chromium通信系统-ipcz系统(九)-ipcz系统代码实现-跨Node通信-代理和代理消除
chromium通信系统-ipcz系统(六)-ipcz系统代码实现-跨Node通信-基础通信 一文我们分析了跨Node的基础通信过程。 a进程和b进程通信的过程。 但在程序中a进程将自己打开的一对portal中的一个portal传递给了b进程。由于篇幅问题这个过程我们并没有分析,这篇文章我们就来分析这个过程。
代理路由的形成
我们已经分析了基础通信过程。这里我们直接从RemoteRouterLink::AcceptParcel 函数开始分析端口的发送过程。
142 void RemoteRouterLink::AcceptParcel(const OperationContext& context,
143 Parcel& parcel) {
144 const absl::Span<Ref<APIObject>> objects = parcel.objects_view();
145
146 msg::AcceptParcel accept;
......
282 // Serialize attached objects. We accumulate the Routers of all attached
283 // portals, because we need to reference them again after transmission, with
284 // a 1:1 correspondence to the serialized RouterDescriptors.
285 absl::InlinedVector<Ref<Router>, 4> routers_to_proxy(num_portals);
286 absl::InlinedVector<RouterDescriptor, 4> descriptors(num_portals);
......
291
292 size_t portal_index = 0;
293 for (size_t i = 0; i < objects.size(); ++i) {
294 APIObject& object = *objects[i];
295
296 switch (object.object_type()) {
297 case APIObject::kPortal: {
298 handle_types[i] = HandleType::kPortal;
299
300 Ref<Router> router = Portal::FromObject(&object)->router();
301 ABSL_ASSERT(portal_index < num_portals);
302 router->SerializeNewRouter(context, *node_link(),
303 descriptors[portal_index]);
304 routers_to_proxy[portal_index] = std::move(router);
305 ++portal_index;
306 break;
307 }
308
......
331 }
332 }
333
334 // Copy all the serialized router descriptors into the message. Our local
335 // copy will supply inputs for BeginProxyingToNewRouter() calls below.
......
359
360 // Now that the parcel has been transmitted, it's safe to start proxying from
361 // any routers whose routes have just been extended to the destination.
362 ABSL_ASSERT(routers_to_proxy.size() == descriptors.size());
363 for (size_t i = 0; i < routers_to_proxy.size(); ++i) {
364 routers_to_proxy[i]->BeginProxyingToNewRouter(context, *node_link(),
365 descriptors[i]);
366 }
367
368 // Finally, a Parcel will normally close all attached objects when destroyed.
369 // Since we've successfully transmitted this parcel and all its objects, we
370 // prevent that behavior by taking away all its object references.
371 for (Ref<APIObject>& object : objects) {
372 Ref<APIObject> released_object = std::move(object);
373 }
374 }
AcceptParcel函数在chromium通信系统-ipcz系统(六)-ipcz系统代码实现-跨Node通信-基础通信 一文已经分析过了,这里我们重点分析portal作为mojohandle传输过程。
282-286行创建routers_to_proxy 和 descriptors, 一个是本进程的router,另一个则用于创建另一个进程的router。
这里有三种情况
- A和B router 是本地链接使用LocalRouterLink链接, 并且链接稳定没有被锁定,可以直接绕过A代理。
- A和B router 是本地链接使用LocalRouterLink链接, 但是没有锁定成功。
- A 和B router 是跨Node链接,使用RemoteRouterLink 链接 。
我们先来看第一种情况( A和B router 是本地链接),我画了两幅图来说明
路由传递到其他Node 2前,如上图所示。 A router 和 B router 是同进程的portal,通过LocalRouterLink进行通信。
将A router传递到Node2 后,建立新的链接如下图:
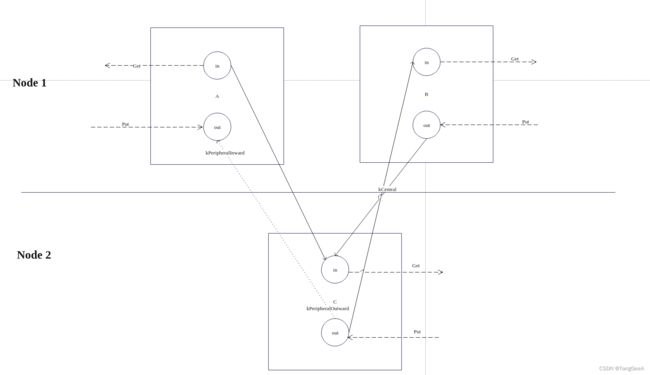
虚线表示衰减链接。
A和B router在Node 1, Node 2收到传递给它的A端口的RouterDescriptor 后会在Node2 中创建Router C。 将B的outward_edge_->primary_link_ 指向同C的链接(RemoteRouterLink)。 然后将C的outward_edge_->primary_link_ 指向B的链接(RemoteRouterLink),将C的outward_edge_->decaying_link_ 指向 C与A的链接(RemoteRouterLink)。 这样向C put 消息一部分会派发到A,一部分会派发到B, 由于C->A 之间是衰减链接,当A收到原本B 发给它的所有消息后 C->A 链接就可以完成衰减了。 之后C的消息都会发送给B。 同时还会将A的inward_edge_->primary_link_ 指向A->C的链接,在这之前B发送个A的消息都将发送给C。 之后当C->A 完成衰减, A->C 消息都发送完成A就可以退出了(代理消除),这样就完全变成B和C之间通信。 这就是传递代理的意义,与远端Node建立新的链接。
有了上面的分析,我们来具体看看代码的实现, 先来看A路由的序列化代码:
685 void Router::SerializeNewRouter(const OperationContext& context,
686 NodeLink& to_node_link,
687 RouterDescriptor& descriptor) {
688 TrapEventDispatcher dispatcher;
689 Ref<Router> local_peer;
690 bool initiate_proxy_bypass = false;
691 {
// 先锁定链接确保链接稳定,之前没有被锁定
692 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
693 traps_.RemoveAll(context, dispatcher);
694 local_peer = outward_edge_.GetLocalPeer();
695 initiate_proxy_bypass = outward_edge_.primary_link() &&
696 outward_edge_.primary_link()->TryLockForBypass(
697 to_node_link.remote_node_name());
698 }
699
// 情况1 本地链接,锁定成功执行SerializeNewRouterWithLocalPeer 进行序列化
700 if (local_peer && initiate_proxy_bypass &&
701 SerializeNewRouterWithLocalPeer(context, to_node_link, descriptor,
702 local_peer)) {
703 return;
704 }
// 情况2、3:非本地链接,或者锁定失败
706 SerializeNewRouterAndConfigureProxy(context, to_node_link, descriptor,
707 initiate_proxy_bypass);
708 }
691-698行 先锁定链接确保链接稳定,之前没有被锁定
700-704 行对应第一种情况,A和B之间是本地链接,并且链接稳定
706 行 对第二种情况(非本地链接,或者锁定失败)的处理
我们来看情况1 的处理,情况2的处理后面分析。
710 bool Router::SerializeNewRouterWithLocalPeer(const OperationContext& context,
711 NodeLink& to_node_link,
712 RouterDescriptor& descriptor,
713 Ref<Router> local_peer) {
714 MultiMutexLock lock(&mutex_, &local_peer->mutex_);
......
// 分配一个RemoteRouterLink 需要的RouterLinkState
720 FragmentRef<RouterLinkState> new_link_state =
721 to_node_link.memory().TryAllocateRouterLinkState();
......
728 const SequenceNumber proxy_inbound_sequence_length =
729 local_peer->outbound_parcels_.current_sequence_number();
730
731 // The local peer no longer needs its link to us. We'll give it a new
732 // outward link in BeginProxyingToNewRouter() after this descriptor is
733 // transmitted.
// 释放B router的outward_edge_->primary_link_
734 local_peer->outward_edge_.ReleasePrimaryLink();
// 分配两个sublink, 一个用于 B->C 的 outward_edge->primary_link_, 一个用于A->C 的 inward_edge->primary_link_
742 const SublinkId new_sublink = to_node_link.memory().AllocateSublinkIds(2);
743 const SublinkId decaying_sublink = SublinkId(new_sublink.value() + 1);
744
// 创建 B->C 的 outward_edge->primary_link_
749 Ref<RouterLink> new_link = to_node_link.AddRemoteRouterLink(
750 context, new_sublink, new_link_state, LinkType::kCentral, LinkSide::kA,
751 local_peer);
752
// 创建A->C 的 inward_edge->primary_link_
753 to_node_link.AddRemoteRouterLink(context, decaying_sublink, nullptr,
754 LinkType::kPeripheralInward, LinkSide::kA,
755 WrapRefCounted(this));
756
// 相关信息序列化到RouterDescriptor中
757 descriptor.new_sublink = new_sublink;
758 descriptor.new_link_state_fragment = new_link_state.release().descriptor();
759 descriptor.new_decaying_sublink = decaying_sublink;
760 descriptor.proxy_already_bypassed = true;
761 descriptor.next_outgoing_sequence_number =
762 outbound_parcels_.GetCurrentSequenceLength();
763 descriptor.num_bytes_produced =
764 outbound_parcels_.total_consumed_element_size();
765 descriptor.next_incoming_sequence_number =
766 inbound_parcels_.current_sequence_number();
767 descriptor.num_bytes_consumed =
768 inbound_parcels_.total_consumed_element_size();
769 descriptor.decaying_incoming_sequence_length = proxy_inbound_sequence_length;
770
771 DVLOG(4) << "Splitting local pair to move router with outbound sequence "
772 << "length " << descriptor.next_outgoing_sequence_number
773 << " and current inbound sequence number "
774 << descriptor.next_incoming_sequence_number;
775
776 if (inbound_parcels_.final_sequence_length()) {
777 descriptor.peer_closed = true;
778 descriptor.closed_peer_sequence_length =
779 *inbound_parcels_.final_sequence_length();
780 }
781
782 // Initialize an inward edge that will immediately begin decaying once it has
783 // a link (established in BeginProxyingToNewRouter()).
784 inward_edge_.emplace();
785 inward_edge_->BeginPrimaryLinkDecay();
786 inward_edge_->set_length_to_decaying_link(proxy_inbound_sequence_length);
787 inward_edge_->set_length_from_decaying_link(
788 outbound_parcels_.GetCurrentSequenceLength());
789 return true;
790 }
函数如我们前面介绍的,创建了两个RemoteRouterLink。一个用于 B->C 的 outward_edge->primary_link_, 一个用于A->C 的 inward_edge->primary_link_,并且将相关信息写到RouterDescriptor中,方便node2 进程创建C router, 和相关RemoteRouterLink。
我们再来看一下 SerializeNewRouterWithLocalPeer函数创建的链接是如何使用的。
867 void Router::BeginProxyingToNewRouter(const OperationContext& context,
868 NodeLink& to_node_link,
869 const RouterDescriptor& descriptor) {
870 Ref<RouterLink> peer_link;
871 Ref<Router> local_peer;
......
