【C#入门详解】C#语言入门详解
前言:
1、入门略。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2、其他:
1.索引器:
索引器(indexer):他使对象能够与数组以相同的方式索引
注:没有静态索引器
- 例:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu["Math"]=90;
var mathScore = stu["Math"];
Console.WriteLine(mathScore);
}
}
class Student
{
private Dictionary scoreDictionary=new Dictionary();
public int? this(string subject)
{
get{
if(this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
return this.scoreDictionary(subject);
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
set{
if(value.HasValue == false)
{
throw new Exception("Score cannot be null.");
}
if(this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
this.scoreDictionay[subject] = value.Value;
}
else
{
this.scoreDictionary.Add(subject,value.Value);
}
}
}
}
2.常量:const
const只读
优势:效率高
1、声明常量
例(圆周率 PI):
public static class Math
{
public const double PI=3.14159;
}
double a= Math.PI*r*r;//实际运算:3.14159*r*r
2、声明的变量不可修改
例:
const int num=100;
num=200;//报错
3.参数:
①值参数:
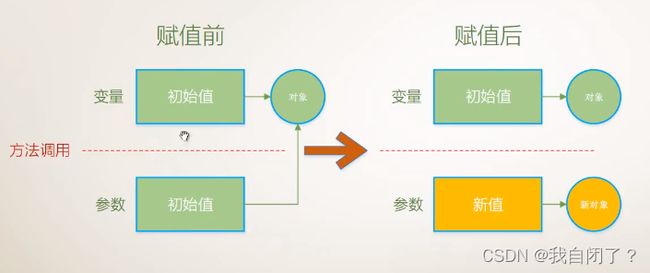
1.传值参数——》引用类型,并且新创建对象
注:
- 值参数创建变量的副本
- 对值参数的操作永远不影响变量的值
例:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student.stu=new Student(){Name="Tim"};
SomeMethod(stu);
//hashCode可以区别变量
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name); //Tim,HashCode不同
}
static void SomeMethod(Student stu)
{
stu = new Student(){Name = "Tim"};
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name); //Tim,HashCode不同
}
}
class Student
{
publish string Name{get;set;}
}
2.传值参数——》引用对象,只操作对象,不创建新对象
注:
- 对象还是那个对象,但对象里的值(字段/属性)已经改变
例:
//hashCode一致
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student.stu=new Student(){Name="Tim"};
UpdateObject(stu);
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);
}
static void UpdateObject(Student stu)
{
//改变对象的值,没有新建对象
stu.Name = "Tom";
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
publish string Name{get;set;}
}
②引用参数:
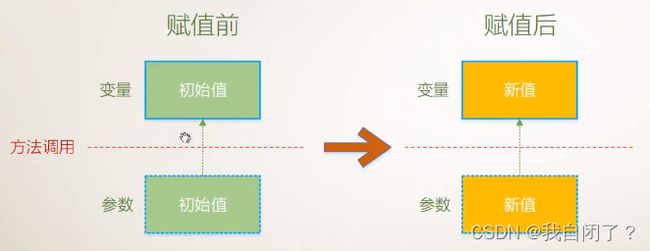
1、引用参数——》值类型
注:
- 引用参数并不创建变量的副本
- 使用ref修饰符显式指出——此方法的副作用是改变实际参数的值
例:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int y=1;
IWantSideEffect(ref y); //有意利用副作用
Console.WriteLine(y); //y=101
}
static void IWantSideEffect(ref int x)
{
x=x+100;
}
}
class Student
{
publish string Name{get;set;}
}
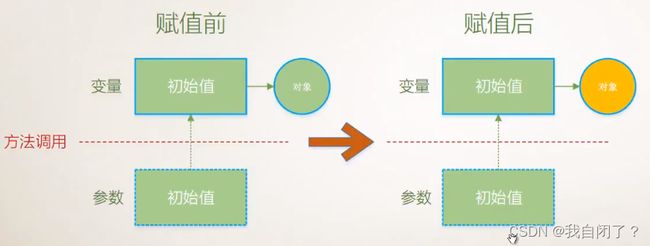
2、引用参数——》引用类型,创建新对象
注:
- 引用参数并不创建变量的副本
- 使用ref修饰符显式指出——此方法的副作用是改变实际参数的值
例:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student outterStu=new Student(){Name="Tim"};
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",outterStu.GetHashCode(),outterStu.Name);
IWantSideEffect(ref outterStu);
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",outterStu.GetHashCode(),outterStu.Name);
//已改变为Tom
}
static void IWantSideEffect(ref Student stu)
{
stu = new Student(){Name = "Tom"};
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
publish string Name{get;set;}
}
3、引用参数——》引用类型,不创建新对象只改变对象值
注:
- 此时与传值参数在效果上并无不同,但激励不一样
例:
//操作的是同一个对象
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student outterStu=new Student(){Name="Tim"};
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",outterStu.GetHashCode(),outterStu.Name);
IWantSideEffect(ref outterStu);
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",outterStu.GetHashCode(),outterStu.Name);
}
static void IWantSideEffect(ref Student stu)
{
stu.Name = "Tom";
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0},Name={1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
publish string Name{get;set;}
}
③输出参数:
使用out修饰的参数,变量在可作为形参传递之前不要求赋值,在方法返回之前,该方法的每个输出形参都必须明确赋值
1、输出参数——》值类型
注:
- 输出参数并不创建变量的副本
- 方法体内必须要有对输出变量的赋值操作
- 使用out修饰符显式指出——此方法的副作用是通过参数向外输出值
- 从语义上来讲——ref是为了“改变”,out是为了“输出”
例:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Please input first number:");
string arg1=Console.ReadLine();
double x=0;
bool b1=double.TryParse(arg1,out x);
if(b1==false)
{
Console.WriteLine("Input error!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Please input second number:");
string arg2=Console.ReadLine();
double y=0;
bool b1=double.TryParse(arg2,out y);
if(b2==false)
{
Console.WriteLine("Input error!");
return;
}
double z=x+y;
Console.WriteLine("{0}+{1}={2}",x,y,z);
}
}
2、输出类型——》引用类型
注:
- 输出参数并不创建变量的副本
- 方法体内必须要有对输出变量的赋值操作
- 使用out修饰符显式指出——此方法的副作用是通过参数向外输出值
- 从语义上来讲——ref是为了“改变”,out是为了“输出”
例:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = null;
bool b = StudentFactory.Create("Tim",34,out stu);
if(b==true)
{
Console.Write("Student{0},age is {1}.",stu.Name,stu.Age);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int Age{get;set;}
public string Name{get;set;}
}
class StudentFactory
{
public static bool Create(string stuName,int stuAge,out Student result)
{
result = null;
if(string.IsNullOrEmpty(stuName))
{
return false;
}
if(stuAge<20||stuAge>80)
{
return false;
}
result = new Student(){Name=stuName,Age=stuAge}
}
}
④数组参数:
- 必须是形参列表中的最后一个,由params修饰
- 举例:String.Format方法和String.Split方法
例1:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//int[] myIntArray = new int[] {1,2,3};
int result = CalculateSum(myIntArray);
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
//static int CalculateSum(params int[] intArray)
static int CalculateSum(params int[] intArray)
{
int sum =0;
foreach(var item in intArray)
{
sum+=item;
}
return sum;
}
}
例2:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str = "Tim;Tom,Amy.Lisa";
string[] result = str.Split(';',',','.');
foreach (var name in result)
{
Console.WriteLine(name);
}
}
}
⑤具名参数:
- 参数的位置不再受约束
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintInfo(age:34,name:"Tim");
}
