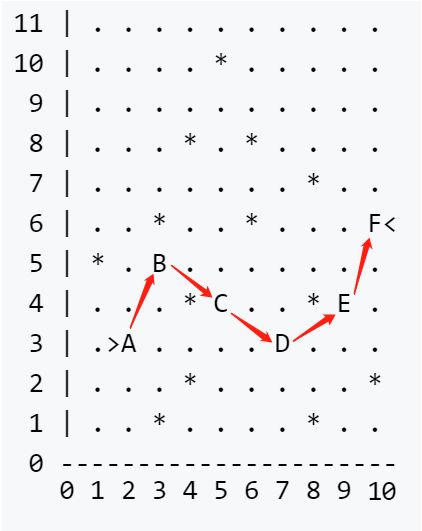
《算法从入门到入土系列》第一集 搜索专题(DFS与BFS)题目解析 + 练习题单(更新ing)
搜索专题(DFS与BFS) 从入门到入土 题目解析 + 练习题单
- 菜鸡笔记,莫怪
-
- 搜索
- BFS
-
-
- AcWing 844. 走迷宫
- POJ 1426 "Find The Multiple"(待更新)
- POJ 3126 "Prime Path"(待更新)
- POJ 3414 Pots
- HDU1240 Asteroids! (daige)
- Flood Fill 算法
-
- AcWing 1097. 池塘计数
- AcWing 1098. 城堡问题
- AcWing 1106. 山峰和山谷
- 最短路模型
-
- AcWing 1076. 迷宫问题(单源最短路)(二维)
- POJ 2251 Dungeon Master (三维迷宫问题)
- AcWing 188. 武士风度的牛
- LUOGU P1443 马的遍历
- POJ 3278 "Catch That Cow"
- 多源BFS
-
- AcWing 173. 矩阵距离
- 最小步数模型
-
- AcWing 1107. 魔板
- 双端队列广搜
-
- AcWing 175. 电路维修
- 双向广搜
-
- HDOJ 3085 Nightmare Ⅱ(待更新)
- AcWing 190. 字符变换(代码待更新)
- A*算法(待更新)
-
- AcWing 178. 第K短路
- AcWing 179. 八数码
-
- DFS
- DFS例题
-
-
- 牛客小白月赛15 E.小雨的矩阵
- 八皇后问题(DFS经典问题)
- DFS之连通性模型
-
- AcWing 1112. 迷宫
- Luogu P1605 迷宫
- AcWing 1113. 红与黑
- Luogu P1101 单词方阵
- DFS之搜索顺序
-
- AcWing 1116. 马走日
- AcWing 1117. 单词接龙
- AcWing 1118. 分成互质组(待更新)
- DFS之剪枝与优化
-
- AcWing 165. 小猫爬山
- AcWing 166. 数独 (代码有点复杂,等写一下注释再上传)
- AcWing 167. 木棒
- AcWing 168. 生日蛋糕(待更新)
- 迭代加深
-
- AcWing 170. 加成序列
- 双向DFS
-
- AcWing 171. 送礼物
- IDA*(待更新)
-
- AcWing 180. 排书
- AcWing 181. 回转游戏
- HDU 1560 "DNA sequence"
- HDU 1667 "The Rotation Game"
-
菜鸡笔记,莫怪
蓝桥杯将近,DFS和BFS作为省赛常考的类型,这里整理一下常见的搜索的题型。(学习交流,比较菜,有什么不对的地方,请批评指正 !!!)
