高并发累加器Striped64
Striped64主要用于支持并发累加器的实现。这个类在高并发环境下被用来做某种计数,【其设计的核心思想是在竞争激烈的时候尽量分散竞争】。
为了达到这一目标,Striped64维护了一个base Count和一个Cell数组。在多线程环境中,当一个线程想要更新计数时,它会首先试图更新base变量。如果成功,则该线程退出计数;否则,由于竞争激烈,该线程会转向Cell数组来分散计数。
Striped64根据线程来计算哈希,然后将不同的线程分散到不同的Cell数组的index上。在这个基础上,这个线程的计数内容就会被保存在该Cell的位置上。最后,为了得到总的计数结果,需要将base值与散落在Cell数组中的所有计数内容进行合并。
高并发下的累加器,两个实现类:LongAdder和DoubleAdder,基本上把longAccumulate方法搞清楚,就都能看懂了。
先来看一下内部类Cell:
@sun.misc.Contended static final class Cell {
volatile long value;
Cell(long x) { value = x; }
final boolean cas(long cmp, long val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapLong(this, valueOffset, cmp, val);
}
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long valueOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> ak = Cell.class;
valueOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(ak.getDeclaredField("value"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
}
可以观察到,对Cell中的value操作只能使用CAS(Compare-and-Swap)操作,因此一定是线程安全的。@sun.misc.Contended解决了伪共享的问题。
几个重要的成员变量:
/** Number of CPUS, to place bound on table size */
// CPU数量
static final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
/**
* Table of cells. When non-null, size is a power of 2.
*/
// cell数组
transient volatile Cell[] cells;
/**
* Base value, used mainly when there is no contention, but also as
* a fallback during table initialization races. Updated via CAS.
*/
// base变量
transient volatile long base;
/**
* Spinlock (locked via CAS) used when resizing and/or creating Cells.
*/
// cell数组是否存在竞争
transient volatile int cellsBusy;
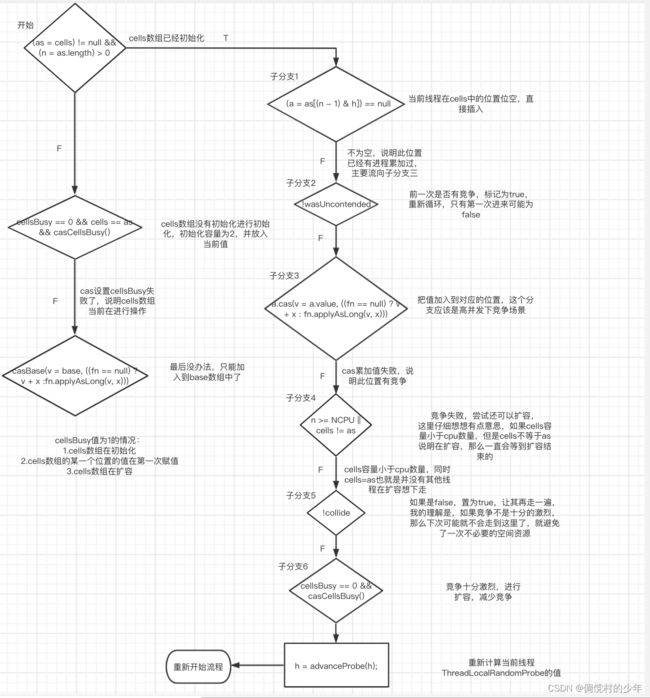
longAccumulate方法
/**
* Handles cases of updates involving initialization, resizing,
* creating new Cells, and/or contention. See above for
* explanation. This method suffers the usual non-modularity
* problems of optimistic retry code, relying on rechecked sets of
* reads.
*
* @param x the value
* @param fn the update function, or null for add (this convention
* avoids the need for an extra field or function in LongAdder).
