【 SQL引擎 - analyze.cpp分析】
SQL引擎 - analyze.cpp分析
(一)SQL简要介绍
数据库的SQL引擎是数据库重要的子系统之一,它对上负责承接应用程序发送过来的SQL语句,对下则负责指挥执行器运行执行计划。其中优化器作为SQL引擎中最重要、最复杂的模块,被称为数据库的“大脑”,优化器产生的执行计划的优劣直接决定数据库的性能。
SQL引擎主要包括查询解析(parser)、查询分流(traffic cop)、查询优化(optimizer)、查询执行(executor)。parser源码目录为/src/common/backend/parser:
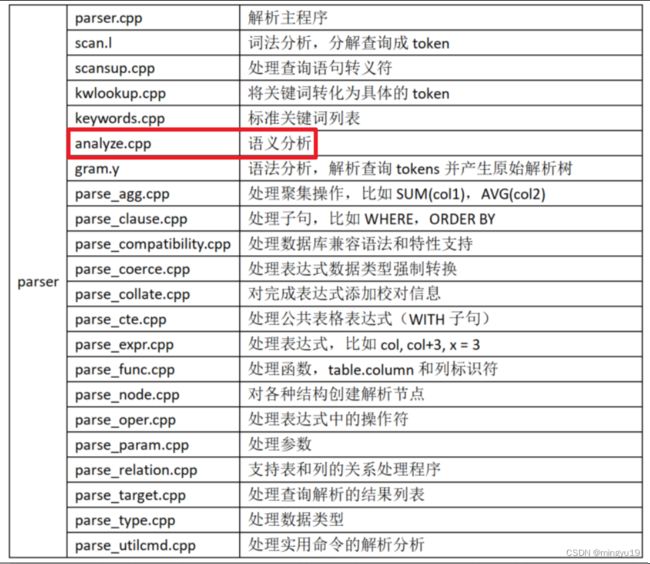
(二)analyze.cpp的功能
对于可优化语句,我们小心翼翼地在每个引用的表上获取合适的锁,后端的其他模块会根据结果保留或重新获取这些锁。因此,可以对这些语句进行重要的语义分析。对于实用程序命令,这里没有获得锁(如果有的话,我们不能确定在执行时我们是否仍然拥有它们)。因此,实用程序命令的一般规则是将它们转储到未转换的查询节点中。 DECLARE CURSOR、EXPLAIN 和 CREATE TABLE AS 是例外,因为它们包含我们应该转换的可优化语句。
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------
*
* analyze.cpp
* /*将原始解析树转换为查询树*/
* transform the raw parse tree into a query tree
*
* For optimizable statements, we are careful to obtain a suitable lock on
* each referenced table, and other modules of the backend preserve or
* re-obtain these locks before depending on the results. It is therefore
* okay to do significant semantic analysis of these statements. For
* utility commands, no locks are obtained here (and if they were, we could
* not be sure we'd still have them at execution). Hence the general rule
* for utility commands is to just dump them into a Query node untransformed.
* DECLARE CURSOR, EXPLAIN, and CREATE TABLE AS are exceptions because they
* contain optimizable statements, which we should transform.
* Portions Copyright (c) 1996-2012, PostgreSQL Global Development Group
* Portions Copyright (c) 1994, Regents of the University of California
* Portions Copyright (c) 2021, openGauss Contributors
*
* src/common/backend/parser/analyze.cpp
*
* -------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
(二)analyze.cpp的三个重要块
* /*解析分析*/
* parse_analyze
* /*分析原始解析树并将其转换为查询形式。*/
* Analyze a raw parse tree and transform it to Query form.
* /*可选地,可以提供有关 $n 参数类型的信息。不允许引用未由 paramTypes[] 定义的 $n 索引。*/
* Optionally, information about $n parameter types can be supplied.
* References to $n indexes not defined by paramTypes[] are disallowed.
*
/*结果是一个查询节点。可优化的语句需要相当多的转换,而实用程序类型的语句只是挂起一个虚拟 CMD_UTILITY 查询节点。*/
* The result is a Query node. Optimizable statements require considerable
* transformation, while utility-type statements are simply hung off
* a dummy CMD_UTILITY Query node.
