反射调用方法
什么是反射
Java 反射是指在运行时,对于任意一个类,都能够了解这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性。这种动态获取信息和动态调用对象的功能被称为 Java 反射。
Java 反射主要用于实现框架、工具类、插件系统、序列化、反序列化等方面。
Java 反射的主要功能包括:
- 获取类的信息:通过 Class 类的 getAnnotations()、getDeclaredAnnotations()、getInterfaces()、getSuperclass() 等方法可以获取类的各种信息,例如注解、方法、字段、父类等。
- 创建对象:通过 Class 类的 newInstance() 方法可以创建没有构造函数的类实例。
- 调用方法:通过 Method 类的 getMethod()、invoke() 方法可以调用类的方法。
- 访问字段:通过 Field 类的 get()、set() 方法可以获取和设置对象的字段值。
- 获取实现接口的方法:通过 Class 类的 getDeclaredMethod()、getDeclaredMethods() 方法可以获取类实现的全部方法。
- 获取注解信息:通过 Class 类的 getAnnotation()、getDeclaredAnnotation() 方法可以获取类的注解信息。
- 动态代理:通过 Proxy 类可以创建代理对象,实现动态代理功能。
Java 反射的使用需要谨慎,因为反射会破坏类的封装性,并且会降低性能。在使用反射时应该优先考虑其他方式,只有在必要时才使用反射。
反射调用方法
要理解反射之中包含了一个“反”字,就必须先从”正“开始解释。
我们正常情况使用某个类时,直接对这个类进行实例化,之后使用这个类对象进行操作。
//直接初始化(正射)
Car car = new Car();
apple.setName("Tesla");
下面开始介绍反射调用方法
1.1 获得 Method 对象
通过Class实例获取所有Method信息
Class类提供了以下几个方法来获取Method:
- Method getDeclaredMethod(name, Class…):获取当前类(不包括父类)的某个Method
- Method getMethod(name, Class…):获取当前类(包括父类)public修饰的某个Method
- Method[] getDeclaredMethods():获取当前类(不包括父类)的所有Method
- Method[] getMethods():获取当前类(包括父类)所有public的Method
public class Reflection {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<Tesla> clazz = Tesla.class;
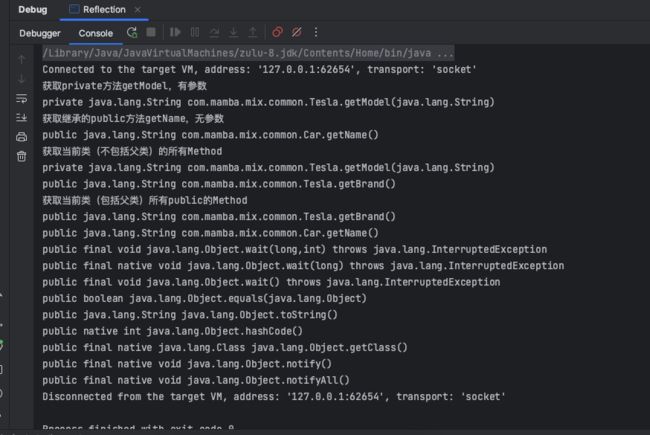
// 获取private方法getModel,有参数
System.out.println("获取private方法getModel,有参数");
System.out.println(clazz.getDeclaredMethod("getModel", String.class));
// 获取继承的public方法getName,无参数:
System.out.println("获取继承的public方法getName,无参数");
System.out.println(clazz.getMethod("getName"));
// 获取当前类(不包括父类)的所有Method
System.out.println("获取当前类(不包括父类)的所有Method");
for (Method declaredMethod : clazz.getDeclaredMethods()) {
System.out.println(declaredMethod);
}
// 获取当前类(包括父类)所有public的Method
System.out.println("获取当前类(包括父类)所有public的Method");
for (Method method : clazz.getMethods()) {
System.out.println(method);
}
}
}
class Tesla extends Car {
public String getBrand() {
System.out.println("Tesla");
return "Tesla";
}
private String getModel(String type) {
System.out.println(type);
return type;
}
}
class Car {
public String getName() {
return "Car";
}
}
控制台输出
Method 对象的信息获取:
一个Method对象包含一个方法的所有信息:
- getName():返回方法名称,例如:“getScore”;
- getReturnType():返回方法返回值类型,也是一个Class实例,例如:String.class;
- getParameterTypes():返回方法的参数类型,是一个Class数组,例如:{String.class, int.class};
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("getModel", String.class);
System.out.println("返回方法名称");
System.out.println(method.getName());
System.out.println("返回方法返回值类型");
System.out.println(method.getReturnType());
System.out.println("返回方法的参数类型");
for (Class<?> parameterType : method.getParameterTypes()) {
System.out.println(parameterType);
}
控制台输出
1.2 调用非静态方法(对象方法)
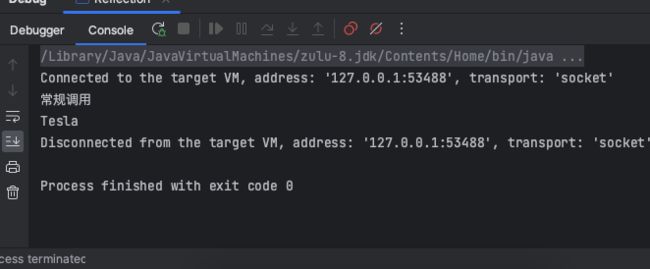
常规调用
public class Reflection {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 常规调用
Tesla tesla = new Tesla();
System.out.println("常规调用");
String brand = tesla.getBrand();
System.out.println(brand);
}
}
class Tesla extends Car {
