OAuth2.0 详解
最近接了个项目,有关这方面的知识和大家分析一下,多多交流
首先呢,我们需要知道OAuth(Open Authorization)是一个关于授权(authorization)的开放网络标准,允许用户授权第三方 应用访问他们存储在另外的服务提供者上的信息,而不需要将用户名和密码提供给第三方移动应用或分享他 们数据的所有内容。OAuth在全世界得到广泛应用,目前的版本是2.0版。
这里是关于oauth的协议地址:RFC 6749 - The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework
然后这是协议特点:
- 简单:不管是OAuth服务提供者还是应用开发者,都很易于理解与使用;
- 安全:没有涉及到用户密钥等信息,更安全更灵活;
- 开放:任何服务提供商都可以实现OAuth,任何软件开发商都可以使用OAuth;
引入依赖
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-oauth2
应用场景:
- 原生app授权:app登录请求后台接口,为了安全认证,所有请求都带token信息,如果登录验证、 请求后台数据。
- 前后端分离单页面应用:前后端分离框架,前端请求后台数据,需要进行oauth2安全认证
- 第三方应用授权登录,比如QQ,微博,微信的授权登录。
下面是一些关于oauth2.0的基本概念:
- Third-party application:第三方应用程序,又称"客户端"(client),即例子中的"豆瓣"。
- HTTP service:HTTP服务提供商,简称"服务提供商",即例子中的qq。
- Resource Owner:资源所有者,又称"用户"(user)。
- User Agent:用户代理,比如浏览器。
- Authorization server:授权服务器,即服务提供商专门用来处理认证授权的服务器。
- Resource server:资源服务器,即服务提供商存放用户生成的资源的服务器。它与授权服务器,可以是同一台服务器,也可以是不同的服务器。
OAuth的作用就是让"客户端"安全可控地获取"用户"的授权,与"服务提供商"进行交互。
我们再来描述一下他的优缺点:
优点:
- 更安全,客户端不接触用户密码,服务器端更易集中保护
- 广泛传播并被持续采用
- 短寿命和封装的token
- 资源服务器和授权服务器解耦
- 集中式授权,简化客户端
- HTTP/JSON友好,易于请求和传递token
- 考虑多种客户端架构场景
- 客户可以具有不同的信任级别
缺点:
- 协议框架太宽泛,造成各种实现的兼容性和互操作性差
- 不是一个认证协议,本身并不能告诉你任何用户信息。
如果使用oauth2.0那我们不得不提起另一个基于spring的框架:Spring Security
Spring Security是一个能够为基于Spring的企业应用系统提供声明式的安全访问控制解决方案的安全框架。Spring Security 主要实现了Authentication(认证,解决who are you? ) 和 Access Control(访问控制,也就是what are you allowed to do?,也称为Authorization)。Spring Security在架构上将认证与授权分离,并提供了扩展点。
认证(Authentication) :用户认证就是判断一个用户的身份是否合法的过程,用户去访问系统资源时系统要求验证用户的身份信息,身份合法方可继续访问,不合法则拒绝访问。常见的用户身份认证方式有:用户名密码登录,二维码登录,手机短信登录,指纹认证等方式。
授权(Authorization): 授权是用户认证通过根据用户的权限来控制用户访问资源的过程,拥有资源的访问权限则正常访问,没有权限则拒绝访问。
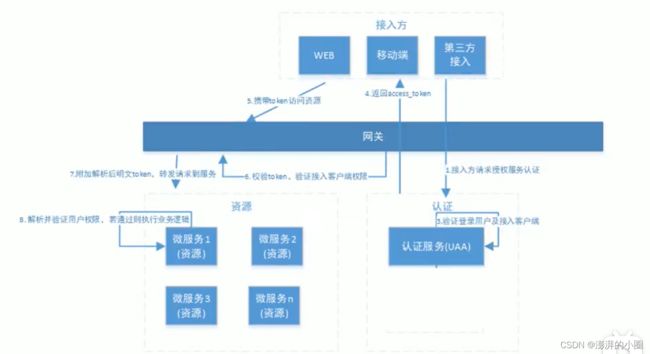
将OAuth2和Spring Security集成,就可以得到一套完整的安全解决方案。我们可以通过Spring Security OAuth2构建一个授权服务器来验证用户身份以提供access_token,并使用这个access_token来从资源服务器请求数据。
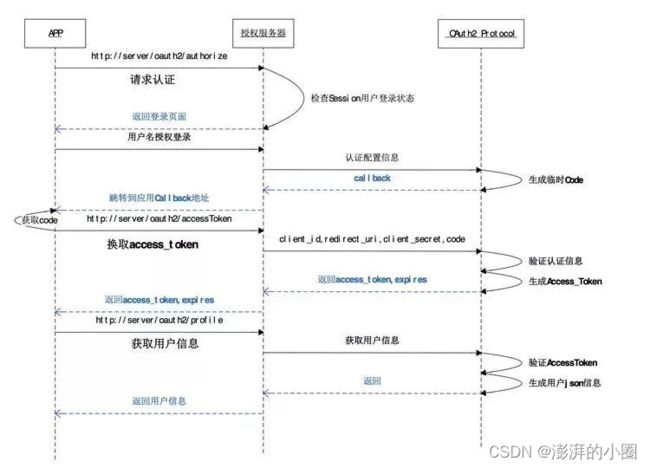
OAuth 2.0的运行流程如下图:
(A)用户打开客户端以后,客户端要求用户给予授权。 (B)用户同意给予客户端授权。 (C)客户端使用上一步获得的授权,向认证服务器申请令牌。 (D)认证服务器对客户端进行认证以后,确认无误,同意发放令牌。 (E)客户端使用令牌,向资源服务器申请获取资源。 (F)资源服务器确认令牌无误,同意向客户端开放资源。
授权模式
客户端必须得到用户的授权(authorization grant),才能获得令牌(access token)。OAuth 2.0一共分成四种授权类型(authorization grant)
- 授权码模式(authorization code)
- 简化模式(implicit)
- 密码模式(resource owner password credentials)
- 客户端模式(client credentials)
授权码模式和密码模式比较常用。
第三方应用申请令牌之前,都必须先到系统备案,说明自己的身份,然后会拿到两个身份识别码:客户端 ID(client ID)和客户端密钥(client secret)。这是为了防止令牌被滥用,没有备案过的第三方应用,是不会拿到令牌的。
授权码模式
授权码(authorization code)方式,指的是第三方应用先申请一个授权码,然后再用该码获取令牌。
这种方式是最常用的流程,安全性也最高,它适用于那些有后端的 Web 应用。授权码通过前端传送,令牌则是储存在后端,而且所有与资源服务器的通信都在后端完成。这样的前后端分离,可以避免令牌泄漏。
适用场景:目前主流的第三方验证都是采用这种模式
配置授权服务器:
注意:实际项目中clinet_id 和client_secret 是配置在数据库中,省略spring security相关配置,可以参考:
@Configuration @EnableAuthorizationServer public class AuthorizationServerConfig extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder; @Autowired private TokenStore tokenStore; @Override public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) throws Exception { endpoints .tokenStore(tokenStore) //指定token存储到redis .allowedTokenEndpointRequestMethods(HttpMethod.GET,HttpMethod.POST); //支持GET,POST请求 @Override public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception { // 基于内存模式,这里只是演示,实际生产中应该基于数据库 clients.inMemory() //配置client_id .withClient("client") //配置client_secret .secret(passwordEncoder.encode("123123")) //配置访问token的有效期 .accessTokenValiditySeconds(3600) //配置刷新token的有效期 .refreshTokenValiditySeconds(864000) //配置redirect_uri,用于授权成功后跳转 .redirectUris("http://www.baidu.com") //配置申请的权限范围 .scopes("all") //配置grant_type,表示授权类型 authorization_code: 授权码 .authorizedGrantTypes("authorization_code"); } }
