JAVA自学笔记
基础语法
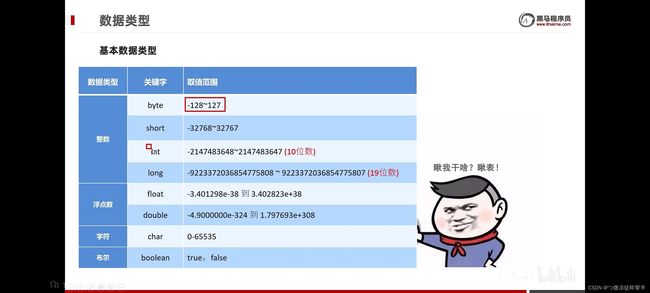
数据类型
| 数据类型 | 关键字 |
|---|---|
| 整数 | byte |
| short | |
| int | |
| long | |
| 浮点数 | float |
| double | |
| 字符 | char |
| 布尔 | boolean |
 |
键盘录入
import java.util.Scanner;//导包
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);//创建对象,用Scanner这个类。
int i=sc.nextInt();//接受数据。
IDEA结构
由上到下等级越低:
project(项目)
module(模块)
package(包)
class(类)
算术运算符
当“+”的操作中出现字符串时,这个“+”是字符串连接符,而不是算术运算符。会与前后拼接成一个新的字符串。
byte、short、char三种类型的数据在运算时,都会直接先提升为int,然后再进行运算
回文数
public class day1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
int x=1234;
int num=0;
while(x!=0){
int ge= x % 10;
x/=10;
num=num*10+ge;
}
System.out.println(num);
}
}
获取随机数
//步骤
import java.util.Random;//导包,Random类
Random r=new Random();//创建对象.
int number=r.nextInt(bound:数字)+数字//生成范围内的随机数。
生成随机数的方法:
例如7~15
1.(bound:9)+7,第一步先括号内外共减去7即(8)+0;
2. 然后再将括号内的数字加一,再将括号外的数字加回原来的7。
import java.util.Random;
public class day1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random r = new Random();
int num = r.nextInt(9) + 7;
System.out.println(num);
}
}
数组
两种定义方法
int [] arr1=new int []{1,2,3}; int[] arr2={1,2,3};
数组地址:
[I@7878dsf7
[表示的是这是数组地址。
i 表示的是这个数组的类型是int
@是分隔符,再它之后的才是真正的地址
数组默认初始化的规律
整形类型:0
小数类型:0.0
字符类型:‘/u0000’ 空格
布尔类型:false
引用数据类型:null
Java内存分配
栈 方法运行时使用的内存,比如main方法运行,进入方法栈中执行。
堆 存储对象或者数组,new来创建的,都储存在堆内存
方法区 存储可以运行的class文件
本地方法栈 JVM在使用操作系统功能的时候使用,和我们开发无关。
寄存器 给CPU使用
int[] arr1={11,22};
int[] arr2=arr1;//此时这两个数组指向同一个地址
arr2[0]=33;
System out println(arr1[0]);//33
System out println(arr2[0]);//33
方法的重载
记忆:同一个类中,方法名相同,参数不同的方法,与返回值无关。参数不同,个数不同,类型不同,顺序不同。
引用数据类型
引用:使用了其他空间的数据。
练习
加密:
public class day1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,9,8,3};
for (int i=0;i< arr.length;i++){
arr[i]=arr[i]+5;
}
for (int i=0;i< arr.length;i++){
arr[i]=arr[i]%10;
}
for (int i=0, j=arr.length-1;i<j;i++,j--){
int temp =arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
int number=0;
for (int i=0;i< arr.length;i++){
number=number*10+arr[i];
}
System.out.println(number);//8346
}
}
面对对象
在Java中要先设置类才能获取对象。
类:是一大部分对象相似的特征。与c语言的结构体写法类似。
自定义类
package com.ideom1;
import javax.swing.*;
public class girlfriend {
//对象的属性
private int age;
private String name;
private String grender;
public void setName(String n){
name=n;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setAge(int a){
if(a>=18&&a<=50) age=a;
else System.out.println("数据错误!");
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
public void setGrender(String g){
grender=g;
}
public String getGrender(){
return grender;
}
//对象的方法
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("sleep");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eat");
}
}
获取实质对象:
package com.ideom1;
public class girlfriendTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
girlfriend g1=new girlfriend();
g1.setAge(18);
g1.setName("小红");
g1.setGrender("女");
System.out.println(g1.getName());
System.out.println(g1.getAge());
System.out.println(g1.getGrender());
g1.eat();
g1.sleep();
}
}
this
this用来区分成员变量和局部变量。
public class GirlFriend(){
int age;//成员变量。
public void method(){
int age = 10;//局部变量
System.out.println(age);
}
}
构造方法
特点:
- 方法名与类名相同,大小写也要一致。
- 没有返回值类型,连void都没有。
- 没有具体的返回值(不能return带回去数据)
执行时机:
- 创建对象的时候由虚拟机调用,不能手动调用构造方法
- 每创建一次对象,就会调用一次构造方法
构造方法的注意事项:
1.构造方法的定义
- 如果没有定义构造方法,系统将给出一个默认的无参数构造方法
- 如果定义了构造方法,系统将不再提供默认的构造方法。
- 构造方法的重载
- 带参构造方法和无参构造的方法,两者方法名相同,但是参数不同,,这叫做构造方法的重载
- 推荐使用方法:
- 无论是否使用,都要书写无参数构造方法,和带全部参数的构造方法。
javabean类
类名需要见名知意
成员变量使用private修饰
提供至少两个构造方法
- 无参构造
- 带全部参数构造
成员方法- 提供每一个成员变量对应的set()get()
- 如果还有其他行为,也要写上。
package com.javabean;
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
//空参
//alt + insert快速生成set、get方法
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
//利用ptg快速生成
// public User(){}
// //带全部的参数的构造
// public User(String username,String password){
// this.username=username;
// this.password=password;
// }
//
//
// /**
// * 获取
// * @return username
// */
// public String getUsername() {
// return username;
// }
//
// /**
// * 获取
// * @return password
// */
// public String getPassword() {
// return password;
// }
//
// /**
// * 设置
// * @param password
// */
// public void setPassword(String password) {
// this.password = password;
// }
//
// public String toString() {
// return "User{username = " + username + ", password = " + password + "}";
// }
}
文字格斗游戏
Role类文件:
package com.wordpersongame;
import java.util.Random;
public class Role {
private String name;
private int blood;
public Role(String name,int blood){
this.name=name;
this.blood=blood;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public int getBlood(){
return blood;
}
public void setBlood(int blood){
this.blood=blood;
}
public void attack(Role role){
Random r =new Random();
int hurt = r.nextInt(20)+1;
int remainBoold = role.getBlood()-hurt;
remainBoold=remainBoold<0?0:remainBoold;
role.setBlood(remainBoold);
System.out.println(this.getName()+"举起拳头,打了"+role.getName()+"一下,"+"造成了"+hurt+"点伤害"+role.getName()+"还剩下"+remainBoold+"点血");
}
}
RoleText测试运行:
package com.wordpersongame;
public class RoleText {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Role r1 = new Role("张三",100);
Role r2 =new Role ("李四",100);
while(true){
r1.attack(r2);
if(r2.getBlood()==0){
System.out.println(r1.getName()+"KO了"+r2.getName());
break;
}
r2.attack(r1);
if(r1.getBlood()==0){
System.out.println(r2.getName()+"KO了"+r1.getName());
break;
}
}
}
}
字符串的定义及其初始化
package
com;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Stringdemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//直接赋值
String s1="abc";
System.out.println(s1);
//new一个新的字符串对象
String s2 =new String("acv");
System.out.println(s2);
//传递一个字符数组,根据字符数组的内容再创建一个新的字符串对象。
char[] chs={'a','c','b'};
String s3 =new String(chs);
System.out.println(s3);
//传递一个字节数组,根据字节数组的内容再创建一个新的字符串对象。
byte[] bytes ={97,98,99,100};
String s4=new String (bytes);
//输入一个字符串和赋值的字符串比较结果为true用equals方法。直接进行比较返回的是false。
System.out.println(s4);
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String s5=sc.next();
boolean result=s5.equals(s1);
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(s5==s1);
}
}
用户登录
package com;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Stringdemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String rightusername="zhangsan";
String rightpassword="123";
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username=sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password=sc.next();
if(username.equals(rightusername) && password.equals(rightpassword)){
System.out.println("登录成功");
break;
}else{
if(i==2){
System.out.println("账户"+ username +"被锁定");
}else{
System.out.println("用户登录失败,您还剩下"+(2-i)+"次机会");
}
}
}
}
}
字符数组练习
package com;
public class Stringdemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a={1,2,3};
String b=contact(a);
String c=reserve(a);
System.out.println(c);
}
//,分开字符串,并连接字符串。
public static String contact(int[] arr){
String result ="[";
if(arr==null){
return "";
}
if(arr.length==0){
return "[]";
}
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(i==arr.length-1){
result=result+arr[i]+"]";
}else{
result=result+arr[i]+", ";
}
}
return result;
}
//将字符串倒过来输出。
public static String reserve(int[] arr){
String result="[";
for(int i=arr.length-1;i>=0;i--){
if(i==0){
result+=arr[i];
}else{
result=result+arr[i]+", ";
}
}
result+="]";
return result;
}
}
- 金额转化
package com;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Srtringdemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int money;
while(true){
money=sc.nextInt();
if(money>0 && money<9999999){
break;
}else{
System.out.println("金额无效!");
}
}
String moneyStr="";
while(true){
int ge =money%10;
String cap=capnum(ge);
moneyStr=cap+moneyStr;
money=money/10;
if(money==0){
break;
}
}
String[] arr={"百","十","万","千","百","十","元"};
int leng=moneyStr.length();
for(int i=0;i<7-leng;i++){
moneyStr="零"+moneyStr;
}
for(int i=0;i<moneyStr.length();i++){
char d=moneyStr.charAt(i);
System.out.print(d);
System.out.print(arr[i]);
}
}
public static String capnum(int nub){
String[] arr={"零","壹","贰","叁","肆","伍","陆","柒","捌","玖"};
return arr[nub];
}
}
截取信息
substring(startindex,endindex);用来截取字符串信息,只有返回值等于获取的值,但是对原来的字符串无影响。
package com;
public class Stringdemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String id="985453214565127541";
String year=id.substring(6,10);
String month=id.substring(10,12);
String day=id.substring(12,14);
System.out.println("出生年月日:"+year+"年"+month+"月"+day+"日");
char gender=id.charAt(16);
int num=gender-48;
if(num%2==0){
System.out.println("女");
}else{
System.out.println("男");
}
}
}
- replace(需要替换的字符串,替换的字符串)
package com;
public class Stringdemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String talk="你TMD,CNM";
String[] arr={"TMD","CNM"};
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
talk=talk.replace(arr[i],"***");
}
System.out.println(talk);
}
}
StringBuilder
public class Stringdemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("abc");
//添加元素
sb.append(1);
sb.append(2);
sb.append(true);
