代码随想录算法训练营第21天|530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差 501.二叉搜索树中的众数 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
JAVA代码编写
530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
给你一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,返回 树中任意两不同节点值之间的最小差值 。
差值是一个正数,其数值等于两值之差的绝对值。
示例 1:
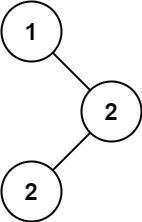
输入:root = [4,2,6,1,3]
输出:1
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,0,48,null,null,12,49]
输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[2, 104] 0 <= Node.val <= 105
**注意:**本题与 783 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-distance-between-bst-nodes/ 相同
教程:https://programmercarl.com/0530.%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E5%B0%8F%E7%BB%9D%E5%AF%B9%E5%B7%AE.html
视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1DD4y11779/
方法一:递归
思路:
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度: O(n),其中n是二叉树中节点的数量
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
class Solution {
TreeNode pre;// 记录上一个遍历的结点
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return 0;
traversal(root);
return result;
}
public void traversal(TreeNode root){
if(root==null)return;
//左
traversal(root.left);
//中
if(pre!=null){
result = Math.min(result,root.val-pre.val);
}
pre = root;
//右
traversal(root.right);
}
}
501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
给你一个含重复值的二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root ,找出并返回 BST 中的所有 众数(即,出现频率最高的元素)。
如果树中有不止一个众数,可以按 任意顺序 返回。
假定 BST 满足如下定义:
- 结点左子树中所含节点的值 小于等于 当前节点的值
- 结点右子树中所含节点的值 大于等于 当前节点的值
- 左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,2,2]
输出:[2]
示例 2:
输入:root = [0]
输出:[0]
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[1, 104]内 -105 <= Node.val <= 105
**进阶:**你可以不使用额外的空间吗?(假设由递归产生的隐式调用栈的开销不被计算在内)
教程:https://programmercarl.com/0501.%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E6%A0%91%E4%B8%AD%E7%9A%84%E4%BC%97%E6%95%B0.html
视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fD4y117gp/
方法一:递归
思路:中序遍历-不使用额外空间,利用二叉搜索树特性
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度: O(n),其中n是二叉树中节点的数量
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
import java.util.ArrayList;
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> resList;
int maxCount;
int count;
TreeNode pre;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
resList = new ArrayList<>();
maxCount = 0;
count = 0;
pre = null;
findMode1(root);
int[] res = new int[resList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < resList.size(); i++) {
res[i] = resList.get(i);
}
return res;
}
public void findMode1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
findMode1(root.left);
int rootValue = root.val;
// 计数
if (pre == null || rootValue != pre.val) {
count = 1;
} else {
count++;
}
// 更新结果以及maxCount
if (count > maxCount) {
resList.clear();
resList.add(rootValue);
maxCount = count;
} else if (count == maxCount) {
resList.add(rootValue);
}
pre = root;
findMode1(root.right);
}
}
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
示例 1:
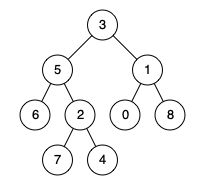
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出:3
解释:节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3 。
示例 2:
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
输出:5
解释:节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5 。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2
输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[2, 105]内。 -109 <= Node.val <= 109- 所有
Node.val互不相同。 p != qp和q均存在于给定的二叉树中。
教程:https://programmercarl.com/0236.%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E8%BF%91%E5%85%AC%E5%85%B1%E7%A5%96%E5%85%88.html
视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1jd4y1B7E2
方法一:递归
思路:自底向上查找就好了。后序遍历(左右中)就是天然的回溯过程,可以根据左右子树的返回值,来处理中节点的逻辑。
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度: O(n),其中n是二叉树中节点的个数
-
空间复杂度: O(n)
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) { // 递归结束条件
return root;
}
// 后序遍历
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(left == null && right == null) { // 若未找到节点 p 或 q
return null;
}else if(left == null && right != null) { // 若找到一个节点
return right;
}else if(left != null && right == null) { // 若找到一个节点
return left;
}else { // 若找到两个节点
return root;
}
}
}