DS|哈希查找
题目一:DS哈希查找 -- 线性探测再散列
题目描述:
定义哈希函数为H(key) = key%11,输入表长(大于、等于11)。输入关键字集合,用线性探测再散列构建哈希表,并查找给定关键字。
输入要求:
测试次数t
每组测试数据为:
哈希表长m、关键字个数n
n个关键字
查找次数k
k个待查关键字
输出要求:
对每组测试数据,输出以下信息:
构造的哈希表信息,数组中没有关键字的位置输出NULL
对k个待查关键字,分别输出:0或1(0—不成功,1—成功)、比较次数、查找成功的位置(从1开始)
输入样例:
1
12 10
22 19 21 8 9 30 33 4 15 14
4
22
56
30
17
输出样例:
22 30 33 14 4 15 NULL NULL 19 8 21 9
1 1 1
0 6
1 6 2
0 1代码示例:
#include
using namespace std;
int swapCnt;
class HashTable {
private:
int* HT;
int maxSize;
int current;
public:
HashTable(int n) {
maxSize = n;
HT = new int[maxSize];
fill(HT, HT + maxSize, -1);
current = 0;
}
~HashTable() { delete[] HT; }
int H(int key);
int HashSearch(int key);
void HashInsert(int key);
int getHT(int i);
};
int HashTable::H(int key) { return key % 11; }
int HashTable::getHT(int i) {
return HT[i];
}
void HashTable::HashInsert(int key) {
int d, j;
d = H(key);
if (HT[d] != -1) {
j = d;
d = (d + 1) % maxSize;
while (d != j && HT[d] != -1) d = (d + 1) % maxSize;
}
if (HT[d] == -1) {
HT[d] = key;
current++;
}
}
int HashTable::HashSearch(int key) {
int d = H(key);
for (int i = 0; i < maxSize; i++) {
swapCnt++;
if (HT[d] == key) return d;
if (HT[d] == -1) return -1;
d = (d + 1) % maxSize;
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int m, n;
cin >> m >> n;
HashTable ht(m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int keyNumber;
cin >> keyNumber;
ht.HashInsert(keyNumber);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (ht.getHT(i) != -1) cout << ht.getHT(i) << "";
else cout << "NULL";
if (i != m - 1) cout << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int k;
cin >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
int keyNumber;
swapCnt = 0;
cin >> keyNumber;
int result = ht.HashSearch(keyNumber);
if (result != -1) {
cout << "1 " << swapCnt << " " << result + 1 << endl;
}
else cout << "0 " << swapCnt << endl;
}
}
} 题目二:DS哈希查找 -- 二次探测再散列
题目描述:
定义哈希函数为H(key) = key%11。输入表长(大于、等于11),输入关键字集合,用二次探测再散列构建哈希表,并查找给定关键字。
输入要求:
测试次数t
每组测试数据格式如下:
哈希表长m、关键字个数n
n个关键字
查找次数k
k个待查关键字
输出要求:
对每组测试数据,输出以下信息:
构造的哈希表信息,数组中没有关键字的位置输出NULL
对k个待查关键字,分别输出:
0或1(0—不成功,1—成功)、比较次数、查找成功的位置(从1开始)
输入样例:
1
12 10
22 19 21 8 9 30 33 4 41 13
4
22
15
30
41
输出样例:
22 9 13 NULL 4 41 NULL 30 19 8 21 33
1 1 1
0 3
1 3 8
1 6 6代码示例:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int swapCnt;
class HashTable {
private:
int* HT;
int maxSize;
int current;
public:
HashTable(int n) {
maxSize = n;
HT = new int[maxSize];
fill(HT, HT + maxSize, -1);
current = 0;
}
~HashTable() { delete[] HT; }
int H(int key);
void HashSearch(int key);
void HashInsert(int key);
int getHT(int i);
};
int HashTable::H(int key) { return key % 11; }
int HashTable::getHT(int i) { return HT[i]; }
void HashTable::HashInsert(int key) {
int d, j;
int sum = 0, count = 0;
d = H(key);
if (HT[d] != -1) {
while (1) {
int pos;
count++;
sum = (count + 1) / 2;
if (count % 2 == 1) pos = (d + sum * sum) % maxSize;
else pos = (d - sum * sum) % maxSize;
while (pos < 0) pos += maxSize;
if (HT[pos] == -1) {
HT[pos] = key;
break;
}
}
}
if (HT[d] == -1) {
HT[d] = key;
current++;
}
}
void HashTable::HashSearch(int key) {
int sum = 0, flag = 0, c;
int d = H(key);
while (1) {
flag++;
if (flag >= 2 && flag % 2 == 0) sum++;
if (flag % 2 == 0) c = 1;
else c = -1;
int p = (d + c * sum * sum) % maxSize;
if (HT[p] == key) {
cout << "1 " << flag << " " << p + 1 << endl;
break;
}
else if (HT[p] == -1) {
cout << "0 " << flag << endl;
break;
}
}
}