/**
* 授权服务器
*
* 授权码模式基于数据库
*/
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class AuthorizationServerConfig1 extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Autowired
private TokenStore tokenStore;
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired
private AuthorizationCodeServices authorizationCodeServices;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("jdbcClientDetailsService")
private ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService;
@Bean("jdbcClientDetailsService")
public ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService() {
JdbcClientDetailsService clientDetailsService = new JdbcClientDetailsService(dataSource);
clientDetailsService.setPasswordEncoder(passwordEncoder);
return clientDetailsService;
}
//设置授权码模式的授权码如何存取
@Bean
public AuthorizationCodeServices authorizationCodeServices() {
return new JdbcAuthorizationCodeServices(dataSource);
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) throws Exception {
endpoints
.tokenStore(tokenStore) //指定token存储到redis
.authorizationCodeServices(authorizationCodeServices)//授权码服务
.allowedTokenEndpointRequestMethods(HttpMethod.GET,HttpMethod.POST); //支持GET,POST请求
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security) throws Exception {
//允许表单认证
security
.tokenKeyAccess("permitAll()") //oauth/token_key是公开
.checkTokenAccess("permitAll()") //oauth/check_token公开
.allowFormAuthenticationForClients();
}
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
//授权码模式
//http://localhost:8080/oauth/authorize?response_type=code&client_id=client&redirect_uri=http://www.baidu.com&scope=all
// 简化模式
// http://localhost:8080/oauth/authorize?response_type=token&client_id=client&redirect_uri=http://www.baidu.com&scope=all
clients.withClientDetails(clientDetailsService);
}
}配置资源服务器:
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceServiceConfig extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().requestMatchers().antMatchers("/user/**");
}
}配置 spring security
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin().permitAll()
.and().authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/oauth/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().logout().permitAll()
.and().csrf().disable();
}
}
@Service
public class UserService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
String password = passwordEncoder.encode("123456");
return new User("test",password, AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin"));
}
}注意事项
以下内容是OAuth2.0中应该重点注意的内容和条款:
1 隐式许可
此流程中,授权服务器不对客户端进行身份验证,客户端的身份可以通过用于向Client传送访问令牌的重定向URI进行验证。
2 访问令牌
可以有不同的格式结构及采用的方法(如, 加密属性等)。
3 刷新令牌
刷新令牌设计只与授权服务器使用,并不会发送到资源服务器。
4 符号约定
除非另有说明,所有协议参数的名称和值都是大小敏感的。
5 授权端点
1) 授权服务器对授权端点必须支持HTTP“GET”方法,也可以支持使用“POST”的方法。
2) 发送的没有值的参数必须被对待为好像它们在请求中省略。
3) 授权服务器必须忽略不能识别的请求参数。
4) 请求和响应参数不能包含超过一次。
6 重定向端点
1) 重定向端点URI不得包含片段部分。
2) 必须注册重定向端点的客户端:公开客户端、采用隐式许可类型的机密客户端。
3) 同一个客户端可以注册多个重定向端点;
4) 客户端不应该在重定向端点的响应中包含任何第三方的脚本;
7 令牌端点
客户端必须使用HTTP “POST”方法发起访问令牌请求。