水质预测模型构建
1.水质数据介绍
1.1数据介绍
本文将水质分为可以用和不可饮用两种,以区分其水质好坏。水质数据来自于开源竞赛网络,具体包括pH value(pH值)、Hardness(硬度)、Solids(总溶解固体-TDS)、Chloramines(氯胺)、Conductivity(电导率)、Organic_carbon(有机碳)、Trihalomethanes(三卤甲烷类)、Turbidity(浊度)、Potability(可饮用性),以下是数据概念介绍。
- 1.pH value(pH值)
- PH是评估水的酸碱平衡的一个重要参数。它也是水状态的酸性或碱性条件的指示器。世界卫生组织建议pH值的最大允许限值为6.5至8.5。目前的调查范围为6.52-6.83,属于世界卫生组织标准范围。
- 2.Hardness(硬度)
- 硬度主要由钙盐和镁盐引起。这些盐是从水通过的地质沉积物中溶解出来的。水与产生硬度的材料接触的时间长度有助于确定原水中的硬度。硬度最初被定义为由钙和镁引起的水沉淀肥皂的能力。
- 3.Solids(总溶解固体-TDS)
- 水能够溶解各种无机和一些有机矿物或盐,如钾、钙、钠、碳酸氢盐、氯化物、镁、硫酸盐等。这些矿物在水的外观上会产生不想要的味道和稀释的颜色。这是用水的重要参数。TDS值高的水表明水具有高度矿化。TDS的理想限值为500mg/l,最大限值为1000mg/l,用于饮用。
- 4.Chloramines(氯胺)
- 氯和氯胺是公共供水系统中使用的主要消毒剂。氯胺最常见的形成是在氯中加入氨来处理饮用水。氯含量高达每升4毫克(mg/L或百万分之四(ppm))被认为是安全的饮用水中。
- 5.Sulfate(硫酸盐)
- 硫酸盐是天然存在的物质,存在于矿物、土壤和岩石中。它们存在于环境空气、地下水、植物和食物中。硫酸盐的主要商业用途是在化学工业中。海水中的硫酸盐浓度约为2700毫克/升(mg/L)。在大多数淡水供应中,它的浓度在3至30mg/L之间,尽管在一些地理位置发现的浓度要高得多(1000mg/L)。
- 6.Conductivity(电导率)
- 纯水不是电流的良好导体,而是一种良好的绝缘体。离子浓度的增加增强了水的导电性。通常,水中溶解固体的量决定了电导率。电导率(EC)实际上是测量溶液的离子过程,使其能够传输电流。根据世界卫生组织标准,EC值不应超过400μS/cm。
- 7.Organic_carbon(有机碳)
- 源水中的总有机碳(TOC)来自腐烂的天然有机物(NOM)和合成来源。TOC是衡量纯水中有机化合物中碳总量的指标。根据美国环保局的规定,经处理/饮用水中的总有机碳含量<2mg/L,用于处理的水源水中的总含量<4mg/L。
- 8.Trihalomethanes(三卤甲烷类)
- THM是一种化学物质,可能存在于经过氯处理的水中。饮用水中THM的浓度根据水中有机物质的水平、处理水所需的氯的量以及被处理水的温度而变化。高达80ppm的THM在饮用水中被认为是安全的。
- 9.Turbidity(浊度)
- 水的浊度取决于悬浮状态下存在的固体物质的数量。这是对水的发光财产的测量,该测试用于指示与胶体物质有关的废物排放质量。WondoGenet校园的平均浊度值(0.98NTU)低于世界卫生组织建议的5.00NTU。
- 10.Potability(可饮用性)
- 表示水对人类消费是否安全,其中1表示可饮用,0表示不可饮用。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import plotly.express as px
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
main_df = pd.read_csv("/kaggle/input/water-potability/water_potability.csv")
df = main_df.copy()
df.head()
|
ph |
Hardness |
Solids |
Chloramines |
Sulfate |
Conductivity |
Organic_carbon |
Trihalomethanes |
Turbidity |
Potability |
| 0 |
NaN |
204.890455 |
20791.318981 |
7.300212 |
368.516441 |
564.308654 |
10.379783 |
86.990970 |
2.963135 |
0 |
| 1 |
3.716080 |
129.422921 |
18630.057858 |
6.635246 |
NaN |
592.885359 |
15.180013 |
56.329076 |
4.500656 |
0 |
| 2 |
8.099124 |
224.236259 |
19909.541732 |
9.275884 |
NaN |
418.606213 |
16.868637 |
66.420093 |
3.055934 |
0 |
| 3 |
8.316766 |
214.373394 |
22018.417441 |
8.059332 |
356.886136 |
363.266516 |
18.436524 |
100.341674 |
4.628771 |
0 |
| 4 |
9.092223 |
181.101509 |
17978.986339 |
6.546600 |
310.135738 |
398.410813 |
11.558279 |
31.997993 |
4.075075 |
0 |
Following are the list of algorithms that are used in this notebook.