883
884 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_primary_link = new_sublink->router_link;
885 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_decaying_link;
886 {
887 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
888 ABSL_ASSERT(inward_edge_);
889
890 if (descriptor.proxy_already_bypassed) {
// 释放B的 outward_edge_->primary_link_
891 peer_link = outward_edge_.ReleasePrimaryLink();
892 local_peer = peer_link ? peer_link->GetLocalPeer() : nullptr;
893 new_decaying_link =
894 new_decaying_sublink ? new_decaying_sublink->router_link : nullptr;
895 }
896
897 if (local_peer && new_decaying_link && !is_disconnected_) {
898 // We've already bypassed this router. Use the new decaying link for our
899 // inward edge in case we need to forward parcels to the new router. The
900 // new primary link will be adopted by our peer further below.
// 设置A的inward_edge_->primary_link_ 为新创建的RmouteRouterLink链接。也就是A后面收到的消息都将发送给C
901 inward_edge_->SetPrimaryLink(std::move(new_decaying_link));
902 } else if (!outbound_parcels_.final_sequence_length() &&
......
913 }
914 }
915
916 if (local_peer && new_primary_link && !new_decaying_link) {
917 // If we have a `local_peer` and no decaying link, this means the decaying
918 // link was successfully adopted for our own inward edge; and the primary
919 // link is therefore meant to serve as our local peer's new outward link
920 // directly to the new remote router.
// 设置B的outward_edge_->primary_link_ 为新创建的另一个RmouteRouterLink链接。
921 local_peer->SetOutwardLink(context, std::move(new_primary_link));
922 }
923
......
939 Flush(context, kForceProxyBypassAttempt);
940 if (local_peer) {
941 local_peer->Flush(context, kForceProxyBypassAttempt);
942 }
943 }
BeginProxyingToNewRouter 代码也比较简单,将两个新创建的RemoteRouterLink 一个设置为A的inward_edge_->primary_link_(也就是A后面收到的消息都将发送给C), 另一个设置为设置B的outward_edge_->primary_link_ (也就是后续B发送的消息都会发送到C)。
接下来我们进入Node2 进程,看一下Node2 进程收到RouterDescriptor 如何处理。
third_party/ipcz/src/ipcz/node_link.cc
519 bool NodeLink::OnAcceptParcel(msg::AcceptParcel& accept) {
520 absl::Span<uint8_t> parcel_data =
521 accept.GetArrayView<uint8_t>(accept.params().parcel_data);
522 absl::Span<const HandleType> handle_types =
523 accept.GetArrayView<HandleType>(accept.params().handle_types);
524 absl::Span<const RouterDescriptor> new_routers =
525 accept.GetArrayView<RouterDescriptor>(accept.params().new_routers);
526 auto driver_objects = accept.driver_objects();
527
528 // Note that on any validation failure below, we defer rejection at least
529 // until any deserialized objects are stored in a new Parcel object. This
530 // ensures that they're properly cleaned up before we return.
531 bool parcel_valid = true;
532 bool is_split_parcel = false;
533 std::vector<Ref<APIObject>> objects(handle_types.size());
534 for (size_t i = 0; i < handle_types.size(); ++i) {
535 switch (handle_types[i]) {
536 case HandleType::kPortal: {
537 if (new_routers.empty()) {
538 parcel_valid = false;
539 continue;
540 }
541
542 Ref<Router> new_router = Router::Deserialize(new_routers[0], *this);
.......
579 }
580 }
......
626 if (is_split_parcel) {
627 return AcceptParcelWithoutDriverObjects(for_sublink, parcel);
628 }
629 return AcceptCompleteParcel(for_sublink, parcel);
630 }
OnAcceptParcel函数在chromium通信系统-ipcz系统(六)-ipcz系统代码实现-跨Node通信-基础通信 一文我们已经分析过了,函数542行对RouterDescriptor进行反序列化,也就是C路由的创建过程。
571 // static
572 Ref<Router> Router::Deserialize(const RouterDescriptor& descriptor,
573 NodeLink& from_node_link) {
574 // All Router deserialization occurs as a direct result of some transport
575 // notification.
576 const OperationContext context{OperationContext::kTransportNotification};
577
578 bool disconnected = false;
// 创建C路由
579 auto router = MakeRefCounted<Router>();
580 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_outward_link;
581 {
582 absl::MutexLock lock(&router->mutex_);
......
601 if (descriptor.proxy_already_bypassed) {
// 创建C->A的链接
611 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_decaying_link =
612 from_node_link.AddRemoteRouterLink(
613 context, descriptor.new_decaying_sublink, nullptr,
614 LinkType::kPeripheralOutward, LinkSide::kB, router);
615 if (!new_decaying_link) {
616 return nullptr;
617 }
// 设置 C->A的链接为衰减链接
618 router->outward_edge_.SetPrimaryLink(std::move(new_decaying_link));
619 router->outward_edge_.BeginPrimaryLinkDecay();
620 router->outward_edge_.set_length_to_decaying_link(
621 router->outbound_parcels_.current_sequence_number());
622 router->outward_edge_.set_length_from_decaying_link(
623 descriptor.decaying_incoming_sequence_length > SequenceNumber(0)
624 ? descriptor.decaying_incoming_sequence_length
625 : descriptor.next_incoming_sequence_number);
626
// 创建C->B链接
627 new_outward_link = from_node_link.AddRemoteRouterLink(
628 context, descriptor.new_sublink,
629 from_node_link.memory().AdoptFragmentRef<RouterLinkState>(
630 from_node_link.memory().GetFragment(
631 descriptor.new_link_state_fragment)),
632 LinkType::kCentral, LinkSide::kB, router);
633 if (!new_outward_link) {
634 return nullptr;
635 }
// 设置C->B链接为primary_link_
636 router->outward_edge_.SetPrimaryLink(new_outward_link);
637
638 DVLOG(4) << "Route extended from "
639 << from_node_link.remote_node_name().ToString() << " to "
640 << from_node_link.local_node_name().ToString() << " via sublink "
641 << descriptor.new_sublink << " and decaying sublink "
642 << descriptor.new_decaying_sublink;
643 } else {
......
667 }
668
......
681 router->Flush(context, kForceProxyBypassAttempt);
682 return router;
683 }
579 行创建c路由
611-626行创建C->A的链接, 并设置该链接为outward_edge_->decaying_link(衰减链接)。
627-642行创建C->B的链接,并且设置该链接为outward_edge_->primary_link。
着这里就形成了 情况1路由传递后 一图的状态。
下面我们来分析第二种情况:A和B router 是本地链接使用LocalRouterLink链接, 但是没有锁定成功。

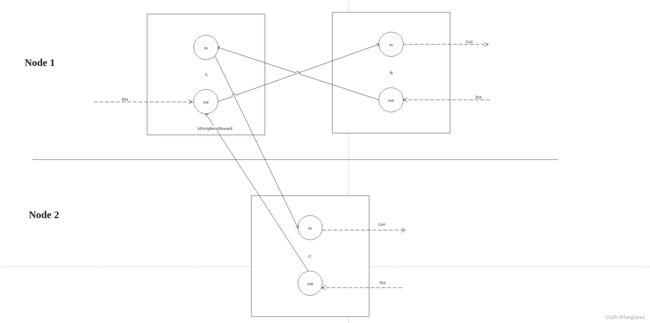
由于A和B的链接不稳定,所以不能直接绕过A代理,使用A代理转发B和C之间的数据。所以A和B的链接并没有被打断,A把A收到的B的数据都转发到C, 并且C把他发送的数据通过A 转发给B, 这时候A就是完全代理的作用。 由于A->C的链接类型是kPeripheralInward, 所以A收到C的数据会直接放到outbound_parcels_中。 我们来看一下代码实现
792 void Router::SerializeNewRouterAndConfigureProxy(
793 const OperationContext& context,
794 NodeLink& to_node_link,
795 RouterDescriptor& descriptor,
796 bool initiate_proxy_bypass) {
797 const SublinkId new_sublink = to_node_link.memory().AllocateSublinkIds(1);
798
799 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
800 descriptor.new_sublink = new_sublink;
......
816
817 if (is_peer_closed_) {
......
829 } else if (initiate_proxy_bypass && outward_edge_.primary_link()) {
......
848 }
849
850 // Once `descriptor` is transmitted to the destination node and the new
851 // Router is created there, it may immediately begin transmitting messages
852 // back to this node regarding `new_sublink`. We establish a new
853 // RemoteRouterLink now and register it to `new_sublink` on `to_node_link`,
854 // so that any such incoming messages are routed to `this`.
855 //
856 // NOTE: We do not yet provide `this` itself with a reference to the new
857 // RemoteRouterLink, because it's not yet safe for us to send messages to
858 // the remote node regarding `new_sublink`. `descriptor` must be transmitted
859 // first.
860 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_link = to_node_link.AddRemoteRouterLink(
861 context, new_sublink, nullptr, LinkType::kPeripheralInward, LinkSide::kA,
862 WrapRefCounted(this));
863 DVLOG(4) << "Router " << this << " extending route with tentative new "
864 << new_link->Describe();
865 }
797 行申请了一个sublink,然后860行创建了一个RemoteRouterLink, kA端指向A router。 类型为LinkType::kPeripheralInward。
再来看BeginProxyingToNewRouter的处理
867 void Router::BeginProxyingToNewRouter(const OperationContext& context,
868 NodeLink& to_node_link,
869 const RouterDescriptor& descriptor) {
870 Ref<RouterLink> peer_link;
871 Ref<Router> local_peer;
872
873 // Acquire references to RemoteRouterLink(s) created by an earlier call to
874 // SerializeNewRouter(). If the NodeLink has already been disconnected, these
875 // may be null.
876 auto new_sublink = to_node_link.GetSublink(descriptor.new_sublink);
......
884 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_primary_link = new_sublink->router_link;
885 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_decaying_link;
886 {
887 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
......
897 if (local_peer && new_decaying_link && !is_disconnected_) {
......
902 } else if (!outbound_parcels_.final_sequence_length() &&
903 !new_decaying_link && !is_disconnected_) {
904 DVLOG(4) << "Router " << this << " will proxy to new router over "
905 << new_primary_link->Describe();
906 inward_edge_->SetPrimaryLink(std::move(new_primary_link));
907
908 Ref<RouterLink> outward_link = outward_edge_.primary_link();
909 if (outward_link && outward_edge_.is_stable() &&
910 inward_edge_->is_stable()) {
911 outward_link->MarkSideStable();
912 }
913 }
914 }
915
......
