c++-智能指针
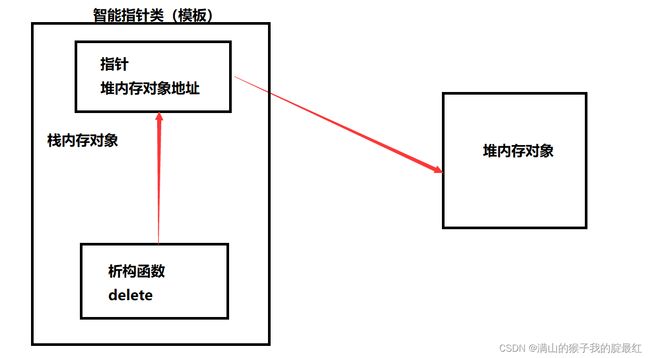
1、概念
堆内存的对象需要手动使用delete销毁,如果忘记使用delete销毁就会造成内存泄漏。
所以C++在ISO 98标注中引入了智能指针的概念,并在C++11 中趋于完善。
使用智能指针可以让堆内存对象具有栈内存对象的特性。原理时给需要自动回收的堆内存对象套上一层栈内存的模板类对象即可。
C++有四种智能指针:
- auto_ptr (自动指针,已经废弃)(C++ISO 98)
- unique_ptr (唯一指针)(C++ISO 11)
- shared_ptr (共享指针)(C++ISO 11)
- weak_ptr (协助指针)(C++ISO 11)
使用智能指针需要引入头文件#include
2、auto_ptr
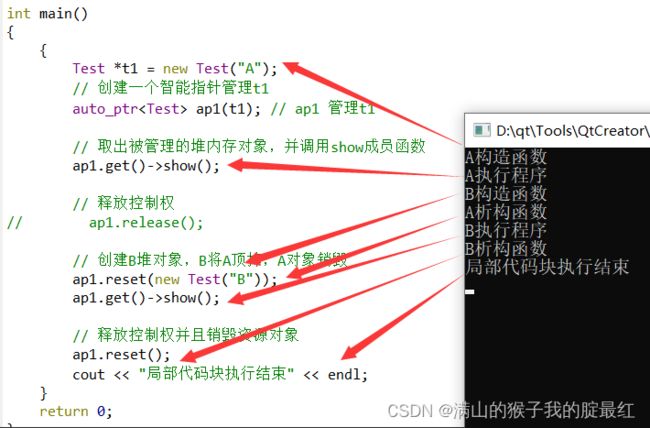
#include ap1(t1); // ap1 管理t1
// 取出被管理的堆内存对象,并调用show成员函数
ap1.get()->show();
// 释放控制权
// ap1.release();
// 创建B堆对象,B将A顶掉,A对象销毁
ap1.reset(new Test("B"));
ap1.get()->show();
// 释放控制权并且销毁资源对象
ap1.reset();
cout << "局部代码块执行结束" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
释放对象不会调用析构函数,只有销毁对象才会有
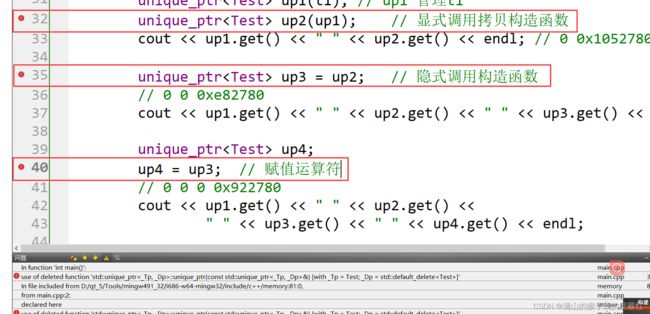
由于成员变量存在指针类型,因此拷贝构造函数与赋值运算符的使用会出现问题。与浅拷贝的问题不同的是,auto_ptr的复制语义会引起资源对象控制权转移的问题。
#include ap1(t1); // ap1 管理t1
auto_ptr ap2(ap1); // 显式调用拷贝构造函数
cout << ap1.get() << " " << ap2.get() << endl; // 0 0x1052780
auto_ptr ap3 = ap2; // 隐式调用构造函数
// 0 0 0xe82780
cout << ap1.get() << " " << ap2.get() << " " << ap3.get() << endl;
auto_ptr ap4;
ap4 = ap3; // 赋值运算符
// 0 0 0 0x922780
cout << ap1.get() << " " << ap2.get() <<
" " << ap3.get() << " " << ap4.get() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3、unique_ptr
作为对auto_ptr的改进,unique_ptr对其他持有的资源对象具有唯一控制权,即不可以通过常规的复制语义转移或拷贝资源对象的控制权。
通过特殊的语法实现控制权的转移效果。
#include 4、shared_ptr
unique_ptr对资源具有独占性,多个shared_ptr对象可以共享资源。
shared_ptr有两种创建方式:
两种创建方式的区别在于后者是一步到位(创建资源对象+关系绑定),前者分为两步完成(先创建资源对象,再进行关系绑定)。
新方式的优点:
- 安全性更好
- 性能更好
新方式的缺点:
- 资源释放效率低
每多一个shared_ptr对资源进行管理,引用计数将+1,每个指向该对象的shared_ptr对象销毁时,引用计数-1,最后一个shared_ptr对象销毁时,计数清零,资源对象销毁。
#include 5、weak_ptr
weak_ptr是一个不控制资源对象的智能指针,也不会影响资源的引用计数,其主要目的是协助shared_ptr工作。
通过weak_ptr的构造函数,参数传入一个持有资源对象的shared_ptr对象或者weak_ptr对象即可创建。
weak_ptr与资源对象呈现弱相关性,所以不支持get等函数直接操作资源对象。
建议weak_ptr调用lock函数之前,先检测引用计数是否大于0,或使用expried()函数检测是否可以转换为shared_ptr。
lock()函数,通过传入持有资源对象的对象创建新对象
#include