【React 源码】(四)reconciler 运作流程
reconciler 运作流程
概览
通过前文宏观包结构和两大工作循环中的介绍, 对react-reconciler包有一定了解.
此处先归纳一下react-reconciler包的主要作用, 将主要功能分为 4 个方面:
- 输入: 暴露
api函数(如:scheduleUpdateOnFiber), 供给其他包(如react包)调用. - 注册调度任务: 与调度中心(
scheduler包)交互, 注册调度任务task, 等待任务回调. - 执行任务回调: 在内存中构造出
fiber树, 同时与与渲染器(react-dom)交互, 在内存中创建出与fiber对应的DOM节点. - 输出: 与渲染器(
react-dom)交互, 渲染DOM节点.
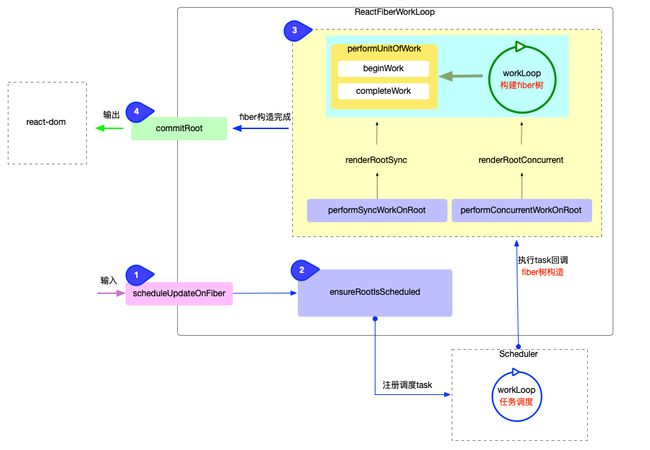
以上功能源码都集中在ReactFiberWorkLoop.js中. 现在将这些功能(从输入到输出)串联起来, 用下图表示:
图中的1,2,3,4步骤可以反映react-reconciler包从输入到输出的运作流程,这是一个固定流程, 每一次更新都会运行.
分解
图中只列举了最核心的函数调用关系(其中的每一步都有各自的实现细节, 会在后续的章节中逐一展开). 将上述 4 个步骤逐一分解, 了解它们的主要逻辑.
输入
在ReactFiberWorkLoop.js中, 承接输入的函数只有scheduleUpdateOnFiber源码地址. 在react-reconciler对外暴露的 api 函数中, 只要涉及到需要改变 fiber 的操作(无论是首次渲染或后续更新操作), 最后都会间接调用scheduleUpdateOnFiber, 所以scheduleUpdateOnFiber函数是输入链路中的必经之路.
// 唯一接收输入信号的函数
export function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(
fiber: Fiber,
lane: Lane,
eventTime: number,
) {
// ... 省略部分无关代码
const root = markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot(fiber, lane);
if (lane === SyncLane) {
if (
(executionContext & LegacyUnbatchedContext) !== NoContext &&
(executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) === NoContext
) {
// 直接进行`fiber构造`
performSyncWorkOnRoot(root);
} else {
// 注册调度任务, 经过`Scheduler`包的调度, 间接进行`fiber构造`
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime);
}
} else {
// 注册调度任务, 经过`Scheduler`包的调度, 间接进行`fiber构造`
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime);
}
}逻辑进入到scheduleUpdateOnFiber之后, 后面有 2 种可能:
- 不经过调度, 直接进行
fiber构造. - 注册调度任务, 经过
Scheduler包的调度, 间接进行fiber构造.
注册调度任务
与输入环节紧密相连, scheduleUpdateOnFiber函数之后, 立即进入ensureRootIsScheduled函数(源码地址):
// ... 省略部分无关代码
function ensureRootIsScheduled(root: FiberRoot, currentTime: number) {
// 前半部分: 判断是否需要注册新的调度
const existingCallbackNode = root.callbackNode;
const nextLanes = getNextLanes(
root,
root === workInProgressRoot ? workInProgressRootRenderLanes : NoLanes,
);
const newCallbackPriority = returnNextLanesPriority();
if (nextLanes === NoLanes) {
return;
}
if (existingCallbackNode !== null) {
const existingCallbackPriority = root.callbackPriority;
if (existingCallbackPriority === newCallbackPriority) {
return;
}
cancelCallback(existingCallbackNode);
}
// 后半部分: 注册调度任务
let newCallbackNode;
if (newCallbackPriority === SyncLanePriority) {
newCallbackNode = scheduleSyncCallback(
performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
);
} else if (newCallbackPriority === SyncBatchedLanePriority) {
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
ImmediateSchedulerPriority,
performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
);
} else {
const schedulerPriorityLevel = lanePriorityToSchedulerPriority(
newCallbackPriority,
);
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
);
}
root.callbackPriority = newCallbackPriority;
root.callbackNode = newCallbackNode;
}ensureRootIsScheduled的逻辑很清晰, 分为 2 部分:
- 前半部分: 判断是否需要注册新的调度(如果无需新的调度, 会退出函数)
- 后半部分: 注册调度任务
performSyncWorkOnRoot或performConcurrentWorkOnRoot被封装到了任务回调(scheduleCallback)中- 等待调度中心执行任务, 任务运行其实就是执行
performSyncWorkOnRoot或performConcurrentWorkOnRoot
执行任务回调
任务回调, 实际上就是执行performSyncWorkOnRoot或performConcurrentWorkOnRoot. 简单看一下它们的源码(在fiber树构造章节再深入分析), 将主要逻辑剥离出来, 单个函数的代码量并不多.
performSyncWorkOnRoot:
// ... 省略部分无关代码
function performSyncWorkOnRoot(root) {
let lanes;
let exitStatus;
lanes = getNextLanes(root, NoLanes);
// 1. fiber树构造
exitStatus = renderRootSync(root, lanes);
// 2. 异常处理: 有可能fiber构造过程中出现异常
if (root.tag !== LegacyRoot && exitStatus === RootErrored) {
// ...