937 // We may have inbound parcels queued which need to be forwarded to the new
938 // Router, so give them a chance to be flushed out.
939 Flush(context, kForceProxyBypassAttempt);
940 if (local_peer) {
941 local_peer->Flush(context, kForceProxyBypassAttempt);
942 }
943 }
903-913行将刚刚创建的RemoteRouterLink设置为A router的inward_edge_->primary_link_, 这样B发给A的消息都会使用这个链接发送给C。
我们再来看node2 收到请求后如何反序列化
571 // static
572 Ref<Router> Router::Deserialize(const RouterDescriptor& descriptor,
573 NodeLink& from_node_link) {
574 // All Router deserialization occurs as a direct result of some transport
575 // notification.
576 const OperationContext context{OperationContext::kTransportNotification};
577
578 bool disconnected = false;
579 auto router = MakeRefCounted<Router>();
580 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_outward_link;
581 {
582 absl::MutexLock lock(&router->mutex_);
583 router->outbound_parcels_.ResetSequence(
584 descriptor.next_outgoing_sequence_number,
585 descriptor.num_bytes_produced);
586 router->inbound_parcels_.ResetSequence(
587 descriptor.next_incoming_sequence_number,
588 descriptor.num_bytes_consumed);
......
600
601 if (descriptor.proxy_already_bypassed) {
......
643 } else {
644 if (!descriptor.new_link_state_fragment.is_null()) {
645 // No RouterLinkState fragment should be provided for this new
646 // peripheral link.
647 return nullptr;
648 }
649 new_outward_link = from_node_link.AddRemoteRouterLink(
650 context, descriptor.new_sublink, nullptr,
651 LinkType::kPeripheralOutward, LinkSide::kB, router);
652 if (new_outward_link) {
653 router->outward_edge_.SetPrimaryLink(new_outward_link);
654
655 DVLOG(4) << "Route extended from "
656 << from_node_link.remote_node_name().ToString() << " to "
657 << from_node_link.local_node_name().ToString()
658 << " via sublink " << descriptor.new_sublink;
659 } else if (!descriptor.peer_closed) {
......
665 }
666 }
667 }
668
......
680
681 router->Flush(context, kForceProxyBypassAttempt);
682 return router;
683 }
649-658将C路由的行将C的输出对接到了B 的outbound_parcels_上面。 如何做到的呢,回过来看Node1 的AcceptParcel
bool NodeLink::AcceptCompleteParcel(SublinkId for_sublink, Parcel& parcel) {
const absl::optional<Sublink> sublink = GetSublink(for_sublink);
......
const LinkType link_type = sublink->router_link->GetType();
if (link_type.is_outward()) {
DVLOG(4) << "Accepting inbound " << parcel.Describe() << " at "
<< sublink->router_link->Describe();
return sublink->receiver->AcceptInboundParcel(context, parcel);
}
ABSL_ASSERT(link_type.is_peripheral_inward());
DVLOG(4) << "Accepting outbound " << parcel.Describe() << " at "
<< sublink->router_link->Describe();
return sublink->receiver->AcceptOutboundParcel(context, parcel);
}
由于A->C的链接是kPeripheralInward类型,所以会调用 A路由的AcceptOutboundParcel函数,这个函数我们分析过,会将消息放到A router的outbound_parcels_中。
最后我们分析第三种情况:A 和B router 是跨Node链接,使用RemoteRouterLink 链接 。

这里与场景2 不同的是 A、B router为跨Node通信, 并且A->B 会直接设置为衰减链接,以尽快达到消除A的目的。
792 void Router::SerializeNewRouterAndConfigureProxy(
793 const OperationContext& context,
794 NodeLink& to_node_link,
795 RouterDescriptor& descriptor,
796 bool initiate_proxy_bypass) {
797 const SublinkId new_sublink = to_node_link.memory().AllocateSublinkIds(1);
798
799 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
816
817 if (is_peer_closed_) {
......
829 } else if (initiate_proxy_bypass && outward_edge_.primary_link()) {
830 RemoteRouterLink* remote_link =
831 outward_edge_.primary_link()->AsRemoteRouterLink();
832 if (remote_link) {
833 descriptor.proxy_peer_node_name =
834 remote_link->node_link()->remote_node_name();
835 descriptor.proxy_peer_sublink = remote_link->sublink();
836 DVLOG(4) << "Will initiate proxy bypass immediately on deserialization "
837 << "with peer at " << descriptor.proxy_peer_node_name.ToString()
838 << " and peer route to proxy on sublink "
839 << descriptor.proxy_peer_sublink;
840
841 inward_edge_->BeginPrimaryLinkDecay();
842 outward_edge_.BeginPrimaryLinkDecay();
843 } else {
......
847 }
848 }
849
......
860 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_link = to_node_link.AddRemoteRouterLink(
861 context, new_sublink, nullptr, LinkType::kPeripheralInward, LinkSide::kA,
862 WrapRefCounted(this));
863 DVLOG(4) << "Router " << this << " extending route with tentative new "
864 << new_link->Describe();
865 }
函数分配了一个sublink, 并将B的节点信息告知Node2,方便Node2 与B 在bypass的时候直接建立链接。
867 void Router::BeginProxyingToNewRouter(const OperationContext& context,
868 NodeLink& to_node_link,
869 const RouterDescriptor& descriptor) {
......
883
884 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_primary_link = new_sublink->router_link;
885 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_decaying_link;
886 {
887 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
888 ABSL_ASSERT(inward_edge_);
889
890 if (descriptor.proxy_already_bypassed) {
891 peer_link = outward_edge_.ReleasePrimaryLink();
892 local_peer = peer_link ? peer_link->GetLocalPeer() : nullptr;
893 new_decaying_link =
894 new_decaying_sublink ? new_decaying_sublink->router_link : nullptr;
895 }
896
897 if (local_peer && new_decaying_link && !is_disconnected_) {
......
902 } else if (!outbound_parcels_.final_sequence_length() &&
903 !new_decaying_link && !is_disconnected_) {
904 DVLOG(4) << "Router " << this << " will proxy to new router over "
905 << new_primary_link->Describe();
906 inward_edge_->SetPrimaryLink(std::move(new_primary_link));
907
908 Ref<RouterLink> outward_link = outward_edge_.primary_link();
909 if (outward_link && outward_edge_.is_stable() &&
910 inward_edge_->is_stable()) {
911 outward_link->MarkSideStable();
912 }
913 }
914 }
915
......
936
937 // We may have inbound parcels queued which need to be forwarded to the new
938 // Router, so give them a chance to be flushed out.
939 Flush(context, kForceProxyBypassAttempt);
940 if (local_peer) {
941 local_peer->Flush(context, kForceProxyBypassAttempt);
942 }
943 }
过程和情况2 一致, 再来看一下Node3 进行反序列化操作
571 // static
572 Ref<Router> Router::Deserialize(const RouterDescriptor& descriptor,
573 NodeLink& from_node_link) {
574 // All Router deserialization occurs as a direct result of some transport
575 // notification.
576 const OperationContext context{OperationContext::kTransportNotification};
577
578 bool disconnected = false;
579 auto router = MakeRefCounted<Router>();
580 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_outward_link;
581 {
582 absl::MutexLock lock(&router->mutex_);
......
601 if (descriptor.proxy_already_bypassed) {
......
643 } else {
644 if (!descriptor.new_link_state_fragment.is_null()) {
645 // No RouterLinkState fragment should be provided for this new
646 // peripheral link.
647 return nullptr;
648 }
649 new_outward_link = from_node_link.AddRemoteRouterLink(
650 context, descriptor.new_sublink, nullptr,
651 LinkType::kPeripheralOutward, LinkSide::kB, router);
652 if (new_outward_link) {
653 router->outward_edge_.SetPrimaryLink(new_outward_link);
654
655 DVLOG(4) << "Route extended from "
656 << from_node_link.remote_node_name().ToString() << " to "
657 << from_node_link.local_node_name().ToString()
658 << " via sublink " << descriptor.new_sublink;
659 } else if (!descriptor.peer_closed) {
......
665 }
666 }
667 }
668
669 if (disconnected) {
......
672 } else if (descriptor.proxy_peer_node_name.is_valid()) {
673 // The source router rolled some peer bypass details into our descriptor to
674 // avoid some IPC overhead. We can begin bypassing the proxy now.
675 ABSL_ASSERT(new_outward_link);
676 router->BypassPeer(context, *new_outward_link,
677 descriptor.proxy_peer_node_name,
678 descriptor.proxy_peer_sublink);
679 }
680
681 router->Flush(context, kForceProxyBypassAttempt);
682 return router;
683 }
反序列化的过程和情况2 一致, 只不过这里执行了 router->ByPassPeer() 函数请求绕过A路由。
Proxy ByPass
通过前面端口传递,我们看到了代理的形成过程。接下来我们看代理的消除过程。端口作为参数传递的过程中, 我们把场景分为了三种,代理消除过程中我们分为两种场景去看,主要是A、B属于LocalRouterLink 和RmoteRouterLink的场景。
我们先来看A和B属于同Node的场景
1286 void Router::Flush(const OperationContext& context, FlushBehavior behavior) {
1287 Ref<RouterLink> outward_link;
1288 Ref<RouterLink> inward_link;
1289 Ref<RouterLink> bridge_link;
1290 Ref<RouterLink> decaying_outward_link;
1291 Ref<RouterLink> decaying_inward_link;
1292 Ref<RouterLink> dead_inward_link;
1293 Ref<RouterLink> dead_outward_link;
1294 Ref<RouterLink> dead_bridge_link;
1295 absl::optional<SequenceNumber> final_inward_sequence_length;
1296 absl::optional<SequenceNumber> final_outward_sequence_length;
1297 bool on_central_link = false;
1298 bool inward_link_decayed = false;
1299 bool outward_link_decayed = false;
1300 bool dropped_last_decaying_link = false;
1301 ParcelsToFlush parcels_to_flush;
1302 TrapEventDispatcher dispatcher;
1303 {
1304 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
1305
1306 // Acquire stack references to all links we might want to use, so it's safe
1307 // to acquire additional (unmanaged) references per ParcelToFlush.
1308 outward_link = outward_edge_.primary_link();
1309 inward_link = inward_edge_ ? inward_edge_->primary_link() : nullptr;
1310 decaying_outward_link = outward_edge_.decaying_link();
1311 decaying_inward_link =
1312 inward_edge_ ? inward_edge_->decaying_link() : nullptr;
1313 on_central_link = outward_link && outward_link->GetType().is_central();
......