System.out.println(sb);//abc12true
//倒置元素
sb.reverse();
int len=sb.length();
System.out.println(len);//9
System.out.println(sb); //eurt21cba
String str =sb.toString();
//转化为字符串
System.out.println(str);//eurt21cba
}
}
- 支持链式写法
- 判断对称字符串
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Stringdemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
String str=str();
sb.append(str);
String text=sb.reverse().toString();
System.out.println(text);
if(str.equals(text)){
System.out.println("是对称字符串");
}else{
System.out.println("不是对称字符串");
}
}
public static String str(){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=sc.next();
return str;
}
}
- 拼接字符串
public class Stringdemo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,3};
String str=arrToString(arr);
System.out.println(str);
}
public static String arrToString(int[] arr){
StringBuilder sb= new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(i==arr.length-1){
sb.append(arr[i]+"]");
}else{
sb.append(arr[i]+", ");
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
StringJoiner
import java.util.StringJoiner;
public class Stringdemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringJoiner sj=new StringJoiner(", ","[","]");//对中间的符号和开头,末尾的符号进行修改。
sj.add("aaa").add("bbb").add("ccc");//[aaa, bbb, ccc]
System.out.println(sj);
int str=sj.length();
System.out.println(str);//15
}
}
综合练习
package com;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.StringJoiner;
public class Stringdemo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
str = sc.next();
boolean flag = checkStr(str);
if(flag){
System.out.println("right");
break;
}else{
System.out.println("error");
continue;
}
}
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char c=str.charAt(i);
int num=c-48;
String s=change(num);
sb.append(s);
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
public static String change(int num){
String[] arr={"","一","二","三","四","五","六","七","八","九"};
return arr[num];
//JDK新特性:
// String str=switch (num){
// case '0'->"";
// case '1'->"一";
// case '2'->"二";
// case '3'->"三";
// case '4'->"四";
// case '5'->"五";
// case '6'->"六";
// case '7'->"七";
// case '8'->"八";
// case '9'->"九";
// default -> str="";
// };
// return str;
}
public static boolean checkStr(String str){
if(str.length()>9){
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char c=str.charAt(i);
if(c <'0' || c>'9'){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
反转字符串
public class Stringdemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 ="abcde";
String str2 = "bcdea";
boolean result =checkStr(str1,str2);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static String rotate(String str){
char first =str.charAt(0);
String end =str.substring(1);
return end+first;
}
public static boolean checkStr(String str1,String str2){
for(int i=0;i<str1.length();i++){
str1= rotate(str1);
if(str1.equals(str2)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
ArrayList
- arraylist是一个集合,它的长度可以该变.可以存引用类型,基本数据类型需要包装类。
- 使用方式:
ArrayList<数据类型> 变量名 = new ArraryList<可写,可不写>()
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Stringdemo12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> al=new ArrayList<>();
//增,该类的add方法返回值是永远是true
al.add("aaa");
al.add("ddd");
System.out.println(al);//[aaa,ddd]
//删
// boolean result=al.remove("aaa");
// System.out.println(result);//true
// System.out.println(al);//ddd
// boolean res=al.remove("vvv");
// System.out.println(res);//false
//改
String res1=al.set(1,"bbb");//返回值是要杯替换的那个元素
System.out.println(res1);//ddd
System.out.println(al);//【aaa,bbb】
//查
String s=al.get(0);
System.out.println(s);//aaa
}
}
基本数据类型的包装类型
| byte | Byte |
|---|---|
| short | Short |
| char | Character |
| int | int |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| boolean | Boolean |
用户查询
定义一个方法,根据id寻找用户,有返回索引值,没有返回-1.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Students> list = new ArrayList<>();
Students s1 = new Students(1, "zhangsan", "123");
Students s2 = new Students(2, "lisi", "456");
Students s3 = new Students(3, "wangwu", "789");
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
int b=contain(list,3);
System.out.println(b);
}
public static int contain(ArrayList<Students> list,int id){
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
int l=list.get(i).getId();
if(l==(id)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
静态变量static
特点:
-
被该类所有对象共享
-
不属于对象,属于类
-
随着类的加载而加载,优先于对象存在
-
没有this关键字
-
静态方法只能访问静态
-
非静态可以访问所有
调用方式: -
类名的调用(推荐)
-
对象名调用
定义:
public static Students main(){
String static teacher
}
调用:
类名调用:
Students.teacher
静态函数
创建:
public class ArrayUtil {
private ArrayUtil(){}
public static String print(int[] arr){
.....//函数内部
}
}
调用:
ArrayUtil。print(arr);
继承
Java只能单继承:一个类只能继承一个直接父类
Java不能支持多继承、但是支持多层继承
Java中所有的类都直接或者间接继承于Object类。
- 使用:
public class 父类(){}
public class 子类 extend 父类(){}
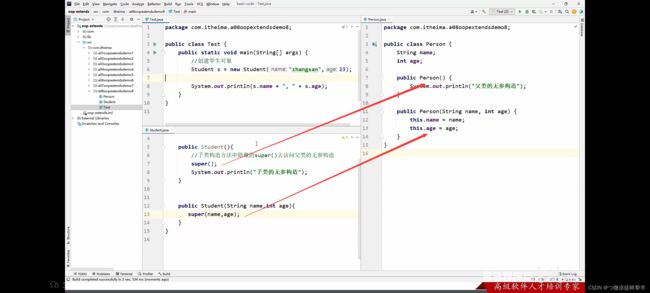
继承中的构造方法和this,super
继承中的构造方法的访问特点:
子类构造方法的第一行,有一个默认的super()必须在第一行
默认先访问父类中方的无参的构造方法,在执行自己、
如果想要方法访问父类的有参构造,必须手动书写
package oopexdemo;
import test.Students;
public class Student {
String name;
int age;
String school;
public Student() {
//表示调用本类其他构造方法
//细节,虚拟机就不会再添加super();
this(null,0,"chuanzhidaxue");
}
public Student(String name, int age, String school) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.school = school;
}
}
多态中调用
多态的优势:可以接收所有的子类对象。
弊端:不能使用子类的特有功能
转换类型与真实对象类型不一致,就会报错。
- 调用成员变量:编译看左边,运行看左边
编译看左边:javac编译代码时,会看左边的父类中有没有这个变量,有成功,否失败。
运行看左边:Java运行代码的时候,实际获取的是左边父类中的成员变量的值
- 调用成员方法:编译看左边,运行看右边
编译看左边:javac编译的时候,会看左边的父类中有没有这个方法,如果有,编译成功,如果没有编译失败。
运行看右边:Java运行的时候,实际上运行的是子类中的方法,(原父类的方法被覆盖)。
- 强制类型转换:
if(a instanceof Dog){//判断该类型是否是Dog类型
Dog d=(Dog) a;//将a原来的父类Animal强转成为Dog类型。
}else if(a inscanceof Cat){
Cat c =(Cat) a;
}
//新特性
if(a instanceof Dog d ){//直接判断并且强转。
d.lookhome();
}
事件
System
是一个工具类,提供了一些与系统相关的方法
常见的方法如下:
//方法名
public static void exit(int status)//终止当前运行的虚拟机 0正常停止,非0异常停止。
public static long currentTimeMillis()//返回当前系统的时间(毫秒)
public static void arraycopy(数据源,起始索引,目的数组,起始索引,拷贝个数)//数组拷贝
int[] arr1={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}
int[] arr2=new int[10];
System.arraycopy(arr1,0,arr2,4,3)//0000123000
//1.数据源和目的数组都是基本数据类型,两者类型必须保持一致,否则报错
//2.在拷贝的时候需要考虑数组的长度,如果超出范围就会报错
//3.如果数据源和目的数组都是引用数据类型,那么子类类型可以赋值给父类,但是会涉及到强转数据类型。
Runtime
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public static Runtime |
当前系统的运行环境 |
public void exit(int status) |
停止虚拟机 |
public int availableProcessors() |
获取CPU的线程数 |
public long maxMemory() |
JVM能从系统中获取的总内存大小(单位byte) |
public long totalMemory() |
JVM已经从系统中获取总内存大小(单位byte) |
public long freeMemory() |
JVM剩余内存大小(byte) |
public Process exec(String command) |
运行cmd命令 |
object
object是所有对象的父类
object.toString()
默认情况下,因为Object类中的toString方法返回的就是地址值
所有打印出来的值就是地址值
如果想要看到对象内部的属性值,我们需要重写toString方法
equals()
String s="abc";
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder("abc");
System.out.println(s.equals(sb));//false
//原因:equals是被s调用的,而s是字符串,所以equals要看String类中的
//字符串中的equals方法,先判断参数是否为字符串,如果是字符串,再比较内部属性,但是如果参数不是字符串,直接返回false
System.out.println(sb.equals(s));//false
//原因:因为equals方法是被sb调用的,而sb是StringBuilder中的,而StringBuilder中的equals方法没有重写,所以使用的是Object中的,在object中的在object当中默认是使用==号比较两个对象的地址值,而
//这里的s和sb记录的地址值不一样,所以结果返回false。
深浅拷贝
区别:
浅拷贝不仅将值复制,还会将地址值复制,当修改拷贝的变量值时,原数据也会改变
深拷贝仅将值复制。
深拷贝实现:
- 重写方法
protected Object clone() throws CloneNoteSupportedException{
int[] data=this.data;
//创建一个新的数组,用来拷贝原来的数据
int[] newData =new int[data.length];
for(int i=0;i<data.length<i++){
newdata[i]=data[i];
}
User u =(User) super.clone();
//因为父类中的克隆方法时浅克隆,替换克隆出来的对象的数组的地址值。
u.data=newdata;
//返回新生成的对象。
return u;
}
- 使用第三方工具类
成员方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public static boolean equals(Object a,Object b) |
先做非空判断,=比较两个对象 |
public static boolean isNull(Object obj) |
判断对象是否是为null,为null返回true,反之 |
public static boolean nonNull(Object obj) |
判断对象是否为null,跟isNull的结果相反 |
BigInteger构造方法
对象一旦创建,内部的记录的值不能发生改变
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public BigInteger(int num,Random rnd) |
获取随机大整数,范围:【0,2num-1】 |
public BigInteger(String val) |
获取指定的大整数 |
public BigInteger(String val,int radix) |
获取指定进制的大整数 |
public static BigInteger valueof(long val) |
静态方法获取BigInteger的对象,内部有优化 |
静态方法获取BigInteger的对象,内部有优化
能表示范围比较小,只能在long的取值范围之内,如果超出long的范围就不行
在内部对常用的数字: - 16~ 16进行优化
提前把-16~16先创建号BigInteger对象,如果多次获取不会重新创建新的。
只要计算都会产生一个新的BigInterger对象
Big Integer表示是一个大整数
获取BigInteger对象:
BigerIneger b1 =BigInteger.valueOf(0.1) BigInteger b1 =new BigInteger(“整数")
BigDecimal
表示较大的小数和解决小数运算精度的失真问题。
获取对象:
BigDecimal bd1=new BigDecimal(‘较大的小数”) BigDecimal bd2=BigDecimal.valueOf(0.1)
正则表达式
- [abc]:代表a或者b,或者c字符中的一个。
- [^abc]:代表除a,b,c以外的任何字符。
- [a-z]:代表a-z的所有小写字符中的一个。
- [A-Z]:代表A-Z的所有大写字符中的一个。
- [0-9]:代表0-9之间的某一个数字字符。
- [a-zA-Z0-9]:代表a-z或者A-Z或者0-9之间的任意一个字符。
- [a-dm-p]:a 到 d 或 m 到 p之间的任意一个字符。
逻辑运算符
&&:并且
| :或者
\ :转义字符
预定义字符
语法示例:
“.” : 匹配任何字符。
“\d”:任何数字[0-9]的简写;
“\D”:任何非数字[^0-9]的简写;
“\s”: 空白字符:[ \t\n\x0B\f\r] 的简写
“\S”: 非空白字符:[^\s] 的简写
“\w”:单词字符:[a-zA-Z_0-9]的简写