static void PrintInfo(string name,int age)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello {0},you are {1}.",name,age);
}
}⑥可选参数:
- 参数因为具有默认值而变得“可选”
- 不推荐使用可选参数
⑦扩展方法(this参数)
- 方法必需是公有的、静态的,即被public static所修饰
- 必需是形参列表中的第一个,由this修饰
- 必需由一个静态类(一般类名为SomeTypeExtension)来统一收纳对SomeType类型的扩展方法
- 举例:LINQ方法
例:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double x=3.14159;
double y=x.Round(4); //3.1415
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}
static class DoubleExtension
{
public static double Round(this double input,int digits)
{
double result = Math.Round(input,digits);
return result;
}
}
例(LINQ方法):
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
list myList = new List(){11,12,13,14,15};
bool result = myList.All(i=>i>10);
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
static bool AllGreaterThanTen(List intList)
{
foreach(var item in intList)
{
if(item<=10)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
⑧各种参数的使用场景总结:
- 传值参数:参数的默认传递方式
- 输出参数:用于除返回值外还需要输出的场景
- 引用参数:用于需要修改实际参数值的场景
- 数组参数:用于简化方法的调用
- 具名参数:提高可读性
- 可选参数:参数拥有默认值
- 扩展方法(this参数):为目标数据类型“追加”方法
4.委托:
①什么是委托:
委托(delegate)是函数指针的“升级版”
- 实例:C/C++中的函数指针
例(函数指针的实例):
#include
typedef int(* Calc)[int a,int b];
int Add(int a,int b)
{
int result=a+b;
return result;
}
int Sub(int a,int b)
{
int result=a-b;
return result;
}
int main()
{
int x=100;
int y=200;
int z=0;
Calc funcPoint1=&Add;//访问地址
Calc funcPoint2=⋐
z=Add(x,y);
printf("%d+%d=%d\n",x,y,z);
z=Sub(x,y);
printf("%d+%d=%d\n",x,y,z);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
例:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator calculator=new Calculator();
Action action = new Action(calculator.Report);
calculator.Report(); //I have 3 methods.
action.Invoke(); //I have 3 methods.
action(); //I have 3 methods.
Func func1=new Func(calculator.Add);
Func func2=new Func(calculator.Sub);
int x=100;
int y=200;
int z=0;
//z=func1.Invoke(x,y);
z=func1(x,y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
//z = func2.Invoke(x,y);
z = func2(x,y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
}
}
class Calculator
{
public void Report()
{
Console.WriteLine("I have 3 methods.");
}
public int Add(int a,int b)
{
int result=a+b;
return result;
}
public int Sub(int a,int b)
{
int result=a+b;
return result;
}
}
②委托的声明(自定义委托)
- 委托是一种类(class),类是数据类型所以委托也是一种数据类型
- 注意声明委托的位置
- 为了避免写错地方结果声明成嵌套类型
- 委托与所封装的方法必需“类型兼容”
- 返回值的数据类型一致
- 参数列表在个数和数据类型上一致(参数名不需要一样)
public delegate double Calc(double x,double y);
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator calculator=new Calculator();
Calc calc1 = new Calc(calculator.Add);
Calc calc2 = new Calc(calculator.Sub);
Calc calc3 = new Calc(calculator.Mul);
Calc calc4 = new Calc(calculator.Div);
double a=100;
double b=200;
double c=0;
c=calc1.Invoke(a,b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c=calc2.Invoke(a,b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c=calc3.Invoke(a,b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c=calc4.Invoke(a,b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
}
class Calculator
{
public double Add(double x,double y)
{
return x+y;
}
public double Add(double x,double y)
{
return x-y;
}
public double Add(double x,double y)
{
return x*y;
}
public double Div(double x,double y)
{
return x/y;
}
}
}
③委托的一般使用
实例:把方法当做参数传给另一个方法
- 正确使用1:模板方法,“借用”指定的外部方法来产生结果
- 相当于“填空题”
- 常位于代码中部
- 委托有返回值
- 正确使用2:回调(callback)方法,调用指定的外部方法
- 相当于“流水线”
- 常位于代码末尾
- 委托无返回值
注意:难精通+易使用+功能强大东西,一旦被滥用则后果非常严重
- 缺点1:这是一种方法级别的紧耦合,现实工作中要慎之又慎
- 缺点2:使可读性下降、debug的难度增加
- 缺点3:把委托回调、异步调用和多线程纠缠在一起,会让代码变得难以阅读和维护
- 缺点4:委托使用不当有可能造成内存泄漏和程序性能下降
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
Func func1 = new Func(productFactory.MakePizza);
Func func2 = new Func(productFactory.MakeToyCar);
Box box1=wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1);
Box box2=wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
}
}
class Product
{
public string Name{get;set}
}
class Box
{
public Product Product{get;set;}
}
class WrapFactory
{
public Box WrapProduct(Func getProduct)
{
Box box = new Box();
Product product = getProduct.Invoke();
box.Product = product;
return box;
}
}
class ProductFactoryd
{
public Product MakePizza()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name="Pizza";
return product;
}
public Product MakeToyCar()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Toy Car";
returnd product;
}
}
④委托的高级实用
多播(multicast)委托
隐式异步调用
- 同步与异步的简介
- 中英文的语言差异
- 同步:你做完了我(在你的基础上)接着做
- 异步:咱们两个同时做(相当于汉语中的“同步进行”)、
- 同步调用与异步调用的对比
- 每一个运行的程序是一个进程(process)
- 每个进程可以有一个或者多个线程(thread)
- 同步调用是在同一线程内
- 异步调用的底层机理是多线程
- 串行==同步==单线程,并行==异步==多线程
- 隐式多线程V.S显示多线程
- 直接同步调用:使用方法名
- 间接同步调用:使用单播/多播委托的Invoke方法
- 隐式异步调用:使用委托的BeginInvoke
- 显示异步调用:使用Thread或Task
- 应该适时地使用接口(interface)取代一些对委托额使用
- Java完全地使用接口取代了委托的功能,即Java没有与C#中委托相对应的功能实体
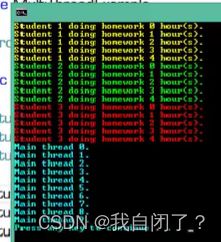
例(单播委托/多播委托):
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1=new Student(){ID = 1,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow};
Student stu2=new Student(){ID = 2,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green};
Student stu3=new Student(){ID = 3,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red};
Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);
Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);
Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);
//单播委托
/*action1.Invoke();
action2.Invoke();
action3.Invoke();*/
//多播委托
action1 +=action2;
action1 +=action3;
action1.Invoke();
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID{get;set;}
public ConsoleColor Pen{get;set;}
public void DoHomework()