1327
1328 CollectParcelsToFlush(outbound_parcels_, outward_edge_, parcels_to_flush);
1329 const SequenceNumber outbound_sequence_length_sent =
1330 outbound_parcels_.current_sequence_number();
1331 const SequenceNumber inbound_sequence_length_received =
1332 inbound_parcels_.GetCurrentSequenceLength();
1333 if (outward_edge_.MaybeFinishDecay(outbound_sequence_length_sent,
1334 inbound_sequence_length_received)) {
1335 DVLOG(4) << "Outward " << decaying_outward_link->Describe()
1336 << " fully decayed at " << outbound_sequence_length_sent
1337 << " sent and " << inbound_sequence_length_received
1338 << " recived";
1339 outward_link_decayed = true;
1340 }
1341
1342 if (inward_edge_) {
1343 CollectParcelsToFlush(inbound_parcels_, *inward_edge_, parcels_to_flush);
1344 const SequenceNumber inbound_sequence_length_sent =
1345 inbound_parcels_.current_sequence_number();
1346 const SequenceNumber outbound_sequence_length_received =
1347 outbound_parcels_.GetCurrentSequenceLength();
1348 if (inward_edge_->MaybeFinishDecay(inbound_sequence_length_sent,
1349 outbound_sequence_length_received)) {
1350 DVLOG(4) << "Inward " << decaying_inward_link->Describe()
1351 << " fully decayed at " << inbound_sequence_length_sent
1352 << " sent and " << outbound_sequence_length_received
1353 << " received";
1354 inward_link_decayed = true;
1355 }
1356 } else if (bridge_link) {
1357 ......
1358 }
1359
......
1477
1478 if (dead_outward_link || !on_central_link) {
1479 // If we're not on a central link, there's no more work to do.
1480 return;
1481 }
1482
1483 if (!dropped_last_decaying_link && behavior != kForceProxyBypassAttempt) {
1484 // No relevant state changes, so there are no new bypass opportunities.
1485 return;
1486 }
1487
1488 if (inward_link && MaybeStartSelfBypass(context)) {
1489 return;
1490 }
1491
1492 if (outward_link) {
1493 outward_link->FlushOtherSideIfWaiting(context);
1494 }
1495 }
在情景1 中由于直接bypass的A路由,我们直接看情景2中的场景。 1478-1487行 由于A->B 是中心路由,并且在BeginProxyingToNewRouter函数(939-942行)中调用Flush 函数中设置了kForceProxyBypassAttempt标志,所以会执行。 我们来分析MaybeStartSelfBypass函数。A路由的inward_link不为空,这里分析A路由的场景
1497 bool Router::MaybeStartSelfBypass(const OperationContext& context) {
1498 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> remote_inward_link;
1499 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> remote_outward_link;
1500 Ref<Router> local_outward_peer;
1501 {
1502 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
......
1516 const NodeName& inward_peer_name =
1517 inward_link->node_link()->remote_node_name();
// 锁定 A->B
1518 if (!outward_link->TryLockForBypass(inward_peer_name)) {
1519 DVLOG(4) << "Proxy bypass blocked by busy " << outward_link->Describe();
1520 return false;
1521 }
1522
1523 remote_inward_link = WrapRefCounted(inward_link);
1524 local_outward_peer = outward_link->GetLocalPeer(); // B 路由
1525 if (!local_outward_peer) {
1526 remote_outward_link = WrapRefCounted(outward_link->AsRemoteRouterLink());
1527 }
1528 }
1529
1530 if (remote_outward_link) {
......
1554 return true;
1555 }
1556
1557 // When the bypass target is local to the same node as this router, we can
1558 // establish the bypass link immediately and send it to the remote inward
1559 // peer.
1560 return StartSelfBypassToLocalPeer(
1561 context, *local_outward_peer, *remote_inward_link,
1562 remote_inward_link->node_link()->memory().TryAllocateRouterLinkState());
1563 }
A路由的inward_link是指向C路由,local_outward_peer 是B路由, 所以会执行StartSelfBypassToLocalPeer 函数。参数local_outward_peer是B路由, remote_inward_link是B->C的链接,由于是边缘路由之前没有分配RouterLinkState, 这里分配一个RouterLinkState传入到StartSelfBypassToLocalPeer函数。
1565 bool Router::StartSelfBypassToLocalPeer(
1566 const OperationContext& context,
1567 Router& local_outward_peer,
1568 RemoteRouterLink& inward_link,
1569 FragmentRef<RouterLinkState> new_link_state) {
......
1588
1589 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_link;
1590 SequenceNumber length_from_outward_peer;
1591 const SublinkId new_sublink =
1592 inward_link.node_link()->memory().AllocateSublinkIds(1);
1593 {
1594 MultiMutexLock lock(&mutex_, &local_outward_peer.mutex_);
1595
1596 const Ref<RouterLink>& outward_link = outward_edge_.primary_link();
1597 const Ref<RouterLink>& peer_outward_link =
1598 local_outward_peer.outward_edge_.primary_link();
......
1611
// 设置A->B和B->A链接衰减
1612 // Decay both of our existing links, as well as the local peer's link to us.
1613 length_from_outward_peer =
1614 local_outward_peer.outbound_parcels_.current_sequence_number();
1615 local_outward_peer.outward_edge_.BeginPrimaryLinkDecay();
1616 local_outward_peer.outward_edge_.set_length_to_decaying_link(
1617 length_from_outward_peer);
1618 outward_edge_.BeginPrimaryLinkDecay();
1619 outward_edge_.set_length_from_decaying_link(length_from_outward_peer);
1620 inward_edge_->BeginPrimaryLinkDecay();
1621 inward_edge_->set_length_to_decaying_link(length_from_outward_peer);
1622
// 创建新的RemoteLocalLink用于B->C 之间链接。
1623 new_link = inward_link.node_link()->AddRemoteRouterLink(
1624 context, new_sublink, new_link_state, LinkType::kCentral, LinkSide::kA,
1625 WrapRefCounted(&local_outward_peer));
1626 }
......
1632
1633 // Inform our inward peer on another node that they can bypass us using the
1634 // new link we just created to our own outward local peer. Once that message
1635 // is sent, it's safe for that local peer to adopt the new link.
// 请求Node2 执行ByPass 同时请求建立C->B的链接。
1636 inward_link.BypassPeerWithLink(context, new_sublink,
1637 std::move(new_link_state),
1638 length_from_outward_peer);
// 设置B->C链接
1639 local_outward_peer.SetOutwardLink(context, std::move(new_link));
1640 return true;
1641 }
函数1612->1622行设置A->B链接衰减,同时设置B->A链接衰减。
1623->1625行创建新的路由,1639行将这个路由设置为B->C 的link,是中心链接。
1636行调用inward_link.BypassPeerWithLink 函数请求Node2 执行ByPass 同时请求建立C->B的链接。
我们重点看一下inward_link.BypassPeerWithLink 函数,inward_link是A->C的链接。
void RemoteRouterLink::BypassPeerWithLink(
const OperationContext& context,
SublinkId new_sublink,
FragmentRef<RouterLinkState> new_link_state,
SequenceNumber inbound_sequence_length) {
msg::BypassPeerWithLink bypass;
bypass.params().sublink = sublink_;
bypass.params().new_sublink = new_sublink;
bypass.params().new_link_state_fragment =
new_link_state.release().descriptor();
bypass.params().inbound_sequence_length = inbound_sequence_length;
node_link()->Transmit(bypass);
}
BypassPeerWithLink_Params的参数
- sublink 可以用于Node2 找到A和C的路由链接。
- new_sublink 指向B->C的链接,用于创建C->B的链接形成链接对。
- new_link_state_fragment 描述B->C 链接的状态, 同时也用于描述C->B的链接状态(link stat用于描述一对链接的状态)。
- inbound_sequence_length: B路由的输出seq,用于C 到A的衰减。
我们看Node2 是如何处理这个请求的
third_party/ipcz/src/ipcz/node_link.cc
743 bool NodeLink::OnBypassPeerWithLink(msg::BypassPeerWithLink& bypass) {
// 找到C->A的router
744 Ref<Router> router = GetRouter(bypass.params().sublink);
745 if (!router) {
746 return true;
747 }
748
// 新的RouterLinkState
749 auto link_state = MaybeAdoptFragmentRef<RouterLinkState>(
750 memory(), bypass.params().new_link_state_fragment);
751 if (link_state.is_null()) {
752 return false;
753 }
754
755 const OperationContext context{OperationContext::kTransportNotification};
// C->的router执行AcceptBypassLink
756 return router->AcceptBypassLink(context, *this, bypass.params().new_sublink,
757 std::move(link_state),
758 bypass.params().inbound_sequence_length);
759 }
760
744 行找到C->A的router。
749行 找到B->C 链接对应的RouterLinkState
756 行 执行AcceptBypassLink, 这个过程中需要使用new_sublink创建C->B的链接。
1006 bool Router::AcceptBypassLink(
1007 const OperationContext& context,
1008 NodeLink& new_node_link,
1009 SublinkId new_sublink,
1010 FragmentRef<RouterLinkState> new_link_state,
1011 SequenceNumber inbound_sequence_length_from_bypassed_link) {
1012 SequenceNumber length_to_proxy_from_us;
1013 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> old_link;
1014 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_link;
1015 {
1016 absl::ReleasableMutexLock lock(&mutex_);
.....
// C->A的链接
1024 old_link =
1025 WrapRefCounted(outward_edge_.primary_link()->AsRemoteRouterLink());
1026 if (!old_link) {
1027 // It only makes sense to receive this at a router whose outward link is
1028 // remote. If we have a non-remote outward link, something is wrong.
1029 DVLOG(4) << "Rejecting unexpected bypass link";
1030 return false;
1031 }
1032
......
1040
1041 length_to_proxy_from_us = outbound_parcels_.current_sequence_number();
// 设置C->A衰减
1042 if (!outward_edge_.BeginPrimaryLinkDecay()) {
1043 DLOG(ERROR) << "Rejecting BypassProxy on failure to decay link";
1044 return false;
1045 }
1046
1047 // By convention the initiator of a bypass assumes side A of the bypass
1048 // link, so we assume side B.
// 创建C->B链接
1049 new_link = new_node_link.AddRemoteRouterLink(
1050 context, new_sublink, std::move(new_link_state), LinkType::kCentral,
1051 LinkSide::kB, WrapRefCounted(this));
1052
1053 if (new_link) {
1054 DVLOG(4) << "Bypassing proxy on other end of " << old_link->Describe()
1055 << " using a new " << new_link->Describe()
1056 << " with length to proxy " << length_to_proxy_from_us
1057 << " and length from proxy "
1058 << inbound_sequence_length_from_bypassed_link;
1059
// 设置C->B 链接。
1060 outward_edge_.set_length_to_decaying_link(length_to_proxy_from_us);
1061 outward_edge_.set_length_from_decaying_link(
1062 inbound_sequence_length_from_bypassed_link);
1063 outward_edge_.SetPrimaryLink(new_link);
1064 }
1065 }
......