“\W”:非单词字符:[^\w]
数量词
语法示例:
X? : 0次或1次
X* : 0次到多次
X+ : 1次或多次
X{n} : 恰好n次
X{n,} : 至少n次
X{n,m}: n到m次(n和m都是包含的)
捕获分组和非捕获分组
捕获分组:
内部: \ \组号
外部:$组号
非捕获分组:
分组后不需要再本组数据,仅仅是把数据括起来
| 符号 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| (?:正则) | 获取所有 |
| (?=正则) | 获取前面部分 |
| (?!正则) | 获取不是指定内容的前面部分 |
包装类
- 什么是把装类
基本数据类型对应的对象
-
JDK5以后对包装类新增了自动装箱、自动拆箱的特性
-
当获取包装类对象时不需要调用方法,直接赋值即可。
集合进阶
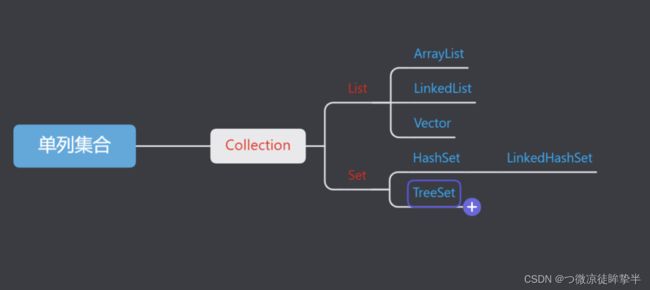
List系列集合:添加的元素是有序、可以重复、有索引(Set相反)
- Collection是单列集合的祖宗接口,它的功能是全部单列集合都可以继承使用的
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public boolean add(E e) | 把给定的对象添加到当前集合中 |
| public void clear() | 清空集合中所有的元素 |
| public boolean remove(E e) | 把给定的对象在当前的集合中删除 |
| public boolean contains(Object obj) | 判断当前集合中是否含给定的对象 |
| public boolean isEmpty() | 判断当前集合是否为空 |
| public int size() | 返回集合元素的个数/集合长度 |
//remove不能通过索引删除,只能通过元素的对象进行删除。
coll.remove("bbb");
Student s1=new Student("zhangsan",18);
Student s2=new Student("lisi",78);
coll.add(s1);
coll.add(s2);
Student s3=new Student("zhangsan",18);
//contains方法在底层依赖的是equals方法判断,比较的是地址值不是数值。
//所以在使用equals时应该重写方法。
System.out.println(coll.contains(s3));
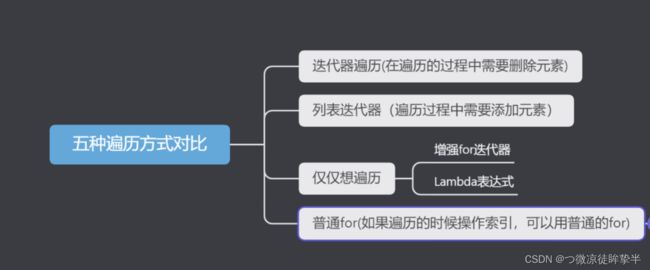
迭代器
迭代器在遍历集合的时候是不依赖索引的
迭代器的三个方法:
Inerator<String> it =list.interator();
//遍历获取元素
while(it.hasnext()){
String str=it.next();
System.out.println(str);
}
注意:
- 如果当前位置没有元素,还要强行获取,回报NoSuchElementException的错误
- 迭代器遍历完成,指针不会复位
- 循环只能用一次next方法
- 迭代器遍历的时候,不能用经济和的方法进行增删
增强for
注意:
修改for中的s变量,不会改变集合中的原本数据。
//(变量类型 变量名 :集合/数组)
for(String s:list){
//s="111";
}
idea中用coll.for直接使用。
lambda表达式遍历
Collection<String> coll=new ArrayList<>();
coll.add("zhangsan");
coll.add("lisi");
coll.add("wangwu");
//2.利用匿名内部类的形式
//底层原理:
//其实也会自己遍历集合依次得到每一个元素
//把得到的每一个元素,传递给下面的accept方法
//s依次表示集合中的每一个元素
coll.forEach(new Consumer<String>(){
@override
public void accept(String s){
System.out.println(s);
}
})
//lambda表达式
coll.forEach(s->System.out.println(s);)
ListIterator列表迭代器
获取一个列表迭代器的对象,里面的指针默认指向0索引
ListIterator<String> it =list.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
if("bbb".equals(str)){
list.add("qqq");
}
}
数据结构
平衡二叉树
- 高度平衡
- 当左右子树高度差超过1时,通过旋转保持平衡
左旋
步骤:
- 以不平衡的点作为支点
- 将根节点的右侧往左拉
- 原先的右节点变成新的父节点,并把多于的左子节点出让,给已经降级的根节点当右子节点
右旋与此相反
需要旋转的四中情况
- 左左:一次右旋
- 左右:先局部左旋,再整体右旋
- 右右:一次左旋
- 右左:先局部右旋,在整体左旋
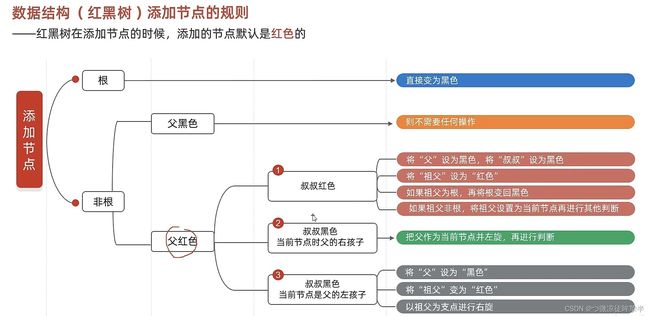
红黑树
- 是一个二叉查找树
- 但是不是高度平衡的
- 条件:特有的红黑规则
Set系列集合
- 无序、不重复、无索引
实现类
- HashSet:无序、不重复、无索引
- LinkedHashSet:有序、不重复、无索引
- TreeSet:可排序、不重复、无索引
Set接口中的方法上基本上写Collection的API一致
哈希值
- 根据hasCode方法算出来的int类型整数
- 该方法定义在Object类中,所有的对象都可以使用,默认使用的地址值进行计算
- 一般情况下,全重写hashCode方法,利用对象内部的属性值计算哈希值
对象哈希值的特点
- 如果没有重写hashCode方法,不同对象算出的哈希值是不同的
- 如果已经重写hashCode方法,不同的对象只要属性相同,计算出的哈希值就不同
- 在小部分情况下,不同的属性值或者不同的地址值计算出来的哈希值也有可能一样(哈希碰撞)
HashSet底层原理
JDK8以后,当链表长度超过8,而且数组长度大于等于64时,自动转换为红黑树
如果集合中的存储的是自定义对象,必须要重写hashCode和equals方法
Students s1=new Students("zhangsan",23);
Students s2=new Students("lisi",24);
Students s3=new Students("wangwu",25);
Students s4=new Students("zhangsan",23);
HashSet<Students> hs=new HashSet<>();
System.out.println(hs.add(s1));
System.out.println(hs.add(s2));
System.out.println(hs.add(s3));
System.out.println(hs.add(s4));
System.out.println(hs);
若没有重写hashcode和equals方法则上述的值全为true
重写用idea的快捷方法alt+Inset
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Students students = (Students) o;
return age == students.age && Objects.equals(name, students.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
重写后是:
true、true、true、false,[Students{name = wangwu, age = 25}, Students{name = lisi, age = 24}, Students{name = zhangsan, age = 23}]
TreeSet
特点:不重复、无索引、可排序(按照元素的默认的规则由小到大排序)
TreeSet集合底层是基于红黑树的数据结构实现排序的,增删改查性能都比较好。
Iterator<Integar> it= ts.iterator();
//遍历集合(三种方式与Collection方式一致->迭代器、增强for、lambda表达式)
TreeSet集合默认的规则
- 对于数值类型:Interger,Double,默认按照从小到大顺序进行排序。
- 对于字符、字符串类型:按照字符在ASCII码表中的数字升序进行排序。
测试类
public class HashCodeText {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Students s2=new Students("lisi",24);
Students s3=new Students("wangwu",25);
Students s1=new Students("zhangsan",23);
TreeSet<Students> ts=new TreeSet<>();
ts.add(s1);
ts.add(s2);
ts.add(s3);
System.out.println(ts);
}
}
对象类
public class Students implements Comparable<Students> {
private String name;
private int age;
public Students() {
}
public Students(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Students students = (Students) o;
return age == students.age && Objects.equals(name, students.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
public String toString() {
return "Students{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Students o) {
return this.getAge()-o.getAge();//正则添加到右面,负则相反。按照红黑树添加。
}
}
Set比较大小的方法
- 根据字符串的长度进行排序。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TreeSet ts=new TreeSet<>(new Comparator() {
// @Override
// public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
// int i=o1.length()-o2.length();
// i=i==0?o1.compareTo(o2):i;
// return i;
// }
// });
//lamdba表达式
TreeSet<String> ts=new TreeSet<>(( o1, o2)->{
int i=o1.length()-o2.length();
i=i==0?o1.compareTo(o2):i;
return i;
});
ts.add("bc");
ts.add("cd");
ts.add("gfdg");
ts.add("c");
System.out.println(ts);
}
创建集合时,自定义的Comparator比较器对象,指定比较规则方式要大于用JavaBean类实现Comparagble接口。
使用场景
- 如果想要集合中的元素可重复
用ArrayList集合,基于数组的。(用的最多)
- 如果想要集合中的元素可以重复,而且当前的增删操作明显多于查询
用LinkList集合,基于链表
3 .如果想对集合中的元素去重
用HashSet集合,基于哈希表。(用的最多)
4.如果想对集合中的元素去重,而且保证存取顺序
用LinkLedHashSet集合,用于哈希表和双链表,效率低于HashSet。
5.如果想对集合中的元素进行排序
用法TreeSet集合,基于红黑树。后续也可以用LIst集合实现排序
双列集合
双列集合的特点:
- 双列集合一次需要存一对数据,分别为键,值
- 键不能重复,值可以重复
- 键和值是一一对应的,每一个键只能找到自己对应的值
- 键+值这个整体我们称之为“键值对”或者“键值对对象”,在Java中叫做“Entry对象”
Map的常见API
Map是双列集合的顶层接口,它的功能是全部双列集合都可以继承使用的
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| V put (K key ,V value) | 添加元素(有键则覆盖原来的元素,并且返回原来的值,不存在该键则返回null) |
| V remove(Object key) | 根据键删除键值对元素 |
| void clear() | 移除所有的键值对元素 |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | 判断集合是否包含指定的键 |
| boolean containsValue(Object value) | 判断是否包含指定的值 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 判断集合是否为空 |
| int size() | 集合的长度,也就是集合中的键值的个数 |
HashMap
HashMap底层原理:
1. HashMap底层是哈希表结构的
2. 依赖hashcode方法和equals方法保证键的唯一
3. 如果键存储的是自定义对象,需要重写hashCode和equals方法
4. 如果值存储自定义对象,不需要重写hashCode和equals方法
练习
hashMap和hashSet不同在于,hashMap对于拥有相同的属性的对象,选择将后添加的对象覆盖前面的对象。
public class hashMaptest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Students,String> hm=new HashMap<>();
Students s1=new Students("zhangsan",23);
Students s2=new Students("lisi",24);
Students s3=new Students("wangwu",25);
Students s4=new Students("wangwu",25);
hm.put(s1,"jiangsu");
hm.put(s2,"shandong");
hm.put(s3,"zhejiang");
hm.put(s4,"shangdong");//覆盖之前添加的键值对
//遍历1:
Set<Students> keys=hm.keySet();
for(Students key: keys){
String value=hm.get(key);
System.out.println(key+","+value);
}
//结果:
//Students{name = wangwu, age = 25},shangdong
//Students{name = lisi, age = 24},shandong
//Students{name = zhangsan, age = 23},jiangsu
//遍历2:
Set<Map.Entry<Students,String>> entries=hm.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<Students,String>entry :entries){
Students key=entry.getKey();
String value=entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
//遍历3:
hm.forEach(new BiConsumer<Students, String>() {
@Override
public void accept(Students students, String s) {
System.out.println(students+"="+s);
}
});
}
}
TreeMap
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s= "aaaaabbbbcccdde";
TreeMap<Character,Integer> tm=new TreeMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c=s.charAt(i);
if(tm.containsKey(c)){
int count=tm.get(c);
count++;
tm.put(c,count);
}else{
tm.put(c,1);
}
}
//StringBuilder写法
// StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
// tm.forEach(new BiConsumer() {
// @Override
// public void accept(Character key, Integer value) {
// sb.append(key).append("(").append(value).append(")");
// }
// });
// System.out.println(sb);
//StringJoiner写法
StringJoiner sj=new StringJoiner("","","");
tm.forEach((key,value)->{
sj.add(key+"").add("(").add(value+"").add(")");
});
System.out.println(sj);
}
综合上面的集合总结
TreeMap添加元素的时候,键不需要hashCode和equals方法
HashMap是哈希表的结构的,JDK8开始右数组、链表、红黑树组成
TreeMap和HashMap在添加8个元素形成链表时,TreeMap的效率更高,一般来说HashMap的效率更高
三种双列集合选择
默认:HashMap(效率最高)
如果要保证存取有序:LinkedHasfhMap
惊醒排序:TreeMap
可变参数
可变参数本质上就是一个数组
作用:在形参中接收多个数据
public static int getSum(int a,int ...args)
注意事项:
- 形参列表中可变参数只能有一个
可变参数必须在形参列表的最后面
Collections
java.util.Collections:是集合工具类
作用:Collectuions不是集合,而是集合的工具类
常用API:
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public static boolean addAll(Collection c,T…elements) | 批量添加元素 |
| public static void shuffle (List list) | 打乱List集合元素的顺序 |
综合练习
随机点名、
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0);
Collections.shuffle(list);
Random r=new Random();
int index=r.nextInt(list.size());
int number= list.get(index);
System.out.println(number);
ArrayList<String> boylist=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> girllist=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(boylist,"nan1","nan2","nan3");
