【数据结构】万字详解7种排序算法-图+示例代码+简单理解(中文版)
前言
笔者在撰写的时候为了方便最先写的是英文版,因此个人认为英文版本相较于中文版本更为完整通畅,有时间的同学可以移步英文版去看看。不过中文版也是很用心重写了的!
总结
| 名称 | 最佳时间复杂度 | 最差时间复杂度 | 平均时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 | 是否稳定 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 归并排序 Merge Sort | O(n*log(n)) | O(n*log(n)) | O(n*log(n)) | O(n) | 是 |
| 冒泡排序 Bubble Sort | O(n) | O(n**2) | O(n**2) | O(1) | 是 |
| 插入排序 Insertion Sort | O(n) | O(n**2) | O(n**2) | O(1) | 是 |
| 选择排序 Selection Sort | O(n**2) | O(n**2) | O(n**2) | O(1) | 否 |
| 希尔排序 Shell Sort | O(n) | O(n**1.3) | O(n**2) | O(1) | 否 |
| 堆排序 Heap Sort | O(n*log(n)) | O(n*log(n)) | O(n*log(n)) | O(1) | 否 |
| 快速排序 Quick Sort | O(n*log(n)) | O(n*log(n)) | O(n**2) | O(log(n))~O(n) | 否 |
1 归并排序 Merge Sort
1.1 定义
一种分而治之的算法。它递归地将数组分成两半,对每一小半进行排序,然后合并排序后的两半。
1.2 简单理解
假设你有一堆编号的扑克牌,你想把它们按从小到大的顺序排列。但是,你一次只能比较两张牌。所以,你要做的是:
1.分而治之: 将大牌堆划分为两个小牌堆,再分别将每个小牌堆分为两个更小的牌堆,以此类推,直到你划出来的所有小牌堆只包含一张牌。
比如你手上有卡片: 5, 3, 7, 2, 8, 4 .
分割 到这样停下: (5, 3), (7, 2), (8, 4).
2.对每一堆进行排序:上一步已经拆整为一,接下来我们要合一为整。
先将最小的牌堆排好序。
选出小牌堆: (3, 5), (2, 7), (4, 8).
3.将它们组合起来:从有序的2×1数列合成有序的4×1数列,再将有序的4×1数列组合合成有序的8×1数列…以此类推,直至数列所有的数都被囊括进最后合成的大数列中。
单位组合:(2, 3, 5, 7), (4, 8).
重复直到完全组合:(2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8).
1.3 Java代码实现
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7};
System.out.println("Original array:");
printArray(array);
mergeSort(array);
System.out.println("\nSorted array:");
printArray(array);
}
// 归并排序
public static void mergeSort(int[] array) {
int n = array.length;
if (n > 1) {
int mid = n / 2;
int[] leftArray = new int[mid];
int[] rightArray = new int[n - mid];
// Copy data to temporary arrays leftArray[] and rightArray[]
System.arraycopy(array, 0, leftArray, 0, mid);
System.arraycopy(array, mid, rightArray, 0, n - mid);
// Recursively sort the two halves
mergeSort(leftArray);
mergeSort(rightArray);
// Merge the sorted halves
merge(array, leftArray, rightArray);
}
}
// 合并两个子数列
public static void merge(int[] array, int[] leftArray, int[] rightArray) {
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
// Merge elements back into the original array in sorted order
while (i < leftArray.length && j < rightArray.length) {
if (leftArray[i] <= rightArray[j]) {
array[k] = leftArray[i];
i++;
} else {
array[k] = rightArray[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
// 复制leftArray[]剩下的元素
while (i < leftArray.length) {
array[k] = leftArray[i];
i++;
k++;
}
// 复制rightArray[]剩下的元素
while (j < rightArray.length) {
array[k] = rightArray[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
// 打印数列
public static void printArray(int[] array) {
for (int value : array) {
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
1.4 gif帮助理解
ps : gif转载自https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/merge-sort.html.