1071
1072 if (new_link->node_link() == old_link->node_link()) {
1073 // If the new link goes to the same place as the old link, we only need
1074 // to tell the proxy there to stop proxying. It has already conspired with
1075 // its local outward peer.
// 请求Node1 执行bypass。
1076 old_link->StopProxyingToLocalPeer(context, length_to_proxy_from_us);
1077 } else {
......
1083 }
1084
1085 Flush(context);
1086 return true;
1087 }
1041-1042 行设置C->A的链接衰减。
1060-1064行设置C->B的链接为outward_edge_->primary_link_。
1076 行通知A router 开始衰减。
void RemoteRouterLink::StopProxyingToLocalPeer(
const OperationContext& context,
SequenceNumber outbound_sequence_length) {
msg::StopProxyingToLocalPeer stop;
stop.params().sublink = sublink_;
stop.params().outbound_sequence_length = outbound_sequence_length;
node_link()->Transmit(stop);
}
这里的sublink_ 参数是A<->C 之间的sublink_ 用于找到A路由。
回到Node1
bool NodeLink::OnStopProxyingToLocalPeer(msg::StopProxyingToLocalPeer& stop) {
Ref<Router> router = GetRouter(stop.params().sublink);
if (!router) {
return true;
}
const OperationContext context{OperationContext::kTransportNotification};
return router->StopProxyingToLocalPeer(
context, stop.params().outbound_sequence_length);
}
A路由的StopProxyingToLocalPeer。
1171 bool Router::StopProxyingToLocalPeer(const OperationContext& context,
1172 SequenceNumber outbound_sequence_length) {
1173 Ref<Router> local_peer;
1174 Ref<Router> bridge_peer;
1175 {
1176 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
1177 if (bridge_) {
1178 ......
1179 } else if (outward_edge_.decaying_link()) {
// B路由
1180 local_peer = outward_edge_.decaying_link()->GetLocalPeer();
1181 } else {
1182 // Ignore this request if we've been unexpectedly disconnected.
1183 return is_disconnected_;
1184 }
1185 }
1186
1187 if (local_peer && !bridge_peer) {
1188 // This is the common case, with no bridge link.
1189 MultiMutexLock lock(&mutex_, &local_peer->mutex_);
//A->B链接
1190 const Ref<RouterLink>& our_link = outward_edge_.decaying_link();
// B->A 链接
1191 const Ref<RouterLink>& peer_link =
1192 local_peer->outward_edge_.decaying_link();
......
1210 // 设置衰减完成的 seq
1211 local_peer->outward_edge_.set_length_from_decaying_link(
1212 outbound_sequence_length);
1213 outward_edge_.set_length_to_decaying_link(outbound_sequence_length);
1214 inward_edge_->set_length_from_decaying_link(outbound_sequence_length);
1215 } else if (bridge_peer) {
1216 ......
1245 } else {
1246 // It's invalid to send call this on a Router with a non-local outward peer
1247 // or bridge link.
1248 DLOG(ERROR) << "Rejecting StopProxyingToLocalPeer with no local peer";
1249 return false;
1250 }
1251
1252 Flush(context);
1253 local_peer->Flush(context);
1254 if (bridge_peer) {
1255 bridge_peer->Flush(context);
1256 }
1257 return true;
1258 }
虚线部分代表衰减链接。 整体的目的就是让A<->C之间A<->B之间的链接衰减,最终B<->C通信。链接衰减部分我们最后分析。
接下来我们对情景3 的代理消除进行分析。 情景3的代理消除由Node3发起。
571 // static
572 Ref<Router> Router::Deserialize(const RouterDescriptor& descriptor,
573 NodeLink& from_node_link) {
574 // All Router deserialization occurs as a direct result of some transport
575 // notification.
576 const OperationContext context{OperationContext::kTransportNotification};
577
......
668
669 if (disconnected) {
670 DVLOG(4) << "Disconnected new Router immediately after deserialization";
671 router->AcceptRouteDisconnectedFrom(context, LinkType::kPeripheralOutward);
672 } else if (descriptor.proxy_peer_node_name.is_valid()) {
673 // The source router rolled some peer bypass details into our descriptor to
674 // avoid some IPC overhead. We can begin bypassing the proxy now.
675 ABSL_ASSERT(new_outward_link);
676 router->BypassPeer(context, *new_outward_link,
677 descriptor.proxy_peer_node_name,
678 descriptor.proxy_peer_sublink);
679 }
680
681 router->Flush(context, kForceProxyBypassAttempt);
682 return router;
683 }
684
Deserialize 函数我们看了好几遍了, 这里主要关注情景3 特有执行的router->BypassPeer() 函数
945 bool Router::BypassPeer(const OperationContext& context,
946 RemoteRouterLink& requestor,
947 const NodeName& bypass_target_node,
948 SublinkId bypass_target_sublink) {
949 NodeLink& from_node_link = *requestor.node_link();
950
951 // Validate that the source of this request is actually our peripheral outward
952 // peer, and that we are therefore its inward peer.
953 {
954 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
// C->A 链接
955 const Ref<RouterLink>& outward_link = outward_edge_.primary_link();
......
970
971 // There are two distinct cases to handle. The first case here is when the
972 // proxy's outward peer lives on a different node from us.
973 if (bypass_target_node != from_node_link.local_node_name()) {
974 Ref<NodeLink> link_to_bypass_target =
975 from_node_link.node()->GetLink(bypass_target_node);
976 if (link_to_bypass_target) {
977 return BypassPeerWithNewRemoteLink(
978 context, requestor, *link_to_bypass_target, bypass_target_sublink,
979 link_to_bypass_target->memory().TryAllocateRouterLinkState());
980 }
981
982 // We need to establish a link to the target node before we can proceed.
983 from_node_link.node()->EstablishLink(
984 bypass_target_node,
985 [router = WrapRefCounted(this), requestor = WrapRefCounted(&requestor),
986 bypass_target_sublink, context](NodeLink* link_to_bypass_target) {
987 if (!link_to_bypass_target) {
988 DLOG(ERROR) << "Disconnecting Router due to failed introduction";
989 router->AcceptRouteDisconnectedFrom(context,
990 LinkType::kPeripheralOutward);
991 return;
992 }
993
994 router->BypassPeerWithNewRemoteLink(
995 context, *requestor, *link_to_bypass_target,
996 bypass_target_sublink,
997 link_to_bypass_target->memory().TryAllocateRouterLinkState());
998 });
999 return true;
1000 }
1001
1002 // The second case is when the proxy's outward peer lives on our own node.
1003 return BypassPeerWithNewLocalLink(context, requestor, bypass_target_sublink);
1004 }
这里的router是C router。bypass_target_node 是Node2 也就是B所在的Node的名称, bypass_target_sublink 是A和B链接对应的sublink。这里有两种情况:
- Node2 和Node3 是同一个Node, 执行BypassPeerWithNewLocalLink 进行Bypass。
- Node2 和Node3 不是同一个Node ,执行974-1000行代码进行Bypass。
我们先分析简单情况Node2 和Node3 是同一个Node的情况。
1960 bool Router::BypassPeerWithNewLocalLink(const OperationContext& context,
1961 RemoteRouterLink& requestor,
1962 SublinkId bypass_target_sublink) {
1963 NodeLink& from_node_link = *requestor.node_link();
// B router
1964 const Ref<Router> new_local_peer =
1965 from_node_link.GetRouter(bypass_target_sublink);
......
1972
1973 Ref<RouterLink> link_from_new_local_peer_to_proxy;
1974 SequenceNumber length_to_proxy_from_us;
1975 SequenceNumber length_from_proxy_to_us;
1976 {
1977 MultiMutexLock lock(&mutex_, &new_local_peer->mutex_);
1978 length_from_proxy_to_us =
1979 new_local_peer->outbound_parcels_.current_sequence_number();
// C->A 链接
1980 length_to_proxy_from_us = outbound_parcels_.current_sequence_number();
1981
1982 DVLOG(4) << "Proxy bypass requested with new local peer on "
1983 << from_node_link.local_node_name().ToString() << " and proxy on "
1984 << from_node_link.remote_node_name().ToString() << " via sublinks "
1985 << bypass_target_sublink << " and " << requestor.sublink()
1986 << "; length to the proxy is " << length_to_proxy_from_us
1987 << " and length from the proxy " << length_from_proxy_to_us;
1988
// B->A 链接
1989 link_from_new_local_peer_to_proxy =
1990 new_local_peer->outward_edge_.primary_link();
......
1995
1996 // Otherwise immediately begin decay of both links to the proxy.
// C->A 链接开始衰减, B->A 开始衰减
1997 if (!outward_edge_.BeginPrimaryLinkDecay() ||
1998 !new_local_peer->outward_edge_.BeginPrimaryLinkDecay()) {
1999 DLOG(ERROR) << "Rejecting BypassPeer on failure to decay link";
2000 return false;
2001 }
2002 outward_edge_.set_length_to_decaying_link(length_to_proxy_from_us);
2003 outward_edge_.set_length_from_decaying_link(length_from_proxy_to_us);
2004 new_local_peer->outward_edge_.set_length_to_decaying_link(
2005 length_from_proxy_to_us);
2006 new_local_peer->outward_edge_.set_length_from_decaying_link(
2007 length_to_proxy_from_us);
2008
2009 // Finally, link the two routers with a new LocalRouterLink. This link will
2010 // remain unstable until the decaying proxy links are gone.
// 创建C->B 和 B->C 链接。primary link
2011 RouterLink::Pair links = LocalRouterLink::CreatePair(
2012 LinkType::kCentral, Router::Pair(WrapRefCounted(this), new_local_peer));
2013 outward_edge_.SetPrimaryLink(std::move(links.first));
2014 new_local_peer->outward_edge_.SetPrimaryLink(std::move(links.second));
2015 }
2016
// 请求A链接停止代理
2017 link_from_new_local_peer_to_proxy->StopProxying(
2018 context, length_from_proxy_to_us, length_to_proxy_from_us);
2019
2020 Flush(context);
2021 new_local_peer->Flush(context);
2022 return true;
2023 }
函数也比较简单
1997-1998行开始让B->A, C->A的链接衰减、
2011-2014行 创建B->C 和C<-B的链接。
2017行请求A 停止代理。
我们深入分析请求A 停止代理的过程。
void RemoteRouterLink::StopProxying(const OperationContext& context,
SequenceNumber inbound_sequence_length,
SequenceNumber outbound_sequence_length) {
msg::StopProxying stop;
stop.params().sublink = sublink_;
stop.params().inbound_sequence_length = inbound_sequence_length;
stop.params().outbound_sequence_length = outbound_sequence_length;
node_link()->Transmit(stop);
}
StopProxying_Params 的参数包括 sublink_,用于找到A路由。
我们进入到Node1:
bool NodeLink::OnStopProxying(msg::StopProxying& stop) {
Ref<Router> router = GetRouter(stop.params().sublink);
if (!router) {
return true;
}
const OperationContext context{OperationContext::kTransportNotification};
return router->StopProxying(context, stop.params().inbound_sequence_length,
stop.params().outbound_sequence_length);
}
函数直接调用A router的StopProxying 方法。
1089 bool Router::StopProxying(const OperationContext& context,
1090 SequenceNumber inbound_sequence_length,
1091 SequenceNumber outbound_sequence_length) {
1092 Ref<Router> bridge_peer;
1093 {
1094 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
1095 if (outward_edge_.is_stable()) {
1096 // Proxies begin decaying their links before requesting to be bypassed,
1097 // and they don't adopt new links after that. So if either edge is stable
1098 // then someone is doing something wrong.
