并查集(Union-Find) (图文详解)
文章目录
- 并查集基础知识
-
- 定义
- C++实现
- 优化
- 精选算法题(Java实现)
-
- 实现并查集
- 交换字符串中的元素
- 最长连续序列 - 字节面试常考
- 连通网络的操作次数
- 最大岛屿数量 (三种解法)
- 省份数量
- 冗余连接
- 冗余连接Ⅱ
- 情侣牵手(困难)
- 移除最多的同行或同列石头
- 等式方程的可满足性
- 结语
并查集基础知识
定义
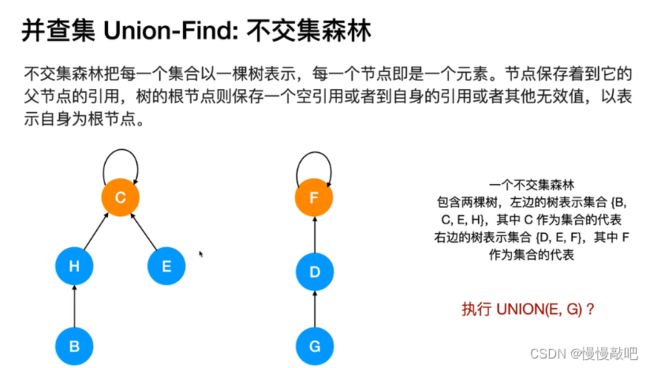
并查集是一种树型的数据结构,用于处理一些不相交集合的合并及查询问题(即所谓的并、查)。比如说,我们可以用并查集来判断一个森林中有几棵树、某个节点是否属于某棵树等。
主要构成:
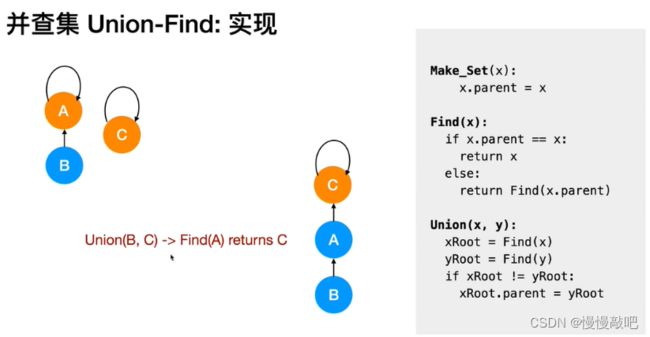
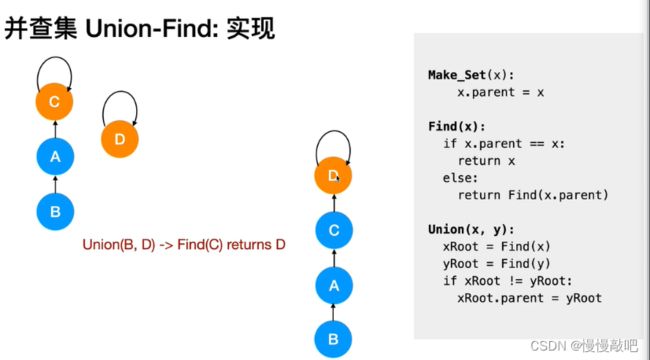
并查集主要由一个整型数组pre[ ]和两个函数find( )、join( )构成。
数组 pre[ ] 记录了每个点的前驱节点是谁,函数 find(x) 用于查找指定节点 x 属于哪个集合,函数 join(x,y) 用于合并两个节点 x 和 y 。
作用:
并查集的主要作用是求连通分支数(如果一个图中所有点都存在可达关系(直接或间接相连),则此图的连通分支数为1;如果此图有两大子图各自全部可达,则此图的连通分支数为2……)
C++实现
class UnionFind{
public:
UnionFind(int n){
size = n;
father = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
father[i] = i;
}
}
//查看x的根节点 -> x所属集合
int find(int x){
int root = x;
while(root != father[root]){
root = father[root];
}
return root;
}
//将x和y染色为同一个颜色 -> 合并x和y的所属集合
void merge(int x, int y){
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if(rootX == rootY) return;
father[rootX] = rootY;
//father[rooY] = rootX;
}
//路径压缩优化的查找
int find(int x){
int root = x;
while(root != father[root]){
root = father[root];
}
while(x != root){
int fx = father[x];
father[x] = root;
x = fx;
}
return root;
}
//针对节点数量优化
void merge(int x, int y){
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if(rootX == rootY) return;
if(treeSize[rootX] < treeSize[rootY]){
father[rootX] = rootY;
treeSize[rootY] += treeSize[rootX];
}else{
father[rootY] = rootX;
treeSize[rootX] += treeSize[rootY];
}
}
public:
int *father, *treeSize, size;
};
int P(UnionFind uf){
for(int i = 0; i < uf.size; i++{
cout << uf.color[i] << " ";
} cout << endl;
}
int main(){
int n = 10;
UnionFind uf(n);
uf.merge(0,1);P(uf);
uf.merge(1,2);P(uf);
uf.merge(5,9);P(uf);
uf.merge(7,8);P(uf);
uf.merge(8,6);P(uf);
uf.merge(1,3);P(uf);
uf.merge(6,1);P(uf);
return 0;
}
问题思考:
- 极端情况下会退化成一条链
- 将结点数量多的接到结点少的树上,导致了退化
- 将较高的树接到较低的树上,导致了退化
优化
精选算法题(Java实现)
实现并查集
/**
* 实现并查集
* @author: William
* @time:2022-04-08
*/
public class UnionFind {
//记录每个节点的根节点
int[] parent;
//记录每个子集的节点数
int[] rank;
//记录并查集中的连通分量数量
int count;
public UnionFind1(int n) {
count = n;
parent = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
rank = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(rank, 1);
}
public int find(int i) {
if(parent[i] != i) parent[i] = find(parent[i]);
return parent[i];
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(x), rootY = find(y);
if(rootX != rootY) {
if(rank[rootX] > rank[rootY]) {
parent[rootY] = rootX;
}else if(rank[rootX] < rank[rootY]) {
parent[rootX] = rootY;
}else {
parent[rootY] = rootX;//相等的情况
rank[rootX] += 1;
}
count--;//维护数量
}
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public boolean connected(int x, int y) {
return find(x) == find(y);
}
}
交换字符串中的元素
/**
* 交换字符串中的元素
* @author: William
* @time:2022-04-12
*/
public class Num1202 {
public String smallestStringWithSwaps(String s, List<List<Integer>> pairs) {
if(pairs.size() == 0) {
return s;
}
//1. 将任意交换的结点对输入并查集
int n = s.length();
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n);
for(List<Integer> pair : pairs) {
uf.union(pair.get(0), pair.get(1));