Collections.addAll(girllist,"nv1","nv2","nv3");
if(number==1){
int boyindex=r.nextInt(boylist.size());
String name=boylist.get(boyindex);
System.out.println(name);
}else{
int girlindex=r.nextInt(girllist.size());
String name=girllist.get(girlindex);
System.out.println(name);
}
}
概率抽奖
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0);
Collections.shuffle(list);
Random r=new Random();
int index=r.nextInt(list.size());
int number= list.get(index);
System.out.println(number);
ArrayList<String> boylist=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> girllist=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(boylist,"nan1","nan2","nan3");
Collections.addAll(girllist,"nv1","nv2","nv3");
if(number==1){
int boyindex=r.nextInt(boylist.size());
String name=boylist.get(boyindex);
System.out.println(name);
}else{
int girlindex=r.nextInt(girllist.size());
String name=girllist.get(girlindex);
System.out.println(name);
}
}
不重复点名
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list1=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list1,"nan1","nan2","nan3","nan4");
ArrayList<String> list2=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++){
System.out.println("第"+i+"轮");
int count =list1.size();
Random r=new Random();
for (int j = 0; j < count; j++) {
int index=r.nextInt(list1.size());
String name=list1.remove(index);
list2.add(name);
System.out.println(name);
}
list1.addAll(list2);
list2.clear();
}
}
创建不可变的集合
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
static ) |
创建具有一个具有指定元素的List集合对象 |
static ) |
创建一个具有指定元素的Set集合对象 |
static ) |
创建一个具有指定元素的Map集合对象 |
这个集合不能添加,不能删除,不能修改
三种方式的细节:
List:直接用
Set:元素不能重复
Map:元素不能重复、键值对数量最多是十个。超过十个用ofEntries方法。JDK10以后的版本也可以用copyof方法。
Steam流
过滤信息
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list1=new ArrayList<>();
list1.add("张无忌");
list1.add("周芷若");
list1.add("张强");
list1.add("张三丰");
list1.stream().filter(name->name.startsWith("张")).filter(name->name.length()==3).forEach(name-> System.out.println(name));
}
- Stream流的使用步骤:
- 显得到一条Stream流(流水线),并将数据放上去。
| 获取方法 | 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 单列集合 | default Stream |
Collectoin中的默认方法 |
| 双列集合 | 无 | 无法直接使用stream流 |
| 数组 | public static |
Arrays工具类中的静态方法 |
| 一堆零散的数据 | public static |
Steam接口中的静态方法 |
public static void main(String[] args) {
//单列集合的stream流遍历元素
ArrayList<String> list1=new ArrayList<>();
list1.add("张无忌");
list1.add("周芷若");
list1.add("张强");
list1.add("张三丰");
list1.stream().forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
//双列集合的stream流的遍历元素
HashMap<String,Integer> hm=new HashMap<>();
hm.put("aaa",111);
hm.put("bbb",222);
hm.put("ccc",333);
//键值对遍历打印
hm.entrySet().forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
//键名遍历打印
hm.keySet().forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
//数组
int[] arr1={1,2,3,4,6,5};
String[] arr2={"a","b","c"};
//基本数据类型
Arrays.stream(arr1).forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
//引用数据类型
Arrays.stream(arr2).forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
//一堆零散的数据
//Stream接口中的静态方法of的细节
//方法的形参是一个可变参数,可以传递基本数据类型,是会将整个数组当成一个元素,放到Stream当中。
Stream.of(1,2,3,4).forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
Stream。of(arr1).forEach(s->System.out,println(s))//打印的是数组的地址。
}
Stream中间方法
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
Stream |
过滤 |
Stream |
获取前几个元素 |
Stream |
跳过前几个元素 |
Stream |
元素去重,依赖(hashCode和equals方法) |
static |
合并a和b两个流为一个流 |
Stream |
转换流中的数据类型 |
中间方法,返回新的Stream流,原来的Stream流只能使用一次,建议使用链式编程
修改Stream流中的数据,不会影响原来集合或者数组中的数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取里面的年龄并进行打印
//数据类型转化String->int
//apply的形参s:依次表示里面的每一个数据
//返回值:表示的是转化后的数据
ArrayList<String> list =new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"zhangwuji-15","zhouzhiruo-14","zhangsanfeng-100");
//原始写法
// list.stream().map(new Function() {
// @Override
// public Integer apply(String s) {
// String[] arr=s.split("-");
// String ageStr=arr[1];
// int age =Integer.parseInt(ageStr);
//
// return age;
// }
// }).forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
//lamda表达式写法
list.stream().map(s->Integer.parseInt(s.split("-")[1])).forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
}
Stream流的终结方法
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
void forEach(Consumer action) |
遍历 |
long count() |
统计 |
toArray() |
收集流中的数据,放到数组中 |
collect(Collectior collector) |
收集流中的数据,放到集合中 |
- toArray的普通写法
//toArray方法的参数作用:负责创建一个指定类型的数组
//toArray方法的底层,会依次得到流里面的每一个数据,并把数据放到数组当中
//toArray方法的返回值:是一个装着流里面使用数据的数组
String[] arr=list.stream().toArray(new IntFunction<String[]>(){
@Override
public String[] apply(int value){
return new String[value];
}
});
lamda表达式
String[] arr2=list.stream().toArray(value->new String[value]);
collection收集方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, "张无忌-男-15", "周芷若-女-14", "赵敏-女-13", "张强-男-20");
//收集List集合当中
List<String> newlist = list.stream().filter(s -> "男".equals(s.split("-")[1])).collect(Collectors.toList());
//System.out.println(newlist);
//收集Set集合当中
Set<String> newlist2 = list.stream().filter(s -> "男".equals(s.split("-")[1])).collect(Collectors.toSet());
//System.out.println(newlist2);
//收集Map集合当中
//键:名 值:年龄
//键不能重复
//toMap:参数一:表示键的生成规则
// 参数二: 表示值的生成规则
/*
* 参数一:Function泛型一:表示流中的每一个数据类型
* 泛型二:表示Map集合中的间的数据类型
* 方法apply形参:依次表示流里面的每一个数据
* 方法体:生成键的代码
* 返回值:已经生成的键
* 参数二:Function泛型一:表示流中的每一个数据的类型
* 泛型二:表示Map集合中的数据类型
* 方法apply形参:依次表示流里面的每一个数据
* 方法体:生成值的代码
* 返回值:已经生成的值
*
*
*
* */
// Map map=list.stream().filter(s->"男".equals(s.split("-")[1])).collect(Collectors.toMap(
// new Function() {
// @Override
// public String apply(String s) {
// return s.split("-")[0];
// }
// }, new Function() {
// @Override
// public Integer apply(String s) {
// return Integer.parseInt(s.split("-")[2]);
// }
// }));
// System.out.println(map);
// }
//lamda表达式:
Map<String, String> map2 = list.stream().filter(s -> "男".equals(s.split("-")[1])).collect(Collectors.toMap(
s -> s.split("-")[0],
s -> s.split("-")[2]
));
System.out.println(map2);
}
方法引用
把已经存在的方法拿过来用,当做函数式接口中的抽象方法的方法体
:: 是方法引用符
方法引用时需要注意
- 需要函数式接口被引用方法必须已经存在
- 被引用方法必须已经存在
- 被引用方法的形参,需要跟抽象方法的第二个形参到最后一个形参保持一致,,返回值需要跟抽象方法保持一致
- 被引用的方法的功能要满足当前的需求
抽象方法形参的详解
第一个参数:表示被引用方法的调用者,决定了可以引用哪些类中的方法。
在stream流中,第一个参数一般都表示流里面的每一个数据。
假设流里面的数据是字符串,那么使用这种方式进行方法进行方法引用,只能引用String这个类中的方法。
第二个参数到最后一个参数:跟被引用方法的形参保持一致,如果没有第二个参数,说明被引用的方法需要是午餐的成员方法。
局限性:
不能引用所有类中的成员方法。
是跟抽象方法的第一个参数有关,这个参数是什么类型的,那么就只能引用这个类的方法。
public class text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] arr={3,5,4,1,2,6};
//匿名内部类写法
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1-o2;
}
});
//lamdba表达式
Arrays.sort(arr,((o1,o2) ->o1-o2 ));
//方法引用
Arrays.sort(arr,text::sub);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static int sub(int a,int b){
return a-b;
}
}
引用静态方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list =new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, "1","2","3");
list.stream().map(Integer::parseInt).forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
}
引用成员方法
格式:
- 其他类:其他类对象::方法名 ->new A :: 方法名
- 本类:this::方法名(引用处不能是静态方法)
- 父类:super::方法名(引用处不能是静态方法)
引用构造方法
格式:类名::new
例子:
需求:集合里面存储姓名和年龄,要求封装成Students对象并收集到List集合中。
Students类 含参数构造
public Students(String str) {
String[] arr = str.split(",");
this.name=arr[0];
this.age=Integer.parseInt(arr[1]);
}
text类
//引用构造方法
ArrayList<String> list =new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, "张无忌,15","周芷若,14","赵敏,13");
List<Students> newlist2 = list.stream().map(Students::new).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(newlist2);
引用数组的构造方法
格式:
数据类型[] :: new
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,1,2,3,4);
//引用数组的构造方法
Integer[] arr2=list.stream().toArray(Integer[]::new);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
//匿名写法
Integer[] arr=list.stream().toArray(new IntFunction<Integer[]>() {
@Override
public Integer[] apply(int value) {
return new Integer[value];
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
综合练习
需求:
集合中存储一些字符串的数据,比如:张三,23。
收集到Students类型的数组当中
public class text5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"张无忌,15","周芷若,14","张强,20");
Students[] arr=list.stream().map(Students::new).toArray(Students[]::new);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
获取姓名放到数组中
使用方法引用。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Students> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Students("zhangsan",12));
list.add(new Students("lisi",12));
list.add(new Students("wangwu",12));
Stream<String> arr = list.stream().map(new Function<Students, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(Students students) {
return students.getName();
}
});
//String[] arr=list.stream().map(Students::getName).toArray(String[]::new);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr.toArray()));
}
异常
作用一:用来查询bug的关键参考信息。
作用二:异常可以作为方法内部的一种特殊返回值,以便通知调用者底层的执行情况。
JVM默认处理异常的方式:
- 把异常的名称,异常原因及异常出现的位置等信息输出在控制台
- 程序停止执行,异常下面的代码不会再执行了。
自己处理异常
格式:
可以让程序继续往下执行,不会停止。
try{
可能出现异常的代码;
}catch(异常类名 变量名){
异常的处理代码;
}
问题:
- 如果try中可能遇到多个问题,怎么执行?
