java基础-String
一. 概念
Sring类位于java.lang包下,因此使用无需导包。String将字面值作为String类实例对象的引用,例如: String s="abc"; 这里的abc就是String类的实例对象。
二. 构造方法
(1)public String() : 空构造
(2) public String(byte[] bytes) : 把字节数组转成字符串
(3) public String(byte[] bytes,int index, int length) : 把字节数组的一部分转成字符串
(4) public String(char[] value) : 把字符数组转成字符串
(5) public String(char[] value,int index, int count) : 把字符数组的一部分转成字符串
代码演示:
public class StringDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 通过构造方法创建String实例,调用方法
String s = new String();
// 将字节数组转成字符串
byte[] bytes={97,98,99};
String s1 = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(s1); // abc
// 将字节数组中的部分转成字符串
String s2 = new String(bytes, 1, 2);
System.out.println(s2); //bc
// 将字符数组转成字符串
char[] chars={'a','b','c'};
String s3 = new String(chars);
System.out.println(s3); // abc
// 将字符数组中的部分转成字符串
String s4 = new String(chars, 1, 2);
System.out.println(s4); //bc
//String s5 = new String("hello");
String s5="hello";
System.out.println(s5); // hello
}
}三. String相关面试题
1. 变量s1和变量s2内存地址及字符串内容是否相等
public class StringDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "abc";
System.out.println(s1 == s2); //true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2) ); //true
}
}图解:
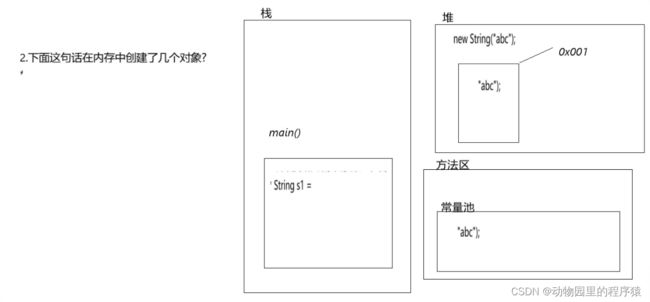
2. String s1 = new String("abc"); 这行代码中共创建了多少对象?
public class StringDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("abc");
}
}
图解:
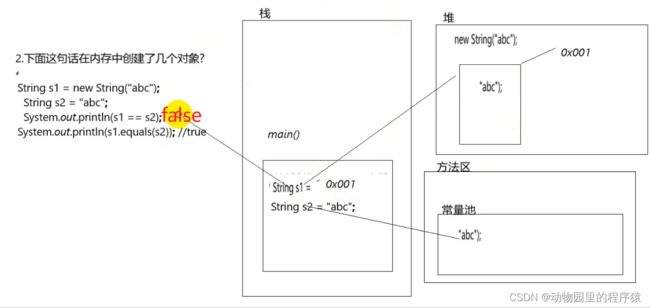
3. 变量s1和变量s2内存地址及字符串内容是否相等
public class StringDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = "abc";
System.out.println(s1==s2); //false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //true
}
}图解:
四. String类中的相关判断方法:
1. boolean equals(bject obj): 比较字符串的内容是否相同,区分大小写
2. boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str): 比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写
3. boolean contains(String str): 判断大字符串中是否包含小字符串
4. boolean startsWith(String str): 判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串开头
5. boolean endsWith(String str): 判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串结尾
6. boolean isEmpty(): 判断字符串是否为空。
代码演示:
public class StringDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*boolean equals(bject obj):比较字符串的内容是否相同,区分大小写
* boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写
* boolean contains(String str):判断大字符串中是否包含小字符串
* boolean startsWith(String str):判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串开头
* boolean endsWith(String str):判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串结尾
* boolean isEmpty():判断字符串是否为空。
* */
String s1="hello";
String s2="hello";
System.out.println("比较字符串是否相同 "+s1.equals(s2)); //true
System.out.println("比较字符串是否相同 "+s1.equals("world")); //false
System.out.println("比较字符串是否相同 "+"world".equals(s1)); //false
String s3=null;
// System.out.println("比较字符串是否相同 "+s3.equals("world")); // NullPointerException 空指针异常
System.out.println("比较字符串是否相同 "+"world".equals(s3)); //false
String s4="Hello";
System.out.println("比较字符串是否相同 "+s1.equals(s4)); //false
System.out.println("忽略大小写比较字符串是否相同 "+s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s4)); //true
String s5="hello world";
System.out.println("判断s5变量字符串是否包含s1变量字符串 "+s5.contains(s1)); //true
