代码随想录算法训练营第16天 | 104.二叉树的最大深度 559.n叉树的最大深度 111.二叉树的最小深度 222.完全二叉树的节点个数
目录
104.二叉树的最大深度
解题思路
递归法
迭代法
实现代码
559.n叉树的最大深度
解题思路
实现代码
111.二叉树的最小深度
解题思路
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
实现代码
222.完全二叉树的节点个数
解题思路
普通二叉树
递归
完全二叉树
实现代码
104.二叉树的最大深度
题目链接:104.二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
返回它的最大深度 3 。
解题思路
在十道题那篇文章中遇到过这道题。
递归法
本题可以使用前序(中左右),也可以使用后序遍历(左右中),使用前序求的就是深度,使用后序求的是高度。
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
- 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
而根节点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度,所以本题中我们通过后序求的根节点高度来求的二叉树最大深度。
我先用后序遍历(左右中)来计算树的高度。
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回这棵树的深度,所以返回值为int类型。
代码如下:
int getdepth(TreeNode* node)
- 确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示高度为0。
代码如下:
if (node == NULL) return 0;
- 确定单层递归的逻辑:先求它的左子树的深度,再求右子树的深度,最后取左右深度最大的数值 再+1 (加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的树的深度。
代码如下:
int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // 左
int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // 右
int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // 中
return depth;
迭代法
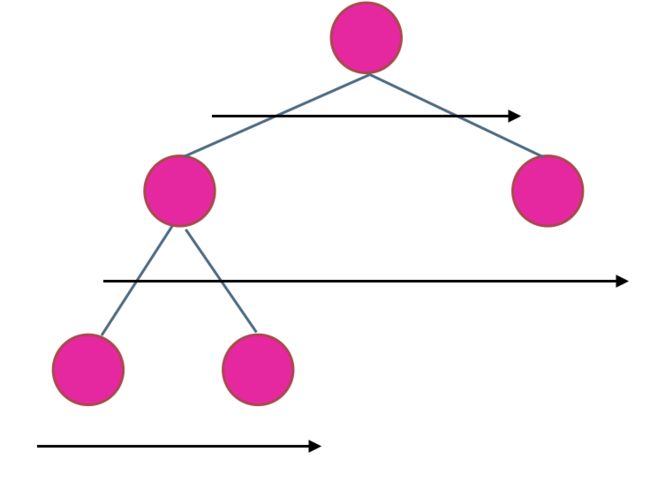
使用迭代法的话,使用层序遍历是最为合适的,因为最大的深度就是二叉树的层数,和层序遍历的方式极其吻合。
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
所以这道题的迭代法就是一道模板题,可以使用二叉树层序遍历的模板来解决的。
实现代码
class solution {
/**
* 递归法
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}
class Solution {
/**
* 递归法(求深度法)
*/
//定义最大深度
int maxnum = 0;
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
ans(root,0);
return maxnum;
}
//递归求解最大深度
void ans(TreeNode tr,int tmp){
if(tr==null) return;
tmp++;
maxnum = maxnum deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int size = deque.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = deque.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
deque.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
deque.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
}
559.n叉树的最大深度
题目链接:559. N 叉树的最大深度
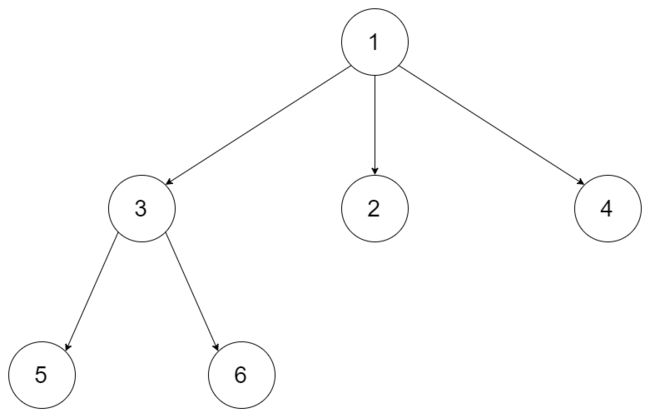
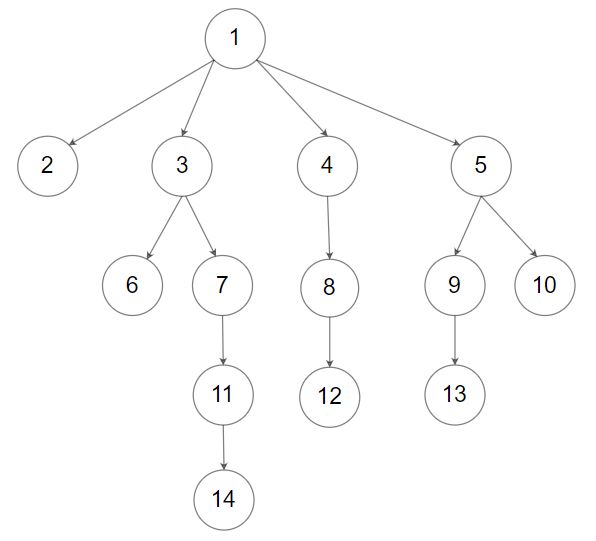
给定一个 N 叉树,找到其最大深度。
最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点总数。
N 叉树输入按层序遍历序列化表示,每组子节点由空值分隔(请参见示例)。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] 输出:3
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] 输出:5
解题思路
依然可以提供递归法和迭代法,来解决这个问题,思路是和二叉树思路一样的。
实现代码
class Solution {
/*递归法,后序遍历求root节点的高度*/
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int depth = 0;
if (root.children != null){
for (Node child : root.children){