稍后逐渐每一份代码会补上 Java代码(我报了Java组的蓝桥杯 希望这次别翻车)
(部分未完成,稍后补上)
搜索
BFS使用队列实现:先将初始状态加入到空的队列中,然后每次取出队首元素,找出队首所能转移到的状态,再将其压入队列中;如此反复,知道队列为空,这样就能保证一个状态再被访问的时候一定是采用的最短路径:
BFS的一般形式:
queue<type> q;
q.push(初始状态);//将初始状态入队
while (!q.empty()) {
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (枚举所有可扩展状态) //找到t的所有可达状态v
if (合法) //v需要满足某些条件,例如,未越界,未被访问过等等
//入队(同时可能需要维护某些信息,例如,维护当前状态是由哪个状态转移过来的,记录路径)
q.push(v);
}
BFS
AcWing 844. 走迷宫
链接:Click here~~
题解:搜索每一个点,以当前点向四周搜索,判断可搜索条件,记录当前点到起点的距离,第一次搜到终点的路径就是最短路径。
#includePOJ 1426 “Find The Multiple”(待更新)
POJ 3126 “Prime Path”(待更新)
POJ 3414 Pots
HDU1240 Asteroids! (daige)
Flood Fill 算法
AcWing 1097. 池塘计数
链接:Click here~~
题意:有一篇N*M的矩形土地,其中 ‘W’ 表示水,’.’ 表示空地,一个水洼,一片连通的水,这个题是八连通,要求统计有多少片水洼。
(连通分两种,一种是四连通,一种是八连通)
解法:一个点一个点的扫描,当扫描到一片水也就是’W’时且这个’W’还没有被标记过,就以当前点为起点进行一次BFS(flood fill),将与当前点连通的地图打标记,最后进行了几次BFS(flood fill)就是有几个连通块。也就是水洼的个数
BFS解法(数组模拟队列):
//Flood Fill
//这里可以开标记数组 bool st[N][N];也可以把走过的 W 改成 . 即可
#includeBFS解法(STL队列):
#includeJava代码
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class pair{
int x, y;
public pair(int x, int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public class Main {
static int N = 1010, n, m;
static char[][] g;
public static void bfs(int xx, int yy) {
Queue<pair> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new pair(xx, yy));
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
pair t = q.poll();
for (int i = t.x - 1; i <= t.x + 1; i++) {
for (int j = t.y - 1; j <= t.y + 1; j++) {
if (i == t.x && j == t.y) continue;
if (i < 0 || i >= n || j < 0 || j >= m) continue;
if (g[i][j] == '.') continue;
q.offer(new pair(i, j));
g[i][j] = '.';
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] cur = in.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(cur[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(cur[1]);
g = new char[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char[] arr = in.readLine().toCharArray();