| Algorithm |
| Logistic Regression |
| Decision Tree |
| Random Forest |
| XGBoost |
| KNeighbours |
| SVM |
| AdaBoost |
print(df.shape)
(3276, 10)
print(df.columns)
Index(['ph', 'Hardness', 'Solids', 'Chloramines', 'Sulfate', 'Conductivity',
'Organic_carbon', 'Trihalomethanes', 'Turbidity', 'Potability'],
dtype='object')
1.2描述性统计
- 各个数据的数量、平均值、标准差、最小最大值等如下表所示。
df.describe()
|
ph |
Hardness |
Solids |
Chloramines |
Sulfate |
Conductivity |
Organic_carbon |
Trihalomethanes |
Turbidity |
Potability |
| count |
2785.000000 |
3276.000000 |
3276.000000 |
3276.000000 |
2495.000000 |
3276.000000 |
3276.000000 |
3114.000000 |
3276.000000 |
3276.000000 |
| mean |
7.080795 |
196.369496 |
22014.092526 |
7.122277 |
333.775777 |
426.205111 |
14.284970 |
66.396293 |
3.966786 |
0.390110 |
| std |
1.594320 |
32.879761 |
8768.570828 |
1.583085 |
41.416840 |
80.824064 |
3.308162 |
16.175008 |
0.780382 |
0.487849 |
| min |
0.000000 |
47.432000 |
320.942611 |
0.352000 |
129.000000 |
181.483754 |
2.200000 |
0.738000 |
1.450000 |
0.000000 |
| 25% |
6.093092 |
176.850538 |
15666.690297 |
6.127421 |
307.699498 |
365.734414 |
12.065801 |
55.844536 |
3.439711 |
0.000000 |
| 50% |
7.036752 |
196.967627 |
20927.833607 |
7.130299 |
333.073546 |
421.884968 |
14.218338 |
66.622485 |
3.955028 |
0.000000 |
| 75% |
8.062066 |
216.667456 |
27332.762127 |
8.114887 |
359.950170 |
481.792304 |
16.557652 |
77.337473 |
4.500320 |
1.000000 |
| max |
14.000000 |
323.124000 |
61227.196008 |
13.127000 |
481.030642 |
753.342620 |
28.300000 |
124.000000 |
6.739000 |
1.000000 |
df.info()
RangeIndex: 3276 entries, 0 to 3275
Data columns (total 10 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 ph 2785 non-null float64
1 Hardness 3276 non-null float64
2 Solids 3276 non-null float64
3 Chloramines 3276 non-null float64
4 Sulfate 2495 non-null float64
5 Conductivity 3276 non-null float64
6 Organic_carbon 3276 non-null float64
7 Trihalomethanes 3114 non-null float64
8 Turbidity 3276 non-null float64
9 Potability 3276 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(9), int64(1)
memory usage: 256.1 KB
print(df.nunique())
ph 2785
Hardness 3276
Solids 3276
Chloramines 3276
Sulfate 2495
Conductivity 3276
Organic_carbon 3276
Trihalomethanes 3114
Turbidity 3276
Potability 2
dtype: int64
print(df.isnull().sum())
ph 491
Hardness 0
Solids 0
Chloramines 0
Sulfate 781
