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/config/initializers/1_settings.rb
Settings.gitlab['default_projects_limit'] ||= 10
修改成你自己所需要的参数,保存
Settings.gitlab['default_projects_limit'] ||= 10000
#重新初始化
[root@gitlab postgresql]# gitlab-ctl reconfigure
#查看修改之后项目数量
注:
这个是在安装完gitlab之后修改,如果已经使用一段时间,在修改项目的数量,需要你自己在自己的用户下修改,第二次初始化,会缩短时间
#第二种方式修改
#首先登录gitlab
#点击Adminstrator这个用户
#点击编辑
#关闭注册功能
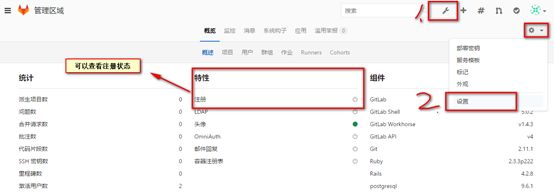
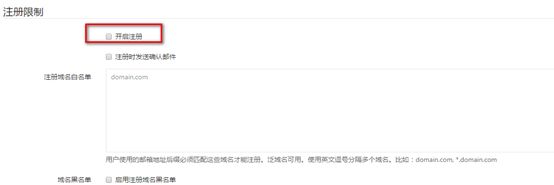
默认注册功能是开启的, 对于个人的gitlab, 没有对外公布的必要
#首先点击管理区域---à在点击设置按钮
找到注册限制
选中,然后保存
#关闭监控
#关闭服务
[root@gitlab gitlab_pack]# gitlab-ctl stop
[root@gitlab gitlab_pack]# vi /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
把true改成false
![]()
prometheus_monitoring['enable'] = true
prometheus_monitoring['enable'] = false
#保存
#重新加载配置文件
[root@gitlab gitlab_pack]# gitlab-ctl reconfigure
#启动服务
[root@gitlab gitlab_pack]# gitlab-ctl start
ok: run: gitaly: (pid 21611) 0s
ok: run: gitlab-workhorse: (pid 21615) 1s
ok: run: logrotate: (pid 21622) 0s
ok: run: nginx: (pid 21628) 1s
ok: run: postgresql: (pid 21633) 0s
ok: run: redis: (pid 21641) 0s
ok: run: sidekiq: (pid 21645) 1s
ok: run: unicorn: (pid 21648) 0s
#很显然没有prometheus这个服务
7.GitLab安全
#Custom password length limits
#初始化器的密码长度设置为最少8个字符
[root@gitlab opt]# cd /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/config/initializers
[root@gitlab initializers]#cp devise_password_length.rb.example devise_password_length.rb
#重启gitlab服务
#Rack attack
为了防止滥用客户造成损害GitLab使用机架攻击,提供一个保护路径
默认情况下,用户登录,用户注册(如果启用)和用户密码重置被限制为每分钟6个请求。尝试6次后,客户端将不得不等待下一分钟再次尝试。
如果发现节流不足以保护您免遭滥用客户端,机架式攻击宝石提供IP白名单,黑名单,Fail2ban样式过滤器和跟踪。
[root@gitlab opt]# cd /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/config/initializers
[root@gitlab initializers]# cp rack_attack.rb.example rack_attack.rb
#编辑application.rb
[root@gitlab config]#vi /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/config/application.rb
config.middleware.use Rack::Attack
保存
#重新启动GitLab实例
#Information exclusivity
Git是分布式版本控制系统(DVCS)。这意味着每个与源代码一起工作的人都具有完整存储库的本地副本。在GitLab中,不是客人的所有项目成员(因此,记者,开发人员和主人)都可以克隆资料库以获取本地副本。获取本地副本后,用户可以随时上传完整的存储库,包括其控制下的另一个项目或其他服务器。结果是您无法构建访问控制,阻止有权访问源代码的用户有意共享源代码。这是DVCS的固有特性,所有git管理系统都有这个限制。很明显,你可以采取措施,防止意外分享和破坏信息,这就是为什么只有一些人被允许邀请他人,没有人可以强制推行一个受保护的分支机构。