g[i] = arr;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (g[i][j] == '.') continue;
bfs(i, j);
ans++;
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
DFS 解法:
#includeAcWing 1098. 城堡问题
链接:Click here~~
题意:编写一个程序,计算城堡共有多少个房间 和 最大房间的面积(方块)
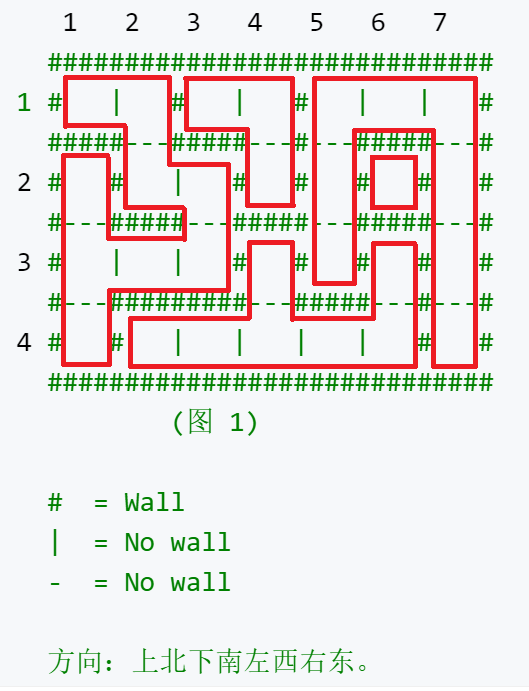
房间的个数如红色框框所示
题解:遍历每个点,用flood fill,
方向:左上右下,对应 1 2 4 8
int dx[4] = {0, -1, 0, 1}, dy[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
g[t.x][t.y] >> i && 1的结果,刚好对应四个方向1 2 4 8
BFS解法(数组模拟队列)
#includeBFS解法 STL队列
#includeAcWing 1106. 山峰和山谷
链接:Click here~~
八连通
山峰:只要周围没有比它高的
山谷:只要周围没有比它低的
如果周围有比它高也有比它低的就 既不是山峰也不是山谷
如果全部高度一样,那么就 既是山峰也是山谷
解法:在做Flood Fill的时候,判断当前格子和它周围格子的关系,在往外扩展的时候,判断一下扩展的格子,如果不属于当前连通块的话,就标记一下这个格子是比当前格子高还是矮。根据这个条件判断出来,每个连通区域是山峰还是山谷
#include最短路模型
当所有边的权重相等的时候,用bfs从起点开始搜,当第一次搜索到的时候,这个路径就是最短路,称作(单源最短路)
AcWing 1076. 迷宫问题(单源最短路)(二维)
链接:Click here~~
题解:找到一条最短路径,从(0,0)到(n-1,n-1),简单的一个bfs
#includePOJ 2251 Dungeon Master (三维迷宫问题)
#includeAcWing 188. 武士风度的牛
链接:Click here~~
题意:这个牛可以跟中国象棋里面的马相同走法,K为起点,H为终点,问从K跳到H,至少需要跳多少次。
路径是:A->B->C->D->E->F,总共五步
#includeLUOGU P1443 马的遍历
链接:Click here~~
题意:有一个 n × m n×m n×m 的棋盘 1 < n , m ≤ 400 1
题解:
最短路模型的模板题,BFS第一次走到的就是最短路径
#includePOJ 3278 “Catch That Cow”
多源BFS
适用于有多个起点的搜索题。
AcWing 173. 矩阵距离
链接:Click here~~
题意:给一个n行m列的01矩阵,求出每个点到1的最近曼哈顿距离(行+列)。
将所有源点加入到队列,求出所有多源起点到所有点的最短距离,多源BFS跟普通的BFS相比,区别只是,刚开始需要将所有的起点先放到队列里面去,然后后面就跟普通的BFS相同即可。
如果给出的01矩阵是
0 0 0 1
0 0 1 1
0 1 1 0
最终的结果是:
3 2 1 0
2 1 0 0
1 0 0 1
#include最小步数模型
假设对棋盘进行操作,把每一个棋盘,看成一个状态,对棋盘进行操作,操作完后变成一个新的棋盘,求当前棋盘变成目标棋盘所需要的最小步数。
最小步数模型 VS 最短路模型
最短路模型:在棋盘内部去搜索路线。
最小步数模型:把棋盘看成一个点,求至少要进行多少步操作,让这个点变成另一种点。
AcWing 1107. 魔板
链接:Click here~~
从一种状态到另一种状态的最小转化步数就是最小步数模型
pre 来记录当前状态的前置状态
看看题目,主要是这3个操作看起来比较复杂,其实题目挺简单的,注意一下字典序指的是: ABC 这个顺序
#include
unordered_map<string, pair<char, string>> pre;
queue<string> q;
string start = "12345678";
//将字符串放进 2 ×4的矩阵中
void set(string k) {
//将前 4个数字放进 2 × 4 的矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) g[0][i] = k[i];