}
//2. 构建映射关系
//char[] charArray = s.toCharArray();
// key:连通分量的代表元,value:同一个连通分量的字符集合(保存在一个优先队列中)
Map<Integer, PriorityQueue<Character>> map = new HashMap<>(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int root = uf.find(i);
// if (map.containsKey(root)) {
// hashMap.get(root).offer(charArray[i]);
// } else {
// PriorityQueue minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();
// minHeap.offer(charArray[i]);
// hashMap.put(root, minHeap);
// }
// 上面六行代码等价于下面一行代码,JDK 1.8 以及以后支持下面的写法
map.computeIfAbsent(root, key -> new PriorityQueue<>()).offer(s.charAt(i));
}
//3. 重组字符串
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int root = uf.find(i);
sb.append(map.get(root).poll());
}
return sb.toString();
}
private class UnionFind {
private int[] parent;
private int[] rank;
public UnionFind(int n) {
this.parent = new int[n];
this.rank = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
this.parent[i] = i;
this.rank[i] = 1;
}
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(x), rootY = find(y);
if(rootX != rootY) {
if(rank[rootX] > rank[rootY]) {
parent[rootY] = rootX;
}else if(rank[rootX] < rank[rootY]) {
// 此时以 rootY 为根结点的树的高度不变
parent[rootX] = rootY;
}else {
parent[rootY] = rootX;
// 此时以 rootX 为根结点的树的高度仅加了 1
rank[rootX]++;
}
}
}
public int find(int x) {
if(parent[x] != x) {
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
}
}
最长连续序列 - 字节面试常考
/**
* 最长连续序列 - 字节面试常考
* @author: William
* @time:2022-04-14
*/
public class Num128 {
public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
int ans = 0;
//用来筛选某个数的左右连续数是否存在
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
//将连续的数字组成一个个集合
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(nums.length);
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(map.containsKey(nums[i])) continue;
if(map.containsKey(nums[i] - 1)) {//往左判断
uf.union(i, map.get(nums[i] - 1));
}
if(map.containsKey(nums[i] + 1)) {//往右判断
uf.union(i, map.get(nums[i] + 1));
}
map.put(nums[i], i);//存储当前数
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {//选出最长的数
if(uf.find(i) != i) continue;//不是根节点
ans = Math.max(ans, uf.rank[i]);
}
return ans;
}
class UnionFind{
int[] parent;
int[] rank;
public UnionFind(int n) {
this.parent = new int[n];
this.rank = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
this.parent[i] = i;
this.rank[i] = 1;
}
}
//这一步很关键 当时写的其他方法失败了
public void union(int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(x), rootY = find(y);
if(rootX != rootY) {
if(rank[rootX] < rank[rootY]) {
int tmp = rootX;
rootX = rootY;
rootY = tmp;
}
parent[rootY] = rootX;
rank[rootX] += rank[rootY];
}
}
public int find(int x) {
if(parent[x] != x){
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
}
}
连通网络的操作次数
/**
* 连通网络的操作次数
* @author: William
* @time:2022-04-14
*/
public class Num1319 {
public int makeConnected(int n, int[][] connections) {
//网线数量太少的情况 n是电脑数
if(connections.length < n - 1) return -1;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n);
for(int[] connection : connections) {
uf.union(connection[0], connection[1]);
}
//只需要操作连通数量-1次即可
return uf.getCount() - 1;
}
class UnionFind{
int count;
int[] parent;
int[] rank;
