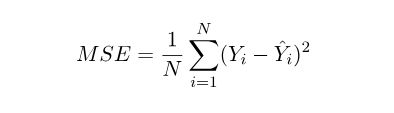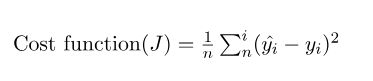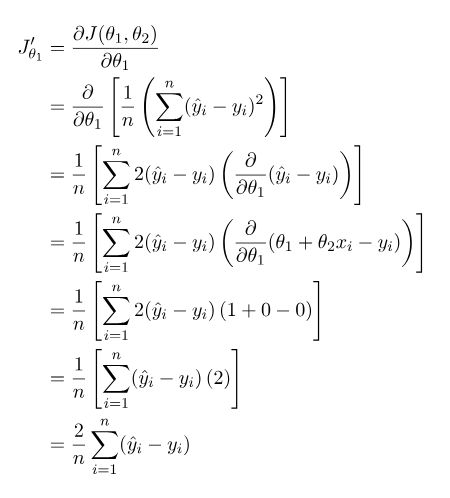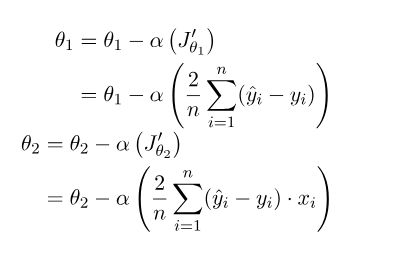用C#实现简单的线性回归
前言
最近注意到了NumSharp,想学习一下,最好的学习方式就是去实践,因此从github上找了一个用python实现的简单线性回归代码,然后基于NumSharp用C#进行了改写。
NumSharp简介
NumSharp(NumPy for C#)是一个在C#中实现的多维数组操作库,它的设计受到了Python中的NumPy库的启发。NumSharp提供了类似于NumPy的数组对象,以及对这些数组进行操作的丰富功能。它是一个开源项目,旨在为C#开发者提供在科学计算、数据分析和机器学习等领域进行高效数组处理的工具。
python代码
用到的python代码来源:llSourcell/linear_regression_live: This is the code for the “How to Do Linear Regression the Right Way” live session by Siraj Raval on Youtube (github.com)
下载到本地之后,如下图所示:
python代码如下所示:
#The optimal values of m and b can be actually calculated with way less effort than doing a linear regression.
#this is just to demonstrate gradient descent
from numpy import *
# y = mx + b
# m is slope, b is y-intercept
def compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, m, points):
totalError = 0
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
totalError += (y - (m * x + b)) ** 2
return totalError / float(len(points))
def step_gradient(b_current, m_current, points, learningRate):
b_gradient = 0
m_gradient = 0
N = float(len(points))
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
b_gradient += -(2/N) * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current))
m_gradient += -(2/N) * x * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current))
new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient)
new_m = m_current - (learningRate * m_gradient)
return [new_b, new_m]
def gradient_descent_runner(points, starting_b, starting_m, learning_rate, num_iterations):
b = starting_b
m = starting_m
for i in range(num_iterations):
b, m = step_gradient(b, m, array(points), learning_rate)
return [b, m]
def run():
points = genfromtxt("data.csv", delimiter=",")
learning_rate = 0.0001
initial_b = 0 # initial y-intercept guess
initial_m = 0 # initial slope guess
num_iterations = 1000
print ("Starting gradient descent at b = {0}, m = {1}, error = {2}".format(initial_b, initial_m, compute_error_for_line_given_points(initial_b, initial_m, points)))
print ("Running...")