* @param wasUncontended false if CAS failed before call
*/
final void longAccumulate(long x, LongBinaryOperator fn,
boolean wasUncontended) {
//获取当前线程的threadLocalRandomProbe值作为hash值,如果当前线程的threadLocalRandomProbe为0,
// 说明当前线程是第一次进入该方法,则强制设置线程的
//threadLocalRandomProbe为ThreadLocalRandom类的成员静态私有变量probeGenerator的值,后面会详细将hash值的生成;
//另外需要注意,如果threadLocalRandomProbe=0,代表新的线程开始参与cell争用的情况
//1.当前线程之前还没有参与过cells争用(也许cells数组还没初始化,进到当前方法来就是为了初始化cells数组后争用的),
//是第一次执行base的cas累加操作失败;
//2.或者是在执行add方法时,对cells某个位置的Cell的cas操作第一次失败,则将wasUncontended设置为false,
//那么这里会将其重新置为true;第一次执行操作失败;
//凡是参与了cell争用操作的线程threadLocalRandomProbe都不为0;
int h;
if ((h = getProbe()) == 0) {
//强制初始化
ThreadLocalRandom.current(); // force initialization
h = getProbe();
wasUncontended = true;
}
//cas冲突标志,表示当前线程hash到的Cells数组的位置,做cas累加操作时与其它线程发生了冲突,cas失败;
//collide=true代表有冲突,collide=false代表无冲突
boolean collide = false; // True if last slot nonempty
//Spin lock + collide标志
for (;;) {
Cell[] as; Cell a; int n; long v;
//这个主干if有三个分支
//1.主分支一:处理cells数组已经正常初始化了的情况(这个if分支处理add方法的四个条件中的3和4)
//2.主分支二:处理cells数组没有初始化或者长度为0的情况;(这个分支处理add方法的四个条件中的1和2)
//3.主分支三:处理如果cell数组没有初始化,并且其它线程正在执行对cells数组初始化的操作,及cellbusy=1;
//则尝试将累加值通过cas累加到base上
//先看主分支一
if ((as = cells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) {
//内部小分支一:这个是处理add方法内部if分支的条件3:如果被hash到的位置为null,说明没有线程在这个位置设置过值,没有竞争,
//可以直接使用,则用x值作为初始值创建一个新的Cell对象,对cells数组使用cellsBusy加锁
,然后将这个Cell对象放到cells[m%cells.length]位置上(这里的add方法都是代表LongAdder里面的add方法的判断)
if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) {
//cellsBusy == 0 代表当前没有线程cells数组做修改
if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Try to attach new Cell
Cell r = new Cell(x); // Optimistically create
//如果cellsBusy=0无锁,则通过cas将cellsBusy设置为1加锁
if (cellsBusy == 0 && casCellsBusy()) {
boolean created = false;
try { // Recheck under lock
Cell[] rs; int m, j;
//再次检查cells数组不为null,且长度不为空,且hash到的位置的Cell为null
if ((rs = cells) != null &&
(m = rs.length) > 0 &&
rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) {
rs[j] = r;
created = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
//生成成功,跳出循环
if (created)
break;
//如果created为false,说明上面指定的cells数组的位置cells[m%cells.length]已经有其它线程设置了cell了,继续执行循环。
continue; // Slot is now non-empty
}
}
//如果执行的当前行,代表cellsBusy=1,有线程正在更改cells数组,代表产生了冲突,将collide设置为false
collide = false;
}
//内部小分支二:如果add方法中条件4的通过cas设置cells[m%cells.length]位置的Cell对象中的value值设置为v+x失败,说明已经发生竞争,将
//wasUncontended设置为true,跳出内部的if判断,最后重新计算一个新的probe,然后重新执行循环;
else if (!wasUncontended) // CAS already known to fail
//设置未竞争标志位true,继续执行,后面会算一个新的probe值,然后重新执行循环。
wasUncontended = true; // Continue after rehash
//内部小分支三:新的争用线程参与争用的情况:处理刚进入当前方法时threadLocalRandomProbe=0的情况,也就是当前线程第一次参与cell争用的cas失败,这
//里会尝试将x值加到cells[m%cells.length]的value ,如果成功直接退出
//我觉得这里并不是threadLocalRandomProbe=0的情况,因为一开始就已经初始化了,怎么会等于0呢,应该是存在大量竞争的情况下发生的
else if (a.cas(v = a.value, ((fn == null) ? v + x :
fn.applyAsLong(v, x))))
break;
//内部小分支四:分支3处理新的线程争用执行失败了,这时如果cells数组的长度已经到了最大值(大于等于cup数量),或者是当前cells已经做了扩容,则将
collide设置为false,后面重新计算prob的值
else if (n >= NCPU || cells != as)
collide = false; // At max size or stale
//内部小分支五:如果发生了冲突collide=false,则设置其为true;会在最后重新计算hash值后,进入下一次for循环
else if (!collide)
//设置冲突标志,表示发生了冲突,需要再次生成hash,重试。 如果下次重试任然走到了改分支此时collide=true,!collide条件不成立,则走后一个分支
collide = true;