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s).",this.ID,i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
结果:
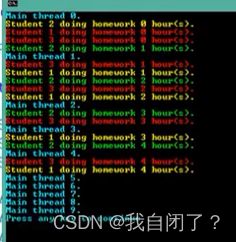
例(同步调用):
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1=new Student(){ID = 1,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow};
Student stu2=new Student(){ID = 2,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green};
Student stu3=new Student(){ID = 3,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red};
//直接同步调用
/*stu1.DoHomework;
stu2.DoHomework;
stu3.DoHomework;*/
Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);
Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);
Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);
//同步调用(单播委托的间接同步调用)
/*action1.Invoke();
action2.Invoke();
action3.Invoke();*/
//同步调用(多播委托的间接同步调用委托)
action1 +=action2;
action1 +=action3;
action1.Invoke();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}.",i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID{get;set;}
public ConsoleColor Pen{get;set;}
public void DoHomework()
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s).",this.ID,i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
结果:
例(异步调用):
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1=new Student(){ID = 1,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow};
Student stu2=new Student(){ID = 2,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Green};
Student stu3=new Student(){ID = 3,PenColor = ConsoleColor.Red};
//显式异步调用(使用Task)
Task task1=new Task(new Action(stu1.DoHomework));
Task task2=new Task(new Action(stu2.DoHomework));
Task task3=new Task(new Action(stu3.DoHomework));
task1.Start();
task2.Start();
task3.Start();
//显式异步调用(使用Thread)
/*Thread thread1=new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu1.DoHomework));
Thread thread2=new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu2.DoHomework));
Thread thread3=new Thread(new ThreadStart(stu3.DoHomework));
thread1.Start();
thread2.Start();
thread3.Start();*/
//隐式异步调用(使用委托的异步调用)
/*Action action1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);
Action action2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);
Action action3 = new Action(stu3.DoHomework);
action1.BeginInvoke(null,null);
action2.BeginInvoke(null,null);
action3.BeginInvoke(null,null);*/
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}.",i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int ID{get;set;}
public ConsoleColor Pen{get;set;}
public void DoHomework()
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.PenColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hour(s).",this.ID,i);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
结果:
5.事件:
①初步了解事件:
定义:单词Event,译为“事件”
角色:使对象或类具备通知能力的成员
- (中译)事件(event)是一种使对象或类能够提供通知的成员
- (原文)An event is a member that enables an object or class to provide notifications.
- "对象O拥有一个事件E"想表达的思想是:当事件E发生的时候,O有能力通知别的对象
使用:用于对象或类间的动作协调与信息传递(消息推送)
原理:事件模型(event model)中的两个“5”
- “发生——>响应”中的5个部分——闹钟响了你起床、孩子饿了你做饭。。。这里隐含着“订阅”关系
- “发生——>响应”中的5个动作——①我有一件事②一个人或者一群人关心的这个事件③我的这个事件发生了④关心这个事件的人会被依次通知到⑤被通知到的人根据拿到的事件信息对事件进行响应(又称“处理事件”)。
提示:
- 事件多用于桌面、手机等开发的客户端编程,因为这些程序经常是通过事件来“驱动”的
- 各种编程语言对这个机制的实现方法不尽相同
- Java语言里没有事件这种成员,也没有委托这种数据类型。Java的“事件”是使用接口来实现的
- MVC、MVP、MVVM等模式,是事件模式更高级、更有效的“玩法”
- 日常开发的时候,使用已有事件的机会比较多,自己声明事件的机会比较少,所以先学使用
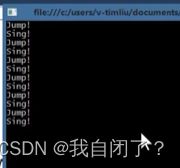
例(★ ):
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.Interval = 1000;
Boy boy =new Boy();
Gril gril=new Gril();
timer.Elapsed+=boy.Action;
timer.Elapsed+=gril.Action;
timer.Start();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class Boy
{
interface void Action(object sender,ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Jump!");
}
}
class Girl
{
interface void Action(object sender,ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Sing!");
}
}
结果:(每一秒钟打印)
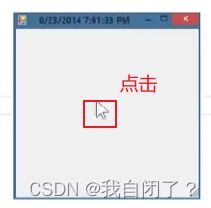
例(★★):
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Form form = new From();
Controller controller = new Controller(form);
form.showDialog();
}
}
class Controller
{
private Form form;
public Controller(Form form)
{
if(form!=null)
{
this.form = form;
this.form.Click+=this.FormClicked;
}
}
private void FormClicked(object sender,EventArgs e)
{
this.form.Text=DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
结果:
例2:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyForm form = new MyForm();
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class MyForm :Form
{
private TextBox textBox;
private Button button;
public MyForm()
{
this.textBox = new TextBox();
this.button= new Button();
this.Controls.Add(this.button);
this.Controls.Add(this.textBox);
this.button.Click+=this.ButtonClicked;
this.button.Text="Say Hello";
this.button.Top=100;
}
private void ButtonClicked(object sender,EventArgs e)
{
this.textBox.Text = "Hello,World!!!!!!!!!!!!!!";
}
}
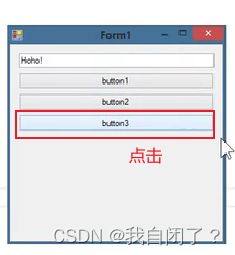
public Form1()
{
InitialzeComponent();
//挂接处理器(匿名)
/*this.button3.Click +=delegate(object sender,EventArgs e){
this.textBox1.Text = "hala!";
};*/
//拉姆达表达式
this.button3.Click +=(object sender,EventArgs e)=>{
this.textBox1.Text = "hala!";
};
//拉姆达表达式(简化版)
/*this.button3.Click +=(sender,e)=>{
this.textBox1.Text = "hala!";
};*/
}
private void ButtonClicked(object sender,EventArgs e)
{
if(sender == this.button1)
{
this.textBox1.Text="Hello!";
}
if(sender == this.button2)
{
this.textBox1.Text="World!";
}
if(sender == this.button3)
{
this.textBox1.Text="Mr.Okay!";
}
}
结果:
总结:
- 一个事件处理器可以被多个事件挂接
- 多个事件也可以挂接多个事件处理器
②事件的声明
事件的声明:
- 完整声明
- 简略声明(字段式声明,field-like)
有了委托字段/属性,为什么还需要事件?