public UnionFind(int n) {
this.count = n;
this.parent = new int[n];
this.rank = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
this.parent[i] = i;
this.rank[i] = 1;
}
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(x), rootY = find(y);
if(rootX != rootY) {
if(rank[rootX] > rank[rootY]) {
parent[rootY] = rootX;
}else if(rank[rootX] < rank[rootY]) {
parent[rootX] = rootY;
}else {
parent[rootY] = rootX;
rank[rootX]++;
}
count--;
}
}
public int find(int x) {
return parent[x] == x ? x : find(parent[x]);
}
}
}
最大岛屿数量 (三种解法)
/**
* 最大岛屿数量
* @author: William
* @time:2022-04-10
*/
public class Num200 {
class UnionFind{
int count;
int[] parent;
int[] rank;
public UnionFind(char[][] grid) {
count = 0;
int m = grid.length;//行数
int n = grid[0].length;//列数
parent = new int[m * n];
rank = new int[m * n];
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] == '1') {
parent[i * n + j] = i * n + j;//规律
count++;
}
rank[i * n + j] = 0;
}
}
}
public int find(int i) {
if(parent[i] != i) parent[i] = find(parent[i]);
return parent[i];
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(x), rootY = find(y);
if(rootX != rootY) {
if(rank[rootX] > rank[rootY]) {
parent[rootY] = rootX;
}else if(rank[rootX] < rank[rootY]) {
parent[rootX] = rootY;
}else {
parent[rootY] = rootX;//相等的情况
rank[rootX] += 1;
}
count--;//维护数量
}
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int nr = grid.length;
int nc = grid[0].length;
int num_islands = 0;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(grid);
for (int r = 0; r < nr; ++r) {
for (int c = 0; c < nc; ++c) {
if (grid[r][c] == '1') {
grid[r][c] = '0';
if (r - 1 >= 0 && grid[r-1][c] == '1') {
uf.union(r * nc + c, (r-1) * nc + c);
}
if (r + 1 < nr && grid[r+1][c] == '1') {
uf.union(r * nc + c, (r+1) * nc + c);
}
if (c - 1 >= 0 && grid[r][c-1] == '1') {
uf.union(r * nc + c, r * nc + c - 1);
}
if (c + 1 < nc && grid[r][c+1] == '1') {
uf.union(r * nc + c, r * nc + c + 1);
}
}
}
}
return uf.getCount();
}
//dfs —— 重点掌握
public int numIslands1(char[][] grid) {
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {//行数
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {//列数
if(grid[i][j] == '1') {//满足条件就继续递归
dfs(grid, i, j);
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
private void dfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j) {
//终止条件
if(i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= grid.length ||
j >= grid[0].length || grid[i][j] == '0') return;
grid[i][j] = '0';
//分别向上下左右递归
dfs(grid, i + 1, j);
dfs(grid, i, j + 1);
dfs(grid, i - 1, j);
dfs(grid, i, j - 1);
}
//bfs
public int numIslands2(char[][] grid) {
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for(int j =0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] == '1') {
bfs(grid, i, j);
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
private void bfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j) {
Queue<int[]> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(new int[] {i, j});
while(!list.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = list.remove();
i = cur[0]; j = cur[1];
if(0 <= i && i < grid.length && 0 <= j &&
j < grid[0].length && grid[i][j] == '1') {