//内部小分支六:扩容cells数组,新参与cell争用的线程两次均失败,且符合扩容条件,会执行该分支
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && casCellsBusy()) {
try {
if (cells == as) { // Expand table unless stale
Cell[] rs = new Cell[n << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
rs[i] = as[i];
cells = rs;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
collide = false;
continue; // Retry with expanded table
}
//为当前线程重新计算hash值
h = advanceProbe(h);
}
//分支二
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && cells == as && casCellsBusy()) {
//初始化标志
boolean init = false;
try { // Initialize table
if (cells == as) {
//初始化cells数组,初始容量为2,并将x值通过hash&1,放到0个或第1个位置上
Cell[] rs = new Cell[2];
rs[h & 1] = new Cell(x);
cells = rs;
//初始化标志
init = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
//初始化成功退出循环
if (init)
break;
}
//分支三
//如果以上操作都失败了,则尝试将值累加到base上;也就是说,只有在cells数组初始化的时候才会累加到base上面
else if (casBase(v = base, ((fn == null) ? v + x :
fn.applyAsLong(v, x))))
break; // Fall back on using base
}
}
有关hash的生成
Hash是LongAdder定位当前线程将值累加到cells的哪个位置上,所以hash值的计算很重要。
追一下代码可以看到,这里使用到了Thread中的一个属性threadLocalRandomProbe。
/** Probe hash value; nonzero if threadLocalRandomSeed initialized */
@sun.misc.Contended("tlr")
int threadLocalRandomProbe;
threadLocalRandomProbe的初始化
线程对LongAdder的累加操作,在没有进入longAccumulate方法前,threadLocalRandomProbe一直都是0,当发生争用后才会进入longAccumulate方法中,进入该方法第一件事就是判断threadLocalRandomProbe是否为0,如果为0,则将其设置为0x9e3779b9。
final void longAccumulate(long x, LongBinaryOperator fn,
boolean wasUncontended) {
int h;
if ((h = getProbe()) == 0) {
//强制初始化
ThreadLocalRandom.current(); // force initialization
h = getProbe();
wasUncontended = true;
}
进入ThreadLocalRandom.current()
/**
* Returns the current thread's {@code ThreadLocalRandom}.
*
* @return the current thread's {@code ThreadLocalRandom}
*/
public static ThreadLocalRandom current() {
if (UNSAFE.getInt(Thread.currentThread(), PROBE) == 0)
//初始化
localInit();
return instance;
}
/**
* Initialize Thread fields for the current thread. Called only
* when Thread.threadLocalRandomProbe is zero, indicating that a
* thread local seed value needs to be generated. Note that even
* though the initialization is purely thread-local, we need to
* rely on (static) atomic generators to initialize the values.
*/
static final void localInit() {
int p = probeGenerator.addAndGet(PROBE_INCREMENT);
int probe = (p == 0) ? 1 : p; // skip 0
long seed = mix64(seeder.getAndAdd(SEEDER_INCREMENT));
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
UNSAFE.putLong(t, SEED, seed);
UNSAFE.putInt(t, PROBE, probe);
}
/**
* The increment for generating probe values
*/
private static final int PROBE_INCREMENT = 0x9e3779b9;
probeGenerator 是static 类型的AtomicInteger类,每执行一次localInit()方法,都会将probeGenerator 累加一次0x9e3779b9这个值;,0x9e3779b9这个数字的得来是 2^32 除以一个常数,这个常数就是传说中的黄金比例 1.6180339887;然后将当前线程的threadLocalRandomProbe设置为probeGenerator 的值,如果probeGenerator 为0,这取1;
threadLocalRandomProbe重新生成
/**
* Pseudo-randomly advances and records the given probe value for the
* given thread.
* Duplicated from ThreadLocalRandom because of packaging restrictions.
*/
static final int advanceProbe(int probe) {
probe ^= probe << 13; // xorshift
probe ^= probe >>> 17;
probe ^= probe << 5;
UNSAFE.putInt(Thread.currentThread(), PROBE, probe);
return probe;
}