- 为了程序的逻辑更加“有道理”、更加安全,谨防“借刀杀人”
所以事件的本质是委托字段的一个包装器
- 这个包装器对委托字段的访问起限制作用,相当于一个“蒙版”、
- 封装(encapsulation)的一个重要功能就是隐藏
- 事件对外界隐藏了委托实例的大部分功能,仅暴露添加/移除事件处理器的功能
用于声明事件的委托类型的命名约定
- 用于声明Foo事件委托,一般命名为FooEventHandler(除非是一个非常通用的事件约束)
- FooEventHandler委托的参数一般有两个(由Win32API演化而来,历史悠久)
- 第一个是object类型,名字为sender,实际上就是事件的拥有者、事件的source。
- 第二个是EvebtArgs类的派生类,类名一般为FooEventArgs,参数名为e。也就是前面讲过的事件参数
- 触发Foo事件的方法一般命名为OnFoo,即“因何引发”、”事出有因“
- 访问级别为protected,不能为public,不然又成了可以“借刀杀人”了
- 事件的命名约定
- 带有时态的动词或者动词短语
- 事件拥有者“正在做”什么事情,用进行时;事件拥有者“做完了”什么事情,用完成时
例:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Customer customer = new Customer();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
customer.Order += waiter.Action;
customer.Action();
customer.PayTheBill();
}
}
public class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs
{
public string DishName{get;set;}
public string Size{get;set;}
}
//public delegate void OrderEventHandler{Customer customer,OrderEventArgs e};
public class Customer
{
public event EventHandler Order;
public double Bill{get;set;}
public void PayTheBill()
{
Console.WriteLine("I will pay ${0}."this.Bill);
}
public void WalkIn()
{
Console.WriteLine("Walk into restaurant.");
}
public void SitDown()
{
Console.WriteLine("Sit down.");
}
public void Think()
{
for(int i= 0;i<5;i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Let me think…");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
this.OnOrder("Kongpao Chicken","large");
}
protected void OnOrder(string dishName,string size)
{
if(this.Order!=null)
{
OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();
e.DishName = dishName;
e.Size = size;
this.Order.Invoke(this.e);
}
}
public void Action()
{
Console.ReadLine();
this.WalkIn();
this.SitDown();
this.Think();
}
}
public class Waiter
{
public void Action(Customer customer,OrderEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("I will serve you the dish - {0}.",e.DishName);
double price = 10;
switch(e.Size)
{
case"small":
price=price*0.5;
break;
case"large":
price=price*1.5;
break;
default:
break;
}
customer.Bill+=price;
}
}
6.类:
①什么是类
- 是一种数据结构
- 是一种数据类型
- 代表现实世界中的“种类”
例:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args){
Student s1 = new Student(1,"Timothy");
Student s2 = new Student(2,"Jacky");
Console.WriteLine(Student.Amount);
}
}
class Student
{
public Student int Amount{get;set;}
//静态构造器
static Student(){
Amount=100;
}
public Student(int id,string name)
{
this.ID=id;
this.Name=name;
Amount++;
}
//析构器(进程结束前执行)
~ Student()
{
Amount--;
}
public int ID{get; set;}
public string Name{get;set;}
public void Report(){
Console.WriteLine($"I'm #{ID}student,my name is {Name}.");
}
}
②类的声明
类声明的全貌
- 声明即定义
最简单的类声明
- 类的访问控制
类成员的访问控制
类的继承
- 派生类对基类的成员获得与访问
- 在派生类中访问基类的成员
- 构造器的不可继承性
③类的修饰符
internal修饰符(默认)
解释:项目里自由访问,外部(项目外)不能访问
public修饰符:类访问级别修饰符
解释:项目之外引用项目能不能使用
④类的继承
- 类在功能上的扩展(extend)
- 只能有一个基类,但可以实现多个接口
- 类访问级别对继承的影响
- sealed类不能被继承
成员的继承与访问
- 派生类对继承成员的访问
- 派生类对基类成员的访问
- 构造器的不可继承性
面向对象的实现风格
- Class-based
- Prototype-based
例1(类的派生类):
namespace HelloOOP{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
Type t = typeof(Car);
Type tb = t.BaseType;
Type tTop = tb.BaseType;
Console.WriteLine(tb.FullName); // HelloOOP.Vehicle
Console.WriteLine(tTop.FullName); //System.Object
Console.WriteLine(tTop.BaseType==null); //True (顶层基类为空)
}
}
class Vehicle{
}
//Car是Vehicle的派生类
class Car : Vehicle{
}
}
例2(”是一个“概念(is a)):
namespace HelloOOP{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
Car car = new Car();
Console.WriteLine(car is Vehicle); //True
Console.WriteLine(car is Object); //True
Console.WriteLine(Vehicle is Car); //False
}
}
class Vehicle{
}
//Car是Vehicle的派生类
class Car : Vehicle{
}
}
注:
- sealed(译-密封的) 修饰的类不能再有基类,它修饰的类或方法将不能被继承或重写
- C#只支持一个基类
- internal类不能有public的派生类(不能超过基类的访问级别),派生类可以同级,或者更低
- 例:public class Vehicle{} internal class Car{}
例(对继承的理解):
namespace HelloAccess {
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
Car car = new Car();
Console.WriteLine(car.Owner);
}
}
class Vehicle{
public Vehicle(){
this.Owner = "N/A";
}
public string Owner{get;set;}
}
class Car:Vehicle{
public Car(){
this.Owner = "Car Owner";
}
}
public void ShowOwner(){
Console.WriteLine(Owner);
}
}例(基类带传参时,派生类的写法):
namespace HelloAccess {
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
Car car = new Car("Timothy");
Console.WriteLine(car.Owner);
}
}
class Vehicle{
public Vehicle(string owner){
this.Owner = owner;
}
public string Owner{get;set;}
}
class Car:Vehicle{
public Car(string owner):base(owner){
this.Owner =owner;
}
}
public void ShowOwner(){
Console.WriteLine(Owner);
}
}
注:
父类的实例构造器不被子类继承(在继承的过程当中,实例构造器不被继承)
跨项目访问(两个类库之间)、项目内
例1:
| HelloAccess |
MyLib |
namespace HelloAccess{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
Vehicle vehicle = new Vehicle();
//报错
vehicle.Owner = "Timothy";
Console.WriteLine(vehicle.Owner);//外部访问private/internal都报错
}
}
namespace MyLib{
public class Vehicle{
private string Owner{get;set;}
//string Owner{get;set;} //默认private(保证安全性)
//internal string Owner{get;set;}
}
public class Car:Vehicle{
public void ShowOwner(){
Console.WriteLine(base.Owner); //内部正常继承internal string Owner
//报错
Console.WriteLine(base.Owner); //内部正常继承,但访问private string Owner报错
}
}
}
例2.1(protected的访问):
namespace MyLib{
public class Vehicle{
protected int _rpm;
private int _fuel;
public void Refuel(){
_fuel+=100;
}
protected void Burn(int fuel){
_fuel-=fuel;
}
public void Accelerate(){
Burn(1); //内部方法可访问protected
_rpm += 1000;
}
public int Speed{get{return _rpm/100;}}
}
public class Car :Vehicle{
public void TurboAccelerate(){
Burn(2); //内部派生类可继承访问protected
_rpm+=3000;
}
}
}
例2.2(protected的访问):
using Mylib;
namespace HelloAccess{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
//Car car = new Car();
//car.TurboAccelerate();
//Console.WriteLine(car.Speed);
Bus bus = new Bus();
bus.SlowAccelerate();
Console.WriteLine(bus.Speed)
}
}
class Bus:Vehicle{
public void SlowAccelerate(){
Burn(1); //外部派生类可访问protected类型Burn()
_rpm+=500; //外部派生类可访问protected类型 _rpm
}
}
}
注:
- protected的应用更多在方法上
- protected访问范围:
- 内部:同类中的其他方法可访问;同项目的派生类可继承访问
- 外部:外部的派生类可继承访问
- protected可与internal组合,(internal protected)、(protected internal)一起用时是或的关系(两种访问权限并集),既可以被方法内的派生类继承访问,也可以被程序集中的所有的其他类访问
7.重写、多态
①类的继承
- 类成员的“横向扩展”(成员越来越多)
- 类成员的“纵向扩展”(行为改变,版本增高)
- 类成员的隐藏(不常用)
- 重写与隐藏的发生条件:函数成员,可见,签名一致
②多态(ploymorphism)
- 基于重写机制(virtual->override)
- 函数成员的具体行为(版本)由对象决定
- 回顾:C#语言的变量和对象都是有类型的,所以会有“代差”
例(重写):
namespace OverrideExample{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
Vehicle v=new Vehicle();
v.Run();
Console.WriteLine(v.Speed);
//重写
var car = new Car();
car.Run(); // Car is running!
var v = new Vehicle();
v.Run(); // I'm running!