Conductivity 0
Organic_carbon 0
Trihalomethanes 162
Turbidity 0
Potability 0
dtype: int64
df.dtypes
ph float64
Hardness float64
Solids float64
Chloramines float64
Sulfate float64
Conductivity float64
Organic_carbon float64
Trihalomethanes float64
Turbidity float64
Potability int64
dtype: object
sns.heatmap(df.isnull())

plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
sns.heatmap(df.corr(), annot= True, cmap='coolwarm')

corr = df.corr()
c1 = corr.abs().unstack()
c1.sort_values(ascending = False)[12:24:2]
Hardness Sulfate 0.106923
ph Solids 0.089288
Hardness ph 0.082096
Solids Chloramines 0.070148
Hardness Solids 0.046899
ph Organic_carbon 0.043503
dtype: float64
ax = sns.countplot(x = "Potability",data= df, saturation=0.8)
plt.xticks(ticks=[0, 1], labels = ["Not Potable", "Potable"])
plt.show()
```python
x = df.Potability.value_counts()
labels = [0,1]
print(x)
0 1998
1 1278
Name: Potability, dtype: int64
sns.violinplot(x='Potability', y='ph', data=df, palette='rocket')

fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols = 5, nrows = 2, figsize = (20, 10))
index = 0
ax = ax.flatten()
for col, value in df.items():
sns.boxplot(y=col, data=df, ax=ax[index])
index += 1
plt.tight_layout(pad = 0.5, w_pad=0.7, h_pad=5.0)
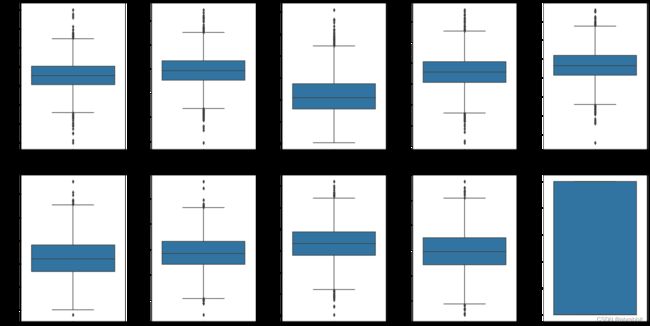
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [20,10]
df.hist()
plt.show()

sns.pairplot(df, hue="Potability")
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [7,5]
sns.distplot(df['Potability'])

df.hist(column='ph', by='Potability')
array([,
], dtype=object)
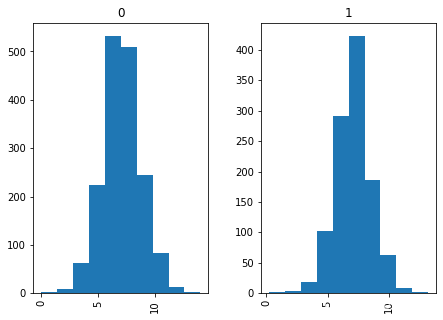
df.hist(column='Hardness', by='Potability')
array([,
], dtype=object)

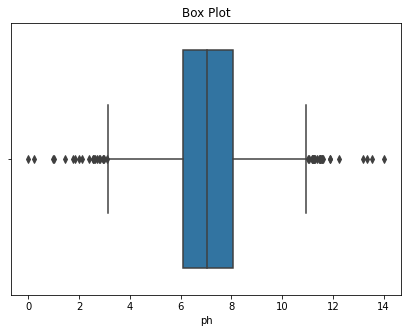
def Box(df):
plt.title("Box Plot")
sns.boxplot(df)
plt.show()
Box(df['ph'])
sns.histplot(x = "Hardness", data=df)

df.nunique()
ph 2785
Hardness 3276
Solids 3276
Chloramines 3276
Sulfate 2495
Conductivity 3276
Organic_carbon 3276
Trihalomethanes 3114
Turbidity 3276
Potability 2
dtype: int64
skew_val = df.skew().sort_values(ascending=False)
skew_val
Solids 0.621634
Potability 0.450784
Conductivity 0.264490
ph 0.025630
Organic_carbon 0.025533
Turbidity -0.007817
Chloramines -0.012098
Sulfate -0.035947
Hardness -0.039342
Trihalomethanes -0.083031
dtype: float64
- Using pandas skew function to check the correlation between the values.