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int m, n;
cin >> m >> n;
HashTable ht(m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int keyNumber;
cin >> keyNumber;
ht.HashInsert(keyNumber);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (ht.getHT(i) != -1) cout << ht.getHT(i) << "";
else cout << "NULL";
if (i != m - 1) cout << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int k;
cin >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
int keyNumber;
swapCnt = 0;
cin >> keyNumber;
ht.HashSearch(keyNumber);
}
}
} 题目三:DS哈希查找 -- 链地址法(表头插入)
题目描述:
给出一个数据序列,建立哈希表,采用求余法作为哈希函数,模数为11,哈希冲突用链地址法和表头插入
如果首次查找失败,就把数据插入到相应的位置中
实现哈希查找功能
输入要求:
第一行输入n,表示有n个数据
第二行输入n个数据,都是自然数且互不相同,数据之间用空格隔开
第三行输入t,表示要查找t个数据
从第四行起,每行输入一个要查找的数据,都是正整数
输出要求:
每行输出对应数据的查找结果
输入样例:
6
11 23 39 48 75 62
6
39
52
52
63
63
52
输出样例:
6 1
error
8 1
error
8 1
8 2代码示例:
#include
using namespace std;
int H(int key) { return key % 11; }
struct Node {
public:
int key;
Node* next;
};
class HashTable {
public:
Node* HT[100];
HashTable(int m) { for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) HT[i] = NULL; }
void headInsert(Node* arr, int i) {
if (HT[i] == NULL) HT[i] = arr;
else {
arr->next = HT[i];
HT[i] = arr;
}
}
void HashInsert(int key) {
int index = H(key);
Node* p = new Node;
p->key = key;
p->next = NULL;
headInsert(p, index);
}
int HashSerach(int key) {
int i = H(key);
int sum = 0;
Node* p = HT[i];
while (1) {
sum++;
if (p == NULL) return 0;
else {
if (p->key == key) return sum;
p = p->next;
}
}
}
};
int main() {
int t, n, key;
cin >> n;
HashTable ht(11);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> key;
ht.HashInsert(key);
}
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
cin >> key;
int sum = ht.HashSerach(key);
if (sum == 0) {
cout << "error" << endl;
Node* p = new Node;
p->key = key;
p->next = NULL;
ht.headInsert(p, H(key));
}
else cout << H(key) << " " << sum << endl;
}
return 0;
} 题目四:DS哈希查找 -- 查找与增补(表尾插入)
题目描述:
给出一个数据序列,建立哈希表,采用求余法作为哈希函数,模数为11,哈希冲突用链地址法和表尾插入
如果首次查找失败,就把数据插入到相应的位置中
实现哈希查找与增补功能
输入要求:
第一行输入n,表示有n个数据
第二行输入n个数据,都是自然数且互不相同,数据之间用空格隔开
第三行输入t,表示要查找t个数据
从第四行起,每行输入一个要查找的数据,都是正整数
输出要求:
每行输出对应数据的查找结果,每个结果表示为数据所在位置[0,11)和查找次数,中间用空格分开
输入样例:
6
11 23 39 48 75 62
6
39
52
52
63
63
52输出样例:
6 1
error
8 1
error
8 2
8 1代码示例:
#include
using namespace std;
int H(int key) {
return key % 11;
}
struct Node {
public:
int key;
Node* next;
};
class HashTable {
public:
Node* HT[100];
HashTable(int m) {
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) HT[i] = NULL;
}
void headInsert(Node* arr, int i) {
if (HT[i] == NULL) HT[i] = arr;
else {
arr->next = HT[i];
HT[i] = arr;
}
}
void tailInsert(Node* arr, int idx) {
Node* p;
p = HT[idx];
if (p == NULL) {
HT[idx] = arr;
return;
}
while (1) {
if (p->next == NULL) {
p->next = arr;
return;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
void HashInsert(int key) {
int index = H(key);
Node* p = new Node;
p->key = key;
p->next = NULL;
tailInsert(p, index);
}
int HashSerach(int key) {
int index = H(key);
int sum = 0;
Node* p = HT[index];
while (1) {
sum++;
if (p == NULL) return 0;
else {
if (p->key == key) return sum;
p = p->next;
}
}
}
};
int main() {
int t, n, key;
cin >> n;
HashTable ht(11);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> key;
ht.HashInsert(key);
}
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
cin >> key;
int sum = ht.HashSerach(key);
if (sum == 0) {
cout << "error" << endl;
Node* p = new Node;
p->key = key;
p->next = NULL;