//没有重写关系
/* Vehicle v = new Car();
v.Run(); // I'm running! */
}
}
}
class Vehicle{
private int _speed;
public virtual int Speed{
get{return _speed;}
set{_speed=value;}
}
//重写
public virtual void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("I'm running!");
_speed = 100;
}
class Car:Vehicle{
private int _rpm;
public override int Speed{
get{return _rpm/100;}
set{_rpm = value*100;}
}
public override void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Car is running!");
_rpm = 5000;
}
}
//没有重写关系
/* public void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("I'm running!");
}
class Car:Vehicle{
public void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Car is running!");
}
} */
}
总结:
- 重写需加virtual、override,重写后派生类会覆盖基类的同名方法,调用时为派生类重写的方法
- 没有重写关系时,相当于派生类有两个同名方法,顺序是先基类后自己,所以调用基类的方法
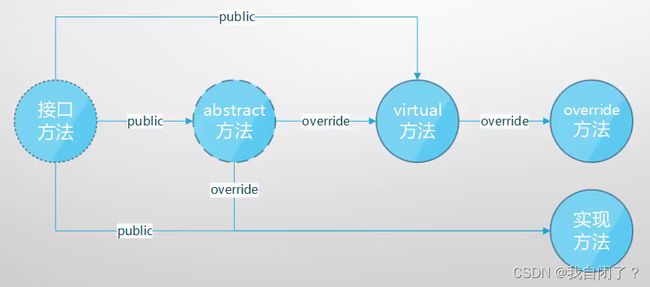
8.接口和抽象类
①什么是接口和抽象类
- 接口和抽象类都是“软件工程产物”
- 具体类->抽象类->接口:越来越抽象,内部实现的东西越来越少
- 抽象类是未完全实现逻辑的类(可以有字段和非public成员,它们代表了“具体逻辑”)
- 抽象类为复用而生:专门作为基类来使用,也具有解耦功能
- 封装确定的,开放不确定的,推迟到合适的子类中去实现
- 接口是完全未实现逻辑的“类”(“纯虚类”;只有函数成员;成员全部public)
- 接口为解耦而生:“高内聚,低耦合”,方便单元测试
- 接口是一个“协约”,早已为工业生产所熟知(有分工必有协作,有协作必有协约)
- 它们都不能实例化,只能用来声明变量,引用具体类(concrete class)的实例
例(为做基类而生的“抽象类”与“开放/关闭原则”):
using System;
namespace Example027{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
Vehicle v = new Car();
v.Run(); // Car is running…
//Vehicle v=new Vehicle(); //抽象类不能创建新实例
Vehicle v=new RaceCar(); //可以创建新的派生类
v.Run(); //Race car is running…
}
}
//使用抽象类简化代码
abstract class Vehicle{
public void Stop(){
Console.WriteLine("Stopped!");
}
public void Fill(){
Console.WriteLine("Pay and fill…");
}
//直接使用抽象修饰简化
public abstract void Run();
/* public virtual void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Vehicle is running…");
} */
}
class Car:Vehicle{
public override void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Car is running…");
}
public override void Stop(){
Console.WriteLine("Truck is running…");
}
}
class Truck:Vehicle{
public override void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Truck is running…");
}
class RaceCar:Vehicle{
public override void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Race car is running…");
}
}
}
注:
- 抽象类作用是为了给其他派生类当基类,因为没有实际方法所以不能新建实例(只要有一个抽象方法,就不能直接调用)。
例(更具体的抽象基类):
using System;
namespace Example027{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
Vehicle v = new RaceCar();
v.Run();
}
}
//完全抽象类(纯虚类)
abstract class VehicleBase{
abstract public void Stop();
abstract public void Fill();
abstract public void Run();
}
abstract class Vehicle: VehicleBase{
public override void Stop(){
Console.WriteLine("Stopped!");
}
public override void Fill(){
Console.WriteLine("Pay and fill…");
}
}
class Car:Vehicle{
public override void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Car is running…");
}
}
}
例(接口使用):
using System;
namespace Example027{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
Vehicle v = new RaceCar();
v.Run();
}
}
//可用接口替换
interface VehicleBase{
void Stop();
void Fill();
void Run();
}
abstract class Vehicle: VehicleBase{
public void Stop(){
Console.WriteLine("Stopped!");
}
public void Fill(){
Console.WriteLine("Pay and fill…");
}
abstract public void Run();
}
class Car:Vehicle{
public override void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Car is running…");
}
}
class Truck:Vehicle{
public override void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Truck is running…");
}
}
}
②接口与单元测试
- 接口的产生:自底向上(重构),自顶向下(设计)
- C#中接口的实现(隐式,显式,多接口)
- 语言对面对对象设计的内建支持:依赖反射,接口隔离,开/闭原则……
例(用接口判断数据类型):
using System.Collections;
namespace InterfaceExaple{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
int[] nums1 = new int[] {1,2,3,4,5};
ArrayList nums2 = new ArrayList{1,2,3,4,5};
Console.WriteLine(Sum(nums1));
Console.WriteLine(Avg(nums1));
Console.WriteLine(Sum(nums2));
Console.WriteLine(Avg(nums2));
}
static int Sum(IEnumerable nums){
int sum = 0;
foreach(var n in nums)sum+=n;
return sum;
}
static double Avg(IEnumerable nums){
int sum = 0;
double count=0;
foreach(var n in nums){sum+=n;count++;}
return sum/count;
}
}
}
例(依赖、紧耦合):
namespace InterfaceExample{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
var engine = new Engine();
var car = new Car(engine);
car.Run(3);
Console.WriteLine(car.Speed);
}
}
class Engine{
public int RPM{get;private set;}
public void Work(int gas){
this.RPM = 1000*gas;
}
}
//Car紧耦合Engine类,Engine出问题就会出问题
class Car{
private Engine _engine;
public Car(Engine engine){
_engine = engine;
}
public int Speed{get;private set;}
public void Run(int gas){
_engine.Work(gas) ;
this.Speed = _engine.RPM/100;
}
}
}
例(解耦):
namespace InterfaceExample{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
// var user = new PhoneUser(new NokiaPhone());
// 手机坏了,只需要换一部手机;同理一部分代码不能用,直接换另一部的代码
var user = new PhoneUser(new EricssonPhone());
user.UsePhone();
}
}
class PhoneUser{
private Iphone _phone;
public PhoneUser(Iphone phone){
_phone = phone;
}
public void UsePhone(){
_phone.Dail();
_phone.PickUp();
_phone.Send();
_phone.Receive();
}
}
interface IPhone{
void Dail();
void PickUp();
void Send();
void Receive();
}
class NokiaPhone:IPhone{