public String getBrand() {
return "Tesla";
}
private String getModel(String type) {
return type;
}
public static int getSeat(){
return 5;
}
}
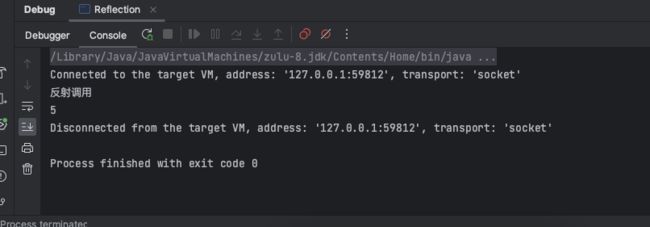
反射调用
先获取 Method 对象 然后再调用 invoke 方法
源码:
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException
{
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatile
if (ma == null) {
ma = acquireMethodAccessor();
}
return ma.invoke(obj, args);
}
对Method实例调用invoke就相当于调用该方法,invoke的第一个参数是对象实例,即在哪个实例上调用该方法,后面的可变参数要与方法参数一致,否则将报错。
public class Reflection {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<Tesla> clazz = Tesla.class;
Tesla tesla = new Tesla();
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("getBrand");
String invoke = (String) method.invoke(tesla);
System.out.println("反射调用");
System.out.println(invoke);
}
}
class Tesla extends Car {
public String getBrand() {
return "Tesla";
}
private String getModel(String type) {
return type;
}
public static int getSeat(){
return 5;
}
}
1.3 调用静态方法
常规调用
public class Reflection {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 常规调用
Tesla tesla = new Tesla();
System.out.println("常规调用");
String brand = tesla.getBrand();
System.out.println(brand);
}
}
class Tesla extends Car {
public String getBrand() {
return "Tesla";
}
private String getModel(String type) {
return type;
}
public static int getSeat(){
return 5;
}
}
反射调用
调用静态方法时,由于无需指定实例对象,所以invoke方法传入的第一个参数永远为null
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Method method = Tesla.class.getDeclaredMethod("getSeat");
int invoke = (Integer) method.invoke(null);
System.out.println("反射调用");
System.out.println(invoke);
}
}
class Tesla extends Car {
public String getBrand() {
return "Tesla";
}
private String getModel(String type) {
return type;
}
public static int getSeat(){
return 5;
}
}
1.4 调用非 public 方法
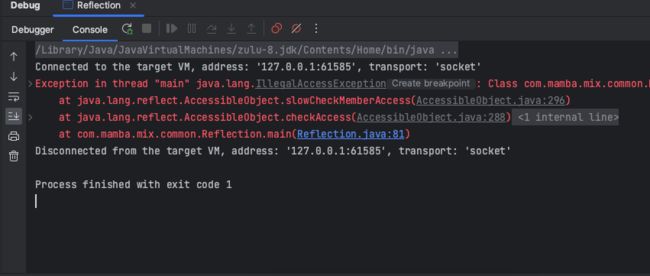
调用非public方法时,虽然可以通过Class.getDeclaredMethod()获取该方法实例,但实际调用的时候会报IllegalAccessException 错误,所以为了调用非public方法,需要设置Method.setAccessible(true)允许其调用,仍然可能会调用失败
未设置method.setAccessible(true)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Method method = Tesla.class.getDeclaredMethod("getSeat");
int invoke = (Integer) method.invoke(null);
System.out.println("反射调用");
System.out.println(invoke);
}
}
class Tesla extends Car {
public String getBrand() {
return "Tesla";
}
private String getModel(String type) {
return type;
}
public static int getSeat(){
return 5;
}
}
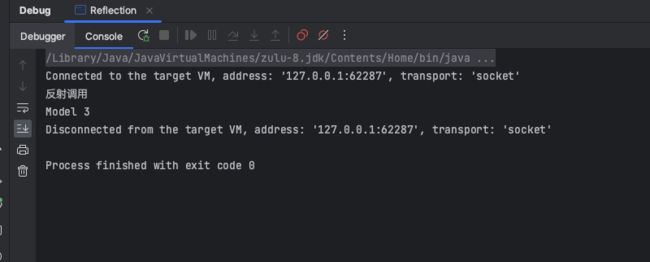
设置method.setAccessible(true)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<Tesla> clazz = Tesla.class;
Tesla tesla = new Tesla();
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("getModel", String.class);
method.setAccessible(true);
String invoke = (String) method.invoke(tesla, "Model 3");
System.out.println("反射调用");
System.out.println(invoke);
}
}
class Tesla extends Car {
public String getBrand() {
return "Tesla";
}
private String getModel(String type) {
return type;
}
public static int getSeat(){
return 5;
}
}