[b, m] = gradient_descent_runner(points, initial_b, initial_m, learning_rate, num_iterations)
print ("After {0} iterations b = {1}, m = {2}, error = {3}".format(num_iterations, b, m, compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, m, points)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()
用C#进行改写
首先创建一个C#控制台应用,添加NumSharp包:
现在我们开始一步步用C#进行改写。
python代码:
points = genfromtxt("data.csv", delimiter=",")
在NumSharp中没有genfromtxt方法需要自己写一个。
C#代码:
//创建double类型的列表
List<double> Array = new List<double>();
// 指定CSV文件的路径
string filePath = "你的data.csv路径";
// 调用ReadCsv方法读取CSV文件数据
Array = ReadCsv(filePath);
var array = np.array(Array).reshape(100,2);
static List<double> ReadCsv(string filePath)
{
List<double> array = new List<double>();
try
{
// 使用File.ReadAllLines读取CSV文件的所有行
string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines(filePath);
// 遍历每一行数据
foreach (string line in lines)
{
// 使用逗号分隔符拆分每一行的数据
string[] values = line.Split(',');
// 打印每一行的数据
foreach (string value in values)
{
array.Add(Convert.ToDouble(value));
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("发生错误: " + ex.Message);
}
return array;
}
python代码:
def compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, m, points):
totalError = 0
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
totalError += (y - (m * x + b)) ** 2
return totalError / float(len(points))
这是在计算均方误差:
C#代码:
public static double compute_error_for_line_given_points(double b,double m,NDArray array)
{
double totalError = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < array.shape[0];i++)
{
double x = array[i, 0];
double y = array[i, 1];
totalError += Math.Pow((y - (m*x+b)),2);
}
return totalError / array.shape[0];
}
python代码:
def gradient_descent_runner(points, starting_b, starting_m, learning_rate, num_iterations):
b = starting_b
m = starting_m
for i in range(num_iterations):
b, m = step_gradient(b, m, array(points), learning_rate)
return [b, m]
def step_gradient(b_current, m_current, points, learningRate):
b_gradient = 0
m_gradient = 0
N = float(len(points))
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
b_gradient += -(2/N) * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current))
m_gradient += -(2/N) * x * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current))
new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient)
new_m = m_current - (learningRate * m_gradient)
return [new_b, new_m]
这是在用梯度下降来迭代更新y = mx + b中参数b、m的值。
因为在本例中,误差的大小是通过均方差来体现的,所以均方差就是成本函数(cost function)或者叫损失函数(loss function),我们想要找到一组b、m的值,让误差最小。
成本函数如下:
对θ1求偏导,θ1就相当于y = mx + b中的b:
再对θ2求偏导,θ2就相当于y = mx + b中的m:
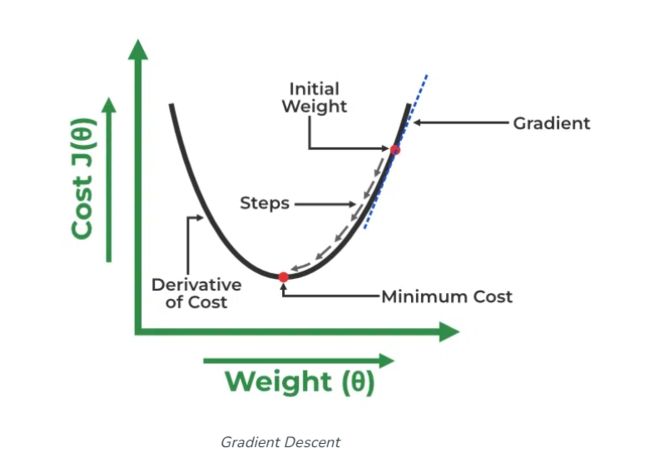
使用梯度下降:
θ1与θ2的表示:
α是学习率,首先θ1、θ2先随机设一个值,刚开始梯度变化很大,后面慢慢趋于0,当梯度等于0时,θ1与θ2的值就不会改变了,或者达到我们设置的迭代次数了,就不再继续迭代了。关于原理这方面的解释,可以查看这个链接(Linear Regression in Machine learning - GeeksforGeeks),本文中使用的图片也来自这里。
总之上面的python代码在用梯度下降迭代来找最合适的参数,现在用C#进行改写:
public static double[] gradient_descent_runner(NDArray array, double starting_b, double starting_m, double learningRate,double num_iterations)
{
double[] args = new double[2];
args[0] = starting_b;
args[1] = starting_m;
for(int i = 0 ; i < num_iterations; i++)
{
args = step_gradient(args[0], args[1], array, learningRate);
}
return args;
}
public static double[] step_gradient(double b_current,double m_current,NDArray array,double learningRate)
{
double[] args = new double[2];