会写多个catch与之对应
细节:如果我们要捕获多个异常,这些异常中如果存在父子关系的花,那么父类一定要写在下面。
JDK7之后,我们可以再catch中同时获取多个异常,中间用 | 进行隔开,表示如果出现了A异常或者B异常的话,采取同一种处理方案。
- 如果try中遇到了问题,那么try下面的其他代码就不会执行了,直接跳转到相应的catch当中,执行catch里面的语句体。
但是如果没有对应的catch与之匹配,那么还是会交给虚拟机进行处理。
异常中的方法
Throwable的成员方法
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public String getMessage() | 返回throwable的详细信息字符串 |
| public String toString() | 返回此可以抛出的简短描述 |
| public void printStackTrace() | 把异常的错误信息输出在控制台,仅仅只是打印信息,不会停止程序运行,包含的信息最多(红字打印) |
抛出处理
- throws:写在方法定义处,表示声明一个异常,告诉调用者,使用本方法可能会有哪些异常。
- throw:写在方法内,结束方法,手动抛出异常对象,交给调用者,方法中下面的代码不再执行。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={};
int max= 0;
try {
max = getMax(arr);
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常");
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("索引越界异常");
}
System.out.println(max);
}
public static int getMax(int[] arr){
if(arr==null){
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if(arr.length==0){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
int max=arr[0];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(arr[i]>max){
max=arr[i];
}
}
return max;
}
结果:索引越界异常 0
自定义报错
意义:为了让控制台的报错信息更加的见名知意
步骤:
1.定义异常类
2.写继承关系
3.空参构造
4.代餐构造
例子:
Grilfriend
package yichang;
public class Girlfriend {
private String name;
private int age;
public Girlfriend() {
}
public Girlfriend(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
if(name.length()>=2&&name.length()<10){
this.name = name;
}else{
throw new NameFormatException(name+"姓名格式不对");
}
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
if(age>=18 && age<=40){
this.age = age;
}else{
throw new AgeOutOfBoundsException(age+"年龄超出范围");
}
}
public String toString() {
return "Girlfriend{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}
AgeOutOfBoundsException
package yichang;
public class AgeOutOfBoundsException extends RuntimeException{
public AgeOutOfBoundsException() {
}
public AgeOutOfBoundsException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
NameFormatException
package yichang;
public class NameFormatException extends RuntimeException{
public NameFormatException() {
}
public NameFormatException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
text2
package yichang;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class text2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
Girlfriend gf=new Girlfriend();
while(true){
try {
System.out.println("请输入姓名:");
String name=sc.nextLine();
gf.setName(name);
System.out.println("请输入年龄:");
String age=sc.nextLine();
gf.setAge(Integer.parseInt(age));
break;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(NameFormatException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(AgeOutOfBoundsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(gf);
}
}
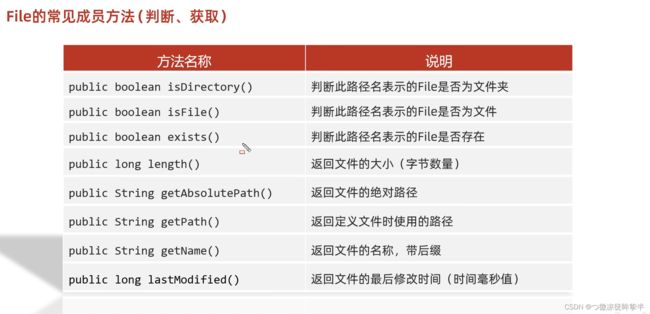
File
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public File (String pathname) | 根据文件路径创建文件对象 |
| public Fiie (String parent,String child) | 根据父路径名字符串和子路径名字符串创建文件对象 |
| public File (File parent,String child) | 根据父路径对应文件对象和子路径名字符串创建文件对象 |
使用:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//根据字符串表示的路径,变成File对象
String str="c:\\User\\alienware\\Desktop\\a.txt";
File f1=new File(str);
System.out.println(f1);
//2.父级路径:c:\User\alienware\Desktop
//子级路径:“a.txt”
String parent="c:\\User\\alienware\\Desktop";
String child="a.txt";
File f2=new File(parent,child);
System.out.println(f2);
File f3 =new File(parent+"\\"+child);
System.out.println(f3);
//把一个File表示的路径和String表示路径进行拼接
File parent2=new File("c:\\User\\alienware\\Desktop");
String child2="a.txt";
File f4=new File(parent2,child2);
System.out.println(f4);
}
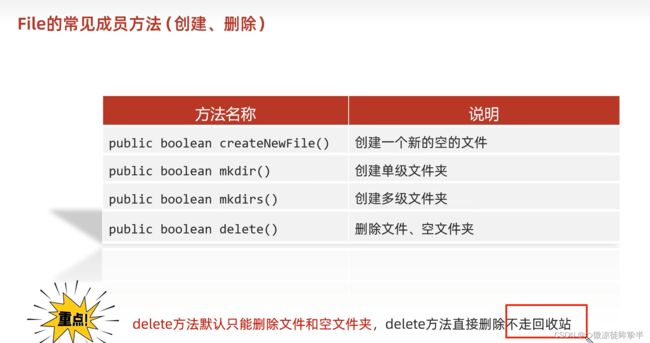
成员方法
listFIles遍历
File f=new File(“文件路径");//创建File对象
File[] files=f.listFiles();
for(File file:files){
System,out,printfln(file);//依次获取文件中的每一个文件夹和文件
}
当调用者File表示的路径不存在时,返回null
当调用者File表示的路径是文件时,返回null
当调用者FIle表示的路径是一个空文件夹时,返回一个长度为0的数组。
当调用者File表示的路径是一个有内容的文件夹时,将里面的所有文件和文件夹的路径放在File数组中返回。
当调用者File表示的路径是一个有隐藏文件的文件夹时,将里面所有文件和文件夹的路径放在FIle数组中返回,包含隐藏文件
当调用者File表示的路径是需要权限才能访问的文件夹时,返回null
综合练习
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//需求:
/*在当前模块下的aaa文件夹中创建一个a.txt文件
*/
//创建a.txt的父级路径
File file=new File("aaa");
//创建路径
file.mkdirs();
//拼接父级路径和子级路径
File src=new File(file,"a.txt");
boolean b=src.createNewFile();
if(b){
System.out.println("sucess");
}else{
System.out.println("false");
}
}
递归寻找AVI文件
package com.file;
import javax.crypto.spec.PSource;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.io.File;
public class FileDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File src=new File("C:\\");
findAVI(src);
}
public static void findAVI(){
//获取本地所有的盘符.
File[] arr=File.listRoots();
for(File f:arr){
findAVI(f);
}
}
public static void findAVI(File src){
//进入文件夹src
File[] files=src.listFiles();
//遍历数组,依次得到src里面的每一个文件或者文件夹
if(files!=null){
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isFile()){
String name =file.getName();
if(name.endsWith(".avi")) {
System.out.println(file);
}
}else{
//判断如果是文件夹,就可以递归.