如侵权,请联系我删除。
1.5 优势和缺点
(总测试次数=5)
通过观察图,我们可以粗略地得知:当数据量很小时,归并排序大体上呈线性增加的趋势。但当数据规模超过某个阈值时,时间反而会减少。因此,有庞大的数据集时,归并排序是一个不错的选择。
优势
- 稳定高效,时间复杂度为O(n log n)。
- 非常适合链表。
缺点
- 需要为归并腾出额外的空间
- 相比冒泡排序或选择排序更为复杂.
代码实现
由于归并排序算法的递归性质,实现它的代码往往较长,通常在50-70行左右。
2 冒泡排序 Bubble Sort
2.1 定义
重复遍历列表,比较相邻的元素,如果他们的顺序错误就把他们交换过来。该算法之所以得名,是因为较小的元素会“冒泡”到列表的顶部。
2.2 简单理解
想象一下,你想把一队孩子按身高从矮到高排成一行。
于是,从排头开始,你将比较每个孩子和他旁边的孩子的身高。如果一个较矮的孩子站在较高的孩子右侧,交换他们的位置。一直这样做,直到排尾。
在第一次遍历后,最高的孩子一定在排尾。
同理,第二次遍历后,第二高的孩子一定在排尾左侧。
继续这个过程,在数次循环后个子最矮的孩子也“冒泡”到了正确的位置,排序终止。
2.3 Java代码实现
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};
System.out.println("Original array:");
printArray(array);
bubbleSort(array);
System.out.println("\nSorted array:");
printArray(array);
}
public static void bubbleSort(int[] array) {
int n = array.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// Swap if the element found is greater than the next element
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
public static void printArray(int[] array) {
for (int value : array) {
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
2.4 gif帮助理解
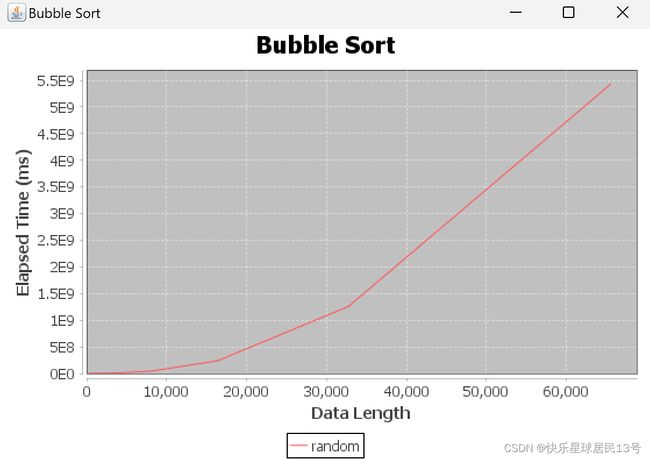
2.5 优势和缺点
优势
- 便于实现.
- 适合小规模数据集和排好序的数据集.
缺点
- 对于大数据集很不便捷 (时间复杂度:O(n^2) ).
- 不稳定,不具有多适用性.