#How to reset your root password
[root@gitlab config]# gitlab-rails console production
Loading production environment (Rails 4.2.8)
irb(main):001:0> user = User.where(id: 1).first#查看信息
=> #
irb(main):002:0> user.password = 'admin123' #设置新的密码
=> "admin123"
irb(main):003:0> user.password_confirmation = 'admin123' #验证密码
=> "admin123"
irb(main):004:0> user.save! #保存密码
Enqueued ActionMailer::DeliveryJob (Job ID: b2ba5d30-853c-405d-8d95-fa938d88f32c) to Sidekiq(mailers) with arguments: "DeviseMailer", "password_change", "deliver_now", gid://gitlab/User/1
=> true
irb(main):005:0> #ctrl+d 退出
#User email confirmation at sign-up
如果您想在所有用户电子邮件登录之前确认,Gitlab管理员可以在注册时启用电子邮件确认
8.GitLab集群
9.GitLab Runner构建任务
官方:https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/
#简介
GitLab Runner是用于运行作业并将结果发送回GitLab的开源项目。它与GitLab CI结合使用,GitLab CI是GitLab中协调工作的开源连续集成服务。
#Requirements
GitLab Runner是用Go编写的,可以作为一个二进制文件运行,不需要任何语言特定的要求。它被设计为在GNU / Linux,macOS和Windows操作系统上运行。只要您可以编译一个Go二进制文件,其他操作系统就可能会工作。
#Features
Allows to run
- multiple jobs concurrently(多个工作同时进行)
- use multiple tokens with multiple server (even per-project)( 使用多个令牌与多个服务器(甚至每个项目))
- limit number of concurrent jobs per-token(限制每个令牌的并发作业数)
Jobs can be run
- locally(本地)
- using Docker containers(使用Docker容器)
- using Docker containers and executing job over SSH(使用Docker容器并通过SSH执行作业)
- using Docker containers with autoscaling on different clouds and virtualization hypervisors(使用Docker容器在不同的云和虚拟化管理程序上进行自动缩放)
- connecting to remote SSH server(连接到远程SSH服务器)
#安装
#安装gitlab-ci-multi-runner源
[root@gitlab ~]#curl -L https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/runner/gitlab-ci-multi-runner/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash
#安装
[root@gitlab ~]#yum install gitlab-ci-multi-runner
#gitlab-runner使用
必须是在8版本以上才能使用这个集成功能
https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/commands/README.html
语法
gitlab-runner
[root@gitlab ~]# gitlab-runner --help
USAGE:
gitlab-runner [global options] command [command options] [arguments...]