findAVI(file);
}
}
}
}
}
统计文件数量
package com.file;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class FileDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file=new File("D:\\CNTV");
HashMap<String,Integer> hm=getCount(file);
System.out.println(hm);
}
public static HashMap<String,Integer> getCount(File src){
HashMap<String,Integer>hm=new HashMap<>();
File[] files=src.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
String name=file.getName();
String[] arr=name.split("\\.");
if(arr.length>=2){
String endname=arr[arr.length-1];
if(hm.containsKey(endname)){
int count=hm.get(endname);
count++;
hm.put(endname,count);
}else{
hm.put(endname,1);
}
}else{
HashMap<String,Integer> sonMap=getCount(file);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = sonMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entries) {
String key=entry.getKey();
int value=entry.getValue();
if(hm.containsKey(key)){
int count=hm.get(key);
count=count+value;
hm.put(key,count);
}else{
hm.put(key,value);
}
}
}
}
return hm;
}
}
IO流
-
什么是IO流
存取数据的解决方案 -
IO流按照流向分类
输出流:程序->文件
输入流:文件->程序 -
按照操作文件的类型可以分类哪两种流
字节流:可以操作所有类型的文件
字符流:只能操作纯文本文件 -
纯文本文件
用windows系统自带的记事本打开并且能读懂的文件
FileOutputStream书写细节
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("src\\IO\\a.txt");
byte[] bytes={97,98,99};
fos.write(bytes);
int b;
fos.close();
}
- 创建字节输出流对象
细节一:参数是字符串表示的路径或者File对象都是可以的
细节二:如果文件不存在会创建一个新的文件,但是要保证父级路径是存在的
细节三:如果文件已经存在,则会清空文件
- 写数据
细节:write方法的参数是整数,但实际上写到文件中的是整数在ASCII上对应的字符
fos.write()
- 释放资源
细节:每次使用完流之后都要释放资源
fos.close()
写入数据的方法
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| void write(int b) | 一次写一个字节数据 |
| viod write(byte[] b) | 一次写一个字节数组数据 |
| void write(byte[]b,int off,int len) | 一次写一个字节数组的部分数据 |
FileinputStream书写细节
-
创建字节输入流对象
细节:如果文件不存在,就直接报错 -
读取数据
细节:一次读取一个字节,读出来的是数据在ASCII上对应的数字
细节:读到文件末尾,read方法返回-1 -
释放资源
细节:每次使用完流必须要释放资源
字节输入流循环读取
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("src\\IO\\a.txt");
int b;
while((b=fis.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char) b);
}
fis.close();
}
文件拷贝
优化前
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建对象
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("src\\IO\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("src\\b.txt");
int b;
//边读边写
while((b=fis.read())!=-1){
fos.write(b);
}
//先开的先关
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
优化后
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("src\\IO\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("src\\c.txt");
int len;
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024*1024*5];
while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}
编码和解码
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String str="ai你哟";
//默认进行编码
byte[] byte1=str.getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(byte1));
//默认GBK进行编码
byte[] byte2=str.getBytes("GBK");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(byte2));
//解码
String str2=new String(byte1);
System.out.println(str2);
//使用指定的方式进行解码
String str3=new String(byte2,"GBK");
System.out.println(str3);
}
}
空参read讲解
read细节:
read():默认一个字节一个字节读取的,如果遇到中文会一次读取多个
在读取之后,方法底层还会进行解码并转成十进制
最终将这个作为返回值
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr=new FileReader("src\\IO\\a.txt");
int ch;
while((ch=fr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char) ch);
}
fr.close();
}
综合练习
- 文件拷贝
public class IODemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File src =new File("src\\IO");
File dest=new File("src\\dest");
copydir(src,dest);
}
private static void copydir(File src, File dest) throws IOException {
dest.mkdirs();
//静茹数据源
File[] files =src.listFiles();
//System.out.println(files);
for (File file : files) {
if(file.isFile()){
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(file);
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,file.getName()));
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}else{
copydir(file,new File(dest,file.getName()));
}
}
}
}
- 文件加密
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis =new FileInputStream("src\\IO\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("src\\ency.txt");
int b;
while((b=fis.read())!=-1){
fos.write(b^2);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
解密话将开头两个文件路径改变一下
- 排序
对2-4-8-9-3-1排序
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr=new FileReader("src\\IO\\a.txt");
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
int ch;
while((ch= fr.read())!=-1){
sb.append((char)ch);
}
fr.close();
System.out.println(sb);
//排序
Integer[] arr = Arrays.stream(sb.toString().
split("-")).
map(Integer::parseInt).
sorted().
toArray(Integer[]::new);
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("src\\a.txt");
String s=Arrays.toString(arr).replace(", ","-");
String result=s.substring(1,s.length()-1);
fw.write(result);
fw.close();
}
利用字节缓冲流拷贝文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//字节缓冲输入流的构造方法
BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\a.txt"));
//字节缓冲输出流的构造方法
BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\IO\\a.txt"));
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
int b;
while((b=bis.read(bytes))!=-1){
bos.write(bytes,0,b);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
缓冲流
- 缓冲流有几种?
- 字节缓冲输入流:BufferedInputStream
- 字节缓冲输出流:BufferedOUtputStream
- 字符缓冲输入流:BufferedReader
- 字符缓冲输出流:BufferedWriter
- 缓冲流为什么能提高性能
- 缓冲流中自带长度为8192的缓冲区
- 可以显著提高字节流的读写性能
- 对于字符流提升不明显,对于字符缓冲流而言关键点是两个特有的方法
- 字符缓冲流两个特有的方法是什么
- 字符缓冲流输入BufferedReader:readLIne()
readLIne方法在读取的时候不会把回车换行读到内存当中
- 字符缓冲输入流BufferedWriter:newLIne()
文件拷贝2
用单列集合写
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\IO\\a.txt"));
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
list.add(line);
}
br.close();
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
int i1 = Integer.parseInt(o1.split("\\.")[0]);
int i2 = Integer.parseInt(o2.split("\\.")[0]);
return i1-i2;
}
});
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\IO\\a.txt"));
for (String s : list) {
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
用双列集合写
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\IO\\a.txt"));
TreeMap<Integer,String> tm=new TreeMap<>();
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
String[] arr=line.split("\\.");
tm.put(Integer.parseInt(arr[0]),arr[1]);
}
br.close();
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\IO\\a.txt"));
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entries = tm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : entries) {
String value=entry.getValue();
bw.write(value);
bw.newLine();
};
bw.close();
}
软件限次使用
IO原则:随用随建立,什么时候不用什么时候关闭
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\a.txt"));
String line=br.readLine();
br.close();
int count=Integer.parseInt(line);
count++;
if(count<=3){
System.out.println("欢迎使用本软件,第"+count+"次使用免费");
}else{
System.out.println("本软件只能免费使用3次");
}
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\a.txt"));
bw.write(count+"");
bw.close();
}
转换流基本用法
- 转换流的名字是什么
- 字符转换输入流:InputStreamReader
- 字符转换输出流:OutputStreamWrite
- 转换流的作用是什么
- 指定字符集读写数据(JDK11之后已淘汰)
- 字节流想要使用字符流中的方法
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr=new FileReader("src\\d.txt",Charset.forName("GBK"));
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("src\\e.txt", Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
int b;
while((b= fr.read())!=-1){
fw.write(b);
}
fr.close();
fw.close();
}
字节流读取文件中的数据,每次读一整行
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("src\\io\\a.txt")));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}
序列化流
注意对象类要实现Serializable接口(标记型接口)只有实现后才能序列化
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Students stu=new Students(45,"zhangsan");
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\e.txt"));
oos.writeObject(stu);
oos.close();
}
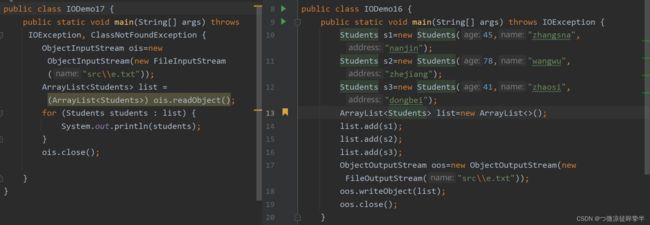
反序列化流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//创建反序列流的对象
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\e.txt"));
Students o=(Students) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(o);
ois.close();
}
- 序列化对象后,修改了Javabean类,再次反序列化,会出现问题,会抛出InvalidClassException异常。
解决方案:给Javabean类添加serialVersionUID(序列号,版本号) - 如果一个对象中的某个成员变量的值,不想被序列化,给该成员变量加transient关键字修饰,使得该成员变量不参与序列化过程。
读写多个对象
打印流
只能写不能读
字节打印流
ps:printf自动换行、自动刷新
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\ency.txt"));
ps.println("hfs");
ps.print(98);
ps.printf("%s sdf %s","时","分");
ps.close();
}
字符打印流
ps:printf自动换行、自动刷新
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("src\\f.txt"));
pw.println("fff");
pw.print("阿巴");
pw.printf("%s %s","asd","sadf");
pw.close();
}
压缩、解压
解压
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File src=new File("C:\\Users\\李奥\\OneDrive\\桌面\\aaa.zip");
File dest=new File("C:\\Users\\李奥\\OneDrive");
unzip(src,dest);
}
private static void unzip(File src, File dest) throws IOException {
ZipInputStream zip=new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));
ZipEntry entry;
while((entry=zip.getNextEntry())!=null){
System.out.println(entry);
if(entry.isDirectory()){
File file=new File(dest,entry.toString());
file.mkdirs();
}else{
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,entry.toString()));
int b;
while((b= zip.read())!=-1){
//写到目的地
fos.write(b);
}
fos.close();
//表示在压缩包中的一个文件处理完成
zip.closeEntry();
}
}
}
压缩
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建File对象表示要压缩的文件
File src=new File("C:\\Users\\李奥\\OneDrive\\桌面\\a.txt");
//创建FIle对象表示压缩包的位置
File dest=new File("C:\\Users\\李奥\\OneDrive\\桌面");
//调用方法来压缩
tozip(src,dest);
}
private static void tozip(File src, File dest) throws IOException {
//创建压缩流关联压缩包
ZipOutputStream zos=new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,"a.zip")));
//创建ZipEntry对象,表示压缩包里面的每一个文件和文件夹
ZipEntry entry=new ZipEntry("a.txt");
//把ZipEntry对象放到压缩包当中
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
//把src文件中的数据写到压缩包当中