}
// 3. 输出: 渲染fiber树
const finishedWork: Fiber = (root.current.alternate: any);
root.finishedWork = finishedWork;
root.finishedLanes = lanes;
commitRoot(root);
// 退出前再次检测, 是否还有其他更新, 是否需要发起新调度
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
return null;
}performSyncWorkOnRoot的逻辑很清晰, 分为 3 部分:
- fiber 树构造
- 异常处理: 有可能 fiber 构造过程中出现异常
- 调用输出
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot
// ... 省略部分无关代码
function performConcurrentWorkOnRoot(root) {
const originalCallbackNode = root.callbackNode;
// 1. 刷新pending状态的effects, 有可能某些effect会取消本次任务
const didFlushPassiveEffects = flushPassiveEffects();
if (didFlushPassiveEffects) {
if (root.callbackNode !== originalCallbackNode) {
// 任务被取消, 退出调用
return null;
} else {
// Current task was not canceled. Continue.
}
}
// 2. 获取本次渲染的优先级
let lanes = getNextLanes(
root,
root === workInProgressRoot ? workInProgressRootRenderLanes : NoLanes,
);
// 3. 构造fiber树
let exitStatus = renderRootConcurrent(root, lanes);
if (
includesSomeLane(
workInProgressRootIncludedLanes,
workInProgressRootUpdatedLanes,
)
) {
// 如果在render过程中产生了新的update, 且新update的优先级与最初render的优先级有交集
// 那么最初render无效, 丢弃最初render的结果, 等待下一次调度
prepareFreshStack(root, NoLanes);
} else if (exitStatus !== RootIncomplete) {
// 4. 异常处理: 有可能fiber构造过程中出现异常
if (exitStatus === RootErrored) {
// ...
}.
const finishedWork: Fiber = (root.current.alternate: any);
root.finishedWork = finishedWork;
root.finishedLanes = lanes;
// 5. 输出: 渲染fiber树
finishConcurrentRender(root, exitStatus, lanes);
}
// 退出前再次检测, 是否还有其他更新, 是否需要发起新调度
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
if (root.callbackNode === originalCallbackNode) {
// 渲染被阻断, 返回一个新的performConcurrentWorkOnRoot函数, 等待下一次调用
return performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root);
}
return null;
}performConcurrentWorkOnRoot的逻辑与performSyncWorkOnRoot的不同之处在于, 对于可中断渲染的支持:
- 调用
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot函数时, 首先检查是否处于render过程中, 是否需要恢复上一次渲染. - 如果本次渲染被中断, 最后返回一个新的 performConcurrentWorkOnRoot 函数, 等待下一次调用.
输出
commitRoot:
// ... 省略部分无关代码
function commitRootImpl(root, renderPriorityLevel) {
// 设置局部变量
const finishedWork = root.finishedWork;
const lanes = root.finishedLanes;
// 清空FiberRoot对象上的属性
root.finishedWork = null;
root.finishedLanes = NoLanes;
root.callbackNode = null;
// 提交阶段
let firstEffect = finishedWork.firstEffect;
if (firstEffect !== null) {
const prevExecutionContext = executionContext;
executionContext |= CommitContext;
// 阶段1: dom突变之前
nextEffect = firstEffect;
do {
commitBeforeMutationEffects();
} while (nextEffect !== null);
// 阶段2: dom突变, 界面发生改变
nextEffect = firstEffect;
do {
commitMutationEffects(root, renderPriorityLevel);
} while (nextEffect !== null);
root.current = finishedWork;
// 阶段3: layout阶段, 调用生命周期componentDidUpdate和回调函数等
nextEffect = firstEffect;
do {
commitLayoutEffects(root, lanes);
} while (nextEffect !== null);
nextEffect = null;
executionContext = prevExecutionContext;
}
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
return null;
}在输出阶段,commitRoot的实现逻辑是在commitRootImpl函数中, 其主要逻辑是处理副作用队列, 将最新的 fiber 树结构反映到 DOM 上.
核心逻辑分为 3 个步骤:
commitBeforeMutationEffects- dom 变更之前, 主要处理副作用队列中带有
Snapshot,Passive标记的fiber节点.
- dom 变更之前, 主要处理副作用队列中带有
commitMutationEffects- dom 变更, 界面得到更新. 主要处理副作用队列中带有
Placement,Update,Deletion,Hydrating标记的fiber节点.
- dom 变更, 界面得到更新. 主要处理副作用队列中带有
commitLayoutEffects- dom 变更后, 主要处理副作用队列中带有
Update | Callback标记的fiber节点.
- dom 变更后, 主要处理副作用队列中带有
总结
本节从宏观上分析了reconciler 运作流程, 并将其分为了 4 个步骤, 基本覆盖了react-reconciler包的核心逻辑.