public void Dail(){
Console.WriteLine("Nokia calling…");
}
public void PickUp(){
Console.WriteLine"Hello! This is Tim!");
}
public void Receive(){
Console.WriteLine"Nokia message ring…");
}
public void Send(){
Console.WriteLine"Hello!");
}
}
class EricssonPhone:IPhone{
public void Dail(){
Console.WriteLine("Nokia calling…");
}
public void PickUp(){
Console.WriteLine"Hello! This is Tim!");
}
public void Receive(){
Console.WriteLine"Nokia message ring…");
}
public void Send(){
Console.WriteLine"Hello!");
}
}
}
例(单元测试):
namespace InterfaceExample{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
var fan = new DeskFan(new PowerSupply());
Console.WriteLine(fan.Work());
}
}
public interface IPowerSupply{
int GetPower();
}
public class PowerSupply:IPhoneSupply{
public int GetPower(){
return 110;
}
}
public class DeskFan{
private IPowerSupply _powerSupply;
public DeskFan(IPowerSupply powerSupply){
_powerSupply = powerSupply;
}
public string Work(){
int power = _powerSupply.GetPower();
if(power<=0){
return "Won't work.";
}else if(power<100){
return "Slow";
}else if(power<200){
return "Work fine"
}else{
// return "Explode!";
return "Warning!";
}
}
}
}
新建测试类:UnitTest1
using System;
using Xunit;
using moq;
namespace InterfaceExample.Tests
{
public class DeskFanTests
{
[Fact]
public void PowerLowerThanZero_OK()
{
var mock = new Mock();
mock.Setup(ps=>ps.GetPower()).Returns(()=>220);
var fan = new DeskFan(mock.Object);
var expected = "Won't work.";
var actual = fan.Work();
Assert.Equal(expected,actual);
}
[Fact]
public void PowerHigherThan200_Warning(){
var mock = new Mock();
mock.Setup(ps=>ps.GetPower()).Returns(()=>220); // Mock()重构,调用IPhoneSupply->GetPower()方法,返回220;
var fan = new DeskFan(mock.Object);
var expected = "Warning!";
var actual = fan.Work();
Assert.Equal(expected,actual);
}
}
/* class PowerHigherThan200:IPowerSupply{
public int GetPower(){
return 220;
}
}
class PowerHigherThan200:IPowerSupply{
public int GetPower(){
return 0;
}
} */
}
9.反射与依赖注入
- 反射:以不变应万变(更送的耦合)
- 反射与接口的结合
- 反射与特性的结合
- 依赖注入:此DI非彼DI,但没有彼DI就没有此DI……
例(接口隔离原则):
namespace IspExample{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
var driver = new Driver(new HeavyTank());
driver.Drive();
}
}
class Driver{
private IVehicle _vehicle;
public Driver(IVehicle vehicle){
_vehicle = vehicle;
}
public void Drive(){
_vehicle.Run();
}
}
interface IVehicle{
void Run();
}
class Car:IVehicle{
public void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Car is running…");
}
}
class Truck:IVehicle{
public void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Truck is running…");
}
}
// 接口隔离原则
interface IWeapon{
void Fire();
}
interface ITank:IVehicle,IWeapon{
}
/* interface ITank{
void Fire();
void Run();
} */
class LightTank:ITank{
public void Fire(){
Console.WriteLine("Boom!");
}
public void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Ka ka ka…");
}
}
class MediumTank:ITank{
public void Fire(){
Console.WriteLine("Boom!");
}
public void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Ka! ka! ka!…");
}
}
class HeavyTank:ITank{
public void Fire(){
Console.WriteLine("Boom!");
}
public void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Ka!! ka!! ka!!…");
}
}
}
例(很多小接口合并成大接口):
using System.Collections;
namespace IspExample2{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
int[] num1={1,2,3,4,5};
ArrayList nums2 = new ArrayList{1,2,3,4,5};
var nums3= new ReadOnlyCollection(num1);
Console.WriteLine(Sum(nums1));
Console.WriteLine(Sum(nums2));
Console.WriteLine(Sum(nums3));
}
static int Sum(IEnumerable nums){
int sum = 0;
foreach(var n in nums){
sum+=(int)n;
}
return sum;
}
}
class ReadOnlyCollection:IEnumerable{
private int[] array;
public ReadOnlyCollection(int[] array){
_array = array;
}
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator(){
return new Enumerator(this);
}
// 成员类
public class Enumerator:IEnumerator{
private ReadOnlyCollection _collection;
private int _head;
public Enumerator(ReadOnlyCollection collection){
_collection = collection;
_head = -1;
}
public object Current{
get{
object o = _collection._array[_head];
return o;
}
}
public bool MoveNext(){
if(++_head<_collection._array.Length){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
public void Reset(){
_head = -1;
}
}
}
}
例(可隐藏方法):
namespace IspExample3{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
IKiller killer = new WarmKiller();
killer.Kill();
var wk = (IGentleman)killer;
wk.Love();
}
}
interface IGentleman{
void Love();
}
interface IKiller{
void Kill();
}
class WarmKiller:IGentleman,IKiller {
public void Love(){
Console.WriteLine("I will love you forever…");
}
// 调用IKiller接口才能使用Kill方法
void IKiller.Kill(){
Console.WriteLine("Let me kill the enemy…");
}
}
}
例(依赖注入):
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; // 封装好的依赖注入
namespace IspExample{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
/*
ITank tank = new HeavyTank();
// =========华丽的分割线==========
// 反射的使用
var t = tank.GetType()
object o = Activator.CreateInstance(t);
MethodInfo fireMi = t.GetMethod("Fire");
MethodInfo runMi = t.GetMethod("Run");
fireMi.Invoke(o,null); // Boom!