- Values between 0.5 to -0.5 will be considered as the normal distribution else will be skewed depending upon the skewness value.
df.isnull().mean().plot.bar(figsize=(10,6))
plt.ylabel('Percentage of missing values')
plt.xlabel('Features')
plt.title('Missing Data in Percentages');

df['ph'] = df['ph'].fillna(df['ph'].mean())
df['Sulfate'] = df['Sulfate'].fillna(df['Sulfate'].mean())
df['Trihalomethanes'] = df['Trihalomethanes'].fillna(df['Trihalomethanes'].mean())
df.head()
|
ph |
Hardness |
Solids |
Chloramines |
Sulfate |
Conductivity |
Organic_carbon |
Trihalomethanes |
Turbidity |
Potability |
| 0 |
7.080795 |
204.890455 |
20791.318981 |
7.300212 |
368.516441 |
564.308654 |
10.379783 |
86.990970 |
2.963135 |
0 |
| 1 |
3.716080 |
129.422921 |
18630.057858 |
6.635246 |
333.775777 |
592.885359 |
15.180013 |
56.329076 |
4.500656 |
0 |
| 2 |
8.099124 |
224.236259 |
19909.541732 |
9.275884 |
333.775777 |
418.606213 |
16.868637 |
66.420093 |
3.055934 |
0 |
| 3 |
8.316766 |
214.373394 |
22018.417441 |
8.059332 |
356.886136 |
363.266516 |
18.436524 |
100.341674 |
4.628771 |
0 |
| 4 |
9.092223 |
181.101509 |
17978.986339 |
6.546600 |
310.135738 |
398.410813 |
11.558279 |
31.997993 |
4.075075 |
0 |
sns.heatmap(df.isnull())
df.isnull().sum()
ph 0
Hardness 0
Solids 0
Chloramines 0
Sulfate 0
Conductivity 0
Organic_carbon 0
Trihalomethanes 0
Turbidity 0
Potability 0
dtype: int64
X = df.drop('Potability', axis=1)
y = df['Potability']
X.shape, y.shape
((3276, 9), (3276,))
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
X = scaler.fit_transform(X)
X
array([[-1.02733269e-14, 2.59194711e-01, -1.39470871e-01, ...,
-1.18065057e+00, 1.30614943e+00, -1.28629758e+00],
[-2.28933938e+00, -2.03641367e+00, -3.85986650e-01, ...,
2.70597240e-01, -6.38479983e-01, 6.84217891e-01],
[ 6.92867789e-01, 8.47664833e-01, -2.40047337e-01, ...,
7.81116857e-01, 1.50940884e-03, -1.16736546e+00],
...,
[ 1.59125368e+00, -6.26829230e-01, 1.27080989e+00, ...,
-9.81329234e-01, 2.18748247e-01, -8.56006782e-01],
[-1.32951593e+00, 1.04135450e+00, -1.14405809e+00, ...,
-9.42063817e-01, 7.03468419e-01, 9.50797383e-01],
[ 5.40150905e-01, -3.85462310e-02, -5.25811937e-01, ...,
5.60940070e-01, 7.80223466e-01, -2.12445866e+00]])
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.33, random_state=42)
2.水质模型构建
2.1逻辑回归模型构建
这几个水质模型构建效果分析(结合各模型图表、指标)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score, classification_report
model_lg = LogisticRegression(max_iter=120,random_state=0, n_jobs=20)
model_lg.fit(X_train, y_train)