System.out.println("判断s5变量字符串是否以H开头 "+s5.startsWith("H")); //false
System.out.println("判断s5变量字符串是否以d结尾 "+s5.endsWith("d")); //true
System.out.println("判断s5变量字符串是否为空 "+s1.isEmpty()); //false
}
}五. 登陆案例
public class LoginDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 需求: 模拟登录,给三次机会,并提示还有几次。
* 用户名和密码都是admin
* 键盘录入
* 循环
* */
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String name = scanner.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password = scanner.next();
if ("admin".equals(name) && "admin".equals(password)) {
System.out.println("恭喜您,登录成功");
break;
} else {
if (i!=2){
System.out.println("登录失败 ,还有" + (3 - i - 1) + " 次机会");
}else {
System.out.println("登陆失败 ,没有机会了");
}
}
}
}
}六. String类中的获取功能:
1. int length (): 获取字符串的长度。
2. char charAt ( int index):获取指定索引位置的字符
3. int indexOf ( int ch): 返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
4. int indexOf (String str): 返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
5. int index0f ( int ch, int fromIndex): 返回指定字符在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引
6. int index0f (String str,int fromIndex): 返回指定字符串在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引
7. String substring ( int start): 从指定位置开始截取字符串, 默认到末尾。
8. String substring ( int start, int end): 从指定位置开始到指定位置结束截取字符串
代码演示:
public class StringDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
int length ():获取字符串的长度。
char charAt ( int index):获取指定索引位置的字符
int indexOf ( int ch):返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
int indexOf (String str):返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
int index0f ( int ch, int fromIndex):返回指定字符在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引
int index0f (String str,int fromIndex):返回指定字符串在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引
String substring ( int start):从指定位置开始截取字符串, 默认到末尾。
String substring ( int start, int end):从指定位置开始到指定位置结束截取字符串
*/
// 获取字符串长度
System.out.println("你好".length()); //2
String name="china hello";
System.out.println(name.length()); //11
// 通过索引获取字符串中的字符
char c = name.charAt(2);
System.out.println(c); //i
// 通过字符获取字符在字符串中的索引位置
System.out.println(name.indexOf("a")); //4
System.out.println(name.indexOf("z")); // 如不存在则返回 -1
// 返回此字符串在字符串中第一次出现的索引位置
System.out.println(name.indexOf("china")); //0
System.out.println(name.indexOf("hello")); //6
System.out.println(name.indexOf("world")); // 如不存在则返回 -1
// 返回此字符在字符串中从指定索引位置出现的第一个位置
String s="1411022000";
System.out.println(s.indexOf("0",0));//4
System.out.println(s.indexOf("0",6));//7
System.out.println(s.indexOf("z",0)); // 如不存在则返回 -1
// 返回字符串在字符串中从指定索引位置第一次出现的位置
System.out.println(name.indexOf("hello",5)); //6
// 截取字符串
System.out.println(name.substring(2)); //ina hello
// 截取字符串 从指定索引位置开始到指定索引位置结束
System.out.println(name.substring(2,7)); //ina h 包含头不包含尾
}
}七. 遍历数组
public class StringDemo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s="Hello world";
//遍历字符串
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
System.out.println(c);
}
System.out.println("================================================");
/*
* 先将字符串转成字符数组
* 然后再遍历字符数组
* */
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(chars)); // [h, e, l, l, o, , j, a, v, a]
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
char aChar = chars[i];