ht.tailInsert(p, H(key));
}
else cout << H(key) << " " << sum << endl;
}
return 0;
} 题目五:DS哈希查找 -- Trie树
题目描述:
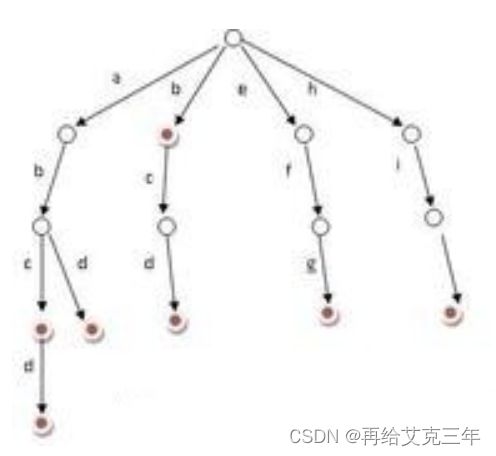
Trie树又称单词查找树,是一种树形结构,如下图所示。
它是一种哈希树的变种。典型应用是用于统计,排序和保存大量的字符串(但不仅限于字符串),所以经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。它的优点是:利用字符串的公共前缀来节约存储空间,最大限度地减少无谓的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希表高。
输入的一组单词,创建Trie树。输入字符串,计算以该字符串为公共前缀的单词数。
(提示:树结点有26个指针,指向单词的下一字母结点。)
输入要求:
测试数据有多组
每组测试数据格式为:
第一行:一行单词,单词全小写字母,且单词不会重复,单词的长度不超过10
第二行:测试公共前缀字符串数量t
后跟t行,每行一个字符串
输出要求:
每组测试数据输出格式为:
第一行:创建的Trie树的层次遍历结果
第2~t+1行:对每行字符串,输出树中以该字符串为公共前缀的单词数。
输出样例:
abcd abd bcd efg hig
3
ab
bc
abcde输出样例:
abehbcficddggd
2
1
0代码示例:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int sum;
class Trie {
public:
bool flag = false;
Trie* next[26] = { NULL };
void insertTrie(string str) {
Trie* node = this;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char c = str[i];
if (node->next[c - 'a'] == NULL) {
node->next[c - 'a'] = new Trie();
}
node = node->next[c - 'a'];
}
node->flag = true;
}
int searchStart(string str) {
Trie* node = this;
sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char c = str[i];
if (node->next[c - 'a'] == NULL) return 0;
node = node->next[c - 'a'];
}
DFS(node);
return sum;
}
void DFS(Trie* Node) {
Trie* tr = new Trie();
tr = Node;
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (tr->next[i]){
DFS(tr->next[i]);
temp = 1;
}
}
if (temp == 0) {
sum++;
return;
}
}
};
void BFS(Trie* Tree) {
queueq;
q.push(Tree);
while (!q.empty()) {
Trie* t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (t->next[i]) {
cout << char('a' + i);
q.push(t->next[i]);
}
}
}
}
int main() {
string str;
Trie* tree = new Trie();
int t;
while (1) {
cin >> str;
if (str[0] >= '0' && str[0] <= '9') {
t = str[0] - '0';
break;
}
tree->insertTrie(str);
}
BFS(tree);
cout << endl;
while (t--) {
cin >> str;
cout << tree->searchStart(str) << endl;
}
} 题目六:DS哈希查找 -- 逆散列问题
题目描述:
给定长度为 N 的散列表,处理整数最常用的散列映射是 H(x)=x%N。如果我们决定用线性探测解决冲突问题,则给定一个顺序输入的整数序列后,我们可以很容易得到这些整数在散列表中的分布。例如我们将 1、2、3 顺序插入长度为 3 的散列表HT[]后,将得到HT[0]=3,HT[1]=1,HT[2]=2的结果。
但是现在要求解决的是“逆散列问题”,即给定整数在散列表中的分布,问这些整数是按什么顺序插入的?
输入要求:
输入的第一行是正整数 N(≤1000),为散列表的长度。第二行给出了 N 个整数,其间用空格分隔,每个整数在序列中的位置(第一个数位置为0)即是其在散列表中的位置,其中负数表示表中该位置没有元素。题目保证表中的非负整数是各不相同的。
输出要求:
按照插入的顺序输出这些整数,其间用空格分隔,行首尾不能有多余的空格。注意:对应同一种分布结果,插入顺序有可能不唯一。例如按照顺序 3、2、1 插入长度为 3 的散列表,我们会得到跟 1、2、3 顺序插入一样的结果。在此规定:当前的插入有多种选择时,必须选择最小的数字,这样就保证了最终输出结果的唯一性。
输入样例:
11
33 1 13 12 34 38 27 22 32 -1 21输出样例:
1 13 12 21 33 34 38 27 22 32代码示例:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int m;
int main()
{
cin >> m;
vectorv(m);
vectortemp;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
cin >> v[i];
if (v[i] != -1)
temp.push_back(v[i]);
}
sort(temp.begin(), temp.end());
int length = temp.size();
vectorfinding_value(length, 0);
vectorhashtable(m, 0);
int num = 0, index = 0;
//length 为插入数据长度
while (num != length)
{
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
if (!finding_value[i]) //如果这个值没有找到位置
{
int posi = temp[i] % m;
//temp[i]的线性探测初始位置
if (v[posi] == temp[i])
{
printf("%d ", temp[i]);
finding_value[i] = 1;
hashtable[posi] = 1;
num++;
break;
}
else
{
for (int t = 0; t < m; t++)
{
int new_posi = (posi + t) % m;
if (hashtable[new_posi])
continue;
if (!hashtable[new_posi] && v[new_posi] != temp[i])
break;
finding_value[i] = hashtable[new_posi] = 1;
printf("%d ", temp[i]);
num++;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}