代码实现 20-30行就可以,短小精悍。
3 插入排序 Insertion Sort
3.1 定义
通过构建有序序列,对于未排序数据,在已排序序列中从后向前扫描,找到相应位置并插入。
3.2 Implemented Java Code
public class InsertionSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6};
System.out.println("Original array:");
printArray(array);
insertionSort(array);
System.out.println("\nSorted array:");
printArray(array);
}
// Function to perform insertion sort
static void insertionSort(int[] array) {
int n = array.length;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int key = array[i];
int j = i - 1;
// Move elements of array[0..i-1] that are greater than key to one position ahead of their current position
while (j >= 0 && array[j] > key) {
array[j + 1] = array[j];
j = j - 1;
}
array[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// Utility function to print an array
static void printArray(int[] array) {
int n = array.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
3.3 gif帮助理解
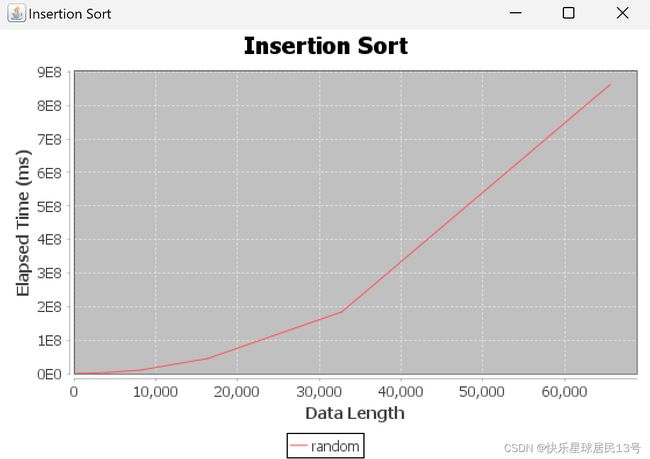
3.4 优势和缺点
优势
-
实现简单 插入排序很容易实现,对于小数据集或部分排序的数据集来说是一个很好的选择。
-
适用小数据集 对于小数据集或几乎排好序的数据集,插入排序可能比一些更复杂的算法更有效。
-
就地排序 它只需要固定数量的额外内存空间。
-
在线算法 它可以一边接收数据一边排序列表,即数据是实时的。
缺点
-
大数据集的低效率 插入排序的时间复杂度为O(n^2),其中n是数组中元素的数量。与合并排序或快速排序等更高级的算法相比,这使得它在处理大型数据集时效率低下,这些算法具有更好的平均和最坏情况时间复杂度。
-
对初始顺序敏感 插入排序的效率高度依赖于元素的初始顺序。如果数组大部分是有序的,则插入排序执行得很好,但对于完全未排序的数据,它可能效率很低。
-
不具有适应性 插入排序不能很好地适应输入数据的变化。如果输入数据发生变化,算法可能无法利用现有的顺序,而必须从头开始。
-
不稳定
代码实现 相对简短和简洁。它由大约30行代码组成,包括注释和空格。该算法的简单性有助于实现的简洁性。
4 选择排序 Selection Sort
4.1 定义
一个简单的排序算法,通过将输入数组划分为已排序和未排序的区域来工作。该算法反复从未排序区域中找到最小(或最大,取决于排序顺序)元素,并将其与未排序区域的第一个元素交换。这个过程一直重复,直到整个数组排序完毕。
4.2 简单理解
1.划分数组 : 将数组划分为已排序和未排序两个区域。最初,排序区域为空,整个数组位于未排序区域。
2.查找最小元素 :遍历未排序区域以查找最小元素。
3.与未排序区域的第一个元素交换 :将找到的最小元素与未排序区域的第一个元素交换。这有效地将最小元素添加到排序区域的末尾。
4.扩展已排序区域 :扩展已排序区域以包含新添加的最小元素。
5.重复 : 重复步骤2-4,直到整个数组被排序。未排序区域缩小,排序区域扩大,直到包含整个数组。
4.3 Java代码实现
public class SelectionSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {64, 25, 12, 22, 11};
System.out.println("Original array:");
printArray(array);
selectionSort(array);
System.out.println("\nSorted array:");
printArray(array);
}
// Function to perform selection sort
static void selectionSort(int[] array) {
int n = array.length;
// One by one move the boundary of the unsorted subarray
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
// Find the minimum element in the unsorted array
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (array[j] < array[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
// Swap the found minimum element with the first element
int temp = array[minIndex];
array[minIndex] = array[i];
array[i] = temp;
}
}
// Utility function to print an array