//将后 4个数字放进 2 × 4 的矩阵
for (int i = 3, j = 4; i >= 0; i--, j++ ) g[1][i] = k[j];
}
//将2 × 4矩阵转成字符串
string get() {
string res;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) res += g[0][i];
for (int i = 3; i >= 0; i--) res += g[1][i];
return res;
}
//执行A操作
string turnA(string k) {
set(k);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) swap(g[0][i], g[1][i]);
return get();
}
//执行B操作
string turnB(string k) {
set(k);
char v0 = g[0][3], v1 = g[1][3];
g[0][3] = g[0][2];
g[0][2] = g[0][1];
g[0][1] = g[0][0];
g[0][0] = v0;
g[1][3] = g[1][2];
g[1][2] = g[1][1];
g[1][1] = g[1][0];
g[1][0] = v1;
return get();
}
//执行C操作
string turnC(string k) {
set(k);
char v = g[0][1];
g[0][1] = g[1][1];
g[1][1] = g[1][2];
g[1][2] = g[0][2];
g[0][2] = v;
return get();
}
void bfs(string end) {
if (start == end) return;
q.push(start);
dist[start] = 0;
while (q.size()) {
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
string m[3];
m[0] = turnA(t);
m[1] = turnB(t);
m[2] = turnC(t);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i ++) {
if (!dist.count(m[i])) {
string str = m[i];
dist[str] = dist[t] + 1;
pre[str] = {'A' + i, t};
q.push(str);
if (str == end) return;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int x;
string end;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i ++) {
cin >> x;
end += char(x + '0');
}
bfs(end);
cout << dist[end] << endl;
string res;
while (end != start) {
res += pre[end].first;
end = pre[end].second;
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
if (res.size()) cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
双端队列广搜
要求最小值,不能只在队尾插入,还需要在队首插入
AcWing 175. 电路维修
链接:Click here~~
双向广搜
BFS可以想象成在一个平静的池塘丢一颗石头,波浪一层一层的向外扩散,直到搜到目标,第一次搜到目标的路径就是最优路径。那么如果同时在起点和终点同时丢一颗石头,两颗石头产生的波浪都向对方扩散,在某个位置中相遇,此时得到了最优路径。
从数据上看:
假设单向BFS的数据是: 6 10 = 60466176 6^{10} = 60466176 610=60466176
则双向BFS的数据则是: 2 × 6 5 = 15552 2×6^5 = 15552 2×65=15552
一般双向BFS解决的问题是在最小步数模型里面。