grid[i][j] = '0';
list.add(new int[] {i + 1, j});
list.add(new int[] {i - 1, j});
list.add(new int[] {i, j + 1});
list.add(new int[] {i, j - 1});
}
}
}
}
省份数量
/**
* 省份数量
* @author: William
* @time:2022-04-11
*/
public class Num547 {
public int findCircleNum(int[][] isConnected) {
int provinces = isConnected.length;
int[] parent = new int[provinces];
//开辟一个parent数组 储存 某个节点的父节点
for(int i =0; i < provinces;i++){
parent[i] = i;
}
for(int i = 0; i < provinces; i++){
for(int j = i + 1; j < provinces; j++){
//两个节点只要是连通的就合并
if(isConnected[i][j] == 1){
union(parent, i, j);
}
}
}
int numProvinces = 0;
//扫描parent数组 如果当前节点对应根节点 就是一个省份
for(int i = 0; i < provinces; i++){
if(parent[i] == i){
numProvinces++;
}
}
return numProvinces;
}
//支持路径压缩的查找函数
public int find(int[] parent, int index){
//父节点不是自己
if(parent[index] != index){
//递归调用查找函数 并把当前结果储存在当前节点父节点数组中
parent[index] = find(parent, parent[index]);
}
//当父节点是本身时
return parent[index];
}
//合并函数
public void union(int[] parent, int index1, int index2){
parent[find(parent , index1)] = find(parent, index2);
}
//dfs
public int findCircleNum1(int[][] isConnected) {
int provinces = isConnected.length;
boolean[] visited = new boolean[provinces];
int numProvinces = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < provinces; i++) {
//如果该城市未被访问过,则从该城市开始深度优先搜索
if(!visited[i]) {
dfs(isConnected, visited, provinces, i);
numProvinces++;
}
}
return numProvinces;
}
private void dfs(int[][] isConnected, boolean[] visited, int provinces, int i) {
for(int j = 0; j < provinces; j++) {
//j时与i相连的邻居节点,相连且未被访问到
if(isConnected[i][j] == 1 && !visited[j]) {
visited[j] = true;
//继续做深度优先搜索
dfs(isConnected, visited, provinces, j);
}
}
}
}
冗余连接
/**
* 冗余连接
* @author: William
* @time:2022-04-11
*/
public class Num684 {
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
int n = edges.length;
int[] parent = new int[n + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int[] edge = edges[i];
int node1 =edge[0], node2 = edge[1];
//说明两个顶点不连通,当前边不会导致环出现
if(find(parent, node1) != find(parent, node2)) {
union(parent, node1, node2);
}else {//已经连通成环 返回该边即可
return edge;
}
}//这种情况表示没有
return new int[0];
}
public void union(int[] parent, int x, int y) {
parent[find(parent, x)] = find(parent, y);
}
public int find(int[] parent, int x) {
if(parent[x] != x) {
parent[x] = find(parent, parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
}
冗余连接Ⅱ
/**
* 冗余连接Ⅱ hard
* @author: William
* @time:2022-04-11
*/
public class Num685 {
public int[] findRedundantDirectedConnection(int[][] edges) {
int n = edges.length;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n + 1);
int[] parent = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
parent[i] = i;
}
int conflict = -1;
int cycle = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int[] edge = edges[i];
int node1 = edge[0], node2 = edge[1];
if (parent[node2] != node2) {
conflict = i;
} else {
parent[node2] = node1;
if (uf.find(node1) == uf.find(node2)) {
cycle = i;
} else {
uf.union(node1, node2);
}
}
}
if (conflict < 0) {
int[] redundant = {edges[cycle][0], edges[cycle][1]};
return redundant;
} else {
int[] conflictEdge = edges[conflict];
if (cycle >= 0) {