| COMMANDS |
|
| 名称 |
作用 |
| exec |
显示runner配置文件 |
| list |
|
| run |
运行多个runner服务 |
| register |
注册一个新的runner |
| install |
安装服务 |
| uninstall |
卸载服务 |
| start |
启动一个服务 |
| stop |
停止一个服务 |
| restart |
重启 |
| status |
一个服务状态 |
| run-single |
运行单独的一个runner |
| unregister |
注销特定的runner |
| verify |
验证所有注册的runner |
artifacts-downloader download and extract build artifacts (internal)
artifacts-uploader create and upload build artifacts (internal)
cache-archiver create and upload cache artifacts (internal)
cache-extractor download and extract cache artifacts (internal)
例子:
#list
[root@gitlab ~]# gitlab-runner list
Listing configured runners ConfigFile=/etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml
#debug
[root@gitlab ~]# gitlab-runner --debug list
Runtime platform arch=amd64 os=linux revision=0118d89 version=9.1.0
Listing configured runners ConfigFile=/etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml
gitlab-ci-multi-runner
[root@gitlab gitlab]# gitlab-ci-multi-runner register --help
Runner类型
GitLab-Runner可以分类两种类型:
Shared Runner(共享型)
Specific Runner(指定型)。
Shared Runner:
这种Runner(工人)是所有工程都能够用的。只有系统管理员能够创建Shared Runner。
Specific Runner:
这种Runner(工人)只能为指定的工程服务。拥有该工程访问权限的人都能够为该工程创建Shared Runner。
注册runner
1,copy 注册授权码
2,register
安装好gitlab-ci-multi-runner这个软件之后,我们就可以用它向GitLab-CI注册Runner了。
向GitLab-CI注册一个Runner需要两样东西:GitLab-CI的url和注册token。
其中,token是为了确定你这个Runner是所有工程都能够使用的Shared Runner还是具体某一个工程才能使用的Specific Runner
#查看register帮助
[root@gitlab gitlab]# gitlab-ci-multi-runner register --help
#注册Shared Runner
在注册Runner的时候,需要填入Token,GitLab根据不同的Token确定这个Runner是被设置为Shared Runner还是Specific Runner
[root@gitlab gitlab]# gitlab-ci-multi-runner register
Running in system-mode.
Please enter the gitlab-ci coordinator URL (e.g. https://gitlab.com/):
http://192.168.201.148/ci #输入ci
Please enter the gitlab-ci token for this runner:
2RBdZavdy6UsZvbyCcMF #注册授权码
Please enter the gitlab-ci description for this runner:
[gitlab.server.com]: test_runner #描述
Please enter the gitlab-ci tags for this runner (comma separated):
hello_tom #写个标签,可以多个,用逗号隔开
Whether to run untagged builds [true/false]:
[false]: #输入回车
Whether to lock Runner to current project [true/false]:
[false]: #输入回车
Registering runner... succeeded runner=2RBdZavd
Please enter the executor: virtualbox, docker-ssh+machine, kubernetes, parallels, shell, ssh, docker+machine, docker, docker-ssh:
shell #输入选择通讯方式
Runner registered successfully. Feel free to start it, but if it's running already the config should be automatically reloaded!
#查看服务是否运行
[root@gitlab gitlab]# ps -ef|grep runner
root 7998 1 0 13:09 ? 00:00:02 /usr/bin/gitlab-ci-multi-runner run --working-directory /home/gitlab-runner --config /etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml --service gitlab-runner --syslog --user gitlab-runner
注意:
如果不运行gitlab-ci-multi-runner register命令,直接在配置文件里面添加Runner的配置信息可以吗
当然不行。因为gitlab-ci-multi-runner register的作用除了把Runner的信息保存到配置文件以外,还有一个很重要的作用,那就是向GitLab-CI发出请求,在GitLab-CI中登记这个Runner的信息并且获取后续通信所需要的token。
3,查看register
# 登陆
http://my_url/admin/runners
#查看gitlab-runner配置文件
[root@gitlab ~]# cat /etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml
concurrent = 1
check_interval = 0
[[runners]]
name = "test_ci"
url = "http://192.168.201.148/ci"
token = "c6f62fe5a2b4ec072f5cc2fb096c02"
executor = "shell"
[runners.cache]
4,运行runner
要让一个Runner运行起来,--url、--token和--executor选项是必要的.
[root@gitlab gitlab]# gitlab-ci-multi-runner run-single --help
[root@gitlab ~]# gitlab-ci-multi-runner install --user=gitlab-runner --working-directory=/home/gitlab-runner
[root@gitlab ~]# gitlab-ci-multi-runner status
gitlab-runner: Service is running!