1099 DLOG(ERROR) << "Rejecting StopProxying on invalid or non-proxying Router";
1100 return false;
1101 }
1102
1103 if (bridge_) {
......
1110 } else if (!inward_edge_ || inward_edge_->is_stable()) {
1111 // Not a proxy, so this request is invalid.
1112 return false;
1113 } else {
1114 inward_edge_->set_length_to_decaying_link(inbound_sequence_length);
1115 inward_edge_->set_length_from_decaying_link(outbound_sequence_length);
1116 outward_edge_.set_length_to_decaying_link(outbound_sequence_length);
1117 outward_edge_.set_length_from_decaying_link(inbound_sequence_length);
1118 }
1119 }
1120
1121 if (bridge_peer) {
1122 MultiMutexLock lock(&mutex_, &bridge_peer->mutex_);
1123 if (!bridge_ || bridge_->is_stable() || !bridge_peer->bridge_ ||
1124 bridge_peer->bridge_->is_stable()) {
1125 // The bridge is being or has already been torn down, so there's nothing
1126 // to do here.
1127 return true;
1128 }
1129
1130 bridge_->set_length_to_decaying_link(inbound_sequence_length);
1131 bridge_->set_length_from_decaying_link(outbound_sequence_length);
1132 outward_edge_.set_length_to_decaying_link(outbound_sequence_length);
1133 outward_edge_.set_length_from_decaying_link(inbound_sequence_length);
1134 bridge_peer->bridge_->set_length_to_decaying_link(outbound_sequence_length);
1135 bridge_peer->bridge_->set_length_from_decaying_link(
1136 inbound_sequence_length);
1137 bridge_peer->outward_edge_.set_length_to_decaying_link(
1138 inbound_sequence_length);
1139 bridge_peer->outward_edge_.set_length_from_decaying_link(
1140 outbound_sequence_length);
1141 }
1142
1143 Flush(context);
1144 if (bridge_peer) {
1145 bridge_peer->Flush(context);
1146 }
1147 return true;
1148 }
下面我们以A路由的视角分析
1089 bool Router::StopProxying(const OperationContext& context,
1090 SequenceNumber inbound_sequence_length,
1091 SequenceNumber outbound_sequence_length) {
1092 Ref<Router> bridge_peer;
1093 {
1094 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
1095 if (outward_edge_.is_stable()) {
1096 // Proxies begin decaying their links before requesting to be bypassed,
1097 // and they don't adopt new links after that. So if either edge is stable
1098 // then someone is doing something wrong.
1099 DLOG(ERROR) << "Rejecting StopProxying on invalid or non-proxying Router";
1100 return false;
1101 }
1102
1103 if (bridge_) {
1104 // If we have a bridge link, we also need to update the router on the
1105 // other side of the bridge.
1106 bridge_peer = bridge_->GetDecayingLocalPeer();
1107 if (!bridge_peer) {
1108 return false;
1109 }
1110 } else if (!inward_edge_ || inward_edge_->is_stable()) { // 被另一端设置为非stable状态了
1111 // Not a proxy, so this request is invalid.
1112 return false;
1113 } else {
1114 inward_edge_->set_length_to_decaying_link(inbound_sequence_length);
1115 inward_edge_->set_length_from_decaying_link(outbound_sequence_length);
1116 outward_edge_.set_length_to_decaying_link(outbound_sequence_length);
1117 outward_edge_.set_length_from_decaying_link(inbound_sequence_length);
1118 }
1119 }
1120
1121 if (bridge_peer) {
......
1141 }
1142
1143 Flush(context);
1144 if (bridge_peer) {
1145 bridge_peer->Flush(context);
1146 }
1147 return true;
1148 }
函数比较简单 请读者自行分析。
最后我们来看一下B 和 C在不同Node的场景。
974 Ref<NodeLink> link_to_bypass_target =
975 from_node_link.node()->GetLink(bypass_target_node);
976 if (link_to_bypass_target) {
// Node3 和 Node2 本身有NodeLink,执行BypassPeerWithNewRemoteLink 进行代理绕过
977 return BypassPeerWithNewRemoteLink(
978 context, requestor, *link_to_bypass_target, bypass_target_sublink,
979 link_to_bypass_target->memory().TryAllocateRouterLinkState());
980 }
981
// Node3 和 Node2 还没有NodeLink 请求建立NodeLink
982 // We need to establish a link to the target node before we can proceed.
983 from_node_link.node()->EstablishLink(
984 bypass_target_node,
985 [router = WrapRefCounted(this), requestor = WrapRefCounted(&requestor),
986 bypass_target_sublink, context](NodeLink* link_to_bypass_target) {
987 if (!link_to_bypass_target) {
988 DLOG(ERROR) << "Disconnecting Router due to failed introduction";
989 router->AcceptRouteDisconnectedFrom(context,
990 LinkType::kPeripheralOutward);
991 return;
992 }
993 // 建立NodeLink后请求代理绕过
994 router->BypassPeerWithNewRemoteLink(
995 context, *requestor, *link_to_bypass_target,
996 bypass_target_sublink,
997 link_to_bypass_target->memory().TryAllocateRouterLinkState());
998 });
函数判断如果C和B之间没有建立NodeLink,就调用EstablishLink 方法去建立NodeLink,然后调用C router的BypassPeerWithNewRemoteLink方法去请求代理绕过。
我们先来看看EstablishLink方法, 这其中需要Broker参与,我们具体分析。
third_party/ipcz/src/ipcz/node.cc
251 void Node::EstablishLink(const NodeName& name, EstablishLinkCallback callback) {
252 Ref<NodeLink> existing_link;
// 尝试建立链接的broker 的NodeLink
253 absl::InlinedVector<Ref<NodeLink>, 2> brokers_to_query;
254 {
255 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
256 auto it = connections_.find(name);
257 if (it != connections_.end()) {
// 链接已经存在(如果当前节点是B所在的broker,则肯定存在)
258 existing_link = it->second.link;
259 } else {
260 if (type_ == Type::kNormal && broker_link_) {
// 当前节点不是broker, 并且已经和broker建立链接,则需要尝试通过broker 和 B建立链接
261 brokers_to_query.push_back(broker_link_);
262 } else if (!other_brokers_.empty()) {
// 当前节点是broker 或者还未和broker建立链接,通过其他broker建立链接(如果不在一个网络没法建立链接)
263 ABSL_ASSERT(type_ == Type::kBroker);
264 brokers_to_query.reserve(other_brokers_.size());
265 for (const auto& [broker_name, link] : other_brokers_) {
266 brokers_to_query.push_back(link);
267 }
268 }
269
270 if (!brokers_to_query.empty()) {
// 等待接受链接建立邀请, B所在的broker收到请求后会主动发起链接
271 auto [pending_it, inserted] =
272 pending_introductions_.insert({name, nullptr});
273 auto& intro = pending_it->second;
274 if (!intro) {
275 intro = std::make_unique<PendingIntroduction>(
276 absl::MakeSpan(brokers_to_query));
277 }
278 intro->AddCallback(std::move(callback));
279 if (!inserted) { // 防止整个网络循环调用,并且保证只能建立一个链接
280 // There was already a pending introduction we can wait for.
281 return;
282 }
283 }
284 }
285 }
286
287 if (!brokers_to_query.empty()) {
// 发起邀请
288 for (const auto& broker : brokers_to_query) {
289 broker->RequestIntroduction(name);
290 }
291 return;
292 }
293 // 当前链接存在,直接回调
294 // NOTE: `existing_link` may be null here, implying that we have failed.
295 callback(existing_link.get());
296 }
EstablishLink 函数如果发现Node3 与Node2已经建立链接则直接调用callback。 如果没有建立就会通过相关broker建立链接,有时候Node2 并不知道B在哪个broker网络下,就要查询与他相连的所有broker, broker收到请求后发现B所在Node是属于自己维护的,就会要求Node 2向Node3发起链接邀请(因为Node2 和Node3 都和这个broker 已经建立了链接)。然后链接建立后执行回调。这个路径还是比较长的,我们通过代码进行验证。
third_party/ipcz/src/ipcz/node_link.cc
void NodeLink::RequestIntroduction(const NodeName& name) {
ABSL_ASSERT(remote_node_type_ == Node::Type::kBroker);
msg::RequestIntroduction request;
request.params().name = name;
Transmit(request);
}
RequestIntroduction_Params 只有一个参数就是Node2的名称。
我们来看broker收到请求后的处理。
third_party/ipcz/src/ipcz/node_link.cc
bool NodeLink::OnRequestIntroduction(msg::RequestIntroduction& request) {
if (node()->type() != Node::Type::kBroker) {
return false;
}
node()->HandleIntroductionRequest(*this, request.params().name);
return true;
}
直接调用Node->HandleIntroductionRequest()
third_party/ipcz/src/ipcz/node.cc
298 void Node::HandleIntroductionRequest(NodeLink& from_node_link,
299 const NodeName& for_node) {
300 // NodeLink must never accept these requests on non-broker nodes.
301 ABSL_ASSERT(type_ == Type::kBroker);
302
//Node3 的名称
303 const NodeName requestor = from_node_link.remote_node_name();
304
305 DVLOG(4) << "Broker " << from_node_link.local_node_name().ToString()
306 << " received introduction request for " << for_node.ToString()
307 << " from " << requestor.ToString();
308
// 当前Node与Node2的链接
309 const absl::optional<Connection> target_connection = GetConnection(for_node);
310 if (!target_connection) {
// 链接不存在请求与自己相连的Broker
311 // We are not familiar with the requested node. Attempt to establish our own
312 // link to it first, then try again.