/*定义一个解析分析*/
Query* parse_analyze(
Node* parseTree, const char* sourceText, Oid* paramTypes, int numParams, bool isFirstNode, bool isCreateView)
{
/*解析状态*/
ParseState* pstate = make_parsestate(NULL);
Query* query = NULL;
/* 自8.4起需要 , 丢出一个断言报告*/
AssertEreport(sourceText != NULL, MOD_OPT, "para cannot be NULL");
/*得到一个源文本*/
pstate->p_sourcetext = sourceText;
if (numParams > 0) {
parse_fixed_parameters(pstate, paramTypes, numParams);
}
PUSH_SKIP_UNIQUE_SQL_HOOK();
query = transformTopLevelStmt(pstate, parseTree, isFirstNode, isCreateView);
POP_SKIP_UNIQUE_SQL_HOOK();
/* 处理插件钩子是不安全的,因为动态库可能会被释放 */
if (post_parse_analyze_hook && !(g_instance.status > NoShutdown)) {
(*post_parse_analyze_hook)(pstate, query);
}
pfree_ext(pstate->p_ref_hook_state);
free_parsestate(pstate);
/* 对于 plpy CTAS 查询。 CTAS 是递归调用。CREATE 查询是第一个重写的。
* 第二个重写的查询是 INSERT SELECT。 没有这个属性,数据库将有分析 INSERT SELECT 查询时不知道 $x 的错误。
*/
query->fixed_paramTypes = paramTypes;
query->fixed_numParams = numParams;
return query;
}
/*
* /*解析分析投影架*/
* parse_analyze_varparams
*
* /*
* 当可以推断有关 $n 的信息时使用此变体来自上下文的符号数据类型。
* 传入的 paramTypes[] 数组可以被修改或扩大(通过 repalloc)。
* */
* This variant is used when it's okay to deduce information about $n
* symbol datatypes from context. The passed-in paramTypes[] array can
* be modified or enlarged (via repalloc).
*/
/*定义一个解析分析投影架*/
Query* parse_analyze_varparams(Node* parseTree, const char* sourceText, Oid** paramTypes, int* numParams)
{
/*解析状态*/
ParseState* pstate = make_parsestate(NULL);
Query* query = NULL;
/* 自8.4起需要 , 丢出一个断言报告 */
AssertEreport(sourceText != NULL, MOD_OPT, "para cannot be NULL");
/*得到一个源文本*/
pstate->p_sourcetext = sourceText;
parse_variable_parameters(pstate, paramTypes, numParams);
/*从顶层结构获得一个询问*/
query = transformTopLevelStmt(pstate, parseTree);
/* 确保参数类型一切正常 */
check_variable_parameters(pstate, query);
/* 处理插件钩子是不安全的,因为动态库可能会被释放 */
if (post_parse_analyze_hook && !(g_instance.status > NoShutdown)) {
(*post_parse_analyze_hook)(pstate, query);
}
pfree_ext(pstate->p_ref_hook_state);
free_parsestate(pstate);
return query;
}
/*
*/* 解析分析子结构 */
* parse_sub_analyze
* /*递归分析子语句的入口点。*/
* Entry point for recursively analyzing a sub-statement.
*/
/*定义一个解析分析子结构*/
Query* parse_sub_analyze(Node* parseTree, ParseState* parentParseState, CommonTableExpr* parentCTE,
bool locked_from_parent, bool resolve_unknowns)
{
/*解析状态*/
ParseState* pstate = make_parsestate(parentParseState);
Query* query = NULL;
pstate->p_parent_cte = parentCTE;
pstate->p_locked_from_parent = locked_from_parent;
pstate->p_resolve_unknowns = resolve_unknowns;
if (u_sess->attr.attr_sql.td_compatible_truncation && u_sess->attr.attr_sql.sql_compatibility == C_FORMAT)
set_subquery_is_under_insert(pstate); /* 为解析状态设置 p_is_in_insert。 */
query = transformStmt(pstate, parseTree);
free_parsestate(pstate);
return query;
}