在最短路模型和Flood Fill里面一般用不到,因为在这两种模型中,搜到的点一般不大,因此直接搜也是可以的
在最小步数模型,整个状态空间数量一般是指数级别的,用双向广搜可极大提升效率
####HDU 1401. Solitaire (待更新)
题意:有一个8 × 8的棋盘,上面有4颗棋子,棋子可以上下左右移动。给定一个初始状态
HDOJ 3085 Nightmare Ⅱ(待更新)
AcWing 190. 字符变换(代码待更新)
题意:给出两个字串A、B和字符变换规则(至多6个)其中( A 1 → B 1 A_1→B_1 A1→B1 表示在A中子串 A 1 A_1 A1 可以变成 B 1 B_1 B1)
例子:
A1 = "abcd" B1 = "xyz"
规则:
Ⅰ. abc → xu
Ⅱ. ud → y
Ⅲ. y → yz
则abcd → xud → xy → xyz
要求:在10步内,求A变成B,输出最少变换次数
最坏的情况下:如果用一般的BFS 20(起点) × 6(变换规则) → 变换10次 $ (20 × 6)^{10}$
所以如果用一般的BFS会容易TLE
A*算法(待更新)
A ∗ A* A∗算法也是一种在图中求解最短路径问题的算法,由Dijkstra算法发展而来,Dijkstra算法会从离起点近的顶点开始,按顺序求出起点到各个顶点的最短路径。也就是说,一些离终点较远的顶点的最短路径也会被计算出来,但这部分其实是无用的。与之不同, A ∗ A* A∗ 就会先估算一个值(从起点到终点的距离)并利用这个值省去一些无用的计算。
AcWing 178. 第K短路
AcWing 179. 八数码
DFS
DFS —— 不撞南墙不回溯 —— 死脑筋
| DFS | BFS |
|---|---|
| stack(栈) | queue(队列) |
| O ( h ) O(h) O(h) | O ( 2 h ) O(2^h) O(2h) |
| 不具有最短路性质 | 具有最短路性质 |
DFS例题
给定一个整数n,将数字1~n排成一排,将会有很多种排列方法。
现在,请你按照字典序将所有的排列方法输出。
输入格式
共一行,包含一个整数n。
输出格式
按字典序输出所有排列方案,每个方案占一行。
数据范围
1 ≤ n ≤ 7 1≤n≤7 1≤n≤7
输入样例:
3
输出样例:
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 1 3
2 3 1
3 1 2
3 2 1

DFS的路线图:
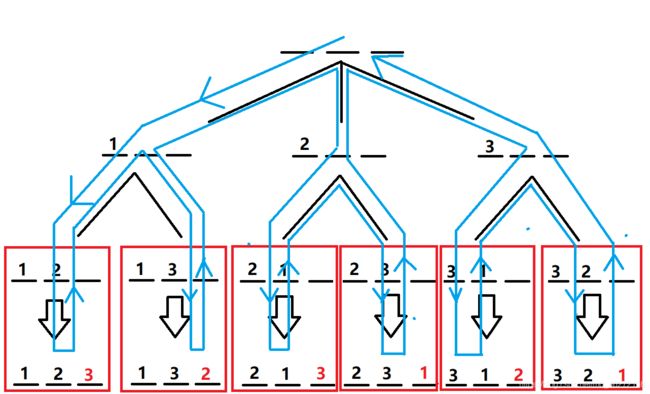
我们不需要存这个树,每次深搜走到底就是一条路线。
回溯的过程中需要注意:恢复原样。
代码(爆搜):
C++代码实现
#includeJava代码实现
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int n;
static int[] path;//保存路径
static boolean[] flag;//打标记
//u代表层数,u == n的时候就是叶节点
public static void dfs(int u) {
if (u == n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(path[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
//如果这个数没有被用过
if (!flag[i]) {
path[u] = i;//填写i
flag[i] = true;
dfs(u + 1);//进入到下一层递归,递归函数之后记得要恢复原状
flag[i] = false;//回溯之后需要恢复原样
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
path = new int[n];
flag = new boolean[n + 1];
// long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
dfs(0);
// long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// System.out.println("运行时间:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