313 EstablishLink(for_node, [self = WrapRefCounted(this),
314 requestor = WrapRefCounted(&from_node_link),
315 name = for_node](NodeLink* link) {
316 if (!link) {
317 requestor->RejectIntroduction(name);
318 return;
319 }
320 // 与Node2建立了链接,重新执行HandleIntroductionRequest处理
321 self->HandleIntroductionRequest(*requestor, name);
322 });
323 return;
324 }
325
// 当前节点是broker, C端节点不是broker,在同一个broker网络
326 const bool is_target_in_network = !target_connection->broker;
// C端节点是broker(broker to broker)
327 const bool is_target_broker =
328 target_connection->link == target_connection->broker;
// B是broker
329 const bool is_requestor_broker =
330 from_node_link.remote_node_type() == Type::kBroker;
331 if (is_requestor_broker && is_target_broker) {
// B 和 C都是Broker,不能介绍只能自己建立链接
332 DLOG(ERROR) << "Invalid introduction request from broker "
333 << requestor.ToString() << " for broker "
334 << for_node.ToString();
335 return;
336 }
337
338 if (is_target_broker || is_requestor_broker || is_target_in_network ||
339 target_connection->broker->link_side().is_side_a()) {
340 // If one of the two nodes being introduced is a broker, or if the target
341 // is in-network (which implies the requestor is too, if it's not a broker)
342 // then we are the only node that can introduce these two nodes.
343 //
344 // Otherwise if this is an introduction between two non-brokers in separate
345 // networks, by convention we can only perform the introduction if we're on
346 // side A of the link between the two relevant brokers.
347 IntroduceRemoteNodes(from_node_link, *target_connection->link);
348 return;
349 }
350
351 // This is an introduction between two non-brokers in separate networks, and
352 // we (one of the networks' brokers) are on side B of the link to the other
353 // network's broker. This introduction is therefore the other broker's
354 // responsibility.
355 msg::RequestIndirectIntroduction request;
// Node3 的名称, Node2 的名称
356 request.params().source_node = from_node_link.remote_node_name();
357 request.params().target_node = target_connection->link->remote_node_name();
358 target_connection->broker->Transmit(request);
359 }
下面用B节点代表Node1,C节点代表Node3
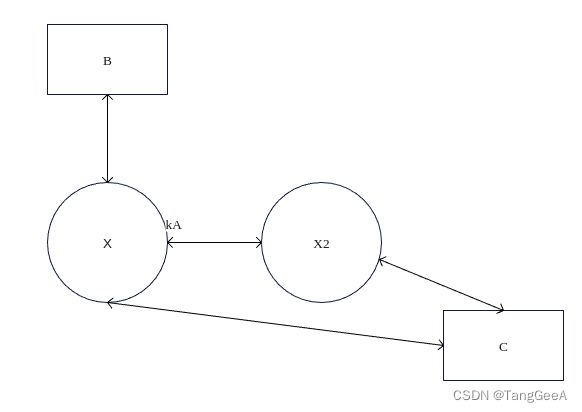
下面假设当前节点是X节点。首先肯定X节点和B节点是直接相连的。 下面用圆圈表示broker节点, 方框表示非broker节点。331-336行, 如果B和C都是broker, X也是broker, 则如下图:

B和C之间由于不存在共享内存,x不能介绍B和C建立链接。
338 行条件成立,表示当前节点可以介绍B和C建立链接,340-347行调用IntroduceRemoteNodes进行介绍。 这里的条件判断包含四种情况,
-
条件1(is_target_broker): X和C都是Broker, B不是broker。 并且X和C直接相连。

B和C有一个节点是broker,C可以提供共享内存。 -
条件2(is_requestor_broker): X是broker,B 是broker,则C不是broker,并且X和C不是直接相连(通过其他Broker建立的链接)。

B是broker 可以提供共享内存 -
条件3(is_target_in_network): X是broker, B和C都不是broker, 所以X、B、C在同一个网络下面。

B和C在同一个Broker,典型的NonBroker 和 NonBroker 链接。 -
条件4(target_connection->broker->link_side().is_side_a()):X是broker,B不是broker,C不是broker, 并且X和C不是直接相连(通过其他Broker建立的链接),且是X节点和另一个Borker节点的链接中属于kA端。 如下图:
X是broker,并且是kA节点,防止重复发起介绍,规定总是有kA端介绍。
355-358行对应的情况如下:
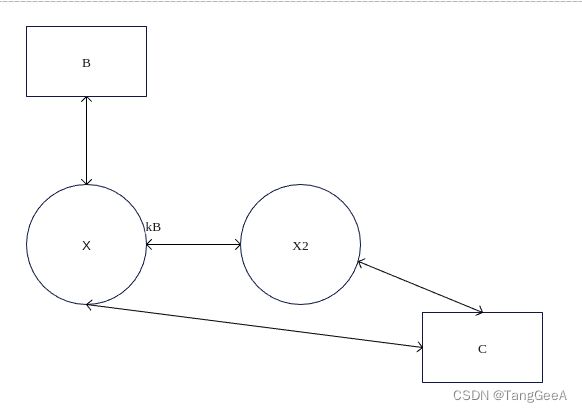
这种情况由于X是kB端,所以需要X2(kA端)发起介绍,这里请求kA帮忙介绍。
这也和注释比较吻合,也就是如果B和C都是Broker 则没有节点可以介绍B和C认识。 如果B和C有一个节点是Broker,或者B和C在同一个网络,只有X节点可以进行B和C的介绍(因为X和其他两点同时相连, 跨网络Broker 只能和Broker链接)。 如果B和C都是非Broker 并且不在同一个网络,则有两个broker 可接介绍B和C节点链接,规定使用kA一端进行介绍。
我们先来分析IntroduceRemoteNodes函数,也就是由当前节点介绍B、C节点建立链接。
third_party/ipcz/src/ipcz/node.cc
621 void Node::IntroduceRemoteNodes(NodeLink& first, NodeLink& second) {
622 // Ensure that no other thread does the same introduction concurrently.
// 生成一个in_progress_introductions_防止重复介绍。
623 const NodeName& first_name = first.remote_node_name();
624 const NodeName& second_name = second.remote_node_name();
625 const auto key = (first_name < second_name)
626 ? IntroductionKey(first_name, second_name)
627 : IntroductionKey(second_name, first_name);
628 {
629 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
630 auto [it, inserted] = in_progress_introductions_.insert(key);
631 if (!inserted) {
632 return;
633 }
634 }
635
636 DriverMemoryWithMapping buffer = NodeLinkMemory::AllocateMemory(driver_);
637 auto [transport_for_first_node, transport_for_second_node] =
638 DriverTransport::CreatePair(driver_, first.transport().get(),
639 second.transport().get());
640 first.AcceptIntroduction(second_name, LinkSide::kA, second.remote_node_type(),
641 second.remote_protocol_version(),
642 std::move(transport_for_first_node),
643 buffer.memory.Clone());
644 second.AcceptIntroduction(first_name, LinkSide::kB, first.remote_node_type(),
645 first.remote_protocol_version(),
646 std::move(transport_for_second_node),
647 std::move(buffer.memory));
648
649 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
650 in_progress_introductions_.erase(key);
651 }
函数有两个NodeLink参数, first代表当前节点与B的链接, second表示当前节点与C的链接。
623-634 生成一个in_progress_introductions_防止重复介绍。
636-647行 由当前节点分配共享内存,并且创建一对Transport。 将共享内存和传输点一端发送给B, 将共享内存和传输点另一端发送给B。 这样B和C之间就有了传输信道以及共享内存, 就可以进行愉快的通信了。
我们来具体分析AcceptIntroduction函数。
third_party/ipcz/src/ipcz/node.cc
void NodeLink::AcceptIntroduction(const NodeName& name,
LinkSide side,
Node::Type remote_node_type,
uint32_t remote_protocol_version,
Ref<DriverTransport> transport,
DriverMemory memory) {
ABSL_ASSERT(node_->type() == Node::Type::kBroker);
msg::AcceptIntroduction accept;
accept.params().name = name;
accept.params().link_side = side;
accept.params().remote_node_type = remote_node_type;
accept.params().padding = 0;
accept.params().remote_protocol_version = remote_protocol_version;
accept.params().transport =
accept.AppendDriverObject(transport->TakeDriverObject());
accept.params().memory = accept.AppendDriverObject(memory.TakeDriverObject());
Transmit(accept);
}
函数创建AcceptIntroduction 消息,参数如下
name:对端Node的名称
link_side: 所属的边
remote_node_type: 对端的node类型
remote_protocol_version:协议版本
transport:和对端通信的Transport
memory: 和对端共同使用的共享内存
我们来看一下B和C收到消息后如何处理
third_party/ipcz/src/ipcz/node_link.cc
bool NodeLink::OnAcceptIntroduction(msg::AcceptIntroduction& accept) {
if (remote_node_type_ != Node::Type::kBroker) {
return false;
}
DriverMemoryMapping mapping =
DriverMemory(accept.TakeDriverObject(accept.params().memory)).Map();
if (!mapping.is_valid()) {
return false;
}
auto transport = MakeRefCounted<DriverTransport>(
accept.TakeDriverObject(accept.params().transport));
node()->AcceptIntroduction(
*this, accept.params().name, accept.params().link_side,
accept.params().remote_node_type, accept.params().remote_protocol_version,
std::move(transport), NodeLinkMemory::Create(node(), std::move(mapping)));
return true;
}
OnAcceptIntroduction函数还原出共享内存和Transport,然后调用Node类的AcceptIntroduction方法。
third_party/ipcz/src/ipcz/node.cc
361 void Node::AcceptIntroduction(NodeLink& from_node_link,
362 const NodeName& name,
363 LinkSide side,
364 Node::Type remote_node_type,
365 uint32_t remote_protocol_version,
366 Ref<DriverTransport> transport,
367 Ref<NodeLinkMemory> memory) {
368 // NodeLink should never dispatch this method to a node if the introduction
369 // didn't come from a broker, so this assertion should always hold.
370 ABSL_ASSERT(from_node_link.remote_node_type() == Node::Type::kBroker);
371
372 const NodeName local_name = from_node_link.local_node_name();
373
374 DVLOG(4) << "Node " << local_name.ToString() << " received introduction to "
375 << name.ToString() << " from broker "
376 << from_node_link.remote_node_name().ToString();
377
378 Ref<NodeLink> new_link = NodeLink::CreateInactive(
379 WrapRefCounted(this), side, local_name, name, remote_node_type,
380 remote_protocol_version, transport, memory);
381 ABSL_ASSERT(new_link);
382
383 std::unique_ptr<PendingIntroduction> pending_introduction;
384 {
385 absl::MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
386 if (type_ == Type::kNormal && !broker_link_) {
387 // If we've lost our broker connection, we should ignore any further
388 // introductions that arrive.