depth = Math.max(depth, maxDepth(child));
}
}
return depth + 1; //中节点
}
}
class solution {
/**
* 迭代法,使用层序遍历
*/
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int depth = 0;
Queue que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root);
while (!que.isEmpty())
{
depth ++;
int len = que.size();
while (len > 0)
{
Node node = que.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < node.children.size(); i++)
if (node.children.get(i) != null)
que.offer(node.children.get(i));
len--;
}
}
return depth;
}
}
111.二叉树的最小深度
题目链接:111.二叉树的最小深度
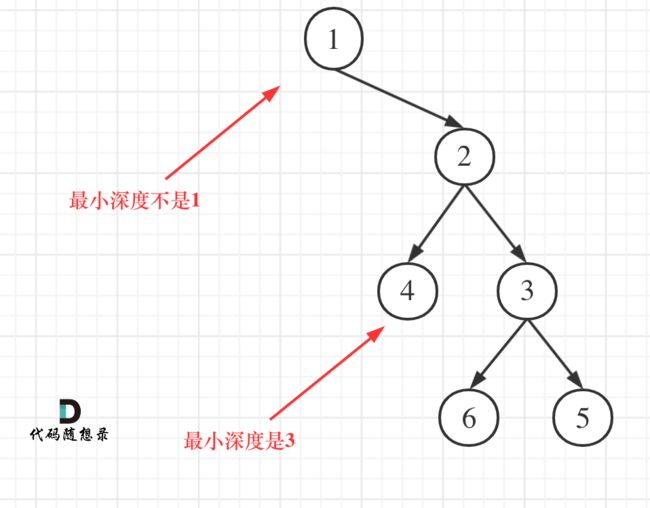
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
返回它的最小深度 2
解题思路
本题依然是前序遍历和后序遍历都可以,前序求的是深度,后序求的是高度。
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
- 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数后者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
那么使用后序遍历,其实求的是根节点到叶子节点的最小距离,就是求高度的过程,不过这个最小距离 也同样是最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
实现代码
class Solution {
/**
* 递归法,相比求MaxDepth要复杂点
* 因为最小深度是从根节点到最近**叶子节点**的最短路径上的节点数量
*/
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = minDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = minDepth(root.right);
if (root.left == null) {
return rightDepth + 1;
}
if (root.right == null) {
return leftDepth + 1;
}
// 左右结点都不为null
return Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}
class Solution {
/**
* 递归法(思路来自二叉树最大深度的递归法)
* 该题求最小深度,最小深度为根节点到叶子节点的深度,所以在迭代到每个叶子节点时更新最小值。
*/
int depth = 0;
// 定义最小深度,初始化最大值
int minDepth = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
dep(root);
return minDepth == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : minDepth;
}
void dep(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return ;
// 递归开始,深度增加
depth++;
dep(root.left);
dep(root.right);
// 该位置表示递归到叶子节点了,需要更新最小深度minDepth
if(root.left == null && root.right == null)
minDepth = Math.min(minDepth , depth);
// 递归结束,深度减小
depth--;
}
}
class Solution {
/**
* 迭代法,层序遍历
*/
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Deque deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int size = deque.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode poll = deque.poll();
if (poll.left == null && poll.right == null) {
// 是叶子结点,直接返回depth,因为从上往下遍历,所以该值就是最小值
return depth;
}
if (poll.left != null) {
deque.offer(poll.left);
}
if (poll.right != null) {
deque.offer(poll.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
}
222.完全二叉树的节点个数
题目链接:222.完全二叉树的节点个数
给出一个完全二叉树,求出该树的节点个数。
示例 1:
- 输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
- 输出:6
示例 2:
- 输入:root = []
- 输出:0
示例 3:
- 输入:root = [1]
- 输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是[0, 5 * 10^4]
- 0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 10^4
- 题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
解题思路
普通二叉树
首先按照普通二叉树的逻辑来求。
递归遍历的顺序依然是后序(左右中)。
递归
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回以该节点为根节点二叉树的节点数量,所以返回值为int类型。
代码如下:
int getNodesNum(TreeNode* cur) {
- 确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示节点数为0。
代码如下:
if (cur == NULL) return 0;
- 确定单层递归的逻辑:先求它的左子树的节点数量,再求右子树的节点数量,最后取总和再加一 (加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的节点数量。
代码如下:
int leftNum = getNodesNum(cur->left); // 左
int rightNum = getNodesNum(cur->right); // 右
int treeNum = leftNum + rightNum + 1; // 中
return treeNum;
完全二叉树
判断其子树是不是满二叉树,如果是则利用公式计算这个子树(满二叉树)的节点数量,如果不是则继续递归,那么 在递归三部曲中,第二部:终止条件的写法应该是这样的:
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
// 开始根据左深度和右深度是否相同来判断该子树是不是满二叉树
TreeNode* left = root->left;
TreeNode* right = root->right;
int leftDepth = 0, rightDepth = 0; // 这里初始为0是有目的的,为了下面求指数方便
while (left) { // 求左子树深度
left = left->left;
leftDepth++;
}
while (right) { // 求右子树深度
right = right->right;
rightDepth++;
}
if (leftDepth == rightDepth) {
return (2 << leftDepth) - 1; // 注意(2<<1) 相当于2^2,返回满足满二叉树的子树节点数量
}
递归三部曲,第三部,单层递归的逻辑:(可以看出使用后序遍历)
int leftTreeNum = countNodes(root->left); // 左
int rightTreeNum = countNodes(root->right); // 右
int result = leftTreeNum + rightTreeNum + 1; // 中
return result;
该部分精简之后代码为:
return countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right) + 1;
实现代码
class Solution {
// 通用递归解法
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}
class Solution {
// 迭代法
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int result = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
while (size -- > 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
result++;
if (cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return result;
}
}
class Solution {
/**
* 针对完全二叉树的解法
*
* 满二叉树的结点数为:2^depth - 1
*/
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
TreeNode left = root.left;
TreeNode right = root.right;
int leftDepth = 0, rightDepth = 0; // 这里初始为0是有目的的,为了下面求指数方便
while (left != null) { // 求左子树深度
left = left.left;
leftDepth++;
}
while (right != null) { // 求右子树深度
right = right.right;
rightDepth++;
}
if (leftDepth == rightDepth) {
return (2 << leftDepth) - 1; // 注意(2<<1) 相当于2^2,所以leftDepth初始为0
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}