LogisticRegression(max_iter=120, n_jobs=20, random_state=0)
pred_lg = model_lg.predict(X_test)
lg = accuracy_score(y_test, pred_lg)
print(lg)
0.6284658040665434
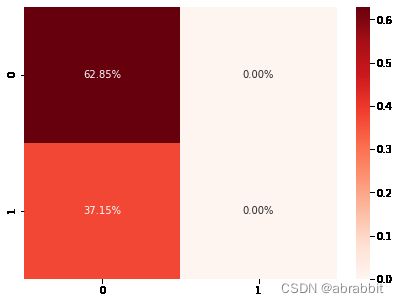
- 逻辑回归的预测精确度为0.6284658040665434
print(classification_report(y_test,pred_lg))
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.63 1.00 0.77 680
1 0.00 0.00 0.00 402
accuracy 0.63 1082
macro avg 0.31 0.50 0.39 1082
weighted avg 0.39 0.63 0.49 1082
cm1 = confusion_matrix(y_test, pred_lg)
sns.heatmap(cm1/np.sum(cm1), annot = True, fmt= '0.2%', cmap = 'Reds')
2.2决策树模型构建
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
model_dt = DecisionTreeClassifier( max_depth=4, random_state=42)
model_dt.fit(X_train,y_train)
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=4, random_state=42)
pred_dt = model_dt.predict(X_test)
dt = accuracy_score(y_test, pred_dt)
print(dt)
0.6451016635859519
- 可见,决策树模型的精确度是0.6451016635859519
print(classification_report(y_test,pred_dt))
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.66 0.90 0.76 680
1 0.56 0.22 0.32 402
accuracy 0.65 1082
macro avg 0.61 0.56 0.54 1082
weighted avg 0.62 0.65 0.60 1082
cm2 = confusion_matrix(y_test, pred_dt)
sns.heatmap(cm2/np.sum(cm2), annot = True, fmt= '0.2%', cmap = 'Reds')

2.3随机森林模型构建
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
model_rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=300,min_samples_leaf=0.16, random_state=42)
model_rf.fit(X_train, y_train)
RandomForestClassifier(min_samples_leaf=0.16, n_estimators=300, random_state=42)
pred_rf = model_rf.predict(X_test)
rf = accuracy_score(y_test, pred_rf)
print(rf)
0.6284658040665434
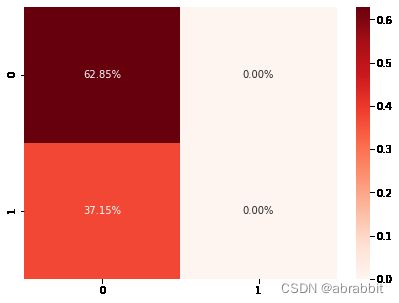
随机森林模型的准确度是0.6284658040665434
print(classification_report(y_test,pred_rf))
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.63 1.00 0.77 680
1 0.00 0.00 0.00 402
accuracy 0.63 1082
macro avg 0.31 0.50 0.39 1082
weighted avg 0.39 0.63 0.49 1082
cm3 = confusion_matrix(y_test, pred_rf)
sns.heatmap(cm3/np.sum(cm3), annot = True, fmt= '0.2%', cmap = 'Reds')
2.4XGBoost模型构建
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
model_xgb = XGBClassifier(max_depth= 8, n_estimators= 125, random_state= 0, learning_rate= 0.03, n_jobs=5)
model_xgb.fit(X_train, y_train)
[01:40:53] WARNING: ../src/learner.cc:1095: Starting in XGBoost 1.3.0, the default evaluation metric used with the objective 'binary:logistic' was changed from 'error' to 'logloss'. Explicitly set eval_metric if you'd like to restore the old behavior.