static void printArray(int[] array) {
int n = array.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
4.4 gif帮助理解
4.4 优势和缺点
优势
- 简单易懂。
- 就地排序。
缺点
- 对于大型数据集效率低下(时间复杂度:O(n^2))。
- 不适应或不稳定的。
代码实现 大约20-30行。
5 希尔排序 Shell Sort
5.1 定义
插入排序的一种优化方法。它首先对彼此相距很远的元素对进行排序,然后逐步缩小要比较的元素之间的间隔。最后一次迭代使用1的间隔,本质上是执行插入排序。
5.2 简单理解
1.从大步长开始
譬如,你有:5,2,9,1,5,6
选定步长 = 2 :5,2,9,1,5,6
经过排序后数组为:5,2,5,1,9,6
2.缩小步长
将步长缩小为1:5,2,5,1,9,6
经过排序后数组为:2,1,5,6,9,5
3.更小的步长
将步长缩小到1:2,1,5,6,9,5
经过排序后数组为: 1,2,5,5,6,9 。排序完毕。
5.3 Java代码实现
public class ShellSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};
System.out.println("Original array:");
printArray(array);
shellSort(array);
System.out.println("\nSorted array:");
printArray(array);
}
public static void shellSort(int[] array) {
int n = array.length;
// Start with a big gap, then reduce the gap
for (int gap = n / 2; gap > 0; gap /= 2) {
// Do a gapped insertion sort for this gap size
for (int i = gap; i < n; i++) {
int temp = array[i];
int j;
for (j = i; j >= gap && array[j - gap] > temp; j -= gap) {
array[j] = array[j - gap];
}
array[j] = temp;
}
}
}
public static void printArray(int[] array) {
for (int value : array) {
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
5.4 gif帮助理解
5.5 优势和缺点
优势
- 是插入排序的改良,针对更大的数据集进行了改进。
- 对于中等规模的数据集,优于插入排序。
缺点
- 不如快速排序或归并排序等高级算法高效。
- 比冒泡排序或选择排序更复杂。
代码实现 通常在40-50行左右。
6 堆排序 Heap Sort
6.1 定义
利用堆这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法-使用二进制堆数据结构来构建堆,然后反复从中提取最大元素。
6.2 *简单理解
若你现在有数组:[4, 10, 3, 5, 1].则它的堆排序将是:
4
/ \
10 3
/ \
5 1
1.初始化循环
(for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i–)):
n 是数组中元素的个数,在本例中是5。
i 从n / 2 - 1开始, 在本例中是2. 所以循环从2开始(数组的中间).
循环将向后遍历数组,一直运行到i >= 0为止。
2.计算索引
(int left = 2 * i + 1; and int right = 2 * i + 2;):
对每个 i, 计算它的左和右子节点的索引。
譬如 i = 2, then 则left = 2 * 2 + 1 = 5 ,right = 2 * 2 + 2 = 6.
在此过程中,算法调整子树中的元素以满足堆属性,当循环结束时,将整个数组转换为堆。然后可以使用这个堆来有效地提取最大元素(堆的根)并继续排序过程。
6.3 Implemented Java Code
public class HeapSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7};
System.out.println("Original array:");
printArray(array);
heapSort(array);
System.out.println("\nSorted array:");
printArray(array);
}
public static void heapSort(int[] array) {
int n = array.length;
// Build max heap
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(array, n, i);
}
// Extract elements from the heap one by one
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
// Swap the root (maximum element) with the last element
int temp = array[0];
array[0] = array[i];
array[i] = temp;
// Heapify the reduced heap
heapify(array, i, 0);
}
}
public static void heapify(int[] array, int n, int i) {