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(src);
int b;
while((b=fis.read())!=-1){
zos.write(b);
}
zos.closeEntry();
zos.close();
}
优化方案
public class IO2Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建File对象表示要压缩的文件夹
File src=new File("C:\\Users\\李奥\\OneDrive\\桌面\\aaa");
//创建File对象表示压缩包放在哪里(压缩包的父级路径)
File destparent=src.getParentFile();
//创建File对象表示压缩包的路径
File dest=new File(destparent,src.getName()+".zip");
//创建压缩流关联压缩包
ZipOutputStream zos=new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest));
//获取src里面的每个文件,变成ZipEntry对象,放入压缩包中
tozip(src,zos,src.getName());
//释放资源
zos.close();
}
/*
* 作用:
* 参数一:数据源
* 参数二:压缩流
* 参数三:压缩包内部的路径
*
* */
public static void tozip(File src,ZipOutputStream zos,String name) throws IOException {
//进入src文件夹
File[] files=src.listFiles();
//遍历数组
for (File file : files) {
if(file.isFile()){
//判断文件,变成ZipEntry对象,放到压缩包当中
ZipEntry entry=new ZipEntry(name+"\\"+file.getName());
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
//读取文件中的数据,写到压缩包
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(file);
int b;
while((b=fis.read())!=-1){
zos.write(b);
}
fis.close();
zos.closeEntry();
}else{
//判断文件夹,递归
tozip(file,zos,name+"\\"+file.getName());
}
}
}
}
网络爬虫
- 爬取姓
package IOAllText;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLConnection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class text1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String xing="https://hanyu.baidu.com/shici/detail?from=kg1&highlight=&pid=0b2f26d4c0ddb3ee693fdb1137ee1b0d&srcid=51369";
String xingstr=webCrawLer(xing);
ArrayList<String> xingTemplist=getData(xingstr,"(.{4})(,|。)",1);
ArrayList<String> xinglist=new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : xingTemplist) {
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
xinglist.add(c+"");
}
}
System.out.println(xinglist);
}
private static ArrayList<String> getData(String xingstr, String s,int index) {
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
Pattern pattern=Pattern.compile(s);
Matcher matcher=pattern.matcher(xingstr);
while (matcher.find()){
String group=matcher.group(index);
list.add(group);
}
return list;
}
private static String webCrawLer(String net) throws IOException {
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
URL url=new URL(net);
URLConnection conn= url.openConnection();
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream());
int ch;
while((ch= isr.read())!=-1){
sb.append((char) ch);
}
isr.close();
return sb.toString();
}
}
随机点名
- 要求一
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\\Users\\李奥\\IdeaProjects\\Mio\\src\\com\\sanyecao\\mytext1\\allnames.txt"));
String line;
while((line= br.readLine())!=null){
list.add(line);
}
br.close();
//解法一:
Random random=new Random();
int index=random.nextInt(list.size());
String randdomeName1=list.get(index);
String[] str = randdomeName1.split("-");
System.out.println(str[0]);
//解法二:
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println(list.get(0).split("-")[0]);
}
- 要求二
package com.sanyecao.mytext2;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Random;
public class Text2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ArrayList boylist=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList grillist=new ArrayList<>();
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\\Users\\李奥\\IdeaProjects\\Mio\\src\\com\\sanyecao\\mytext2\\allnames.txt"));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
String sex=line.split("-")[1];
if(sex.equals("男")){
boylist.add(line.split("-")[0]);
}else{
grillist.add(line.split("-")[0]);
}
}
br.close();
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0);
int boycount=0;
int grilcount=0;
Random random=new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
int index=random.nextInt(list.size());
int weight= list.get(index);
if(weight==1){
int boynum=random.nextInt(boylist.size());
String boyname = (String) boylist.get(boynum);
//System.out.println(boyname);
boycount++;
}else{
int grilnum=random.nextInt(grillist.size());
String grilname = (String) boylist.get(grilnum);
//System.out.println(grilname);
grilcount++;
}
}
System.out.println("抽取100万次,其中男生被抽中了"+boycount);
System.out.println("抽取100万次,其中男生被抽中了"+grilcount);
System.out.println((float) boycount/1000000);
System.out.println((float)grilcount/1000000);
}
}
- 要求三
package com.sanyecao.mytext3;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Text3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\\Users\\李奥\\IdeaProjects\\Mio\\src\\com\\sanyecao\\mytext3\\allnames.txt"));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
list.add(line.split("-")[0]);
}
br.close();
BufferedReader br2=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\\Users\\李奥\\IdeaProjects\\Mio\\src\\com\\sanyecao\\mytext3\\count.txt"));
String countstr = br2.readLine();
int count=Integer.parseInt(countstr);
br.close();
count++;
if(count>=3){
System.out.println("张三");
}else{
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println(list.get(0));
}
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\李奥\\IdeaProjects\\Mio\\src\\com\\sanyecao\\mytext3\\count.txt"));
bw.write(count+"");
bw.close();
}
}
- 要求四
/*需求:
一个文件里面存储了班级同学的姓名,每一个姓名占一行。
要求通过程序实现随机点名器。
运行结果要求:
被点到的学生不会再被点到。
但是如果班级中所有的学生都点完了, 需要重新开启第二轮点名。
核心思想:
点一个删一个,把删除的备份,全部点完时还原数据。
*/
package com.sanyecao.mytext4;
import cn.hutool.Hutool;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Text4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String src="C:\\Users\\李奥\\IdeaProjects\\Mio\\src\\com\\sanyecao\\mytext4\\allnames.txt";
String src2="C:\\Users\\李奥\\IdeaProjects\\Mio\\src\\com\\sanyecao\\mytext4\\del.txt";
ArrayList<String> list = readFile(src);
Collections.shuffle(list);
if(list.size()==0){
list=readFile(src2);
writeFile(src,list,false);
new File(src2).delete();
}
String stu = list.remove(0);
System.out.println(stu);
writeFile(src,list,false);
writeFile(src2,stu,true);
}
private static void writeFile(String src2, String stu, boolean isAppend) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(src2,isAppend));
bw.write(stu);
bw.newLine();
bw.close();
}
private static ArrayList<String> readFile(String src) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src));
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
list.add(line.split("-")[0]);
}
br.close();
return list;
}
private static void writeFile(String src,ArrayList<String> list,boolean isAppend) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(src,isAppend));
for (String s : list) {
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
}
登录
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("C:\\Users\\李奥\\IdeaProjects\\Mio\\src\\com\\sanyecao\\mytext5\\userinfo.txt"));
String line=br.readLine();
br.close();
String[] user=line.split("&");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String username=sc.nextLine();
String rightname=user[0].split("=")[1];
String password=sc.nextLine();
String rightpassword=user[1].split("=")[1];
if(username.equals(rightname) && password.equals(rightpassword)){
System.out.println("success");
}else{
System.out.println("false");
}
}
- 存档和读档要使用序列化对象进行
properties
properties是一个双列集合,拥有Map集合所有特点
- 与IO流的结合写法
- 写
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties prop=new Properties();
prop.put("aaa","bbb");
prop.put("ccc","ddd");
prop.put("ddd","eee");
prop.put("fff","ggg");
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("src\\a.properties");
prop.store(fos,"test");
fos.close();
}
- 读
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties prop=new Properties();
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("src\\a.properties");
prop.load(fis);
fis.close();
System.out.println(prop);
}
多线程
有了多线程,我们可以让程序同时做很多事情
在想要同时运行多个事情的时候
- 并发:在同一时刻,有多个指令在单个CPU上交替进行
- 并发:在同一时刻,有多个指令在多个CPU上同时进行
多线程的实现方式
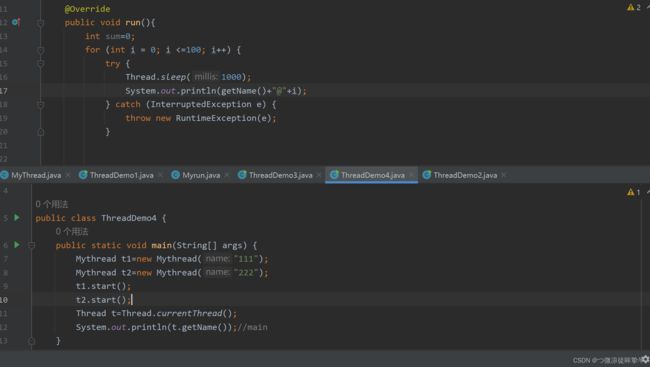
- 第一种(继承Thread):重构run方法,创建thread对象,用start启动线程。
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread t1=new MyThread();
MyThread t2=new MyThread();
t1.setName("1");
t2.setName("2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
- 第二种:自己定义一个类实现Runnable接口,重写run方法,创建Thread类,并开启多线程
public class Myrun implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
Thread t=Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(t.getName()+"helloworld");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Myrun mr=new Myrun();
Thread t1=new Thread(mr);
Thread t2=new Thread(mr);
t1.setName("1");
t2.setName("2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
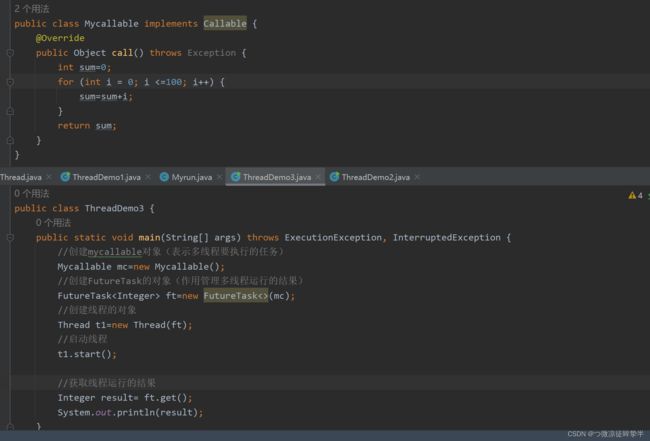
- 第三种
特点:可以获取多个线程的运行结果
- 创建一个类Mycallable实现Callable接口
- 重写call(是有返回值的,表示多线程运行的结果)
- 创建FutureTask对象(作用管理多线程的运行结果)
- 创建Thread类的对象,并启动(表示线程)
| 优点 | 缺点 | |
|---|---|---|
| 继承Thread类 | 编程比较简单,可以直接使用Thread类中的方法 | 可以扩展性比较差,不能继承其他的类 |
| 实现Runnable接口 | 扩展性强,实现该接口的同时还可以继承其他的类 | 编程相对复杂,不能使用知道Thread类中的方法 |
| 实现Callable接口 |
多线程的方法
String getName()返回此现成的名称
void setName(String name)设置线程的名字(构造方法也可以设置名字)
细节:
- 如果没有给线程设置名字,线程也是有默认的名字的
格式:Thread-序号(从0开始)
2.如果我们要给线程设置名字,可以使用set方法进行设置
static void sleep(long time)让线程休眠指定时间
setPriortiy()设置线程的优先级
getPriortiy()获取线程的优先级(默认的优先级是5,至少1,最多10)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mythread t1=new Mythread("111");
Mythread t2=new Mythread("222");
t1.setPriority(1);
t2.setPriority(10);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
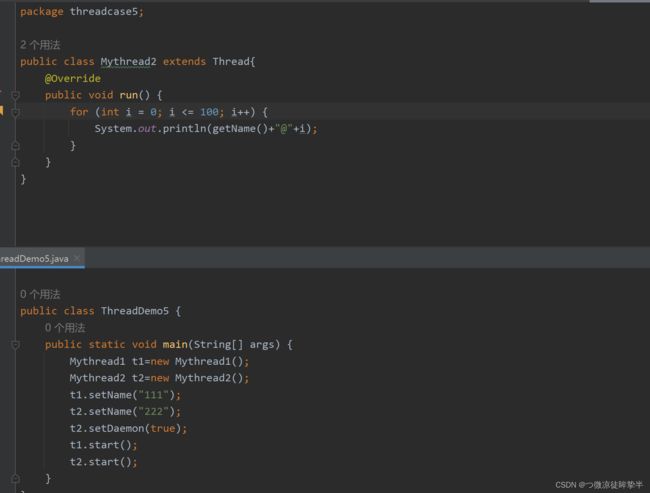
守护线程(备胎线程)
final void setDaemon(boolean on)设置为守护线程
细节:当其他的非守护线程执行完毕后守护线程会陆续结束
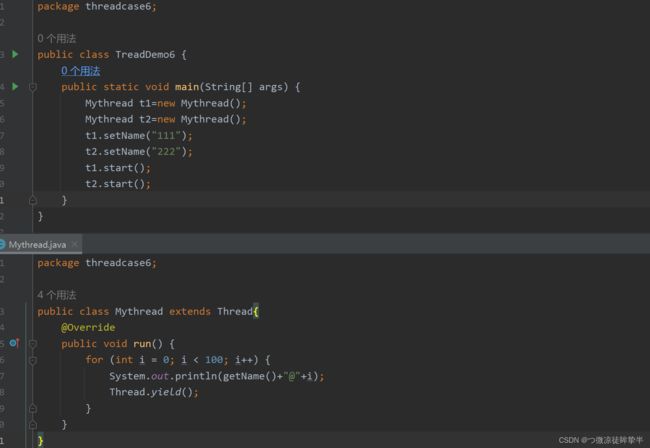
出让线程
作用:让线程执行的更加均匀
插入线程
表示把一个线程插入当前线程之间。
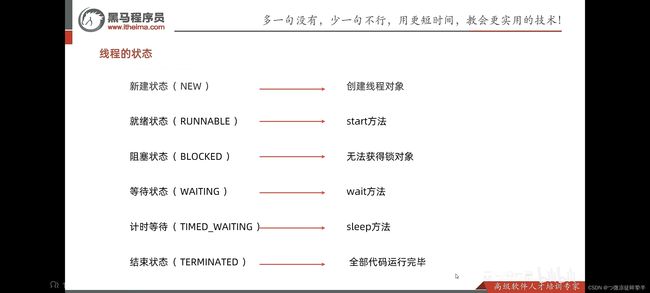
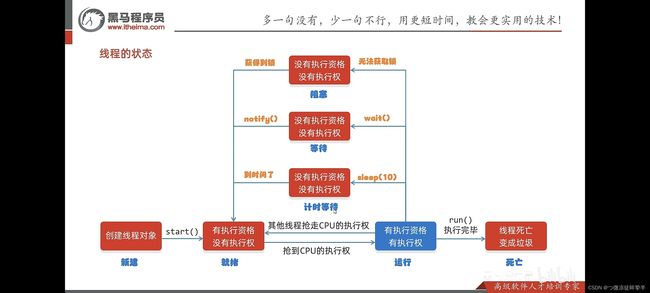
线程的生命周期
线程安全问题
Mythreadt1
package threadText;
public class Mythreadt1 extends Thread{
//创建的三个对象的三个变量同时用一个变量
static int ticket=0;
//锁对象一定是唯一的
@Override
public void run() {
while(Myrthreadt1.class){
//同步代码块
synchronized (obj){
if (ticket<1000){