[root@gitlab test]# gitlab-ci-multi-runner list
Listing configured runners ConfigFile=/etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml
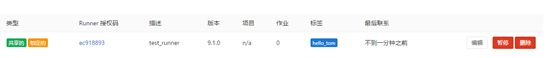
popop Executor=shell Token=8bfcd3b988ae348111b5500a355273 URL=http://192.168.201.149/ci
5,yaml
Keyword reference for the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file | GitLab
从7.12版本开始,GitLab CI使用YAML 文件(.gitlab-ci.yml)来配置project's builds
.gitlab-ci.yml 使用YAML语法, 需要格外注意缩进格式,要用空格来缩进,不能用tabs来缩进。
10.测试-http客户端
#创建测试目录
[root@client ~]# mkdir test2
[root@client ~]# cd test2
#把服务器的上仓库clone下来
[root@cleint test2]# git clone http://gitlab.server.com/root/test.git
Cloning into 'test'...
warning: You appear to have cloned an empty repository.
Checking connectivity... done.
或者
[root@cleint test2]# git clone http://gitlab.server.com/root/test.git
Username for 'http://git.server.com': root
Password for 'http://[email protected]': adminroot
Counting objects: 3, done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 216 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
To http://git.server.com/root/go.git
* [new branch] master -> master
Branch master set up to track remote branch master from origin.
[root@git test2]# ls
test
#配置用户
[root@cleint test2]# git config --global user.name "Administrator"
[root@client test2]# git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
[root@client test2]# cd test/
#创建文件
[root@client test]# touch README.md
[root@client test]# vi README.md
[root@client test]# git add README.md
[root@client test]# git commit -m "add README"
[master (root-commit) 874889b] add README
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 README.md
#push
[root@client test]# git push -u origin master
Username for 'http://git.server.com': root
Password for 'http://[email protected]': adminroot
Counting objects: 3, done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 223 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
To http://git.server.com/root/test.git
* [new branch] master -> master
Branch master set up to track remote branch master from origin.
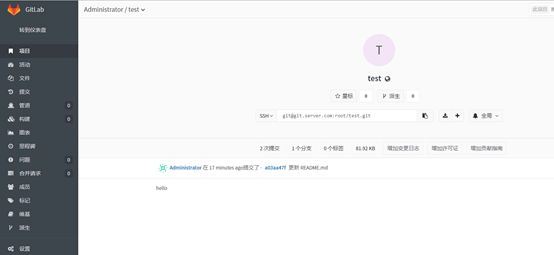
从web上查看test仓库下是否上传了README.md这个文件
#查看是否成功
上传成功
11.测试-ssh客户端
#生成公钥
[root@node6 .ssh]# ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
d9:0d:43:2b:17:cc:3b:01:fa:c9:cb:2c:6e:b7:27:6d root@node6
The key's randomart image is:
+--[ RSA 2048]----+
| .+o |
| . .+o |
| . . =o |
| o *o+ |
| S ... |
| o . |
| . +. |
| ...o E |
| ....= |
+-----------------+
[root@node6 .ssh]#
[root@node6 .ssh]# ls
id_rsa id_rsa.pub
[root@node6 .ssh]# cat id_rsa.pub
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEAoOLsYhPPlHPOnGh6SoVDPlVn2o8rfO55J60Gz7E0EDB0ugKgTu4VGOE8vVta7HH5exNAjw2UqHIliYcmVvrj5eFbvXLdLYGypiMfuP4H7dVwGXfxSzeG17aIbZma0fpB2bTQr3tN+nVA7tokVSmO+jC61/H6Qj9G1TEiedq0wtTuSQ8pza5hyeWRO9oi0W7ccZkYg7lSQ3Eo2n2/RJbmQHWdIcoBO8c64h5vq/gB1s7ZjHKUjSFvGTyHu7uYE6yD2PXylavLfq2FHUc4syV8yAvyW2ehgIcc+xDWMFC85SNuPvTOt0YNzG628gWB2lm+D8CPhZBUbz2IUkFN0jEdyQ== root@node6
#添加域名(如果是真实的域名,这步不需要做)
[root@node6 .ssh]# vi /etc/hosts
192.168.201.131 git.server.com
#添加到gitlab上
#测试ssh是否可用
[root@node6 .ssh]# ssh -T [email protected]
The authenticity of host 'git.server.com (192.168.201.134)' can't be established.