}
牛客小白月赛15 E.小雨的矩阵

题解:爆搜求从起点到终点有多少种路径和。
开一个st数组存储当前路径的点权和是否已经存在。
#include在这里插入代码片
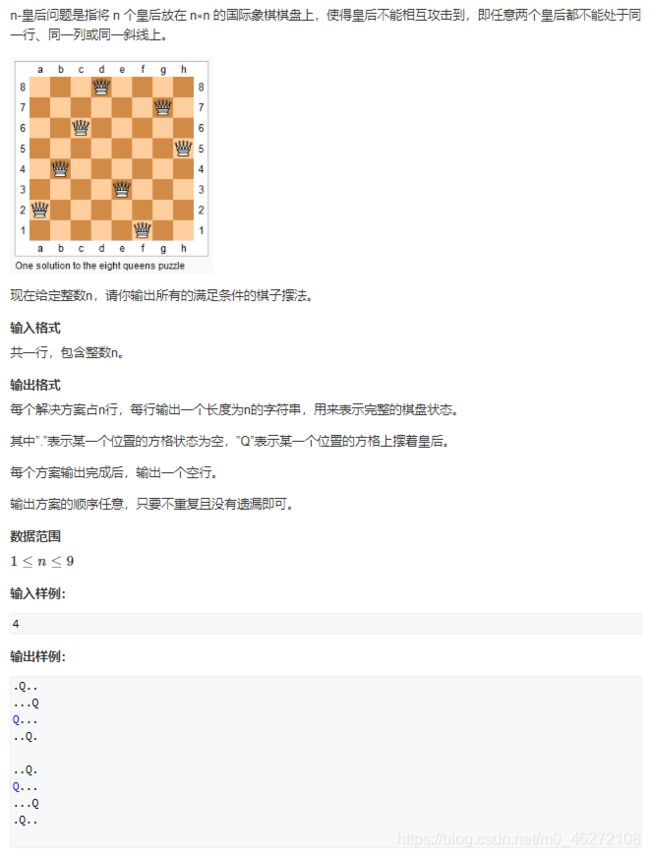
八皇后问题(DFS经典问题)
第一种搜索方式 (全排列思想):
#include第二种搜索方式 :
#includeDFS之连通性模型
AcWing 1112. 迷宫
链接:Click here~~
做一个简单的DFS
#includeLuogu P1605 迷宫
链接:Click here~~
题解:四连通,建图,先将所有的点初始化为1,如果是障碍的话,就把当前障碍的点改为0,然后做一个简单的DFS。
#includeAcWing 1113. 红与黑
链接:Click here~~
#includeLuogu P1101 单词方阵
链接:Click here~~
连通性的一个问题,在第11届蓝桥杯(省赛)也有一个搜索2020的个数,这个是搜索 “yizhong” 这个字符串的个数,并输出相应位置。
#includeDFS之搜索顺序
搜索变量的两个经典顺序:
- 每次枚举当前剩余选择最少的变量(每次)
- 每次枚举对后面影响最大的变量(出现在最多的未被满足的约束里)
- 具体问题具体分析。
AcWing 1116. 马走日
链接:Click here~~
注意方向数组要满足马走日的坐标即可,也是一个简单的DFS而已
#includeAcWing 1117. 单词接龙
链接:Click here~~
#includeAcWing 1118. 分成互质组(待更新)
DFS之剪枝与优化
剪枝:在搜索的过程中,可以通过某种条件判断,当前节点所在的子树均不满足要求,便可以不再往下搜索。
剪枝通常比较难估算时间复杂度,因为每一种情况的剪枝都有可能不同。
- 优化搜索顺序:大部分情况下,优先搜索分支较少的节点
- 排除等效冗余
- 可行性剪枝
- 最优性剪枝
AcWing 165. 小猫爬山
链接:Click here~~
- 优化搜索顺序:分支较少的节点,限定了缆车的承重,先放重的猫,分支少。
- 排除等效冗余:无冗余
- 可行性剪枝:选择这个分支,当前这个格子枚举的数字,不能与所在的行,所在的列,所在的九宫格,有重复。
- 最优性剪枝:无,因为本体是找可行性方案,不是找最优方案。
#includeAcWing 166. 数独 (代码有点复杂,等写一下注释再上传)
链接:Click here~~
首先考虑爆搜解题过程:随意选择空格子,填数,选取合适的方案
剪枝优化:
- 优化搜索顺序:分支较少的节点,选择分支最少的格子,例:如果当前格子能填 1~9任何一个数字,另一个格子能填1、2两个数字,那么自然是先选后者,这样子形成的分支会少。
- 排除等效冗余:一个个放的话,不会产生等效冗余
- 可行性剪枝:在当前各自枚举数字,判断不能与所在行,所在列,所在九宫格内已有的数字相同
- 最优性剪枝:本题因为是求可行性方案,不是求最优性方案,所以没有最优性剪枝。
本题有个特殊的位运算优化:
行:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
列:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
九宫格:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
用二进制来表示当前数字是否已经存在,0表示这个数已经存在,1表示不存在。所以用0~511的二进制数,存储行,列,九宫格已经存在数字的情况。
只有在 行[i]&列[i]&九宫格[i]==1 这个位置就能放这个数字。
在枚举可选数字的时候,如果正常枚举1~9,需要循环9次,可以用 lowbit() 在取二进制数中的最后一个数字,这样当前状态下,有多少个1,就需要循环多少次。 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 只需要循环4次。
AcWing 167. 木棒
链接:Click here~~
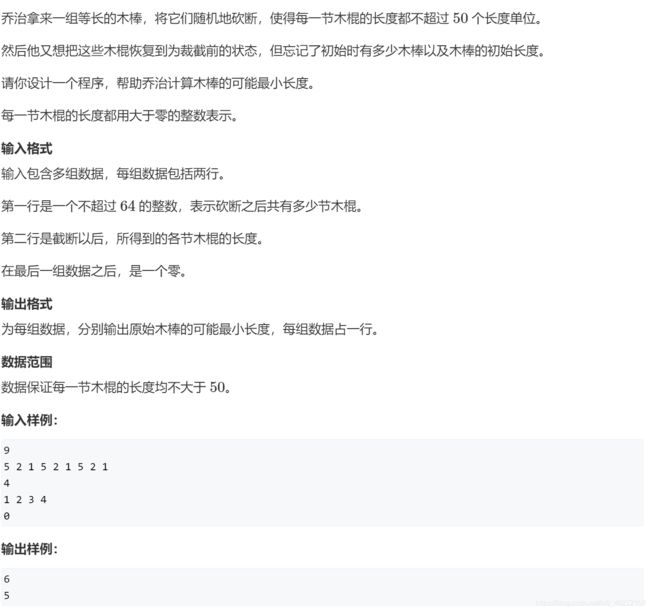
样例:5 2 1 5 2 1 5 2 1
分成4组
5 1
5 1
5 1
2 2 2
长度是6
定义:
木棒:一组等长的木棒
木棍:砍断之后的(题目中输入的数据)