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ticket++;
System.out.println(getName()+"正在卖第"+ticket+"张票");
}else{
break;
}
}
}
}
}
ThreadTDemo1
package threadText;
import threadcase7.Mythread;
public class ThreadTDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mythreadt1 t1=new Mythreadt1();
Mythreadt1 t2=new Mythreadt1();
Mythreadt1 t3=new Mythreadt1();
t1.setName("111");
t2.setName("222");
t3.setName("333");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
同步代码块的同步方法
Lock锁
lock是接口不能直接实例化,这里采用他的实现类ReentrantLock来实例化
用lock锁改写
package threadText2;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import java.util.stream.StreamSupport;
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
//表示所有对象共享同一把锁。
static Lock lock=new ReentrantLock();
static int ticket=0;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
lock.lock();
try {
try {
if (extracted()) break;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
private synchronized boolean extracted() throws InterruptedException {
if(ticket==100){
return true;
}else{
Thread.sleep(10);
ticket++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"@"+ticket);
}
return false;
}
}
生产者和消费者(等待唤醒模式)
- 常见方法
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void wait () | 当前的线程等待,直到被其他线程唤醒 |
| void notify() | 随即唤醒单个线程 |
| void notifyAll | 唤醒所有线程 |
desk
package threadwaitandnotify;
public class Desk {
public static int foodFlag=0;
public static int count=10;
public static Object lock=new Object();
}
cook
package threadwaitandnotify;
public class Cook extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
synchronized (Desk.lock){
if(Desk.count==0){
break;
}else{
if(Desk.foodFlag==1){
try {
Desk.lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
//如果没有。就制作面条
System.out.println("厨师做了一碗面条");
//修改桌子的食物状态
Desk.foodFlag=1;
//叫醒等待的消费者开吃
Desk.lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
}
}
}
foodie
package threadwaitandnotify;
public class Foodie extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
synchronized (Desk.lock){
//判断桌子上还有几碗面
if(Desk.count==0){
break;
}else{
//判断桌子上是否是空的,空的就关闭
if(Desk.foodFlag==0){
try {
Desk.lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
//每次吃一碗
Desk.count--;
System.out.println("吃货在吃面条,还能再吃"+Desk.count+"碗");
Desk.lock.notifyAll();
//告诉厨师不用做面条了
Desk.foodFlag=0;
}
}
}
}
}
}
ThreadDemo
package threadwaitandnotify;
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cook c=new Cook();
Foodie f=new Foodie();
c.setName("cooker");
f.setName("fooder");
c.start();
f.start();
}
}
等待唤醒机制(阻塞队列)
cook
package threadwaitandnotify2;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class Cook extends Thread{
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue;
public Cook(ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
//不断把棉条放入堵塞中
queue.put("noodles");
System.out.println("cook make a bow of noodles");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
foodie
package threadwaitandnotify2;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class Foodie extends Thread{
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue;
public Foodie(ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
//不断从堵塞中获取食物
String food=queue.take();
System.out.println(food);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
threaddemo
package threadwaitandnotify2;
import threadwaitandnotify.Cook;
import threadwaitandnotify.Foodie;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//只能创建以一个ArrayBlockingQueue对象
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue=new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1);
Cook c=new Cook();
Foodie f=new Foodie();
c.start();
f.start();
}
}
线程的状态
线程池的主要核心原理
- 创建一个池子,池子是空的
- 提交任务时,池子会创建新的线程对象,不需要创建新的线程,直接复用已有的线程既可。
- 但是如果提交任务时,池子没有空闲线程,也无法创建新线程,任务就会排队等待。
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool | 创建一个没有上限的线程池 |
| public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) | 创建有上限的线程池 |
//创建
ExecutorService pool= Executors.newCachedThreadPool()
//提交任务
pool.submit()
//销毁
pool.shutdown()
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor pool=new ThreadPoolExecutor(
3,//核心线程数
6,//最大线程数,不能小于0
60,//空闲线程最大存活时间
TimeUnit.SECONDS,//时间单位
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3),//任务队列
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),//创建线程工厂
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()//任务的拒绝策略
);
查询自己的最大线程数
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count=Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
System.out.println(count);
}
线程池多大合适
- CPU密集型运算:最大并行数+1
- I/O密集型运算:最大并行数 * 期望CPU利用率 * (总时间(CPU计算时间+等待时间)/CPU计算时间)
网络编程
概念:计算机跟计算机之间通过网络进行数据传输
- 常见的软件建构:CS/BS
CS->客户端
BS->浏览器
网络三要素
IP、端口号、协议
- IP
- IP的作用:设备在网络中的地址,是唯一的标识。
- IPv4的特点:目前主流的方案,最多2^32个方案
细节:特殊的IP:127.0.0.1(永远表示本机)
常见的CMD命令:ipconfig查看本机的IP地址,ping检查网络是否连通
- IPv6的特点:最多有2^128个ip
- 端口号
应用程序在设备中的唯一标识
端口号:由两个字节表示的整数,取值范围:0~65535
其中0~1023之间的端口号用于一些比较知名的网络服务或者应用
注意一个端口只能被一个应用程序使用
- 协议
计算机网络中,连接和通信的规则被称为网络通信协议
- UDP协议
用户数据报协议
UPD是面向无连接通信协议
速度快,有大小限制一次最多发送64K,数据不安全,容易丢失数据
- TCP协议
传输控制协议TCP
TCP协议是面向连接的通信协议
速度慢,没有大小限制,数据安全
InetAddress类的使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {
//获取InetAdress的对象
//IP的对象 一台电脑的对象
InetAddress address=InetAddress.getByName("LAPTOP-BE8I51G2");//可以写IP地址或者时设备名称
System.out.println(address);
//获取设备名称
String name=address.getHostName();
System.out.println(name);
//获取设备的IP地址
String ip=address.getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip);
}
UDP发送数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建DatagramSocket对象
//细节:
//绑定端口,通过端口发送
//空参:所有可的端口中随机一个
//有参:指定端口进行绑定
DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket();
//打包数据
String str="11111";
byte[] bytes=str.getBytes();
InetAddress address=InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port=10086;
DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length,address,port);
//发送数据
ds.send(dp);
//释放资源
ds.close();
}
UDP通信程序(接收数据)
UPD综合练习(聊天室)
单播、组播、广播
组播:
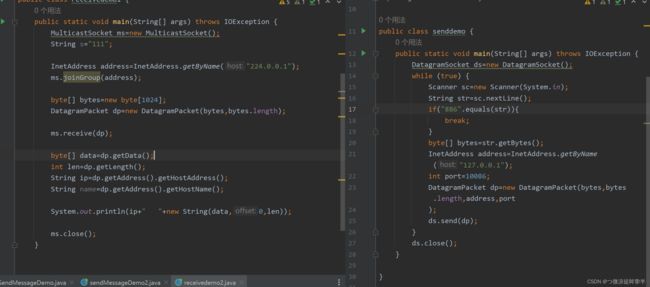
广播:
将传输地址改成255.255.255.255
TCP协议
发送数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//发送数据
//创建Scoket对象
//在创建对象的同时会连接服务器
//如果连不上,代码就会报错
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",10000);
//可以从连接通道中获取输出流
OutputStream os=socket.getOutputStream();
//写出数据
os.write("你好你好".getBytes());
//释放资源
os.close();
socket.close();
}
接收数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//接收数据
//创建对象ServerSocker
ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(10000);
//监听客户端链接
Socket socket=ss.accept();
//从连接通道中获取输入流读取数据
// InputStream is=socket.getInputStream();
// InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(is);
// BufferedReader br=
//链式写法:
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
int b;
while((b=br.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char) b);
}
socket.close();
//释放资源
ss.close();
}
接收中文时有乱码,可以将字节读取改为字符读取
三次握手(确保链接建立)、四次挥手(确保连接断开,且数据处理完毕)
TCP练习
练习一:需求
客户端:多次发送数据
服务端:接收多次数据,并打印
- 客户端
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",10000);
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
OutputStream os=socket.getOutputStream();
while(true){
String str=sc.nextLine();
if("886".equals(str)){
break;
}
os.write(str.getBytes());
}
socket.close();
}
- 服务端
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(10000);
Socket socket=ss.accept();
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream());
int b;
while((b= isr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)b);
}
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
练习二:
需求:客户端向服务器发送信息并打印,服务器对信息进行反馈
- server服务器
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(10000);
Socket socket=ss.accept();
InputStream is=socket.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(is);
int b;
while((b=isr.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char) b);
}
String str="how happy";
OutputStream os=socket.getOutputStream();
os.write(str.getBytes());
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
- client客户端
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",10000);
String str="next meet you";
OutputStream os=socket.getOutputStream();
os.write(str.getBytes());
//写出一个结束标记
socket.shutdownOutput();
//接收服务端回写的数据
InputStream is=socket.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(is);
int b;
while((b=isr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char) b);
}
socket.close();
}
反射
反射允许对成员变量,成员方法和构造方法的信息进行编程访问
作用:
获取一个类里面所有的信息,获取到之后,再执行其他的业务逻辑
结合配置文件,动态的创建对象并调用方法
获取class对象的三种方式
- Class.forName(“全类名”)
- 类名.class
- 对象.getClass()
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//最常用的
Class aClass = Class.forName("MyReflectDemo.Student");
System.out.println(aClass);//class MyReflectDemo.Student
//一般用作参数进行传递
//例如synchronized (student.class)
Class<Student> studentClass = Student.class;
System.out.println(studentClass);//class MyReflectDemo.Student
//当有这个类的对象的时候使用
Student student=new Student();
Class<? extends Student> aClass1 = student.getClass();
System.out.println(aClass1);
}

获取含参数的构造方法,需要在括号中写入String、int等的字节码文件:String.class、int.class

综合练习(通过配置文件获取对象方法并运行)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//读取配置文件的信息
Properties prop=new Properties();
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\李奥\\IdeaProjects\\myReflect\\prop.properties");
prop.load(fis);
fis.close();
System.out.println(prop);
//获取全类名的方法名
String classname=(String) prop.get("classname");
String methodname=(String) prop.get("method");
//利用反射创建对象并运行
Class clazz=Class.forName(classname);
//获取构造方法
Constructor con=clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
//用无参的构造方法创建对象实例
Object o=con.newInstance();
System.out.println(o);
//获取成员方法并运行
Method method=clazz.getDeclaredMethod(methodname);
method.setAccessible(true);
method.invoke(o);
}
动态代理
- 为什么需要代理
代理可以无侵入式的给对象增强其他功能
- 代理什么样
代理里面就是对象要被代理的方法
- Java通过什么来保证代理的样子
通过接口保证,后面的对象和代理需要实现同一个接口,接口就是被代理的所有方法