System.out.println(aChar);
}
}
}八. String类中的转换功能:
1. byte[] getBytes(): 把字符串转换为字节数组
2. char[] toCharArray(): 把字符串转换为字符数组。
3. static String valueOf(char[] chs): 把字符数组转成字符串
4. static String valueOf(int i): 把int类型的数据转成字符串 注意:String类的valueof方法可以把任意类型的数据转成字符串
5. String toLowerCase (): 把字符串转成小写。(了解)
6. String tolpperCase(): 把字符串转成大写。
7. String concat(String str): 把字符串拼接。
代码演示:
public class StringDemo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
字符串转换为字节数组、字符数组 字符数组、字节数组转换为字符串 连接字符串
byte[] getBytes():把字符串转换为字节数组
char[] toCharArray():把字符串转换为字符数组。
static String valueOf(char[] chs):把字符数组转成字符串
static String valueOf(int i):把int类型的数据转成字符串
注意:String类的valueof方法可以把任意类型的数据转成字符串
String toLowerCase ():把字符串转成小写。(了解)
String tolpperCase():把字符串转成大写。
String concat(String str):把字符串拼接。*/
String s="hello java";
// getBytes() 把字符串转成字节数组
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes)); //[104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 106, 97, 118, 97]
// toCharArray():把字符串转换为字符数组。
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(chars)); // [h, e, l, l, o, , j, a, v, a]
/*for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
char aChar = chars[i];
System.out.println(aChar);
}*/
System.out.println("================================================");
String s1 = String.valueOf(s);
System.out.println(s1); //hello java
String s2 = String.valueOf(chars);
System.out.println(s2); //hello java
System.out.println("================================================");
// 把字符串转成大写
String s3 = s.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(s3); //HELLO JAVA
// 把字符串转成小写
String s4="Hello";
String s5 = s4.toLowerCase();
System.out.println(s5); // hello
// 字符串拼接
System.out.println(s.concat("yy")); //hello javayy
String yy = s.concat("yy");
System.out.println(yy); //hello javayy
}
}九. 统计字符串中不同字符类型的个数
public class StringDemo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 统计一个字符串中大写字母字符,小写字母字符,数字字符出现的次数,其他字符出现的次数。
1.计数思想big small num other
2.遍历字符串
3.多条件判断 if... else if ... else
4.打印输出结果*/
String s = "ACBDefg123哈哈嘻嘻嘿嘿";
int big = 0;
int small = 0;
int num = 0;
int other = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char charAt = s.charAt(i);
if (charAt >= 'A' && charAt <= 'Z') {
big++;
} else if ( charAt>='a'&& charAt <= 'z') {
small++;
}else if (charAt>='0' && charAt <= '9') {
num++;
}else{
other++;
}
}
System.out.println("大写字母的个数 "+big); //大写字母的个数 4
System.out.println("小写字母的个数 "+small); //小写字母的个数 3
System.out.println("数字的个数 "+num); //数字的个数 3
System.out.println("其他的个数 "+other); //其他的个数 6
}
}十. 字符串反转:
public class StringDemo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s="我爱你中国";
/*
* 0 4 4-0
* 1 3 4-0-1
* 2 2 4-0-2
* */
char[] strAsByteArray = s.toCharArray();
char[] result = new char[strAsByteArray.length];
// 倒序存储字字节数组中的内容到临时字节数组中
for (int i = 0; i < strAsByteArray.length; i++) {
result[i] = strAsByteArray[strAsByteArray.length - i - 1];
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
System.out.println("=========================");
/*
把字符串反转 举例: 键盘录入“abc
输出结果:"cba
1.键盘录入 next()
2.遍历字符串
*/
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入内容");
String str = scanner.next();
for (int i = str.length()-1; i >=0; i--) {
System.out.println(str.charAt(i));
}
}
}