int largest = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
// If left child is larger than root
if (left < n && array[left] > array[largest]) {
largest = left;
}
// If right child is larger than largest so far
if (right < n && array[right] > array[largest]) {
largest = right;
}
// If largest is not the root
if (largest != i) {
int swap = array[i];
array[i] = array[largest];
array[largest] = swap;
// Recursively heapify the affected sub-tree
heapify(array, n, largest);
}
}
public static void printArray(int[] array) {
for (int value : array) {
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
6.4 gif帮助理解
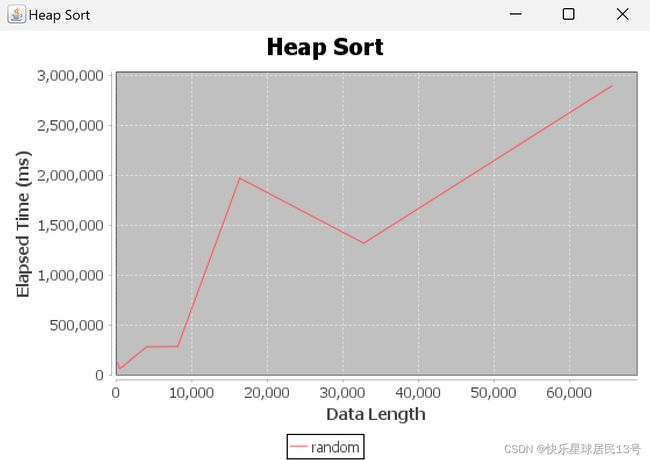
6.4 优势和缺点
优势
- 就地排序。时间复杂度为 O(n log n) 。
- 适用于大数据集。
缺点
- 不稳定
- 比冒泡排序或选择排序在实现上更为复杂
代码实现 50-60行
7 快速排序 Quick Sort
7.1 定义
一种分而治之的算法. 它的工作原理是从数组中选择一个“支点”元素,并根据它们是小于还是大于支点,将其他元素划分为两个子数组。然后将该过程递归地应用于子数组。
7.2 简单理解
想象一下,你有一堆动物玩具,每个上面都有一个数字。你要把它们按顺序排列。
1.选择一个领导者 首先,你选择一个动物作为领导者。假设它是一头狮子。
2.分组 你把所有数字较低的动物放在狮子的一边,数字较高的动物放在另一边。
3.狮子在正确的位置 现在,狮子在正确的位置,因为所有在它左边的动物数量较少,而在它右边的动物数量较多。
4.每边重复 现在,你对左边和右边的动物做同样的事情。你为每组挑选一个领导,根据他们的人数进行分组,并确保每个领导都在正确的位置。
5.重复此过程 一直这样做,直到每个动物都是自己群体的领导者,每个群体的动物都有正确的顺序。
6.把它们放在一起 最后,你把所有的动物放在一起,然后根据它们的数量从最小到最大进行排序。
7.3 Java代码实现
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7};
System.out.println("Original array:");
printArray(array);
quickSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
System.out.println("\nSorted array:");
printArray(array);
}
public static void quickSort(int[] array, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// Partition the array, elements <= pivot on the left, elements > pivot on the right
int pivotIndex = partition(array, low, high);
// Recursively sort the sub-arrays
quickSort(array, low, pivotIndex - 1);
quickSort(array, pivotIndex + 1, high);
}
}
public static int partition(int[] array, int low, int high) {
// Choose the rightmost element as the pivot
int pivot = array[high];
// Index of the smaller element
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
// If current element is smaller than or equal to the pivot
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
// Swap array[i] and array[j]
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
// Swap array[i + 1] and array[high] (pivot)
int temp = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = array[high];
array[high] = temp;
return i + 1;
}
public static void printArray(int[] array) {
for (int value : array) {
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
7.4 gif帮助理解
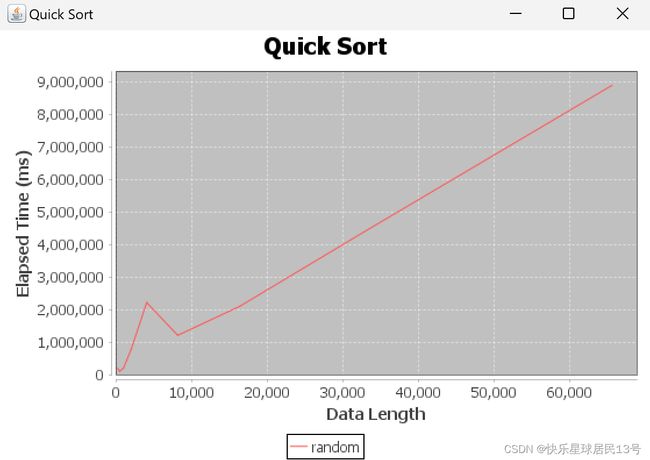
7.5 优势和缺点
优势
- 平均和最佳情况下的时间复杂度为O(n log n)。
- 就地排序。
缺点
- 最差的时间复杂度可以到 O(n**2)
- 不稳定.
代码实现 40-50 行.