double b_gradient = 0;
double m_gradient = 0;
double N = array.shape[0];
for (int i = 0; i < array.shape[0]; i++)
{
double x = array[i, 0];
double y = array[i, 1];
b_gradient += -(2 / N) * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));
m_gradient += -(2 / N) * x * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));
}
double new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient);
double new_m = m_current - (learningRate * m_gradient);
args[0] = new_b;
args[1] = new_m;
return args;
}
用C#改写的全部代码:
using NumSharp;
namespace LinearRegressionDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//创建double类型的列表
List<double> Array = new List<double>();
// 指定CSV文件的路径
string filePath = "你的data.csv路径";
// 调用ReadCsv方法读取CSV文件数据
Array = ReadCsv(filePath);
var array = np.array(Array).reshape(100,2);
double learning_rate = 0.0001;
double initial_b = 0;
double initial_m = 0;
double num_iterations = 1000;
Console.WriteLine($"Starting gradient descent at b = {initial_b}, m = {initial_m}, error = {compute_error_for_line_given_points(initial_b, initial_m, array)}");
Console.WriteLine("Running...");
double[] Args =gradient_descent_runner(array, initial_b, initial_m, learning_rate, num_iterations);
Console.WriteLine($"After {num_iterations} iterations b = {Args[0]}, m = {Args[1]}, error = {compute_error_for_line_given_points(Args[0], Args[1], array)}");
Console.ReadLine();
}
static List<double> ReadCsv(string filePath)
{
List<double> array = new List<double>();
try
{
// 使用File.ReadAllLines读取CSV文件的所有行
string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines(filePath);
// 遍历每一行数据
foreach (string line in lines)
{
// 使用逗号分隔符拆分每一行的数据
string[] values = line.Split(',');
// 打印每一行的数据
foreach (string value in values)
{
array.Add(Convert.ToDouble(value));
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("发生错误: " + ex.Message);
}
return array;
}
public static double compute_error_for_line_given_points(double b,double m,NDArray array)
{
double totalError = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < array.shape[0];i++)
{
double x = array[i, 0];
double y = array[i, 1];
totalError += Math.Pow((y - (m*x+b)),2);
}
return totalError / array.shape[0];
}
public static double[] step_gradient(double b_current,double m_current,NDArray array,double learningRate)
{
double[] args = new double[2];
double b_gradient = 0;
double m_gradient = 0;
double N = array.shape[0];
for (int i = 0; i < array.shape[0]; i++)
{
double x = array[i, 0];
double y = array[i, 1];
b_gradient += -(2 / N) * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));
m_gradient += -(2 / N) * x * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));
}
double new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient);
double new_m = m_current - (learningRate * m_gradient);
args[0] = new_b;
args[1] = new_m;
return args;
}
public static double[] gradient_descent_runner(NDArray array, double starting_b, double starting_m, double learningRate,double num_iterations)
{
double[] args = new double[2];
args[0] = starting_b;
args[1] = starting_m;
for(int i = 0 ; i < num_iterations; i++)
{
args = step_gradient(args[0], args[1], array, learningRate);
}
return args;
}
}
}
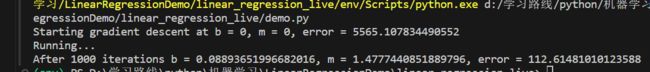
python代码的运行结果:
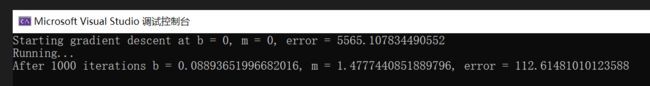
C#代码的运行结果:
结果相同,说明改写成功。
总结
本文基于NumSharp用C#改写了一个用python实现的简单线性回归,通过这次实践,可以加深对线性回归原理的理解,也可以练习使用NumSharp。