搜索顺序:从前往后依次拼接,一次枚举每根木棒是怎么拼出来的(每根木棒是由哪些木棍拼出来的)将木棒内部木棍排个序,以组合数的形式来枚举木棍(木棍内部顺序是无所谓的,保证总和相等即可)
对于固定长度,如果恰好把所有木棍拼成当前枚举的这个长度,则将此称为合法方案
剪枝:
枚举长度:len
满足:len|sum ,sum一定是len的倍数,只枚举sum的约数即可。
搜索顺序的优化:
先找分支较少的,先枚举较长的木棍
枚举方式: 按组合(不考虑内部顺序)方式枚举,而不是排列(考虑内部顺序)
传一个参数: 表示下一个数的下标从哪个数开始枚举,保证从小到大枚举。
排除等效冗余: (证明如下)
- 如果当前枚举的木棍失败,那么与当前木棍长度相同的木棍直接忽略。
- 如果是木棒的第一根木棒拼接失败,则一定失败,直接回溯
- 如果是木棒的最后一根木棒拼接失败,则一定失败,直接回溯
#includeAcWing 168. 生日蛋糕(待更新)
迭代加深
概念:迭代加深搜索,实质上就是限定下界的深度优先搜索。即首先允许深度优先搜索K层搜索树,如果没有发现有解4,再将K+1层加入搜索范围,重复执行以上步骤,直至搜到解为止。
解决的问题一般是:搜索树可能很深,但是答案在很浅的位置。
迭代加深是一层层搜的,有点类似BFS
但是迭代加深算法其实是结合了DFS和BFS算法特点的搜索算法。在搜索之前会预设搜索的层数,然后在该层数以内进行DFS,这样子就规避了DFS可能出现的效率低下的问题。
迭代加深也可以说是有条件的DFS,DFS本来是循着一条路一直走下去,直到找到答案或者到叶节点了才会回头,但是这样即使找到答案有可能不是最优,也不是最快的, 甚至有可能会T,尤其是SPJ的题,就很容易T。因此在搜索之前会预设搜索的层数,然后在该层数以内进行DFS,所以适用于当答案处于深度不深的层次时使用。
那么迭代加深相比于BFS好在哪呢?
BFS的空间复杂度是:指数级别的(比较浪费空间)
而迭代加深本质上还是DFS,只会记录某一条路径上的信息,所以是 O ( h ) O(h) O(h) 的
那么会不会时间比较长呢?
无容置疑是会的。
迭代加深,假设答案在第3层:
第一次会搜第一层, 第二次会搜第一层和第二层,第三次会搜第一层,第二层,第三层, 前面的节点会被重复搜索。
从实际应用上,迭代加深搜索的效果比较好,并不比BFS慢很多,但是空间复杂度却与BFS相比小很多,在一些层次遍历的题目中,迭代加深也是一种解决的好办法。
AcWing 170. 加成序列
题意:
加成序列:满足这四个条件的序列a被称为“加成序列”:
- a[1] = 1
- a[m] = n
- a[1] < a[2] < a[3] < … < a[m-1] < a[m]
- 对于每个 k ( 2 ≤ k ≤ m ) k(2≤k≤m) k(2≤k≤m) 都存在两个整数 i i i 和 j j j ( 1 ≤ i , j ≤ k − 1 ) (1≤i,j≤k-1) (1≤i,j≤k−1) ,使得 a[k] = a[i] + a[j];
题目要求:给定一个整数n,找出符合上述条件的长度m最小的 “加成序列”,答案不唯一,任意输出一个即可。
剪枝1:搜索顺序 —— 优先枚举较大的数
剪枝2:排除等效冗余
在枚举前两个数的和的时候,假设前面有5个数,那么有 C 5 2 + 5 C_5^2 + 5 C52+5 种选择(5表示, i i i 和 j j j 可以相等,可以同时为一个相同的数)。所以在搜索当前层的数时,搜索过的数不会再搜,用布尔数组st存储在该层该数是否被搜过
但是迭代加深的代码还是比较短的:
#include双向DFS
比只用单向DFS好的原理:和BFS一样
优化原理:用空间换时间
AcWing 171. 送礼物
链接:Click here~~
- 将所有物品按重量从大到小排序
- 先将前K件物品能凑出的所有重量达标。然后排序并判重
- 搜许哦剩下的N-K件物品的选择方式,然在表中二分出不超过W的最大值。
用空间换时间
分成两段来做dfs
#includeIDA*(待更新)
IDA* 指的是:通过估算下界提前剪枝优化后的算法。
IDA* 是以迭代加深DFS的搜索框架为基础,则立即从当前分支回溯
IDA* 还有另外一个名字(迭代加深的A*算法)
把原来简单的深度限制加强为:
若当前深度+未来估计步数>深度限制,则立即从当前分支回溯
AcWing 180. 排书
AcWing 181. 回转游戏
HDU 1560 “DNA sequence”
HDU 1667 “The Rotation Game”
现文约3万字,更新ing