runMi.Invoke(o,null); // Ka!! ka!! ka!!…
*/
// 横向对比上面的内容:如果程序升级heavyTank变为mediumTank,如果全部修改则会出现异常,因为有些new操作隶属于其他方法;但如果使用依赖注入,就可以区分,改起来更方便
// 依赖注入实现Driver开LightTank:Ka ka ka…
var sc = new ServiceCollection(); // 微软内置的IOC(控制反转)容器
sc.AddScoped(typeof(ITank),typeof(MadiumTank)); sc.AddScoped(typeof(IVehicle),typeof(LightTank));// 生命周期-作用域,在作用域中是唯一实例
sc.AddScoped();
var sp = sc.BuildServiceProvider(); // 构造生成器
// ========华丽的分割线=======
var driver = sp.GetService();
driver.Drive();
ITank tank =sp.GetService();
tank.Fire();
tank.Run();
}
}
class Driver{
private IVehicle _vehicle;
public Driver(IVehicle vehicle){
_vehicle = vehicle;
}
public void Drive(){
_vehicle.Run();
}
}
interface IVehicle{
void Run();
}
class Car:IVehicle{
public void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Car is running…");
}
}
class Truck:IVehicle{
public void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Truck is running…");
}
}
// 接口隔离原则
interface IWeapon{
void Fire();
}
interface ITank:IVehicle,IWeapon{
}
class LightTank:ITank{
public void Fire(){
Console.WriteLine("Boom!");
}
public void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Ka ka ka…");
}
}
class MediumTank:ITank{
public void Fire(){
Console.WriteLine("Boom!");
}
public void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Ka! ka! ka!…");
}
}
class HeavyTank:ITank{
public void Fire(){
Console.WriteLine("Boom!");
}
public void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Ka!! ka!! ka!!…");
}
}
}
解析:
[依赖注入实现Driver开LightTank:Ka ka ka…]
var sc = new ServiceCollection(); // 微软内置的IOC(控制反转)容器
sc.AddScoped(typeof(IVehicle),typeof(LightTank));// 生命周期-作用域,在作用域中是唯一实例
sc.AddScoped();
var sp = sc.BuildServiceProvider(); // 构造生成器
// ========华丽的分割线=======
var driver = sp.GetService();
driver.Drive(); 相当于:
namespace IspExample{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
var driver = new Driver(new LightTank());
driver.Drive();
}
}
class Driver{
private IVehicle _vehicle;
public Driver(IVehicle vehicle){
_vehicle = vehicle;
}
public void Drive(){
_vehicle.Run();
}
}
interface IVehicle{
void Run();
}
class LightTank:IVehicle{
public void Run(){
Console.WriteLine("Ka ka ka…");
}
}
}
10.泛型(generic)
无处不在
- 为什么需要泛型:避免成员膨胀或者类型膨胀
- 正交性:泛型类型(类/接口/委托/……)、泛型成员(属性/方法/字段/……)
- 类型方法的参数推断
- 泛型与委托、lambda表达式
11.partial类
- 减少类的派生
- partial类与Entity Framework
- partial类与Windows Forms,WPF,ASP.Net Core
例(泛型):
using System;
namespace HelloGeneric{
internal class Program{
public static void Main(string[] args){
Apple apple = new Apple(){Color = "Red"};
Book book = new Book(){Name = "New Book"};
Boxbox1 = new Box(){Cargo = apple};
Boxbox2 = new Box(){Cargo = book};
// 泛型处理之后可以访问属性
Console.WriteLine(box1.Cargo.Color);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Cargo.Name);
}
}
class Apple{
public string Color{get;set;}
}
class Book{
public string Name{get;set;}
}
// 泛型<类型参数>-类型参数:变量
class Box{
public TCargo Cargo {get;set;}
}
}
例1(泛型接口是什么):
namespace HelloGeneric{
internal class Program{
public static void Main(string[] args){
// Studentstu = new Student();
// stu.ID = 1;
Studentstu = new Student();
stu.ID = 10000000000000;
stu.Name = "Timothy";
}
}
interface Iunique{
Tid ID{get;set;}
}
class Student:IUnique{
public Tid ID{get;set;}
public string Name{get;set;}
}
} 例2(泛型接口-类型参数固定):
namespace HelloGeneric{
internal class Program{
public static void Main(string[] args){
Student student = new Student();
student.ID = 1000000000000000;
student.Name ="Timothy";
}
}
interface Iunique{
Tid ID{get;set;}
}
// 类型参数固定ulong
class Student:IUnique{
public ulong ID {get; set;}
public string Name{get; set;}
}
}
例3(泛型接口-类型参数固定):
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace HelloGeneric{
internal class Program{
public static void Main(string[] args){
IList list = new List();
for (int i = 0;i<100;i++){
list.Add(i);
}
foreach(var item in list){
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
}
}
}
例4(带有不止一个的泛型接口和泛型类):
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace HelloGeneric{
internal class Program{
public static void Main(string[] args){
// Dictionary
// 使用int类型特化了Tkey类型,使用string类型特化了Tvalue类型;
// 使用特化后的IDictionary类型的变量去引用一个特化后的Dictionary类型的实例
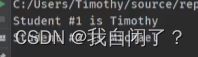
IDictionary dict = new Dictionary();
dict[1]="Timothy";
dict[2]="Michael";
Console.WriteLine($"Student #1 is {dict[1]}");
Console.WriteLine($"Student #2 is {dict[2]}");
}
}
}
}
结果:
例5(泛型方法改装):
namespace HelloGeneric{
internal class Program{
public static void Main(string[] args){
int[] a1= {1,2,3,4,5};
int[] a2= {1,2,3,4,5,6};
double[] a3 = {1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,.5.5};
double[] a4 = {1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,.5.5,6.6};
var result1 = Zip(a1,a2);// 泛型方法传参时可以省略显式特化,编译器可自行推断
var result2 = Zip(a3,a4);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",",result));
}
// static int[] Zip(int[] a,int[] b)
// 升级如下
// 无论什么类型都能适配
static T[] Zip(T[] a,T[] b){
T[] zipped = new T[a.Length +b.Length];
int ai =0 ,bi = 0,zi = 0;
do{
if(ai 例6(Action(没有返回值方法)泛型委托):
namespace HelloGeneric{
internal class Program{
public static void Main(string[] args){
// 创建Action泛型委托,指什么方法
// Action委托只能引用没有返回值的委托
Action a1 = Say;
// a1.Invoke("Timothy");
// 委托本身可调用
a1("Timothy");
Action a2 = Mul;
a2(1);
}
static void Say(string str){
Console.WriteLine($"Hello,{str}!");
}
static void Mul(int x){
Console.WriteLine(x*100);
}
}
}
例6(Func(有返回值方法)泛型委托):
namespace HelloGeneric{
internal class Program{
public static void Main(string[] args){
// Func可引用有返回值的方法
// Func指多少个参数,每个参数是什么类型的,最后一个参数指明返回值类型是什么
Func func1=Add;
Func func2=Add; // 特化Func泛型委托,自动匹配
var result1 = func1(100,200);
var result2 = func2(100,200);
Console.WriteLine(result1); // 300
Console.WriteLine(result2); // 300.3
}
static int Add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
static double Add(double a,double b){
return a+b;
}
}
}
注:
如果方法很简单不想占用名称空间可这样做:
Func
partial类:减少类的派生,可支持多种语言编程
12.枚举类型:
- 人为限定取值范围的整数
- 整数值的对应