RSA key fingerprint is 45:1f:76:55:cb:72:fe:65:22:75:10:eb:d5:2e:35:d5.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added 'git.server.com,192.168.201.134' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
Welcome to GitLab, Administrator!
证明成功
#克隆数据
[root@node6 .ssh]# git clone [email protected]:root/test.git
Initialized empty Git repository in /root/.ssh/test/.git/
remote: Counting objects: 3, done.
remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
Receiving objects: 100% (3/3), 223 bytes, done
12.测试-GitLab Runner
在创建register之前,需要拿到token和ci地址
1,找到你要register的项目地址
2,进入到这个项目
3,点击设置
4,点击pipline,查看token和ci
#register
[root@gitlab test]# gitlab-ci-multi-runner register
#查看register
# 登陆
http://my_url/admin/runners
#查看gitlab-runner配置文件
[root@gitlab ~]# cat /etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml
concurrent = 1
check_interval = 0
[[runners]]
name = "test_ci"
url = "http://192.168.201.148/ci"
token = "c6f62fe5a2b4ec072f5cc2fb096c02"
executor = "shell"
[runners.cache]
#配置pipline
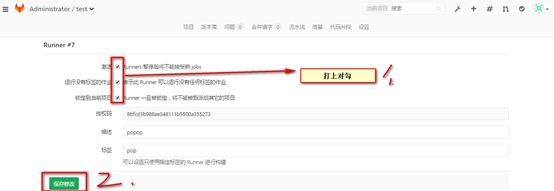
1,打开runner
2,编辑runner
#clone仓库
[root@gitlab test]# git clone http://[email protected]/root/test.git
[root@gitlab test]#cd test
#创建gitlab-ci.yml文件
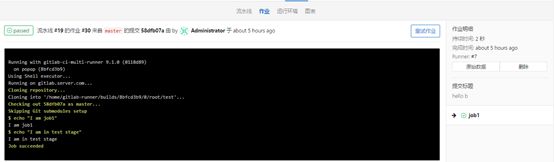
[root@gitlab test]# cat .gitlab-ci.yml
stages:
- test
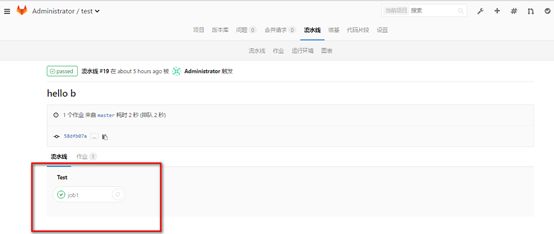
job1:
stage: test
script:
- echo "I am job1"
- echo "I am in test stage"
#上传到gitlab仓库中
[root@gitlab test]# git add .gitlab-ci.yml
[root@gitlab test]# git commit -m "kskksksk"
[master 9376c70] kskksksk
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+), 1 deletion(-)
[root@gitlab test]# git push origin master
Password for 'http://[email protected]':
Counting objects: 5, done.
Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 363 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0)
To http://[email protected]/root/test.git
df0b7b4..9376c70 master -> master
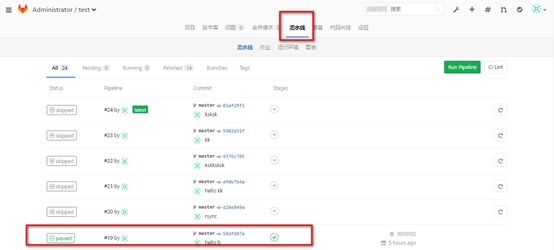
#查看效果
#点击passwd
总结
本文主要介绍了Gitlab相关概念,线下环境实战搭建gitlab详细步骤,持续更新中......