XGBClassifier(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=1,
colsample_bynode=1, colsample_bytree=1, gamma=0, gpu_id=-1,
importance_type='gain', interaction_constraints='',
learning_rate=0.03, max_delta_step=0, max_depth=8,
min_child_weight=1, missing=nan, monotone_constraints='()',
n_estimators=125, n_jobs=5, num_parallel_tree=1, random_state=0,
reg_alpha=0, reg_lambda=1, scale_pos_weight=1, subsample=1,
tree_method='exact', validate_parameters=1, verbosity=None)
pred_xgb = model_xgb.predict(X_test)
xgb = accuracy_score(y_test, pred_xgb)
print(xgb)
0.6709796672828097
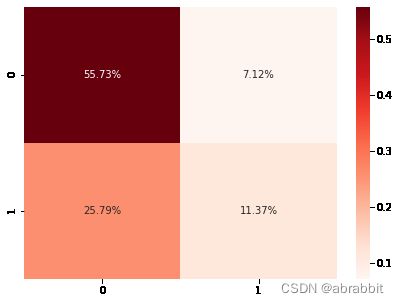
- XGBoost模型的准确度是0.6709796672828097
print(classification_report(y_test,pred_xgb))
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.68 0.89 0.77 680
1 0.61 0.31 0.41 402
accuracy 0.67 1082
macro avg 0.65 0.60 0.59 1082
weighted avg 0.66 0.67 0.64 1082
- XGBoost模型的召回率、F1分数指标如上图所示。
cm4 = confusion_matrix(y_test, pred_xgb)
sns.heatmap(cm4/np.sum(cm4), annot = True, fmt= '0.2%', cmap = 'Reds')
2.5KNN模型构建
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
model_kn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=9, leaf_size=20)
model_kn.fit(X_train, y_train)
KNeighborsClassifier(leaf_size=20, n_neighbors=9)
pred_kn = model_kn.predict(X_test)
kn = accuracy_score(y_test, pred_kn)
print(kn)
0.6534195933456562
- KNN模型的准确度是0.6534195933456562
print(classification_report(y_test,pred_kn))
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.69 0.82 0.75 680
1 0.55 0.37 0.44 402
accuracy 0.65 1082
macro avg 0.62 0.60 0.59 1082
weighted avg 0.64 0.65 0.63 1082
cm5 = confusion_matrix(y_test, pred_kn)
sns.heatmap(cm5/np.sum(cm5), annot = True, fmt= '0.2%', cmap = 'Reds')

2.6支持向量机模型构建
from sklearn.svm import SVC, LinearSVC
model_svm = SVC(kernel='rbf', random_state = 42)
model_svm.fit(X_train, y_train)
SVC(random_state=42)
pred_svm = model_svm.predict(X_test)
sv = accuracy_score(y_test, pred_svm)
print(sv)
0.6885397412199631
print(classification_report(y_test,pred_kn))
cm6 = confusion_matrix(y_test, pred_svm)
sns.heatmap(cm6/np.sum(cm6), annot = True, fmt= '0.2%', cmap = 'Reds')

from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
model_ada = AdaBoostClassifier(learning_rate= 0.002,n_estimators= 205,random_state=42)
model_ada.fit(X_train, y_train)
AdaBoostClassifier(learning_rate=0.002, n_estimators=205, random_state=42)
pred_ada = model_ada.predict(X_test)
ada = accuracy_score(y_test, pred_ada)
print(ada)
0.634011090573013
- 可见,SVM模型准确率是0.634011090573013
print(classification_report(y_test,pred_ada))
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.63 0.99 0.77 680
1 0.62 0.04 0.07 402
accuracy 0.63 1082
macro avg 0.62 0.51 0.42 1082
weighted avg 0.63 0.63 0.51 1082
cm7 = confusion_matrix(y_test, pred_ada)
sns.heatmap(cm7/np.sum(cm7), annot = True, fmt= '0.2%', cmap = 'Reds')

3.各模型效果比较
models = pd.DataFrame({
'Model':['Logistic Regression', 'Decision Tree', 'Random Forest', 'XGBoost', 'KNeighbours', 'SVM', 'AdaBoost'],
'Accuracy_score' :[lg, dt, rf, xgb, kn, sv, ada]
})
models
sns.barplot(x='Accuracy_score', y='Model', data=models)
models.sort_values(by='Accuracy_score', ascending=False)
|
Model |
Accuracy_score |
| 5 |
SVM |
0.688540 |
| 3 |
XGBoost |
0.670980 |
| 4 |
KNeighbours |
0.653420 |
| 1 |
Decision Tree |
0.645102 |
| 6 |
AdaBoost |
0.634011 |
| 0 |
Logistic Regression |
0.628466 |
| 2 |
Random Forest |
0.628466 |

比较了各个模型的预测精度后发现,SVM模型有着更高的精准度。



