- 比特未式用法
13.结构体(struct)
- 值类型,可装/拆箱
- 可实现接口,不能派生自类/结构体
- 不能有显式无参构造器
例(枚举类型):
namespace HelloEnum{
internal class Program{
public static void Main(string[] args){
Person boss= new Person();
boss.Level = "Boss";
Person manager= new Person();
manager.Level = "Manager";
Console.WriteLine(boss.Level>manager.Level); // True --(2>1)
// 枚举类型本质上是人为限定取值范围的整数
Console.WriteLine((int)Level.Employee); // 0
Console.WriteLine((int)Level.Manager); // 1
Console.WriteLine((int)Level.Boss); // 2
Console.WriteLine((int)Level.BigBoss); // 3
//比特未式法(2进制取或法-遇1为1)
person.Skill = Skill.Drive | Skill.Drive | Skill.Program | Skill.Teach;
Console.WriteLine(person.Skill); // 15
// 判断会不会做饭(2进制取与法-遇0为0)
//Console.WriteLine((person.Skill & Skill.Cook)>0);
Console.WriteLine((person.Skill & Skill.Cook)==Skill.Cook);
}
}
}
//定义枚举值
/*
enum Level{
Employee,
Manager,
Boss,
BigBoss,
} */
enum Level{
// 可人为修改
// 编译器扫描发现枚举值有的赋值有的没赋值,就在没赋值的在赋值了的基础上加1
Employee = 100,
Manager, // 101
Boss =300,
BigBoss, // 301
}
// 枚举值比特未式用法
enum Skill{
Drive = 1,
Cook = 2,
Program = 4,
Teach = 8,
}
class Person {
public int ID{get;set;}
public string Name{get; set;}
public Level Level{get;set;} //设置级别时,只能在Employee,Manager,Boss,BigBoss里选
}
例(结构体类型):
namespace HelloEnum{
internal class Program{
public static void Main(string[] args){
// 1.直接赋值
Student student = new Student(){ID=101,Name="Timothy"};
// 2.值类型备份(不同于引用类型,备份的是完整的值类型,而不是引用的地方)
object obj = student;
// 装箱
Student student2 = (Student)obj;
// 拆箱
Console.WriteLine($"#{student2.ID} Name:{student2.Name}");
//值类型备份举例
Student stu1 = new Student(){ID=101,Name="Timothy"};
Student stu2 = stu1;
stu2.ID = 1001;
stu2.Name = "Michael";
Console.WriteLine($"#{stu2.ID} Name:{stu2.Name}"); // #1001 Name:Michael
// 3.可调用接口
stu1.Speak(); // I'm #101 student Thmothy
//调用有参构造器
Student student = new Student(1,"Chris");
student.Speak(); // I'm #1 student Chris
}
interface ISpeak{
void Speak();
}
// 值类型
struct Student:ISpeak{
// 5.结构体类型不可拥有显示的无参构造器
public Student(){}// 不能没有参数
public Student(int id,string name){
this.ID=id;
this.Name=name;
}
public Student(int id,string name){
this.
}
public int ID{get;set;}
public string Name{get;set;}
public void Speak(){
Console.WriteLine($"I'm #{this.ID} student {this.Name}");
}
}
// 4.结构体类型不可由其他结构体类型派生而来
struct SuperStudent:Student{
}
}
}
14.委托,lambda,LINQ
①什么是委托
委托类型怎么声明?
泛型委托
我们必须自己创建委托吗?
泛型委托的类型参数推断
②Lambda
方法与lambda表达式之间的关系
如何把一个Lambda表达式赋值给一个委托类型的变量
如何把一个Lambda表达式“喂”给一个委托类型参数
③LINQ
例(委托是一种引用类类型):
namespace HelloEnum{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
//dele1这个变量引用着一个MyDele类型的实例,这个实例里“包裹”着M1这个方法
MyDele dele1=new MyDele(M1); //注不要用M1(),这相当于调用M1,而现在则是指M1这个函数
Student stu = new Student();
// dele1+=stu.Sayhello; // 一次调用可以调用好几个函数,多播委托
dele1 +=(new Student()).SayHello;
// dele1.invoke(); // 可间接调用M1的方法,调两次
dele1();
}
static void M1(){
Console.WriteLine("M1 is called!");
}
}
class Student{
public void SayHello(){
Console.WriteLine("Hello,I'm a student!");
}
}
delegate void MyDele();
}
注:
委托类型是一种特殊的类类型:
1.功能特殊:方法封装器-(正常类型一般是事物实例:车、人、东西。。。而委托类型则是包裹着方法,是一组函数封装器);
2.声明特殊:不用class声明,而用delegate
例(委托间接调用有参方法):
namespace Combine{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
MyDele dele = new MyDele(Add);
int res = dele(100,200);
// 使用委托间接调用包裹在里面的函数
Console.WriteLine(res);
}
static int Add(int x,int y){
return x+y;
}
}
delegate int MyDele(int a,intb);
}
例(泛型委托):
namespace Combine{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
MyDele deleAdd = new MyDele(Add);
int res = deleAdd(100,200);
Console.WriteLine(res); // 300
// 泛型委托有效避免类膨胀
MyDele deleMul = new MyDele(Mul);
double mulRes = deleMul(3.0,4.0);
Console.WriteLine(mulRes); // 7.0
}
static int Add(int x,int y){
return x+y;
}
static double Mul(double x,double y){
return x*y;
}
}
delegate T MyDele(T a,T b);
}
例(Action):
namespace Combine{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
// Action action = new Action(SayHello);
var action = new Action(SayHello);
action("Tim",3);
}
static void M1(){
Console.WriteLine("M1 is called");
}
static void SayHello(string name,int round){
for(int i=0;i(T a,T b);
}
}
例(function):
namespace Combine{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
Func func = new Func(Add);
int res = func(100,200);
Console.WriteLine(res); // 300
}
static void M1(){
Console.WriteLine("M1 is called");
}
static void SayHello(string name,int round){
for(int i=0;i(T a,T b);
}
}
例(Lambda):
namespace Combine{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
//Func func = new Func((int a,int b)=>{return a+b;});
// 可简化为:
Func func = (a,b)=>{return a+b;};
int res = func(100,200);
Console.WriteLine(res);
func = (x,y)=>{return x*y;};
res = func(3,4);
Console.WriteLine(res);
}
}
}
注:
Lambda表达式作用:1.匿名方法;2.Inline方法
例(Lambda综合小例子):
namespace Combine{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
DoSomeCalc((a,b)=>{return a*b;},100,200);
}
static void DoSomeCalc(Func func ,T x,T y){
T res=func(x,y);
Console.WriteLine(res); // 300
}
}
}
例(LINQ-全称:.NET Language Integrateed Query):
using Combine.Models;
namespace Combine{
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args){
// entity framwork
var dbContext = new AdventureWorks2014Entities();
/*
// 先选人,才能选名字
var allPeople = dbContext.People.ToList();
foreach(var p in allPeople){
Console.WriteLine(p.FirstName);
} */
// 直接选名字
var allFristNames = dbContext.People.Select(p=>p.FirstName).ToList();
foreach(var fn in allFirstNames){
Console.WriteLine(fn); // 名字
}
var allFullNames = dbContext.People.Select(p=>p.FirstName +""+p.LastName).ToList();
foreach(var fn in allFullNames ){
Console.WriteLine(fn); // 全名
}
// 选出Timothy
var allFullNames = dbContext.People.Where(p=>p.FirstName=="Timothy")
.Select(p=>p.FirstName +""+p.LastName).ToList();
// 计数
var groups = dbContext.People.GroupBy(p=>p.FristName).ToList();
foreach(var g in groups){
Console.WriteLine("Name:{0} \t Count:{1}",g.Key,g.Count());
}
var count = dbContext.People.Count(p=>p.FirstName == "Timothy");
Console.WriteLine(count);
}
}
}