389 return;
390 }
391
392 auto [connection_it, inserted] =
393 connections_.insert({name,
394 {
395 .link = new_link,
396 .broker = WrapRefCounted(&from_node_link),
397 }});
398 if (!inserted) {
399 // If both nodes race to request an introduction to each other, the
400 // broker may send redundant introductions. It does however take care to
401 // ensure that they're ordered consistently across both nodes, so
402 // redundant introductions can be safely ignored by convention.
403 return;
404 }
405
406 // If this node requested this introduction, we may have callbacks to run.
407 // Note that it is not an error to receive an unrequested introduction,
408 // since it is only necessary for one of the introduced nodes to have
409 // requested it.
410 auto it = pending_introductions_.find(name);
411 if (it != pending_introductions_.end()) {
412 pending_introduction = std::move(it->second);
413 pending_introductions_.erase(it);
414 }
415 }
416
417 new_link->Activate();
418 if (pending_introduction) {
419 pending_introduction->Finish(new_link.get());
420 }
421 }
378-380 行创建NodeLink, 然后386-397行创建Connection,并添加到Node成员变量connections_集合维护,这里是Connection.link 和Connection.broker 不相等的一个场景。
410-413行由于链接已经建立,从pending_introductions_ 中移除pending_introduction
417行激活传输点。
418-420 行,对于主动发起请求的一端,pending_introduction不为空,调用Finsh回调函数。这时候会执行回调函数。我们回顾一下请求建立链接的过程。
974 Ref<NodeLink> link_to_bypass_target =
975 from_node_link.node()->GetLink(bypass_target_node);
976 if (link_to_bypass_target) {
// Node3 和 Node2 本身有NodeLink,执行BypassPeerWithNewRemoteLink 进行代理绕过
977 return BypassPeerWithNewRemoteLink(
978 context, requestor, *link_to_bypass_target, bypass_target_sublink,
979 link_to_bypass_target->memory().TryAllocateRouterLinkState());
980 }
981
// Node3 和 Node2 还没有NodeLink 请求建立NodeLink
982 // We need to establish a link to the target node before we can proceed.
983 from_node_link.node()->EstablishLink(
984 bypass_target_node,
985 [router = WrapRefCounted(this), requestor = WrapRefCounted(&requestor),
986 bypass_target_sublink, context](NodeLink* link_to_bypass_target) {
987 if (!link_to_bypass_target) {
988 DLOG(ERROR) << "Disconnecting Router due to failed introduction";
989 router->AcceptRouteDisconnectedFrom(context,
990 LinkType::kPeripheralOutward);
991 return;
992 }
993 // 建立NodeLink后请求代理绕过
994 router->BypassPeerWithNewRemoteLink(
995 context, *requestor, *link_to_bypass_target,
996 bypass_target_sublink,
997 link_to_bypass_target->memory().TryAllocateRouterLinkState());
998 });
也就是B和C链接建立之后会调用Router->BypassPeerWithNewRemoteLink()函数请求代理绕过。我们再来通过示意图表示一下当前的链接场景

BypassPeerWithNewRemoteLink函数参数
- requestor表示B->A的链接(RemoutRouterLink)
- link_to_bypass_target:Node2到Node3的NodeLink
- bypass_target_sublink: Node2 到Node1的NodeLink
-link_to_bypass_target->memory().TryAllocateRouterLinkState(): Node2和Node3 之间共享内存。 目标是B和C直接建立RouterLink,绕过A节点。
1883 bool Router::BypassPeerWithNewRemoteLink(
1884 const OperationContext& context,
1885 RemoteRouterLink& requestor,
1886 NodeLink& node_link,
1887 SublinkId bypass_target_sublink,
1888 FragmentRef<RouterLinkState> new_link_state) {
......
1906
1907 // Begin decaying our outward link.
1908 SequenceNumber length_to_decaying_link;
1909 Ref<RouterLink> new_link;
1910 const SublinkId new_sublink = node_link.memory().AllocateSublinkIds(1);
1911 {
1912 absl::ReleasableMutexLock lock(&mutex_);
.....
// 开始衰减B->C链接
1920 if (!outward_edge_.BeginPrimaryLinkDecay()) {
1921 DLOG(ERROR) << "Rejecting BypassPeer on failure to decay link";
1922 return false;
1923 }
1924
1925 length_to_decaying_link = outbound_parcels_.current_sequence_number();
1926 outward_edge_.set_length_to_decaying_link(length_to_decaying_link);
// 创建B->C 链接
1927 new_link = node_link.AddRemoteRouterLink(
1928 context, new_sublink, new_link_state, LinkType::kCentral, LinkSide::kA,
1929 WrapRefCounted(this));
1930 }
1931
......
1939
1940 const NodeName proxy_node_name = requestor.node_link()->remote_node_name();
1941 DVLOG(4) << "Sending AcceptBypassLink from "
1942 << node_link.local_node_name().ToString() << " to "
1943 << node_link.remote_node_name().ToString() << " with new sublink "
1944 << new_sublink << " to replace a link to proxy "
1945 << proxy_node_name.ToString() << " via sublink "
1946 << bypass_target_sublink;
1947
// 通知Node3 创建链接
1948 node_link.AcceptBypassLink(proxy_node_name, bypass_target_sublink,
1949 length_to_decaying_link, new_sublink,
1950 std::move(new_link_state));
1951
1952 // NOTE: This link is intentionally set *after* transmitting the
1953 // above message. Otherwise the router might race on another thread to send
1954 // messages via `new_sublink`, and the remote node would have no idea where
1955 // to route them.
// 打通B->C
1956 SetOutwardLink(context, std::move(new_link));
1957 return true;
1958 }
函数1920开始衰减B->A链接
1927-1929 创建B->C链接。
1948->1950 请求Node3 创建C->B链接
1956 打通B->C链接。
我们重点看一下node_link.AcceptBypassLink 函数,也就是Node2 创建C->B链接。
void NodeLink::AcceptBypassLink(
const NodeName& current_peer_node,
SublinkId current_peer_sublink,
SequenceNumber inbound_sequence_length_from_bypassed_link,
SublinkId new_sublink,
FragmentRef<RouterLinkState> link_state) {
msg::AcceptBypassLink accept;
accept.params().current_peer_node = current_peer_node;
accept.params().current_peer_sublink = current_peer_sublink;
accept.params().inbound_sequence_length_from_bypassed_link =
inbound_sequence_length_from_bypassed_link;
accept.params().new_sublink = new_sublink;
accept.params().new_link_state_fragment = link_state.release().descriptor();
Transmit(accept);
}
B向C发送了一个AcceptBypassLink消息。
我们看下C如何处理
third_party/ipcz/src/ipcz/node_link.cc
687 bool NodeLink::OnAcceptBypassLink(msg::AcceptBypassLink& accept) {
688 Ref<NodeLink> node_link_to_peer =
689 node_->GetLink(accept.params().current_peer_node);
690 if (!node_link_to_peer) {
691 // If the link to the peer has been severed for whatever reason, the
692 // relevant route will be torn down anyway. It's safe to ignore this
693 // request in that case.
694 return true;
695 }
696
697 const Ref<Router> receiver =
698 node_link_to_peer->GetRouter(accept.params().current_peer_sublink);
699 if (!receiver) {
700 // Similar to above, if the targeted Router cannot be resolved from the
701 // given sublink, this implies that the route has already been at least
702 // partially torn down. It's safe to ignore this request.
703 return true;
704 }
705
706 auto link_state = MaybeAdoptFragmentRef<RouterLinkState>(
707 memory(), accept.params().new_link_state_fragment);
708 if (link_state.is_null()) {
709 // Bypass links must always come with a valid fragment for their
710 // RouterLinkState. If one has not been provided, that's a validation
711 // failure.
712 return false;
713 }
714
715 const OperationContext context{OperationContext::kTransportNotification};
716 return receiver->AcceptBypassLink(
717 context, *this, accept.params().new_sublink, std::move(link_state),
718 accept.params().inbound_sequence_length_from_bypassed_link);
719 }
函数反序列化后直接调用C路由的AcceptBypassLink方法。
third_party/ipcz/src/ipcz/router.cc
1006 bool Router::AcceptBypassLink(
1007 const OperationContext& context,
1008 NodeLink& new_node_link,
1009 SublinkId new_sublink,
1010 FragmentRef<RouterLinkState> new_link_state,
1011 SequenceNumber inbound_sequence_length_from_bypassed_link) {
1012 SequenceNumber length_to_proxy_from_us;
1013 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> old_link;
1014 Ref<RemoteRouterLink> new_link;
1015 {
1016 absl::ReleasableMutexLock lock(&mutex_);
......
1023
// C->A链接
1024 old_link =
1025 WrapRefCounted(outward_edge_.primary_link()->AsRemoteRouterLink());
......
1041 length_to_proxy_from_us = outbound_parcels_.current_sequence_number();
// C->A 链接开始u筛检
1042 if (!outward_edge_.BeginPrimaryLinkDecay()) {
1043 DLOG(ERROR) << "Rejecting BypassProxy on failure to decay link";
1044 return false;
1045 }
1046
1047 // By convention the initiator of a bypass assumes side A of the bypass
1048 // link, so we assume side B.
// 创建C->B 链接
1049 new_link = new_node_link.AddRemoteRouterLink(
1050 context, new_sublink, std::move(new_link_state), LinkType::kCentral,
1051 LinkSide::kB, WrapRefCounted(this));
1052
1053 if (new_link) { // C->B链接设置为primary_link
1054 DVLOG(4) << "Bypassing proxy on other end of " << old_link->Describe()
1055 << " using a new " << new_link->Describe()
1056 << " with length to proxy " << length_to_proxy_from_us
1057 << " and length from proxy "
1058 << inbound_sequence_length_from_bypassed_link;
1059
1060 outward_edge_.set_length_to_decaying_link(length_to_proxy_from_us);
1061 outward_edge_.set_length_from_decaying_link(
1062 inbound_sequence_length_from_bypassed_link);
1063 outward_edge_.SetPrimaryLink(new_link);
1064 }
1065 }
1066
1067 if (!new_link) {
1068 AcceptRouteDisconnectedFrom(context, LinkType::kCentral);
1069 return true;
1070 }
1071
1072 if (new_link->node_link() == old_link->node_link()) {
1073 // If the new link goes to the same place as the old link, we only need
1074 // to tell the proxy there to stop proxying. It has already conspired with
1075 // its local outward peer.
1076 old_link->StopProxyingToLocalPeer(context, length_to_proxy_from_us);
1077 } else {
1078 // Otherwise, tell the proxy to stop proxying and let its inward peer (our
1079 // new outward peer) know that the proxy will stop.
1080 old_link->StopProxying(context, length_to_proxy_from_us,
1081 inbound_sequence_length_from_bypassed_link);
1082 new_link->ProxyWillStop(context, length_to_proxy_from_us);
1083 }
1084
1085 Flush(context);
1086 return true;
1087 }
这个函数请读者自行分析。