int[] redundant = {parent[conflictEdge[1]], conflictEdge[1]};
return redundant;
} else {
int[] redundant = {conflictEdge[0], conflictEdge[1]};
return redundant;
}
}
}
}
class UnionFind{
int[] parent;
public UnionFind(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
parent[find(x)] = find(y);
}
public int find(int x) {
if(parent[x] != x) {
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
}
情侣牵手(困难)
/**
* 情侣牵手 hard
* @author: William
* @time:2022-04-12
*/
public class Num765 {
//如果一对情侣恰好坐在了一起,并且坐在了成组的座位上,
//其中一个下标一定是偶数,另一个一定是奇数,并且偶数的值 + 1 = 奇数的值。
//例如编号数对 [2, 3]、[9, 8],
//这些数对的特点是除以 2(下取整)得到的数相等。
public int minSwapsCouples(int[] row) {
int len = row.length;
int N = len >> 1;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(N);
for(int i = 0; i < len; i += 2) {
uf.union(row[i] >> 1, row[i + 1] >> 1);
}
return N - uf.getCount();
}
private class UnionFind {
private int[] parent;
private int count;
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public UnionFind(int n) {
this.count = n;
this.parent = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public int find(int x) {
if(parent[x] != x) {
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(x), rootY = find(y);
if(rootX == rootY) return;
parent[rootX] = rootY;
count--;
}
}
}
移除最多的同行或同列石头
/**
* 移除最多的同行或同列石头
* @author: William
* @time:2022-04-14
*/
public class Num947 {
public int removeStones(int[][] stones) {
int sum = stones.length;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(sum);
for(int i = 0; i < sum; i++) {
//j 是 i 下一个石头
for(int j = i + 1; j < sum; j++) {
int x1 = stones[i][0], y1 = stones[i][1];
int x2 = stones[j][0], y2 = stones[j][1];
if(x1 == x2 || y1 == y2) {//处于同行或同列
uf.union(i, j);//粉碎石头
}
}
}
return sum - uf.getCount();
}
class UnionFind{
int count;
int[] parent;
int[] rank;
public UnionFind(int n) {
this.count = n;
this.parent = new int[n];
this.rank = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
this.parent[i] = i;
this.rank[i] = 1;
}
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(x), rootY = find(y);
if(rootX != rootY) {
if(rank[rootX] < rank[rootY]) {
int tmp = rootX;
rootX = rootY;
rootY = tmp;
}
parent[rootY] = rootX;
rank[rootX] += rank[rootY];
count--;
}
}
public int find(int x) {
return parent[x] == x ? x : find(parent[x]);
}
}
}
等式方程的可满足性
/**
* 等式方程的可满足性
* @author: William
* @time:2022-04-11
*/
public class Num990 {
public boolean equationsPossible(String[] equations) {
int[] parent = new int[26];
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
for(String str : equations) {
if(str.charAt(1) == '=') {
int x = str.charAt(0) - 'a';
int y = str.charAt(3) - 'a';
union(parent, x, y);
}
}
for(String str : equations) {
if(str.charAt(1) == '!') {
int x = str.charAt(0) - 'a';
int y = str.charAt(3) - 'a';
//说明连过了
if(find(parent, x) == find(parent, y)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public void union(int[] parent, int x, int y) {
parent[find(parent, x)] = find(parent, y);
}
public int find(int[] parent, int x) {
while(parent[x] != x) {
parent[x] = parent[parent[x]];
x = parent[x];
}
return x;
}
}
结语
并查集对我们来说是一个模板,无论理解还是不理解,都应该在笔试的时候可以快速写出来,很多时候看起来与连接有关的题,找到规律之后都能用并查集快速解出来