学习JavaScript数据结构与算法(七)——散列表(二)
处理散列表中的冲突
有时候,一些键会有相同的散列值。不同的值在散列表中对应相同位置的时候,称其为冲突。
举个例子来看,见如下代码。其中,HashTable类的创建见博客 学习JavaScript数据结构与算法(七)——散列表(一) 。
var hash = new HashTable();
hash.put('Jack', '[email protected]');
hash.put('John', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Ben', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Jim', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Tyrion', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Aaron' ,'[email protected]');
hash.put('Jonathan', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Jamie', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Sue', '[email protected]');
console.log('-------');
hash.print();处理冲突的方法有:分离链接、线性探查和双散列法。
1、分离链接
为散列表的每一个位置创建一个链表并将元素存储在里面。
可以这么简单地理解,一个年级在操场集合,操场上划分不同的区域,每个班占一个区域(位置),而一个班级里人依次排列,就好比是一个链表。
它是解决冲突的最简单的方法,但是它在HashTable实例之外还需要额外的存储空间。
function HashTableSeparateChaining () {
var table = [];
var loseloseHashCode = function(key){
var hash = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 37;
};
/*
ValuePair
辅助类,表示将要加入LinkedList实例的元素。
只会将key和value存储在一个Object实例中。
*/
var ValuePair = function(key, value){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.toString = function(){
return '[' + this.key + ' - ' + this.value + ']';
}
};
/*重写put()、get()、remove()方法*/
this.put = function(key, value){
var position = loseloseHashCode(key);
/*
验证要加入新元素的位置是否已经被占据。
如果这个位置是第一次被加入元素,则在这个位置初始化一个LinkedList实例。
*/
if (table[position] == undefined) {
table[position] = new LinkedList();
}
table[position].append(new ValuePair(key,value));
};
this.get = function(key){
var position = loseloseHashCode(key);
//确定在特定的位置上是否有元素存在
if (table[position] !== undefined) {
var current = table[position].getHead();//遍历之前先获取链表表头的引用
//遍历链表来寻找键/值(从头到尾)
while (current.next) {
if (current.element.key === key) {
return current.element.value;
}
current = current.next;
}
//检查元素在链表第一个或最后一个节点的情况
if (current.element.key === key) {
return current.element.value;
}
}
return undefined;
};
this.remove = function(key){
var position = loseloseHashCode(key);
if (table[position] !== undefined) {
var current = table[position].getHead();
while (current.next) {
if (current.element.key === key) {
table[position].remove(current.element);
//如果链表为空了,就将散列表这个位置的值设为undefined。
if (table[position].isEmpty()) {
table[position] = undefined;
}
return true;
}
current = current.next;
}
//检查是否为第一个或最后一个元素
if (current.element.key === key) {
table[position].remove(current.element);
if (table[position].isEmpty()) {
table[position] = undefined;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
this.print = function() {
for (var i = 0; i < table.length; ++i) {
if (table[i] !== undefined) {
console.log(i + ": " + table[i].toString());
}
}
};
}测试代码:
var hash = new HashTableSeparateChaining();
hash.put('Jack', '[email protected]');
hash.put('John', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Ben', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Jim', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Tyrion', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Aaron' ,'[email protected]');
hash.put('Jonathan', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Jamie', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Sue', '[email protected]');
hash.print();
console.log('-------');
console.log(hash.get('Jack'));
console.log('-------');
hash.remove('John');
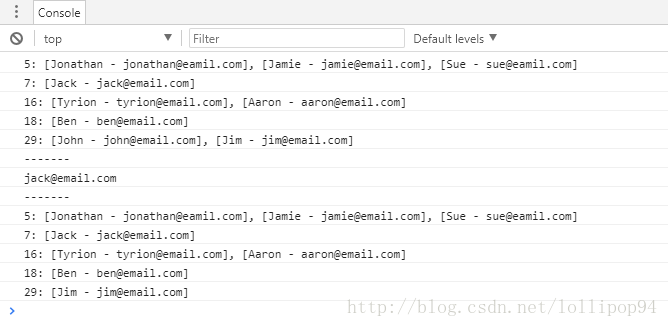
hash.print();测试结果如下:
2、线性探查
当想向表中某个位置加入一个新元素的时候,如果索引为index的位置已经被占据了,就尝试index+1的位置。如果index+1的位置也被占据了,就尝试index—+2的位置。以此类推。
function HashTableLinearProbing () {
var table = [];
var loseloseHashCode = function(key){
var hash = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 37;
};
var ValuePair = function(key, value){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.toString = function(){
return '[' + this.key + ' - ' + this.value + ']';
}
};
this.put = function(key,value){
var position = loseloseHashCode(key);
if (table[position] == undefined) {
table[position] = new ValuePair(key,value);
}
else {
var index = ++position;
while (table[index] != undefined) {
index++;
}
table[index] = new ValuePair(key,value);
}
};
this.get = function(key){
var position = loseloseHashCode(key);
if (table[position] !== undefined) {
if (table[position].key === key) {
return table[position].value;
}
else {
var index = ++position;
while (table[index] === undefined || table[index].key != key) {
index++;
}
if (table[index].key === key) {
return table[index].value;
}
}
}
return undefined;
};
this.remove = function(key){
var position = loseloseHashCode(key);
if (table[position] !== undefined) {
if (table[position].key === key) {
table[position] = undefined;
}
else {
var index = ++position;
while (table[index] === undefined || table[index].key != key) {
index++;
}
if (table[index].key === key) {
table[index] = undefined;
}
}
}
return undefined;
};
this.print = function() {
for (var i = 0; i < table.length; ++i) {
if (table[i] !== undefined) {
console.log(i + ": " + table[i].toString());
}
}
};
}测试代码:
var hash = new HashTableLinearProbing();
hash.put('Jack', '[email protected]');
hash.put('John', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Ben', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Jim', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Tyrion', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Aaron' ,'[email protected]');
hash.put('Jonathan', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Jamie', '[email protected]');
hash.put('Sue', '[email protected]');
hash.print();
console.log('-------');
console.log(hash.get('Jack'));
console.log('-------');
hash.remove('John');
hash.print();测试结果如下:
3、双散列法
事先准备多个散列函数。每当发生散列地址冲突时,就换一个散列函数计算,直到把冲突解决。
这种方法使得关键字不产生聚集,也增加了计算的时间。
创建更好的散列函数
在上面实现的“lose lose”散列函数不是一个表现良好的散列函数,因为它会产生很多的冲突。
一个表现良好的散列函数由以下几个方面构成:
插入和检索元素的时间(即性能),较低的冲突可能性。
下面来创建一个更好的散列函数djb2:
var djb2HashCode = function(key){
//初始化一个hash变量并赋为一个质数
var hash = 5381;//大多实现使用5381
//迭代参数key
for (var i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
//将hash与33相乘(用来当作一个魔力数),并和当前迭代到的字符的ASCII码值相加
hash = hash *33 + key.charCodeAt(i);
}
//使用相加的和与另一个随机质数相除的余数
//随机质数比我们认为的散列表的大小要大
//本例中,我们认为散列表大小为1000
return hash % 1013;
};用之前冲突的那个例子做测试,会发现输出的结果显示没有冲突。
这并不是最好的散列函数,但这是最被社区推荐的散列函数之一。